Biology chapter 4 McGraw Hill
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:39 PM on 10/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
cell
smallest unit of living matter
2
New cards
cell theory
1. All organisms are composed of cells
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms
3. Cells come only from preexisting cells because cells are self reproducing
Created by Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms
3. Cells come only from preexisting cells because cells are self reproducing
Created by Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow
3
New cards
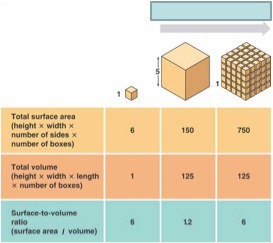
surface area to volume ratio
dividing a large cube into smaller cubes provides more surface area overall
reason why cells are as small as they are
reason why cells are as small as they are
4
New cards
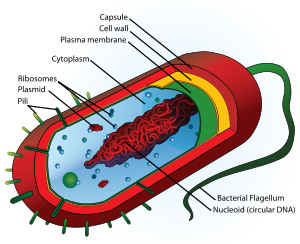
Prokaryotic cells
cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus
5
New cards
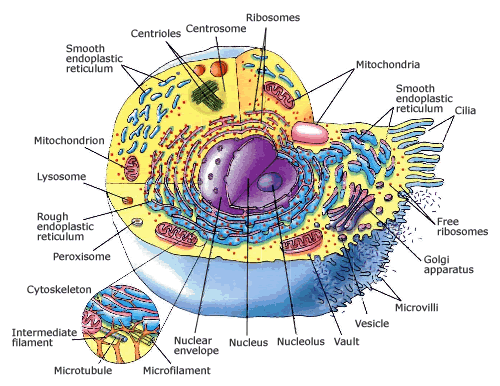
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that have a nucleus
6
New cards
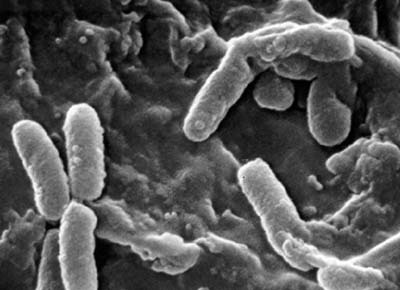
bacillus
rod shaped bacterium
7
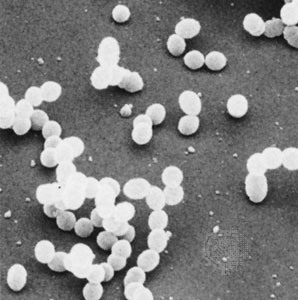
New cards
coccus
spherical shaped bacterium
8
New cards
spirilla
long rods twisted into spirals
rigid
rigid
9
New cards
spirochetes
long rods twisted into spirals
flexible
flexible
10
New cards
cell envelope
includes the plasma membrane and cell wall
11
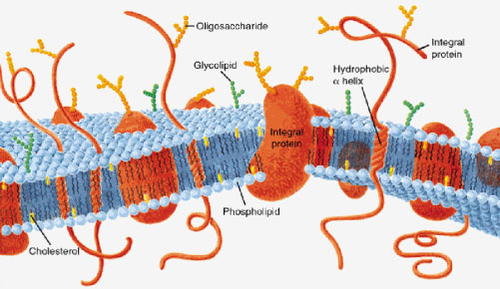
New cards
plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
12
New cards
ribosomes
tiny structures that use dna to perform protein synthesis
13
New cards
cyanobacteria
bacteria that can perform photosynthesis
14
New cards
thylakoids
internal membranes where chlorophyll and other pigments absorb solar energy to produce carbohydrates
15
New cards
flagella
A long appendage used for mobility of a cell
16
New cards
Fimbriae
small bristlelike fibers that sprout from the surface of a cell
used to attach a prokaryote to a surface
used to attach a prokaryote to a surface
17
New cards
Conjugation pili
rigid tubular structures used by prokaryotes to pass DNA from cell to cell
18
New cards
organelles
membrane bound compartments
distinguish eukaryotes from prokaryotes
distinguish eukaryotes from prokaryotes
19
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
theory that the mitochondria and chloroplasts were prokaryotes taken up by larger cells
20
New cards
transport vesicles
membranous sacs that enclose molecules and separate them from the cytoplasm
use the cytoskeleton to move around
use the cytoskeleton to move around
21
New cards
cytoskeleton
network of protein fibers
maintains the cell shape and assists with cell movement
maintains the cell shape and assists with cell movement
22
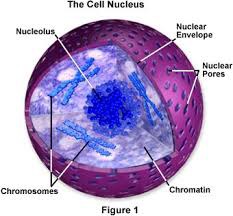
New cards
nucleus
contains genetic information that is passed on from cell to cell
specifies the information used by ribosomes to perform protein synthesis
command center of the cell
specifies the information used by ribosomes to perform protein synthesis
command center of the cell
23
New cards
nucleoplasm
semifluid matrix within the nucleus
24
New cards
chromatin
combination of proteins and nucleic acids
network of strands that are compressed into chromosomes
network of strands that are compressed into chromosomes
25
New cards
chromosomes
carry genetic information
compressed form of dna
compressed form of dna
26
New cards
genes
basic units of heredity
27
New cards
nucleolus
dark region of chromatin where rRNA joins with proteins to form subunits of ribosomes
28
New cards
nuclear envelope
double membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
29
New cards
nuclear pores
tiny pores in the nuclear envelope that allow ribosomal subunits and mRNA to pass through
30
New cards
polyribosomes
groups of ribosomes
31
New cards
endomembrane system
consists of the
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
several vesicles
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
several vesicles
32
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum
organelle with a complicated system of membranous channels and saccules (flattened vesicles)
33
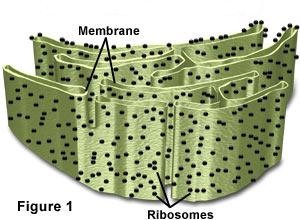
New cards
Rough ER
studded with ribosomes
Right against the nucleus
proteins fold in this organelle
contains enzymes that can add sugar to protein chains
Right against the nucleus
proteins fold in this organelle
contains enzymes that can add sugar to protein chains
34
New cards
Smooth ER
Touches the Rough ER
does not have attached ribosomes
helps produce lipids
does not have attached ribosomes
helps produce lipids
35
New cards
Golgi apparatus
consists of a stack of 3 to 20 slightly curved and flattened saccules
inner side is the cis face
outer side is the trans face
packages proteins into vesicles for exocytosis
inner side is the cis face
outer side is the trans face
packages proteins into vesicles for exocytosis

36
New cards
Lysosome
membrane bound vesicles with digestive enzymes
breaks down substances and worn out cell parts
breaks down substances and worn out cell parts
37
New cards
peroxisome
membrane bound vesicles that enclose enzymes involved with breaking down fatty acids
contains catalase to neutralize a harmful byproduct of its reactions, h2o2
contains catalase to neutralize a harmful byproduct of its reactions, h2o2
38
New cards
vacuoles
membrane bound organelles used to expel waste and store macromolecules
39
New cards
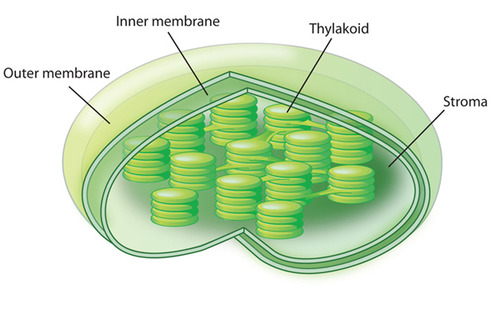
chloroplasts
organelles that use solar energy to synthesize carbohydrates
40
New cards
photosynthesis equation
solar energy + carbon dioxide + water -> carbonhydrate + oxygen
41
New cards
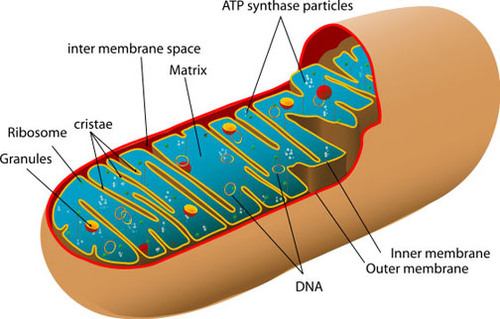
mitochondria
organelles that perform celluar respiration to break down carbohydrates and create atp
42
New cards
celluar respiration equation
carbohydrate + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water + energy
43
New cards
stroma
semifluid in a chloroplast
44
New cards
granum
stack of thylakoids
45
New cards
plastid
plant organelles surrounded by a double membrane
46
New cards
cristae
membrane in a mitochondria that increase surface area
47
New cards
semifluid matrix
contains mitochondrial dna and ribosomes
48
New cards
actin filaments
long, extremely thin, flexible fibers that occur in bundles or meshlike networks
contains two chains of globular actin monomers twister around each other in a helical manner
contains two chains of globular actin monomers twister around each other in a helical manner
49
New cards
intermediate filament
intermediate in size between actin filaments and microtubules
form a ropeike assembly of fibrous polypeptides
form a ropeike assembly of fibrous polypeptides
50
New cards
microtubules
small hollow cylinders made of a globular protein called tubulin
51
New cards
centrosome
an organelle that serves as the microtubule organizing center
lies near the nucleus
lies near the nucleus
52
New cards
centriole
short cylinders with a 9 + 0 pattern of microtubule triplets
replicate at right angles to each other before a cell divides
replicate at right angles to each other before a cell divides
53
New cards
cilia
hairlike parts of a cell used for movement
54
New cards
signal peptide
It is the starting sequence of amino acids that determines whether or not the protein will go to the rough ER because it binds to the SRP, which binds to the receptor on the ER
55
New cards
central dogma of molecular biology
DNA -> mRNA -> protein