Econ Diagrams / gvt policies / eval.
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Absolute advantage
can produce a good with fewer resources, countries should specialize
Comparative Advantage
a country can produce a good with lower opportunity cost
Limitations of theory:
unrealistic assumptions (free trade, fixed fop, full employment, perfect comp, no transport costs)
risk of excessive specialization
inability of developing countries to diversify manufacturing
Import Tariff
Pros:
domestic producers gain revenue
workers gain as domestic production increases
gvt revenue
Cons:
price goes up
wellfare loss
imported goods more expensive, domestic productions more expensive
loss of export competitiveness as production price increases
foreign producers lose
global economy lose
risk of retaliation
potential corruption
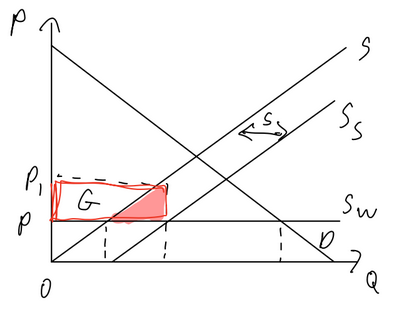
Import Quota
Pros:
domestic producers gain revenue
workers gain as domestic production increases
Cons:
price goes up
wellfare loss
imported goods more expensive, domestic productions more expensive
loss of export competitiveness as production price increases
foreign producers lose
global economy lose
risk of retaliation
potential corruption
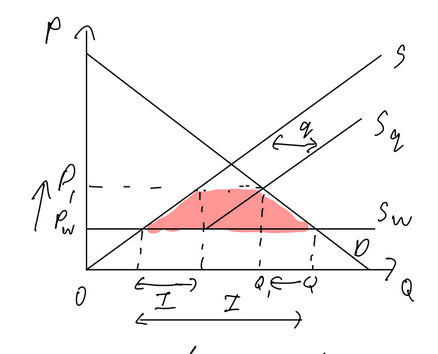
Subsidy (global)
Pros:
domestic producers gain revenue
workers gain as domestic production increases
Cons:
gvt debt
wellfare loss
imported goods more expensive, domestic productions more expensive
loss of export competitiveness as production price increases
foreign producers lose
global economy lose
risk of retaliation
potential corruption
Trade protection
Pros
protect infant industries
diversification of developing countries
national security
health, safety, env. standards
gvt revenue
overcoming trade deficit
anti-dumping
protect domestic jobs
cons
difficult to select what industry to protect
can be used to “protect’ unrelated industries
when relying on tariffs for gvt rev. probabluy means theres a problem w the tax system
retaliation is possible
hard to prove dumping
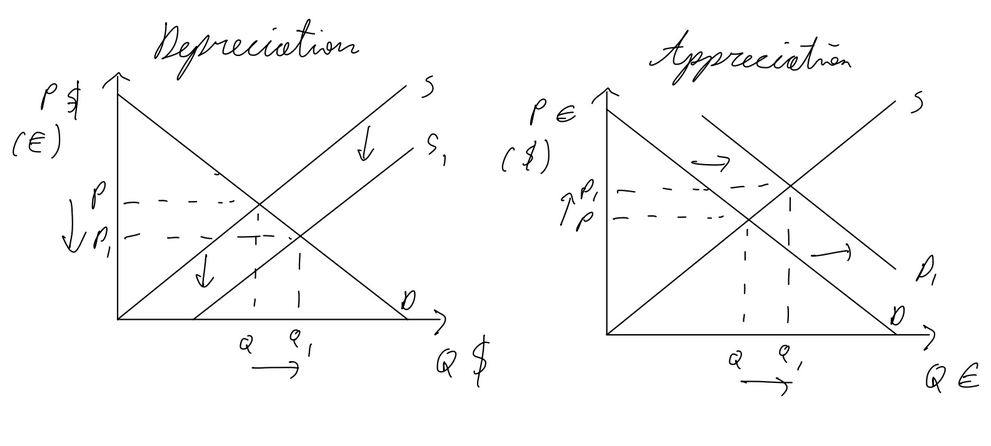
Freely Floating Exchange Rate
Appreciation: occurs with excess demand. if Americans buy euros w dollars, the demand for euros increases, appreciating the currency
Deppreciation: osccurs with excess supply. the americans buying euros means theyre selling dollars, increasing supply of dollars, leading to depreciation
pros:
allows for greater flexibilty in monetary policies
allows for automatic adjustments to external shocks
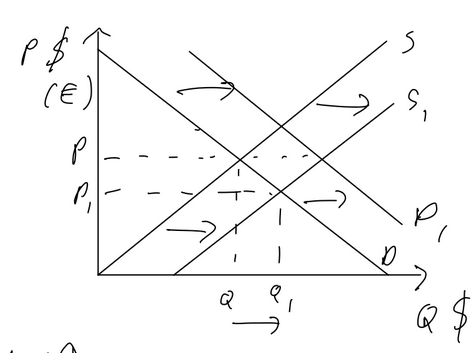
Fixed Exchange Rate
fixed at partiy: 1 to 1 ratio, usually doesn’t happen
Appreciation: CB buys it on forex market to increase demand
deppreciation: CB sells it on forex, increase supply
revaluation: change where the exchange rate is fixed to higher price
devaluation: change where the exchange rate is fixed to lower price
pros:
provides stability and predictability
lowers speculative trading and currency volatility
cons:
limits a country’s ability to conduct monetary policies as focus is on exhcange rate and not interest rate
Managed Exchange Rate
allowed to fluctuatie within a specific band, CB intervenes when exchange rate leaves band
Appreciation: CB buys it on forex market to increase demand
deppreciation: CB sells it on forex, increase supply
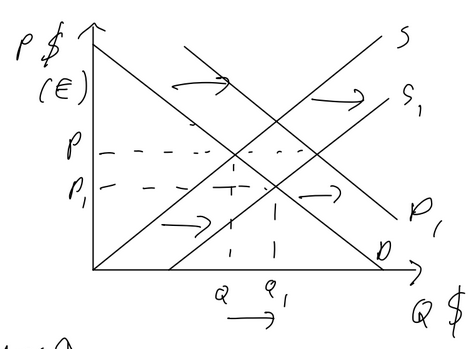
Consequences of curency depreciation
imports are more expensive, exports are cheaper. therefore net exports increase, shifting AD right
cose push inflation as imported raw materials are more expensive
demand pull inflation as AD increases
unemployment falls as exports increase
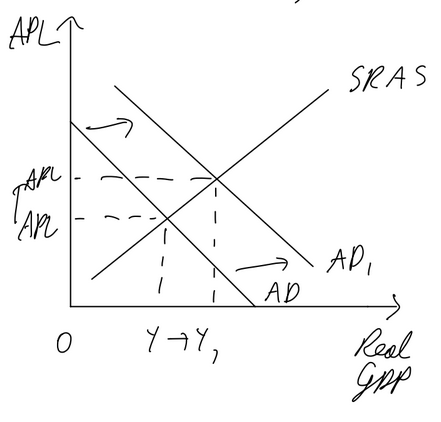
Consequences of currency appreciation
imports are cheaper, exports are more expensive. net exports decrease, AD shifts left
cost push deflation as imported raw materials are cheaper
demand pull deflation as net exports fall
unemployment may increase as less is exported
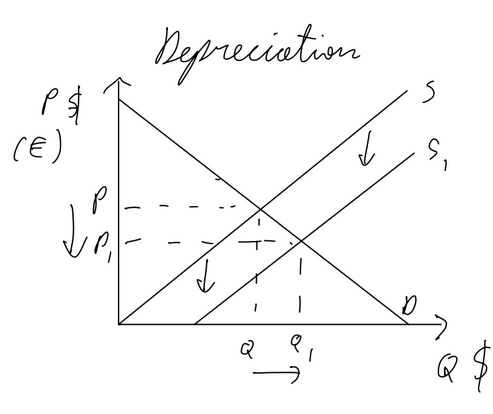
impact of currenccy depreciation on current account
depreciation → net exports increase → current account balance improves
the extent to which depends on Marshall-Lerner condition
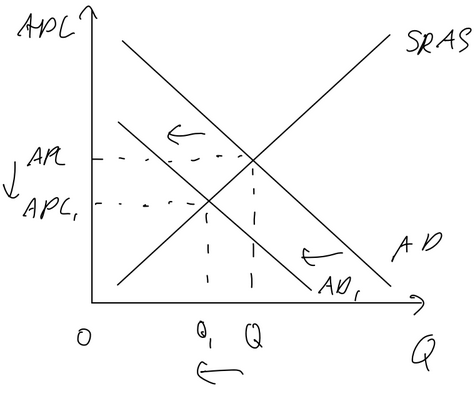
impact of currency appreciation on current account
appreciation → net exports decrease → current account balance worsens
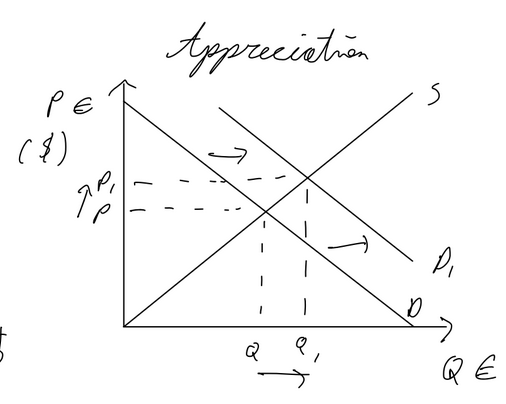
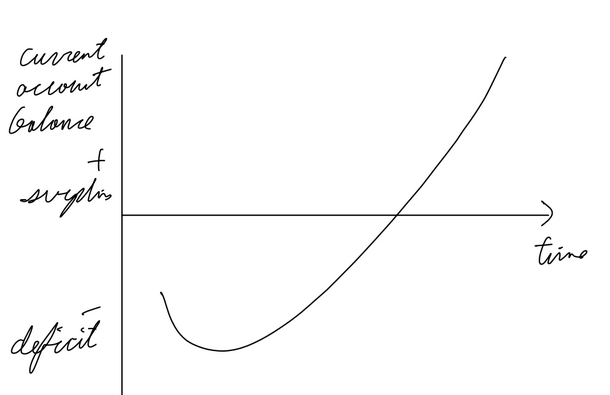
Marshall-Lerner condition / J-Curve
ML condition: extent to which a currency depreciation improves the current account balance, PED imports + PED exports > 1
Time lag between depreciation of a currency and an improvement in current account balance explained by J curve.
If a country’s currency depreciates, its good will become cheaper for other countries. However, it will take time before the other countries switch to that country’s goods as they aren’t sure whether the exchange rate my return in the short run
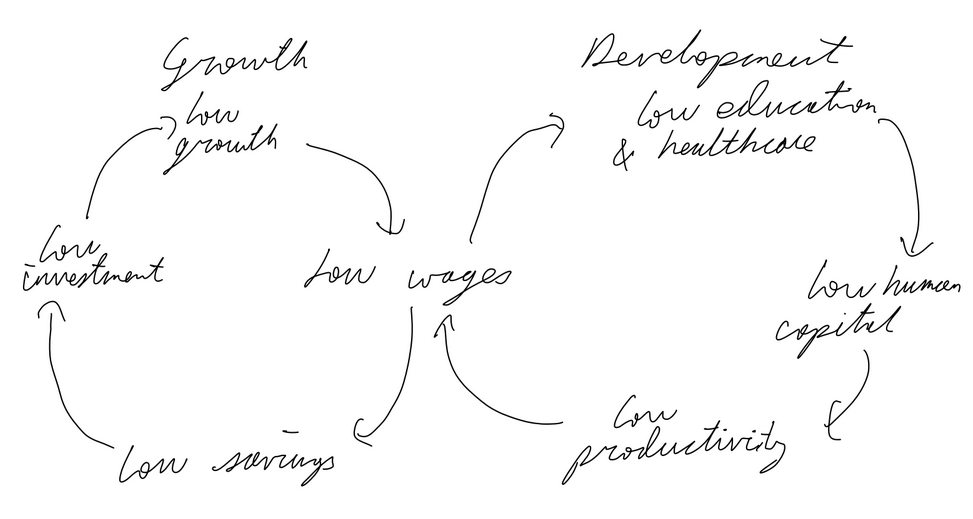
Poverty Cycle
A situation where poverty tends to perpetuate itself from one generation to the next.
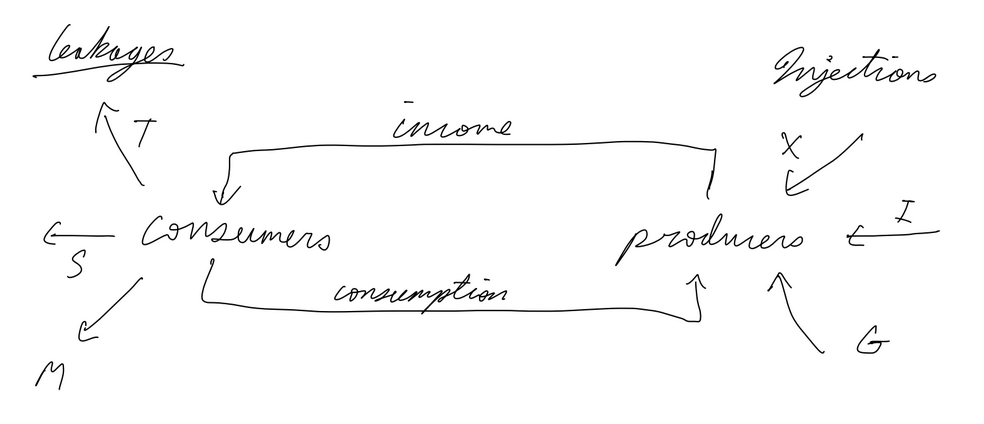
Circular Flow Model
Business Cycle
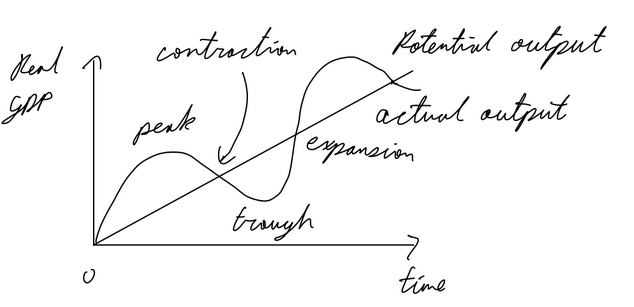
Monetarist AD AS SR
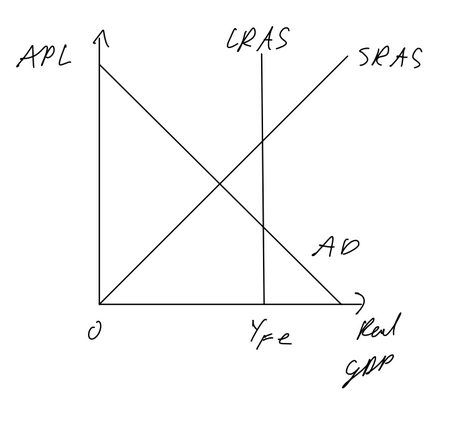
Monetarist AD AS LR
Deflationary gap SR: originally output = yfe, AD decreases, SRAS will increase in LR as prices of wages and resources will also fall bringing output back to yfe
Inflationary gap SR: orignally output = yfe, AD increases, SRAS will decrease in LR as prices of wages and resources increase, bringing output back to yfe
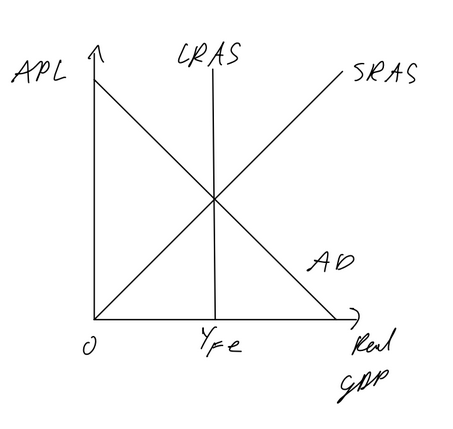
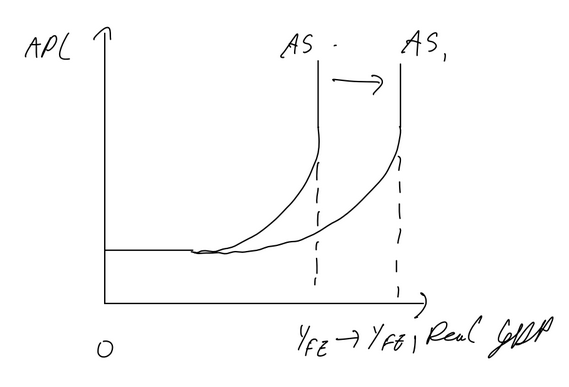
Keynesian AD AS
Assumption:
stickey wages (due to contracts, minimum wages, etc, APL can only fall to a certain extent, therefore APL reaches minimum at horizontal
at low output, spare capacity of the economy is high so firms can increase output without upward pressure on FOP prices, APL won’t change
vertical section exists as AS can’t go past potential output (all resources are used efficiently)
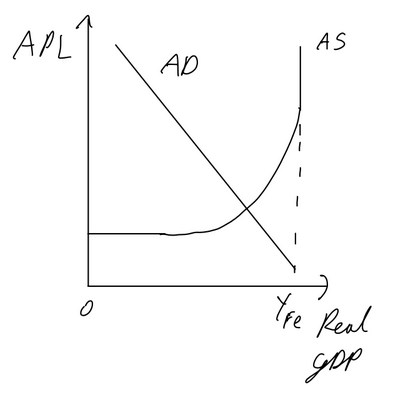
Keynseian AD AS potential growth
Caused by:
increases in quantity of FOP
improvement in quality of FOP
improvement in tech
reduction in natural rate of unemployment
improvement in efficiency
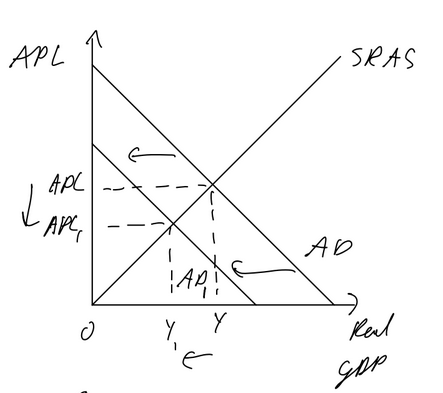
Malign (bad) deflation
Deflation due to fall in AD
as APL falls, consumers and firms avoid spending as they wait for cheaper prices
leads to cycle: APL falls, less spending, AD falls, etc
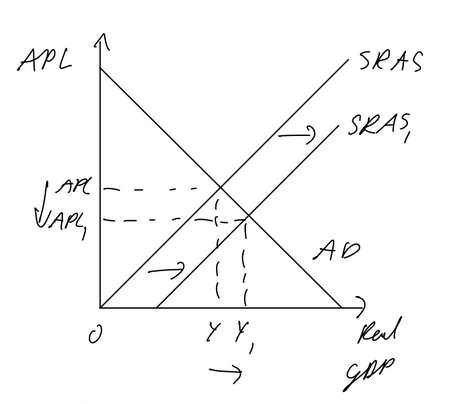
Benign (good) deflation
Deflation due to increase in AS
doesn’t lead to same cycle as Malign deflation
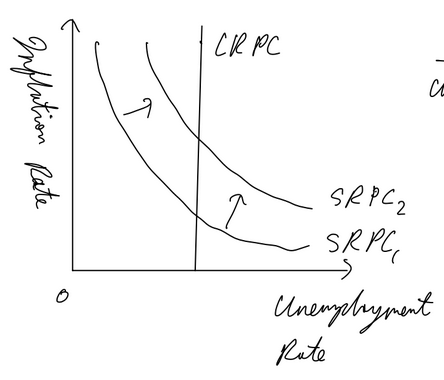
Phillips Curve SR
shows inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment
SR PC assumes fixed SRAS, only movement along
when SRAS decreases, SRPC shifts out (inflation increases and output falls
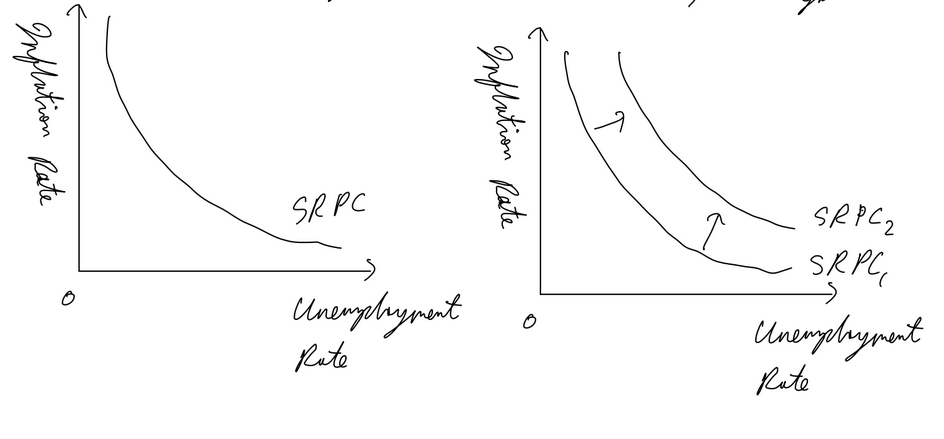
Phillips Curve LR
as wages and FOP prices change w APL in long run, no trade off exists in LR
LRPC is vertical (in the long run, unemployment rate is independent to APL as monetarist assumes in LR output is alwasy yfe)
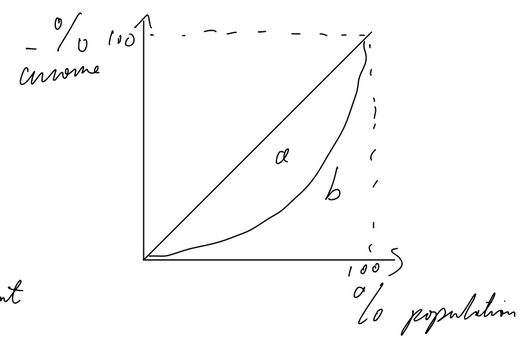
Lorenz Curve
Representation of income distribution
diagonal represents perfect income inequality
curve is Lorenz Curve
Gini coefficient = a/(a+b)
GC = 0 → perfect equality, vice versa
Expansionary/contractionary fiscal policy
By gvt to decrease deflationary/inflationary gap
increase/decrease gvt. spending
reduce/increase taxes
Pros:
targets specific sectors
pulls economy out of deep recession
can impact potential output (if gvt spending done right)
gvt spending guaranteed impact on AD
Cons:
major time lag
political constraints
inflationary
budget deficit
crowding out (gvt must borrow to pay for increase in spending, leads to lower investment and consumption as cost of borrowing increases, cancels out AD increase partially)
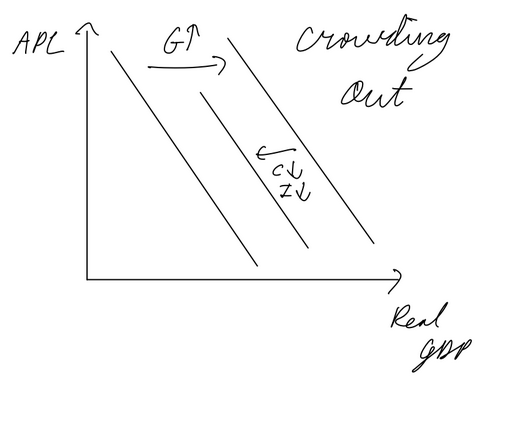
expansionary/contractionary Monetary Policy
Done by CB in order to close deflationary/inflationary gap
decrease/increase in interest rate
pros
no political constraints (CB is independant)
interest rates can be adjested incrementaly (bit by bit)
quicker to implement
no budget deficit
no crowding out
Cons:
time lags (not as bad as fiscal policy)
may not be enough in a deep recession
inflationary
cost push inflation
Interventionist supply side policies
gvt intervention to increase LRAS
Done by:
investing in human capital
investing infrastructure
investment in new tech
industrial policies (tax breaks, low interest loans, subsidies to specific industries)
Pro:
provide direct support to areas important for growth
create new jobs and reduce structural unemployment
downwards pressure on inflation (monetarist, same AD curve w higher LRAS curve has lower APL)
economic growth and potential growth
improved equity if investments in human capital are broad
Cons:
long time lag
government spending opp. cost
budget deficit
gvt. has imperfect info. (may support wrong industry)
Market based supply side policy
institutional changes in economy to develop free, competitive markets and their efficiency
done by:
Encouraging competition:
privitization (give company control from gvt. to private owners. as they profit maximzie, efficiency increases)
anti monopoly (increase competition and efficiency)
deregulation (stop protecting firms from competition, let inefficient firms go bankrups)
trade liberalization (foreign competition, domestic firms incentivized to improve efficiency)
Labour market reforms:
reduce labour union power (wages drop, more employment, structural unemployment falls, potential output increases)
abolish/reduce minimum wage (lower labour costs, potential output increases)
reduce unemployment benefit (people want to work more, potential output increases)
reduce job security
Incentive related policies:
cuts in personal income taxes (more income, want to work more)
cuts in business taxes (firms have more profit to invest)
cuts in taxes on capital gains (taxes on profits decreases, people mroe likely to save. more funds for banks to invest in firms, R&D)
Pros:
improved efficiency in production
improved allocation of resources as resources are used better
creation of new jobs
improvement in product quality
downward pressure on inflation as LRAS increases)
economic growth
Cons:
Competition:
privitization leads to higher prices, lower output, increased unemployment
deregulation leads to increased unemployment
trade liberalization lilkey to cause short term losses as inefficient companies shut down
labour market reforms
lower social protection
lower wages, poverty worsens
Incentive related:
income tax cuts may not be enough as people j want to use profits to spend more time on vacation
business tax cuts may worsen equity
bigger budget deficit as taxes decrease
Automatic stabilizers
features in the economy that limit fluctuations in SR
progressive income taxes:
deflationary gap: as GDP and income falls, taxes fall by relatively less, leaving consumers w more income to spends → AD falls less
inflationary gap: as gdp and income increases, taxes rise faster when progressive, disposable taxes rise less, consumers spend less → AD increases less
Unemployment benefits
deflationary gap: as unemployment increases, gvt spending on unemployment benefits increases too, AD falls less as gvt spends on benefits
inflationary gap: as unemployment falls, gvt spending decreases, less gvt. spending means AD increases less
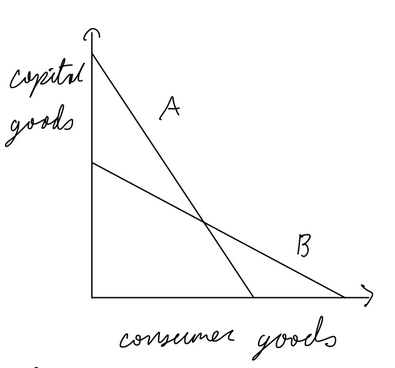
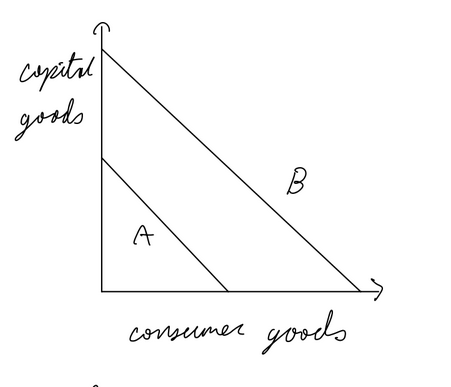
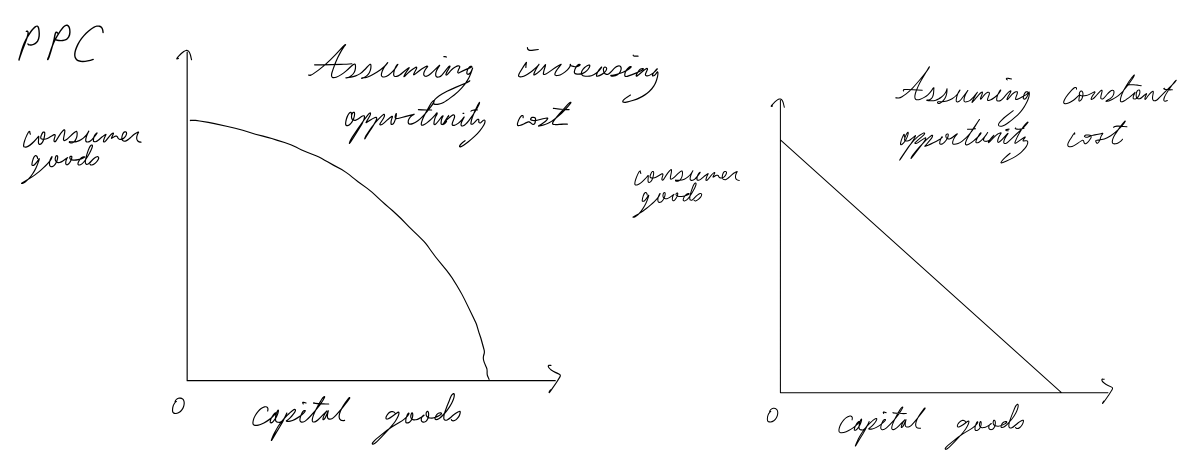
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
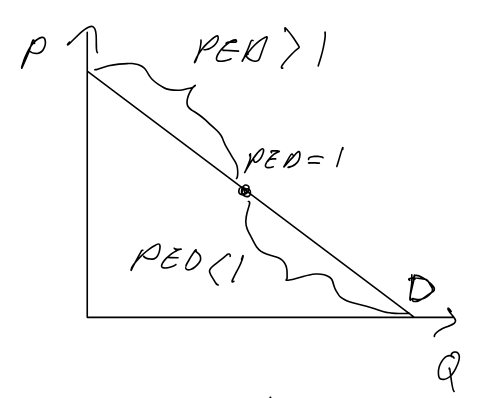
PED
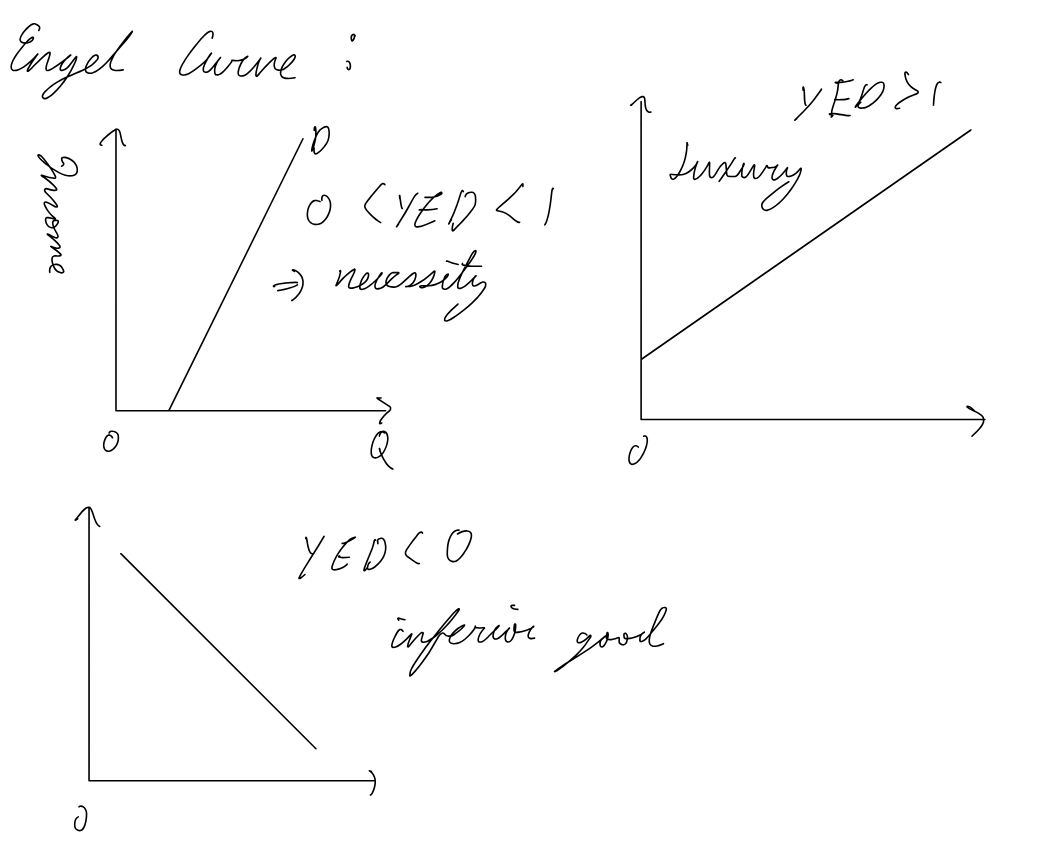
Engel Curve
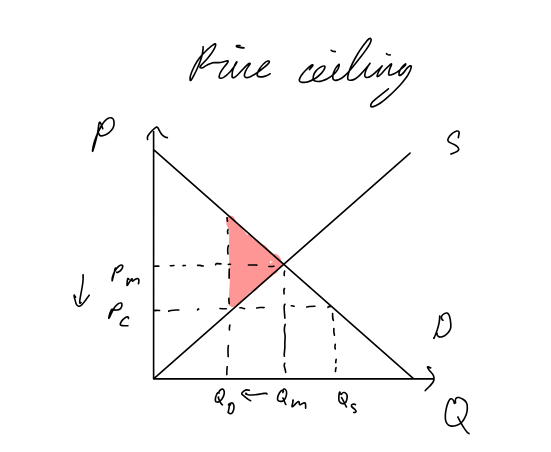
Price Ceiling (Maximum Price)
Pros:
makes necessities affordable for poor people
Cons:
shortages → first come first served, favoritism, parallel markets
inefficient resource allocation → welfare loss
fall in output may lead to unemployment
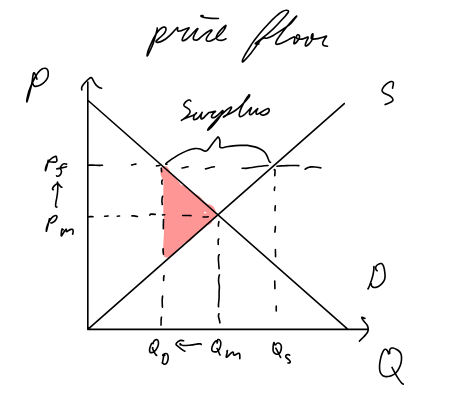
Price Floor (government buys surplus, protect industry eg. farmers)
Pros:
support farmers’ income (protection from sudden disturbances, natural disasters, drought, etc.)
increase in employment as Q increases
Cons:
Gvt spending increases
allows firms with high cost of production (inefficient) to produce → no incentive to become more efficient, r&d etc.
overallocation of resources → welfare loss
higher P for consumers

Price Floor (government doesn’t buy surplus, demerit good / wages)
pros:
protects low skilled workers with minimum wage
decreases incentive to consume demerit goods
cons:
Inefficient resource allocation (overallocation)
surplus, leads to unemployment
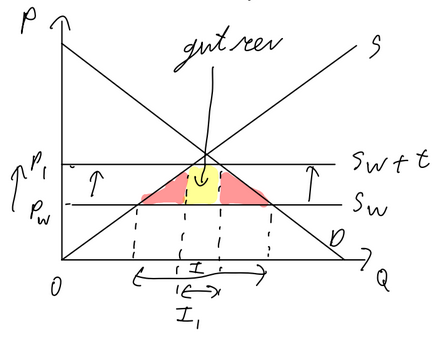
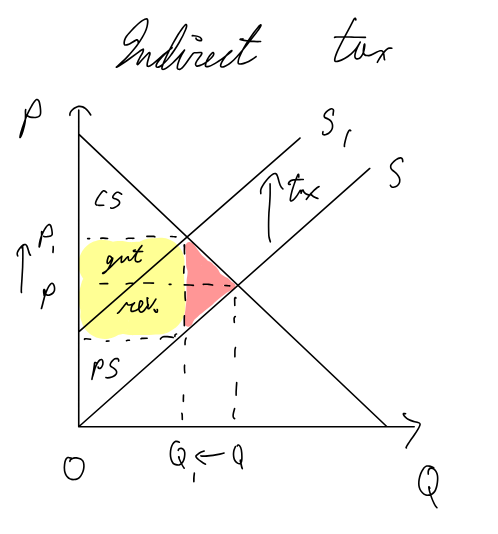
Indirect tax, specific Tax (set value) / pigouvian tax / carbon tax
Pros
can internalize the externality (firm/consumer responsible for third party costs also pays)
less costs than reg. / leg.
gvt. rev
for ext. of production: taxes on emissions and tradable permits are best as they give firms financial incentive to improve sustainability
for ext of consumption: price increase incentivizes consumers to consume less. if the good has price inelastic demand, gvt. rev will be high
Cons:
Taxes / tradable permits: hard to set a value on the external costs of production, therefore hard to set right tax amount to eliminate externality
For consumers: hard to measure value of external costs, therefore right tax amount
if the good has a price inelastic, Q might not decrease by a lot
indirect taxes are regressive (higher % of income for poorer households)
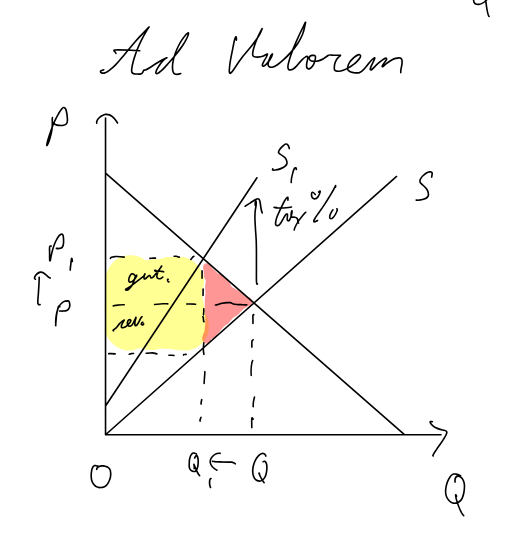
Ad valorem (percentage of P)
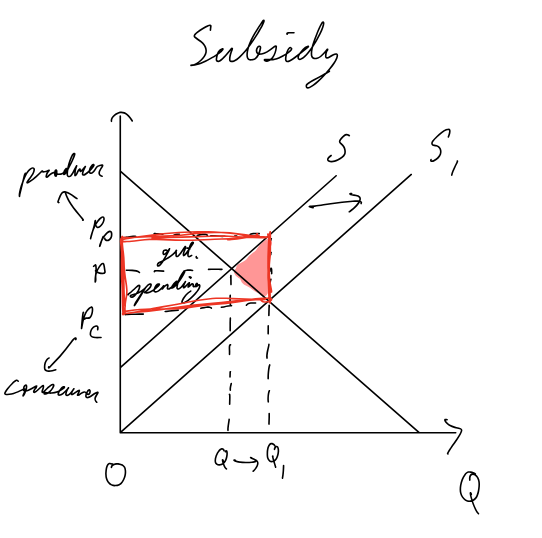
Subsidy
Pros:
effective in increasing R&D
effective in increasing Q
key in making important goods/services affordable to all (education, healthcare, etc.)
Cons:
hard to set right subsidy value
gvt spending
hard to decide what to subsidize (opp. cost), subject to political pressure
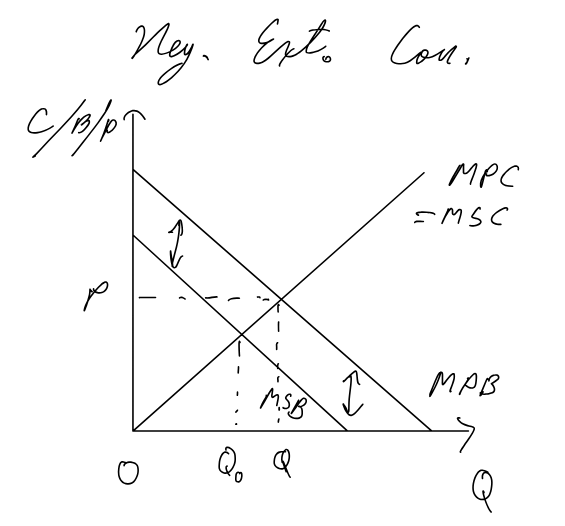
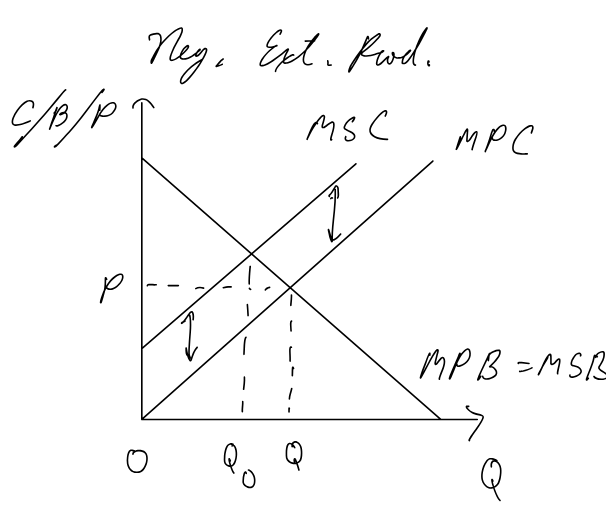
Negative Externalities of consumption
Negative Externalities of production
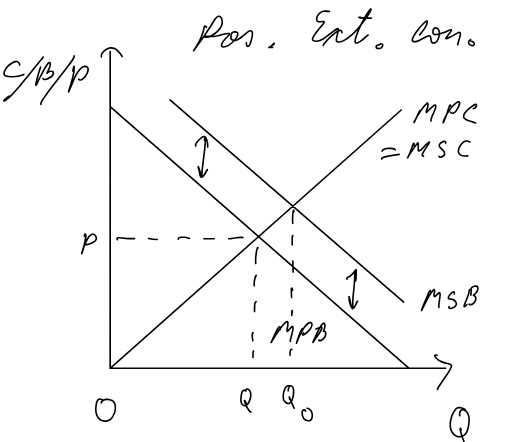
Positive Externalities of consumption
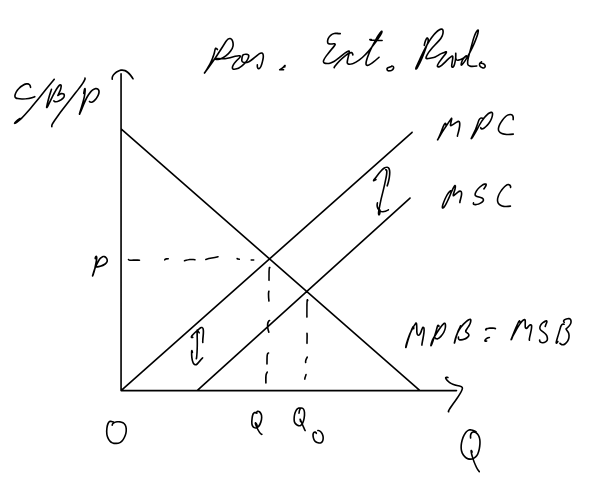
positive externalities of production
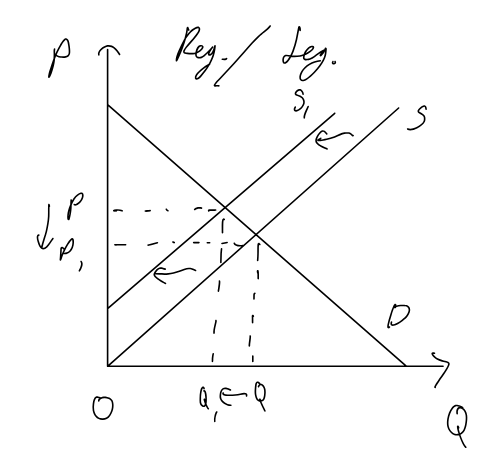
Regulations / legislation (consumer) / education against demerit goods
Pros:
simpole to implement
will atleast partially reduce demand for good
could be more appropriatie compared to market based (drinking age, etc.)
Cons:
probably won’t lower Q enough
funds required for advertizing and education
costs of enforcing rules
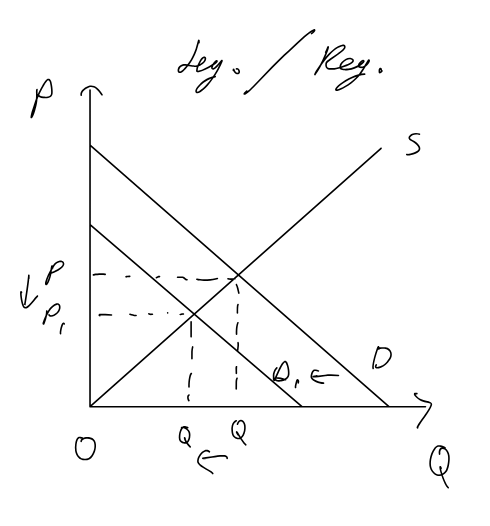
Regulations / legislation (producer)
Pros
simpler to implement
effective at least partially
can be more appropriate than market solutions
Cons
costs of monitoring and enforcement
are inefficient as all firms are treated the same
do not provide incentive for firms to improve
no way to know exactly how much production should be limited
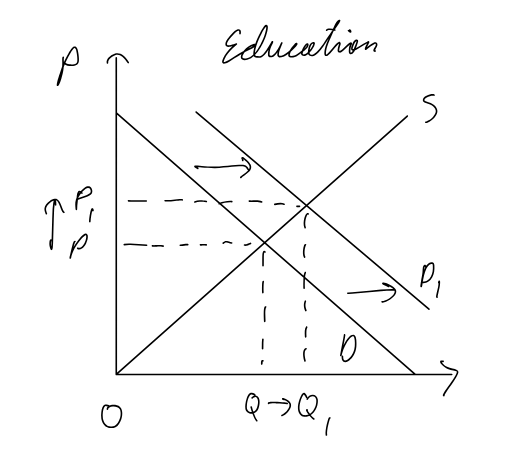
Education for merit goods
Pros:
simple to implement
effective in atleast partially increasing Q
Cons:
likely wont increase Q enough
costs for advertizing/education
hard to enforce
Higher D means higher P, could make goods unaffordable to low income households
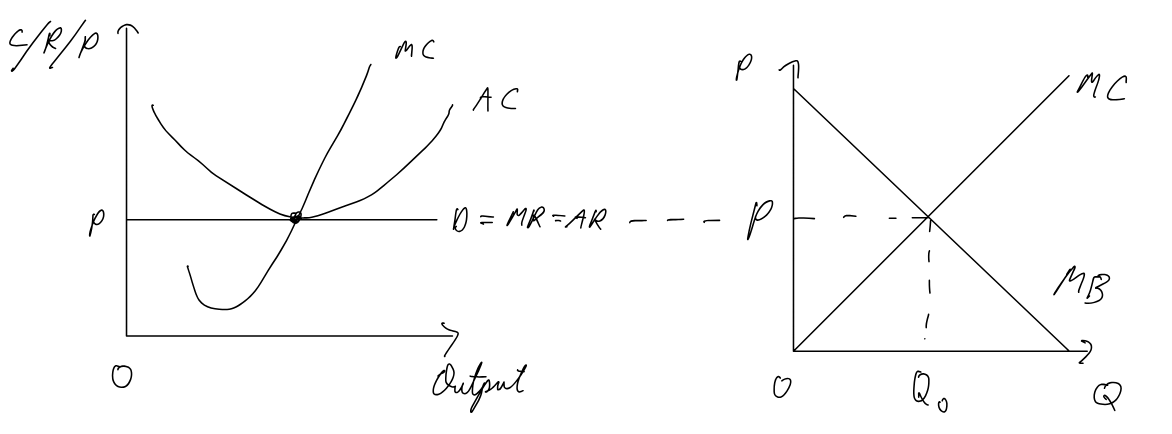
Perfect Competition
Assumptions:
many small firms
homogenous goods
perfect information
no barriers to entry/exit
perfect resource mobility
Pros:
achievement of productive efficiency in LR (minimzed AC)
allocative efficiciency
higher cost (inefficient) firms are forced out
consumers benefit from low costs
consumers decide what is produced and how much
Cons:
unrealistic assumptions
small firms, no economies of scale
firms open and close constantly, could waste resources
homogenous goods, no choice
all firms earn normal profit, unlikley for R&D to occur
only efficient when no externalities
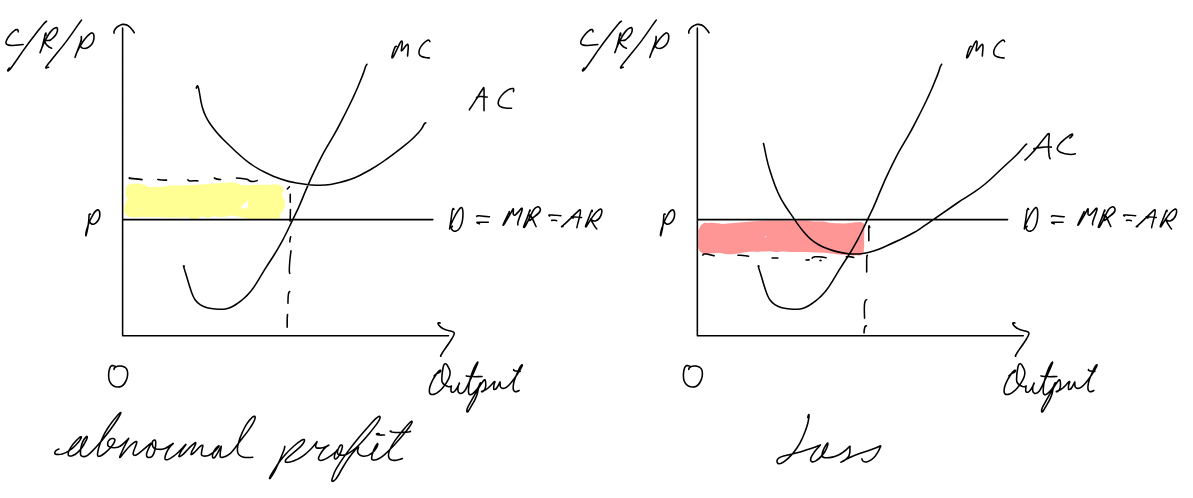
Perfect competition short run
abnormal profit: firms join, supply increases, lower price until normal profit
loss: firms leave, supply decreases, higher price until normal profit
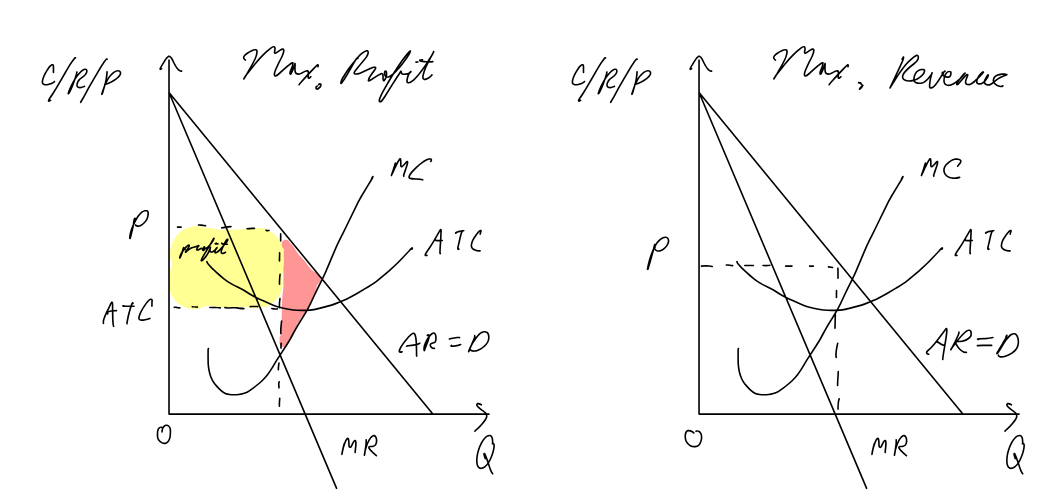
Monopoly / collusive oligopoly acting as monopoly
Assumptions Monopoly:
single dominant firm
no close substitutes
high barriers to entry
Assumptions Oligopoly:
small # of large firms
homogenous goods
high barriers to entry
interdependance among firms
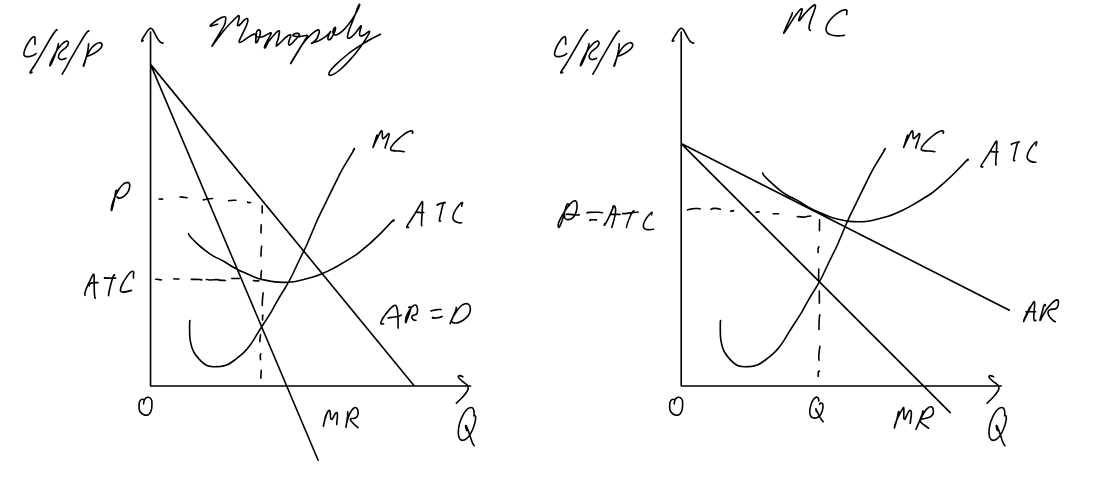
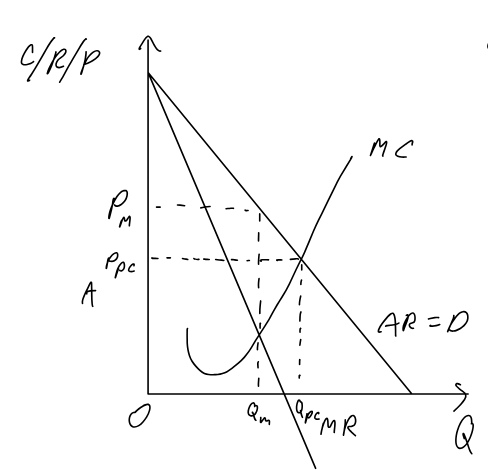
Profit maximizing monopoly vs. perfect competition
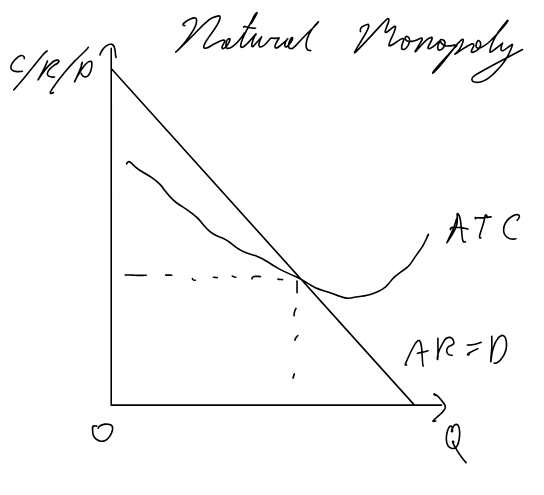
Natural monopoly
AR=D intersects ATC when ATC is still falling (still experiences economies of scale)
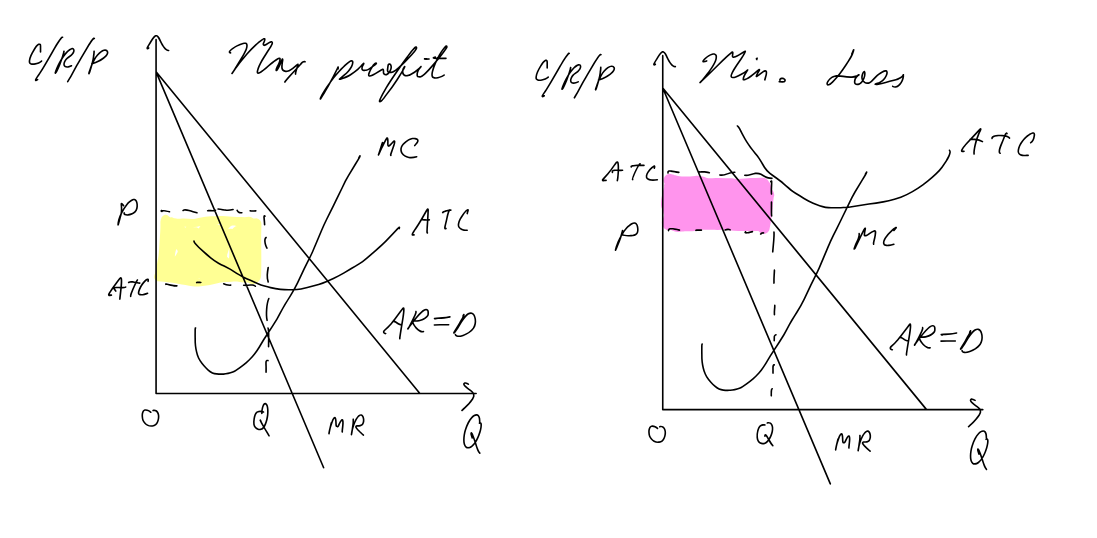
Monopolistic Competition SR
Assumptions:
large number of firms
no barriers to entry/exit
product differentiation
Monopolistic Competition LR
Assumptions:
large number of firms
no barriers to entry/exit
product differentiation
due to no barriers of entry/exit firms earn normal profit in LR
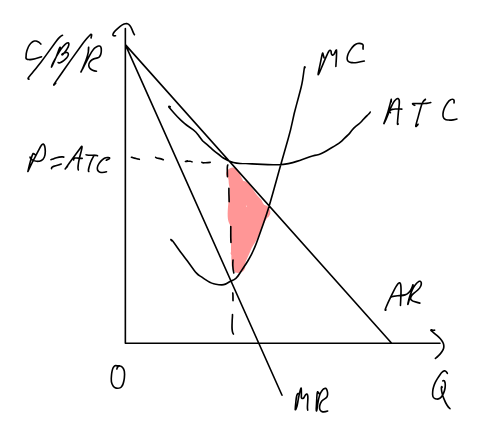
Monopoly vs. Monopolistic Competition
Monopoly demand more inelastic (no close substitutes)