Pulmonology Exam II (Sandy PE, Pleural Effusions, Pneumothorax only)
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
This is the 3rd MC cause of death in hospital patients
pulmonary embolism
1st MC cause of death in hospital patients
Pneumonia
What can precipitate a PE?
Virchows triad (and many more)
What is the MC ddx of a PE
anxiety
1. Surgery > 30 min
2. long bone fracture
3. pregnancy and prolonged vaginal delivery
4. CHF, CVA, immobilized patients
5. BCP's and smoking
ALL of these make you ______?
hypercoagulable
Inflammatory disorders trigger cytokines and cytokines can make you ________. For example Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can present with pleuritic chest pain.
hypercoagulable
What is the MC inherited predisposition for a PE?
Factor V Leiden
If a patient develops a DVT or PE out of no where with no risk factors, what should be recommended to the patient?
Genetic work up to make sure they dont have a predisposition to form clots
Occurs when venous thrombus becomes dislodged from its site and enters the pulmonary circulation
Embolization
Half of all patients that have a DVT, had a _____ and they are totally asymptomatic. Why?
PE; bc they got reabsorbed which is good bc they're very small
You most commonly get a DVT's that embolism when they are ______ (location). A DVT at this location has a much higher chance of embolisation.
above the knee
MOST PE's arise from ________ veins of the leg but can also happen in __________
large deep veins; upper extremities
Patient has been sitting in the hospital not moving and you notice that his right arm is tremendous and his left arm isn't. How do you evaluate the patient ? What is the dx?
Doppler
UE PE
This is the MC to embolize into the pulmonary circulation and originates in the deep veins of the calf
Thrombus formation
What should you do if you meet resistance when flushing a central line in the IJ? What is the risk of this?
Inject with TPA. There could be a clot or vegetation, and if you continue pushing it, it will go straight to the right side of the heart and into the pulmonary circulation, causing a PE
This type of embolisms can be seen in patients with pelvic fractures or long bone fractures that cause sheering of blood vessels and patients present with petechial rashes.
Fat embolism
When you see a patient with acute tricuspid endocarditis, what type of patient should you be thinking about and what type of embolism ?
IV drug abusers
Septic emboli
What is the MC cause of death from PE?
Right ventricular failure
Large PEs cause an inc/dec pulmonary vascular resistance and airway resistance
_______ gas exchange
alveolar hyper/hypoventilation
inc/dec pulmonary compliance
___V failure
increased pulmonary vascular resistance and airway resistance
impaired gas exchange
alveolar hyperventilation
decreased pulmonary compliance
RV failure
A PE is very difficult to diagnose clinically because SxS are not specific and depend on?
Size of emboli
What are the 3 MC signs/symptoms of PE?
Dyspnea (most common symptom - most MC)
Tachypnea (most common sign)
Chest pain (pleuritic)
What are some other sxs of a patient with a PE ?
-syncope
-hypotension
-cyanosis
-anxiety
-hemoptysis
-Tachycardia (one of the most specific findings)****
-Low grade fever (inflammatory markers)
-JVD
Usually with a PE, the HR is greater than ?
> 90 bpm
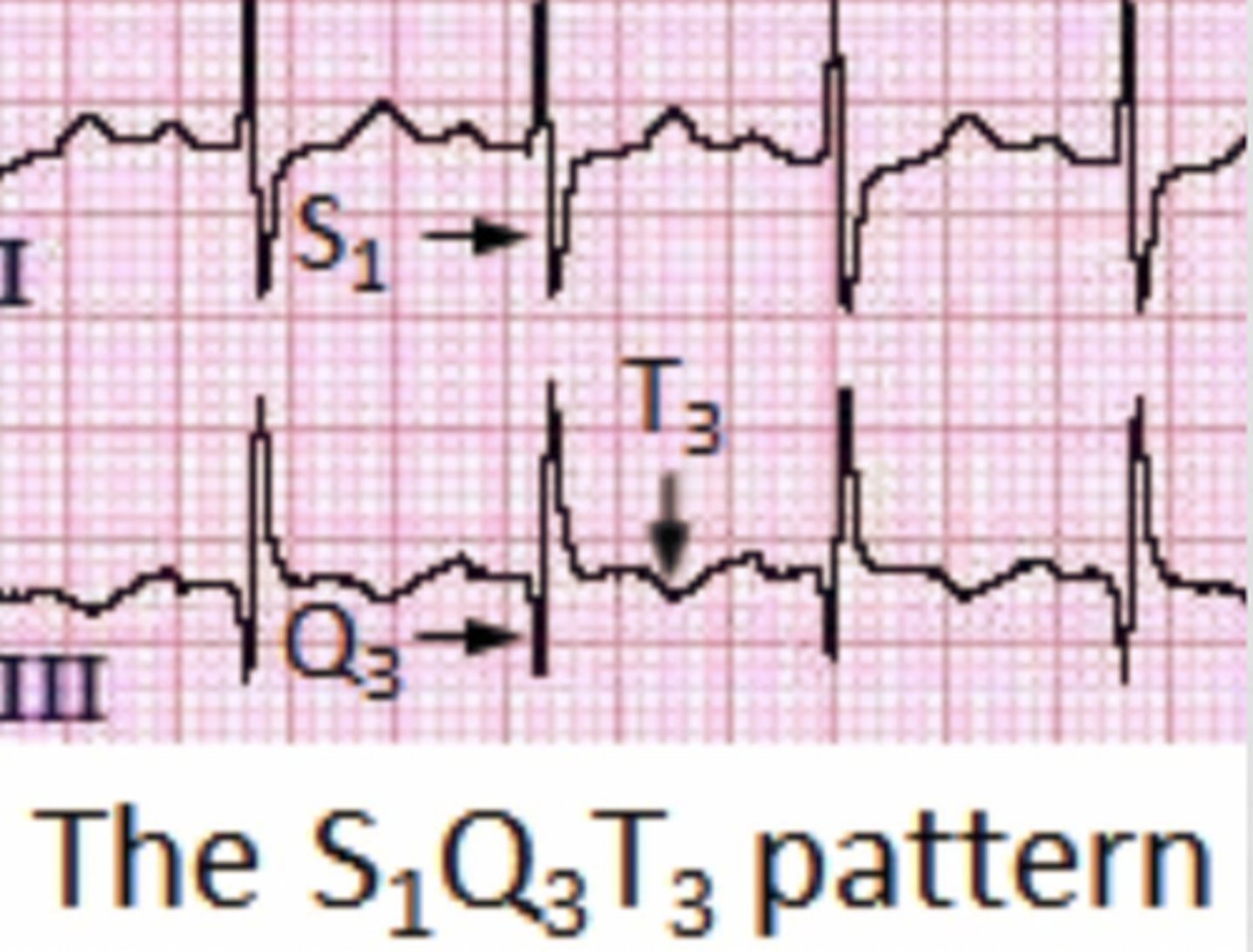
What is the classic EKG finding of PE (recall, this does not occur in all cases)?
S1Q3T3
Significant hypoxia in a patient with a negative CXR should make you suspicious of ____
PE
Although ABG has 0 predictive value for PE, what ABG findings might you see in a patient with a PE?
Respiratory alkalosis due to hyperventilation
Which blood test should always be checked in a patient suspected of having a PE?
D-dimer
D-dimers are great test to show _______ and are useful but they are 97% _______ and not specific so they are so diagnostic
clotting; sensitive
what 2 other things can throw ddimers our of wack? (that weber said)
- recent surgery (ex: tummy tuck 3 weeks ago, comes in with CP)
- covid
A patient has a negative D-dimer and has no risk factors, do you still have to work them up for a PE?
ehh maybe study say that you can let it go (This test has to fit the patient appropriately)
Are chest X-ray good for diagnosing PE?
not really but they do help you
A patient that is in severe distress with hypoxia, chest pain , SOB, tachypnic and pulse ox at 89% on room air and HR is 110 with clear chest x-ray. What should you be suspicious for?
PE because we dont see a lot PE on chest x-ray
Normally CXR will be normal but what is the MC finding on a CXR with a PE ? What else can you see on CXR?
Pleural Effusion with blunting of costophrenic angle (specifically unilateral) - MC
atelectesis (68%)
hemidiaphragm elevation (24-50%)
Focal vasoconstriction distal to an embolus seen on CXR
Westermark sign
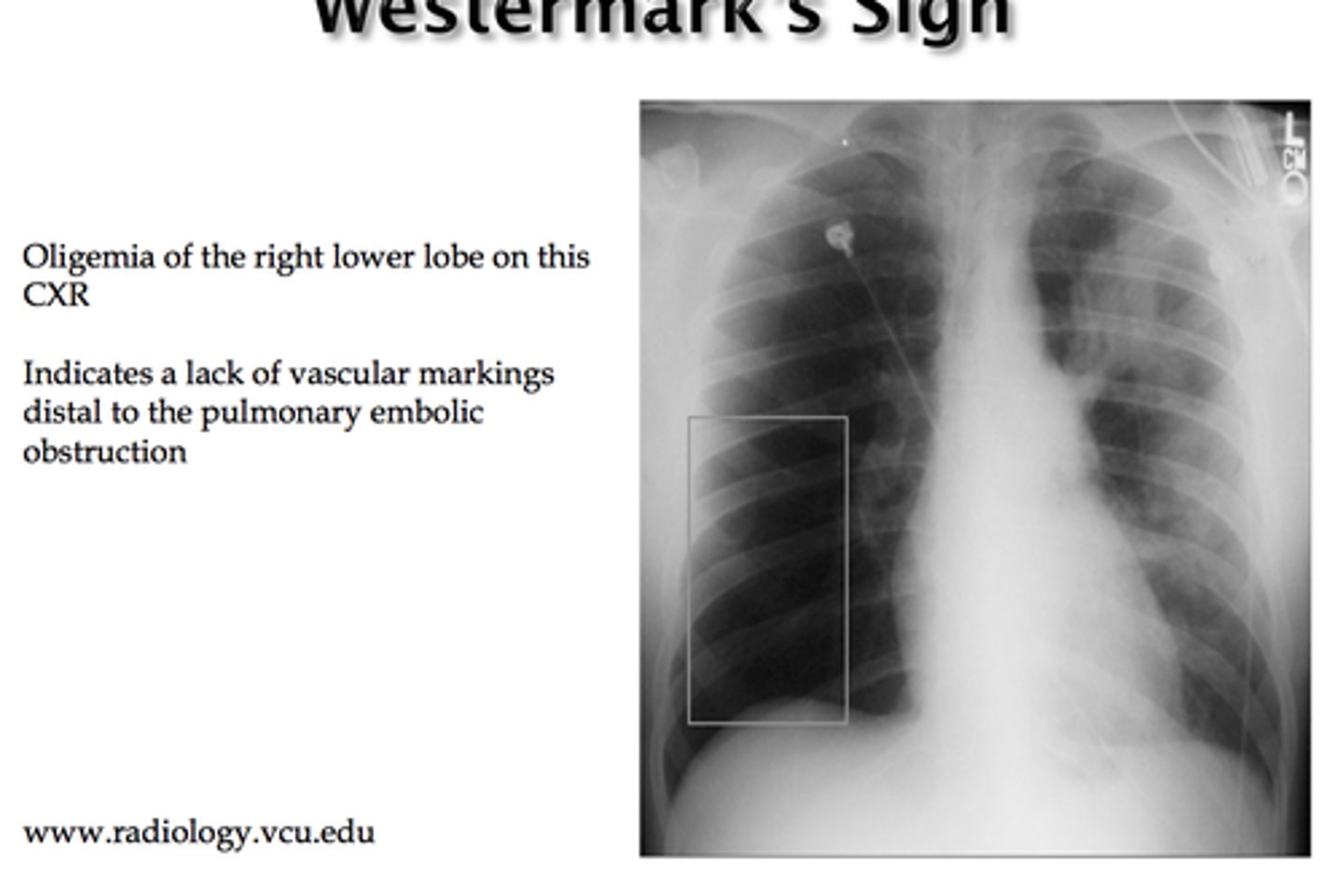
What condition is Westermark sign associated with?
PE
Peripheral wedge-shaped density above the diaphragm pointing to the hilum seen on CXR
Hampton's hump
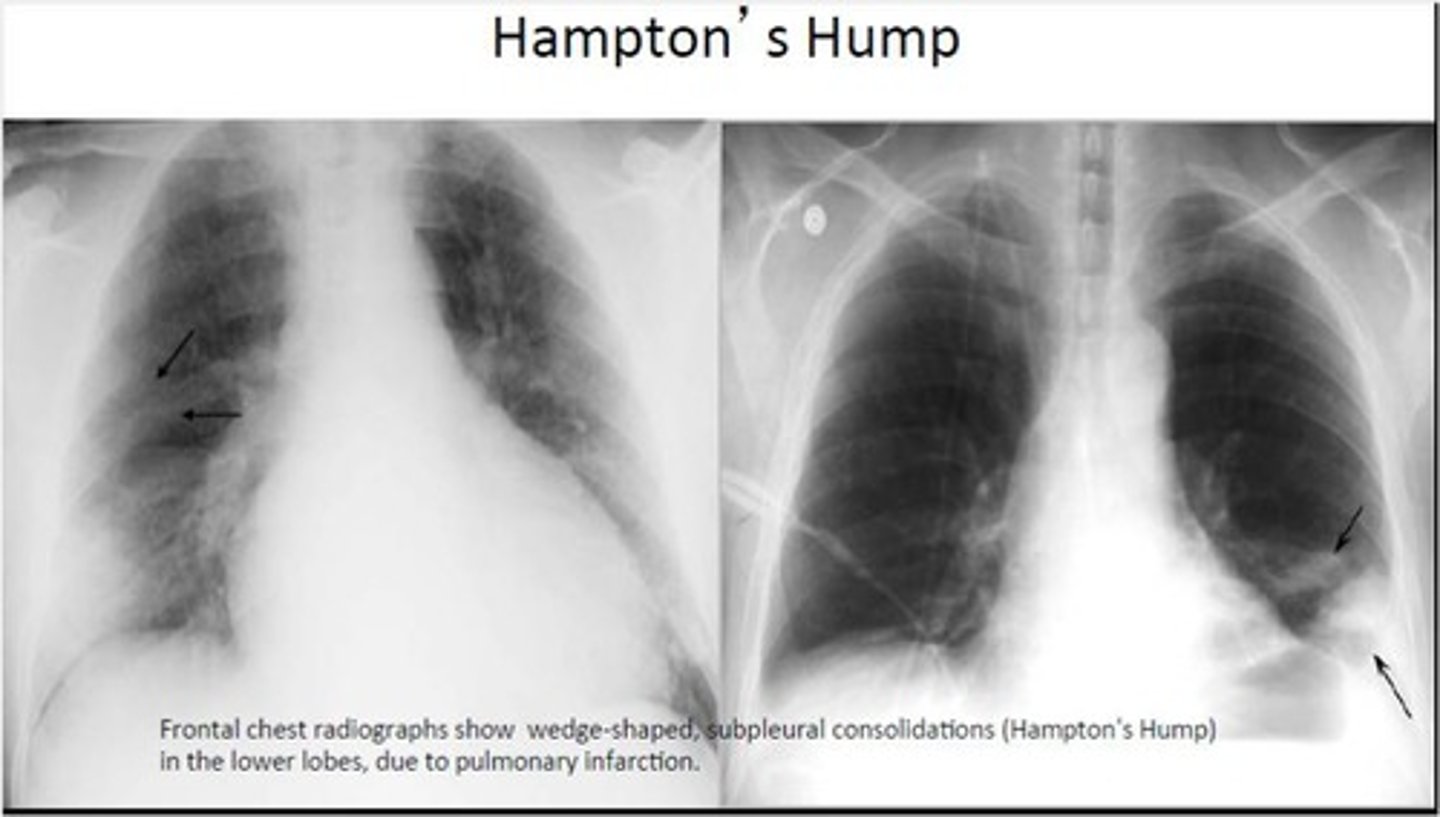
What condition is Hampton's hump associated with?
PE (specific for PE)
Enlarged right descending pulmonary artery seen on CXR
Palla's sign
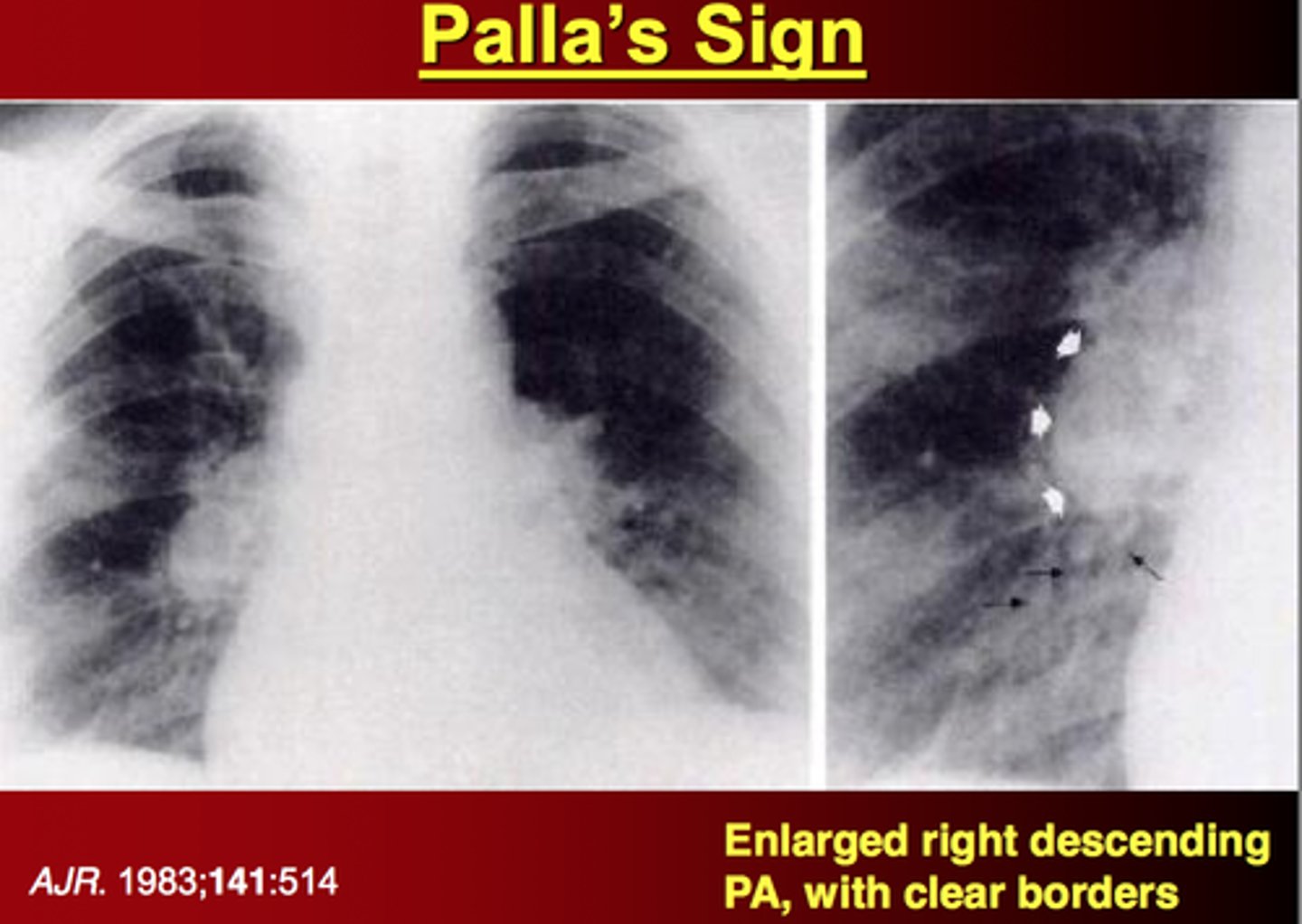
What condition is Palla's sign associated with?
PE
what is used to evaluate the deep venous system of the lower extremity to rule out DVT?
venous ultrasonography - its not the best test for PE but it's a quick way to know what's going on
Nuclear medicine scan that uses radioactive material to examine airflow (ventilation) and blood flow (perfusion) in the lungs
VQ scan
An abnormal VQ scan is indicative of what condition?
PE
What is the gold standard for diagnosing a PE that can detect emboli 1-2 mm. It is safe but very invasive because it can cause renal dysfunctions.
Pulmonary angiography
(but we dont use it much even tho its the gold standard due to it being very invasive)
What do we utilize more when diagnosing a PE ?
CT pulmonary angiography (CT-PA)
If you cannot utilize a CT-PA due to whatever reason, what test would be the next best to use to evaluate a PE?
V/Q scan
If creatinine is >_____, IV contrast shouldn't be used
>1.5
Patient with creatinine of 3.2 and concerned about PE what's the diagnostic test of choice?
V/Q scan because it DOES NOT USE CONTRAST
______ is comparable to VQ scan for the DX of PE
spiral CT
what is used for rapid triage for acutely ill pts who may have PE?
it can differentiate bw MI, pericardial tamp, aortic dissection, and PE with R sided HF
Echo
common rxns to pulmonary angiography
allergic
renal dysfunction
arrhythmias
IF a PE is likely and a CT-PA is positive what does this mean?
PE confirmed
If a PE is likely and a CT-PA is negative what does this mean?
PE excluded
If a PE is unlikely and a D-dimer assay is <500 ng/mL what does this mean?
PE excluded
If a PE is unlikely and the D-dimer Assay is >500 ng/mL, what must be done next?
CT-PA to r/o PE
What are the Well's criteria for determining a patient's likelihood of a PE?
Holy Hell I Have My Crappy Pulm exam
HR > 100 (1.5 points)
History of DVT or PE (1.5 points)
Immobilization (1.5 points)
Hemoptysis (1 point)
Malignancy (1 point)
Clinical s/s of DVT (3 points)
PE more likely than anything else (3 points)
Based on the Well's criteria, what is the classification of low, moderate and high risk for PE?
Low risk = less than 2 points
Moderate risk = 2-6 points
High risk > 6 points
True/False
HR is one of the BIGGEST thing's weber looks at (HR of 115 with chest pain, dyspnea = CONCERNED)
true
What are the PE Rule out Criteria (PERC rule)? weber likes this
Always HeR Out Here ExPecting US ... have to fulfill all of these to be considered low risk
Age < 50
HR < 100
Oxyhemoglobin > 95%
NO.......
Hemoptysis
Estrogen use
Prior history DVT/PE
Unilateral leg swelling
Surgery or trauma requiring hospitalization in the last 4 weeks
To prevent a PE we can start a patient on heparin or ______ and monitor their INR. Once INR get to _____ we stop both.
Lovanox
2-3
Patients with recurrent PEs despite anticoagulation and fall risks should receive a ________ to prevent future PE
Greenfield filter/ IVC filter
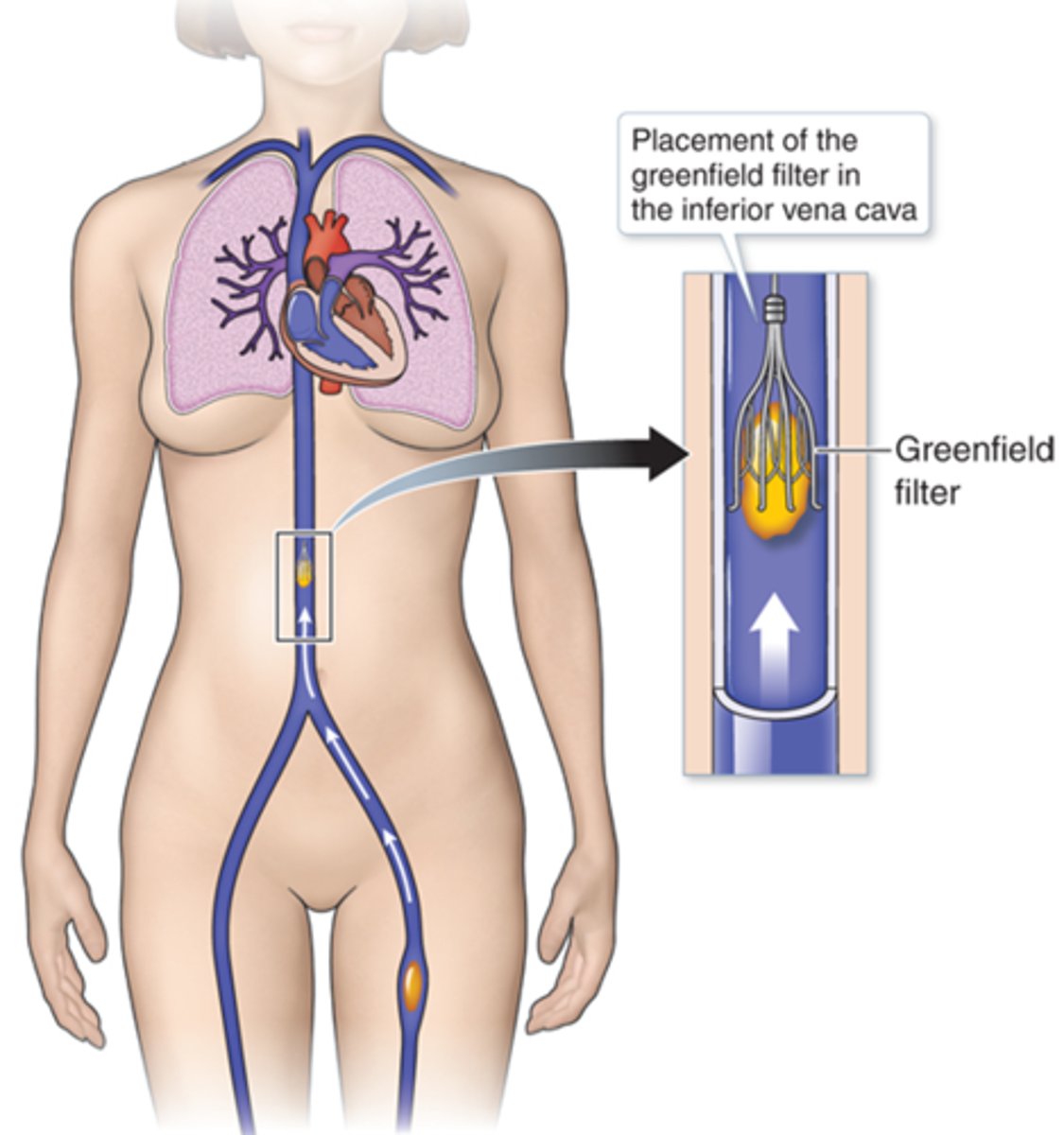
How do we tx a patient with a PE?
Start heparin to lyse the clot followed by at least 6 months of Coumadin (other anticoagulants as well)
(he doesn't like to put anyone on Coumadin because their INR needs to be monitored)
Goal of tx for PE is to maintain an aPTT of ________ x normal control
2-2.5 x
which medication do we use for PE in which thrombocytopenia is less common, there'e no need for coagulation monitoring, and is great for home based tx of PE?
low molecular weight heparin - lovanox
Goal of tx for PE is to monitor plt count bc of risk of
thrombocytopenia
What should you monitor with pts are on coumadin?
what should you beware of?
what should you keep the INR at?
monitor PT and INR
beware of vitamin K
keep INR at 2.5
IIf the INR gets too high bc of too much coumadin, what can you do?
give vitamin K!! bc its the reversing agent of coumadin
start coumadin while on heparin for _____ days. why?
5-7 - bc it takes 5-7 days for coumadin to become therapeutic
This drug, among others, are preferred over Coumadin now, because they work better and do not require monitoring
Xarelto (cost is the problem)
What medication is used to tx PE has the best safety profile and lowest chance of bleed with better compliance. No monitoring required and do have reversal agents. The only problem is the cost of these medications.
Eliquis or pradaxa
what is TPA seen with increased risk of?
hemorrhage
how does tpa work?
it stops clotting throughout the whole body
When do we TPA patients with a PE?
We dont use it unless the patient is literally on deaths doorstep typically last resort for patients with a saddle embolism because the risk of bleeding is so high (double edge sword
what are 2 absolute contraindications of tpa?
major contraindications?
Active internal bleeding, stroke with in 2 months
Uncontrolled HTN, surgery or trauma with in 6 months
Fluid accumulation between the parietal and visceral pleura (pleural space)
Pleural effusion
Since there is too much fluid with a pleural effusion, it causes?
pleuritic pain
SOB
decrease breathe sounds
What are the 5 major types of pleural effusion?
1. Transudate
2. Exudate
3. Empyema (pus)
4. Hemorrhagic (blood)
5. Chylous (lymph)
Normal Pleural fluid is... MUST KNOW
1. Clear, pH ________
2. Protein content less than ____
3. _______ WBCs per cubic mm
4. Glucose content similar to _______
5. LDH level _____ of plasma
6. Na+. K+ and Ca2+ concentration similar to __________
1. Clear, pH 7.60-7.64
2. Protein content less than 2%
3. < 1000 WBCs per cubic mm
4. Na+. K+ and Ca2+ concentration similar to interstitial fluid
5. Glucose content similar to plasma
6. LDH level <50% of plasma
This is the Lytes criteria for distinguishing an exudate from a transudate.
1. Pleural fluid protein: serum ratio >____
2. Pleural fluid LDH: serum ratio > _____
3. Pleural fluid LDH > _____ the upper limit of normal serum LDH
1. Pleural fluid protein: serum ratio > 0.5
2. Pleural fluid LDH: serum ratio > 0.6
3. Pleural fluid LDH > 2/3 the upper limit of normal serum LDH
Exudate will have one or more of the following, while transudate will have NONE of these
1. What is the normal pH of pleural fluid?
2. Inside the pH range you're probably looking at a ______ disease.
3. Outside of the pH range you're probability looking at an _______ disease.
1. 7.60- 7.64 (normal)
2. Transudative
3. Exudative
What is the MC cause of transudative effusion?
What is the MC cause of exudative effusion?
Transudate = CHF
Exudate = Pneumonia
- CHF
-Nephrotic syndrome
-Cirrhosis and Ascites
-Peritoneal Dialysis
-Constrictive Pericarditis
-Superior vena cava obstruction
-P.E (can go both ways)
What are these considered, transudate or exudate ?
transudative
- Pneumonia
- Cancer, P.E
- Empyema, T.B
- Viral , Fungal or Rickettsial infection
- Pancreatic disease (amylase & lipase)
- Asbestos, Sarcoidosis
- Post-MI syndrome
What are these considered, transudate or exudate ?
Exudate
What does it mean when weber said a PE is noncommittal
it cant commit to either transudate or exudate because it can be hemorrhage which falls under exudate
(he said to be very careful with this)
If there is a mix of pleural fluid and blood that clears with each tube that you fill are we concerned about it?
no probably some minor trauma
Grossly bloody plural fluid that continuously fill each vile with blood are we concerned? Why?
Yes because it can be due to trauma, cancer, PE
what does empyema look like??
Purulent and turbid
what does a hemorrhagic effusion look like??
Mix of blood and pleural fluid
what is a chylous effusion due to? what does it look like?
Due to disruption of the thoracic duct
Milky, cloudy fluid
How do we tell the difference between a chylous effusion and an empyemic effusion?
Centrifuge it. If it separates, it is empyema. If it does not separate, it is chyle
What are the symptoms of pleural effusion... Think about it ....
1. If we continuously pour fluid into a small space in the lung and cause compression of the lung, what will this cause?
2. What are you going to hear?
3. On percussion it would be?
4. Do you always have pain?
5. Do you always have a tracheal shift?
6. What test will be positive?
1. Dyspnea (MC) and coughing
2. Crackles
3. Dullness
4. No always but can have pleuritic chest pain
5. Not always but can if its a large effusion
6. Egophony (eee to aaa)
When will there be a tracheal shift with pleural effusion
if its a very large effusion
What is the MC sign of pleural effusion?
dyspnea (this is also the MC sign of PE!! yay)
Greater than ____ cc of fluid must be present on thoracentesis in order for a pleural effusion to be detected on CXR
250 cc
If you TAP a patient and drain their chest, at ____ cc we must stop draining because we can cause hypotension. Stop it, clap it, let them recover for an hour and then continue.
800 cc
Meniscal line on CXR is indicative of ____
Pleural effusion
______ labs will look like this
1. Normal protein, pH (7.63) and LDH
2. WBC < 1,000
3. Glucose= serum glucose
also clear
transudate
_______ labs will look like this
1. Presence of malignant cells
2. Positive culture
3. pH < 7.30
4. Low glucose
5. increase amylase
(bloody or cloudy)
exudative labs
These types of illnesses are very common with effusions on the left side of the chest due to their ducts actually drains into the thorax at the thoracic duct. If you test ______, it will be positive with these.
Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer
Amylase
When we tx pleural effusions we must tx the ?
underlying disease
Since the MC of transudate effusions is CHF, how do we tx CHF normally?
Diuretics- decrease hydrostatic pressure below the oncotic pressure so the fluid goes into the vessels and we pee it out
(simple, no need to memorize lol)