1.3 Computer networks, connections and protocols
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
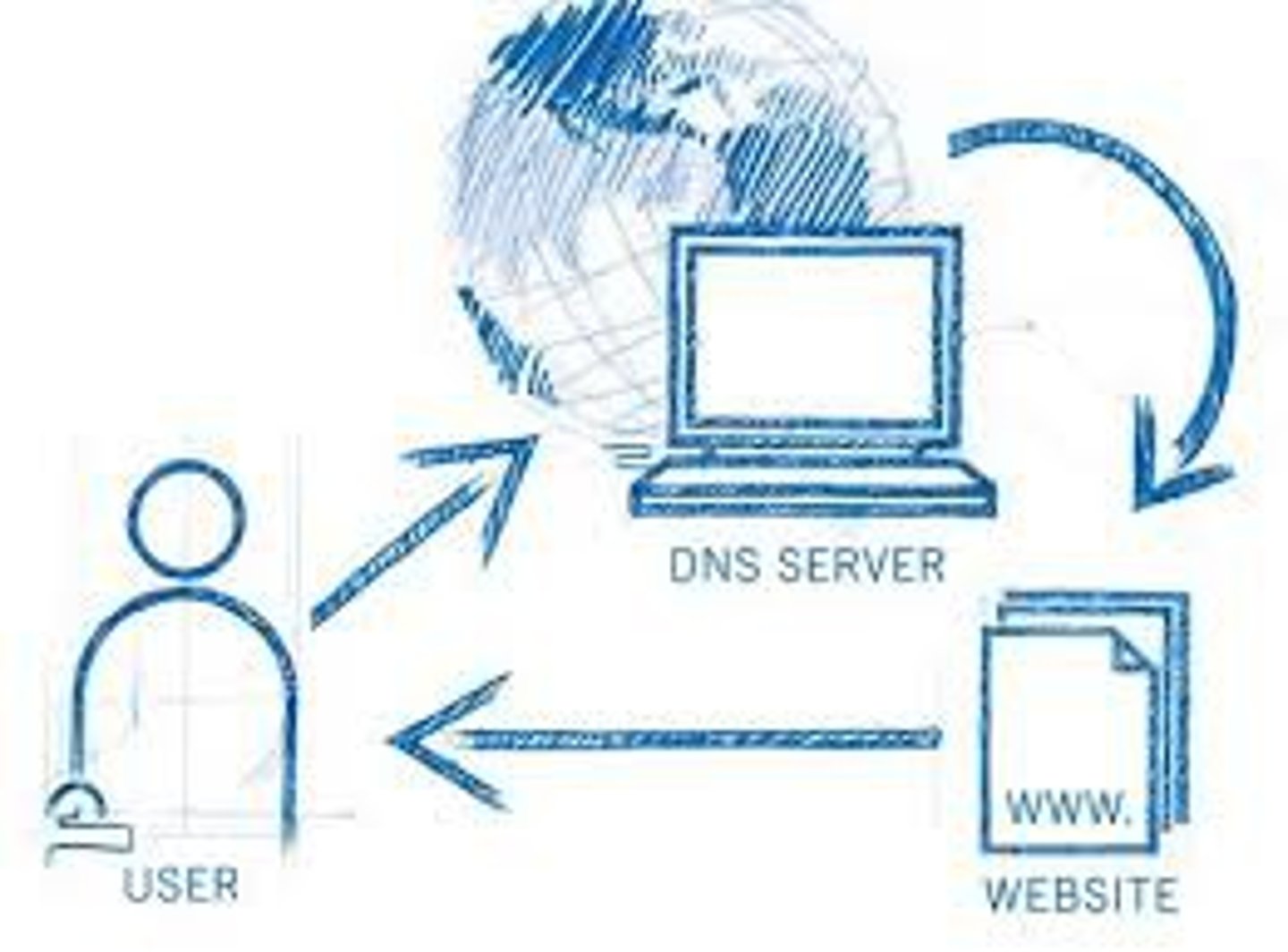
Domain Name System
Looks up the URL to find the IP address of the website requested by the client
Hosting
Storing and sharing a website on the WWW on behalf of someone else. We sometimes talk about Cloud hosting

Web Server
The computer that runs a website and makes it available on the WWW

Internet
A global network made of devices, cables, satellite links and protocols. It sits underneath the WWW and routes the data

Client
A computer which connects to a web server and requests web pages and displays them in a browser
Uniform Resource Locator
The unique address used to locate a resource on the world wide web. An example is http://www.bbc.co.uk

Bandwidth
The rate at which data can be transferred over a network, measured in bits per second (bps)

World Wide Web
A collection of websites, apps and streaming services. They can be accessed using the internet. Abbreviated to WWW

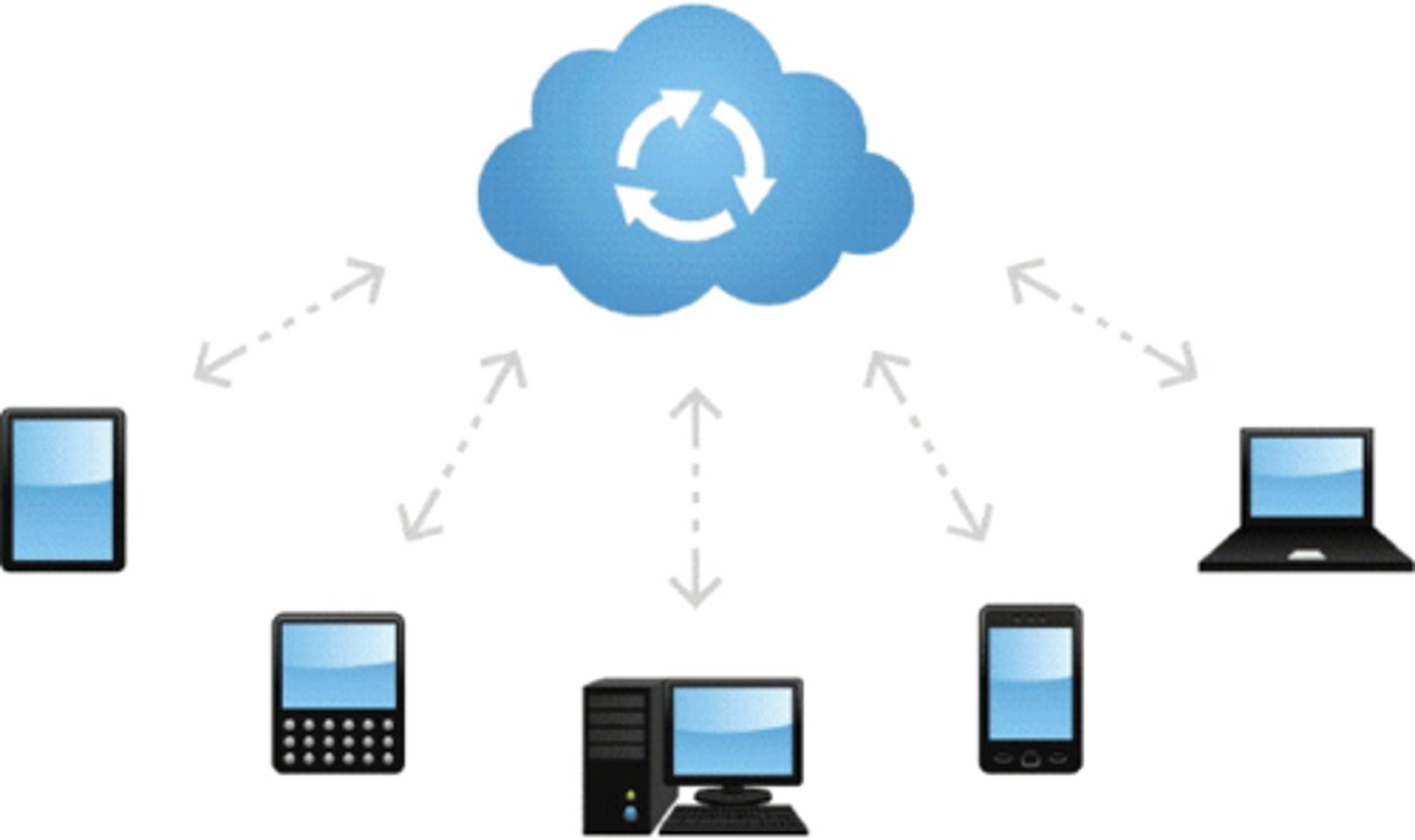
Cloud
A collection of computing services provided by companies over the internet, including data storage, backup, web hosting, payment services and software platforms
https://www.quizlet.com
The URL of the Quizlet website
104.16.15.221
The IP address of the Quizlet website

Backup
A typical cloud service that saves a copy of your data. You can restore data from your cloud copy if your local data is lost through hardware failure or destroyed by malware
Software
We can run this in the cloud, for example REPL.IT is a cloud Python IDE. Amazon, Google and Microsoft can run applications for you in the cloud such as financial services or AI chatbots

Storage
Data is saved here, which can be in the cloud. Data in the cloud can be accessed anywhere with an internet connection, but some people worry about security

Network
A collection of computers or devices connected via cables or Wi-Fi to share data, peripherals or an internet connection
Node
Any single machine connected to a network
Topology
The physical arrangement of connected devices on a network, the shape of a network (mesh, star)
Personal Area Network
Small network for data transmission over short distance. For personal use such as headphones, often uses Bluetooth
Local Area Network
Network covering a small geographic area such as a building or site. All hardware is usually owned by the user's organisation, e.g. school.
Wide Area Network
Network covering a large geographical area such as a city or country. Often uses 3rd party hardware, cables or satellite connections.
Wired
A physical network connection using a cable
Wireless
A network connection that uses radio waves
Star
All devices are connected to a central switch or hub which directs data and requests in this versatile topology
Mesh
A network topology where nodes have many connections to other nodes meaning it is fast and reliable but expensive
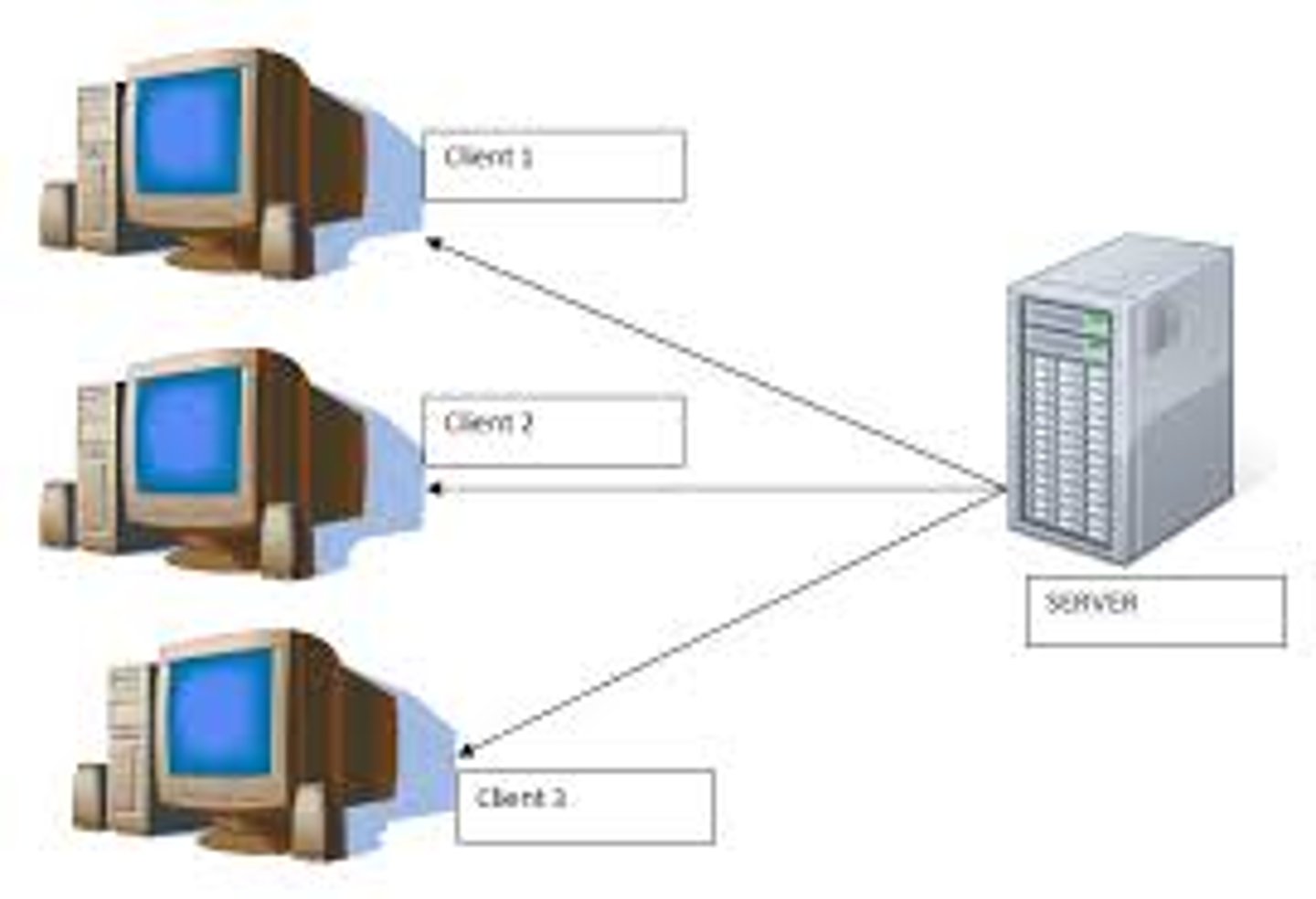
Client-Server
A network model with a central server where files are stored and clients who request services from the server. More secure and reliable than peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer
All computers on the network are equal in this model and data may be shared between them. Insecure and unreliable but cheap
Cheap
Peer-to-peer networking model is this
Secure
Client-server model of networking is this
Small
The geographic area of a LAN is this
School
A typical business that will use a LAN in a Star topology with a client-server model
Internet
The world's biggest WAN, it's made of millions of routers connected to other WANs and LANs
Server
A powerful computer attached to a network that awaits and responds to requests for data from the clients
Client
A computer that requests data or services stored on a server. The computer you use in school is a client
Request
A message sent from a client computer to a server asking for data in a client-server network
Switch
A network device that directs packets of data on a local area network. It uses MAC addresses to route traffic to the correct device
Hub
This dumb network device has no means of storing MAC addresses so it sends all packets to all devices connected to it
Router
This network device joins two LANs or a LAN to a WAN. It uses the IP address on a device to route traffic to another router, which passes it on to its own LAN. A router connects your home LAN to the internet
Network Interface Card
A hardware component that connects a device to a computer network. Every networked device needs one, it has a unique MAC address
MAC Address
Unique identifier assigned to every NIC by the manufacturer. Switches use this to route packets. Short for Media Access Control Address, it can't be changed. Consists of six bytes written in hex, like this: A1:9E:13:7C:FF:04
Fibre Optic
This transmission media is a cable that has a glass core. Data is sent as pulses of light and these cables have much higher bandwidth and suffer less interference than copper but are expensive
Copper
The metal used inside standard data cables, this media is cheap and reliable but has more limited length and bandwidth
Wireless Access Point
Network component which allows Wi-Fi enabled devices to connect to a network. Usually built into a "home hub" internet router, and can be seen on the ceilings of schools and public buildings
Media
The method of connecting devices to a network, types are copper cable, fibre optic cable and wireless
Congestion
Caused by too many devices being connected to a network at once, or all the traffic filling up the bandwidth, this causes a network to slow down
Obstruction
An obstacle such as a walls or floor. It can reduce the strength of the wireless signal which means lots of packets get lost and have to be resent. This reduces bandwidth and slows down the connection
IP Address
A unique number that identifies each device on the network, this can change every time and is usually assigned by a Router or Switch. Traditionally four bytes written in decimal like this: 10.124.7.32
B1:5B:1A:72:EF:35
This is an example of a MAC address
192.0.1.44
This is an example of an IP address (in format IPv4)
Owned
All the hardware devices and transmission media that make up a LAN are this
Satellite
You would only see this device used in a WAN that spans the globe, never a LAN
Local
Another word for nearby, it's the L in LAN
Dumb
A hub doesn't know anything about the devices connected to it, so we say it is this
Smart
A Switch knows all the MAC addresses of its connected devices so it is intelligent, also called this
Smartphone
A phone that runs apps and has a network connection, it connects wirelessly to a LAN through a Wireless Access Point