Psych Brain Areas
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What did descartes say?
mind & body are seperate → we know this isn’t true
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
motor control & balance → if drunk, cerebellum is affected (hindbrain)
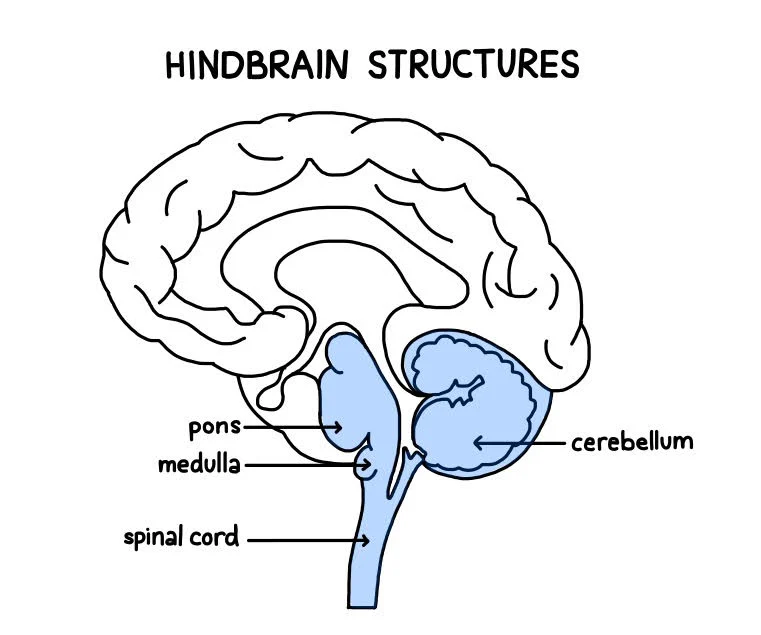
What is the medulla responsible for?
coordinates heart rate, circulation and respiration → without medulla, me die (hindbrain)
What information does the hindbrain coordinate?
information coming in and out of the spinal cord
What is the hindbrain responsible for doing?
most basic functions of life → respiration, alertness and motor skills
What is the reticular formation responsible for?
regulates sleep, wakefulness and arousal → rest-icular formation (hindbrain)
What is pons responsible for?
relays information from the cerebullum to the rest of the brain → it’s like a bridge ov er a pon(d)s (hindbrain)
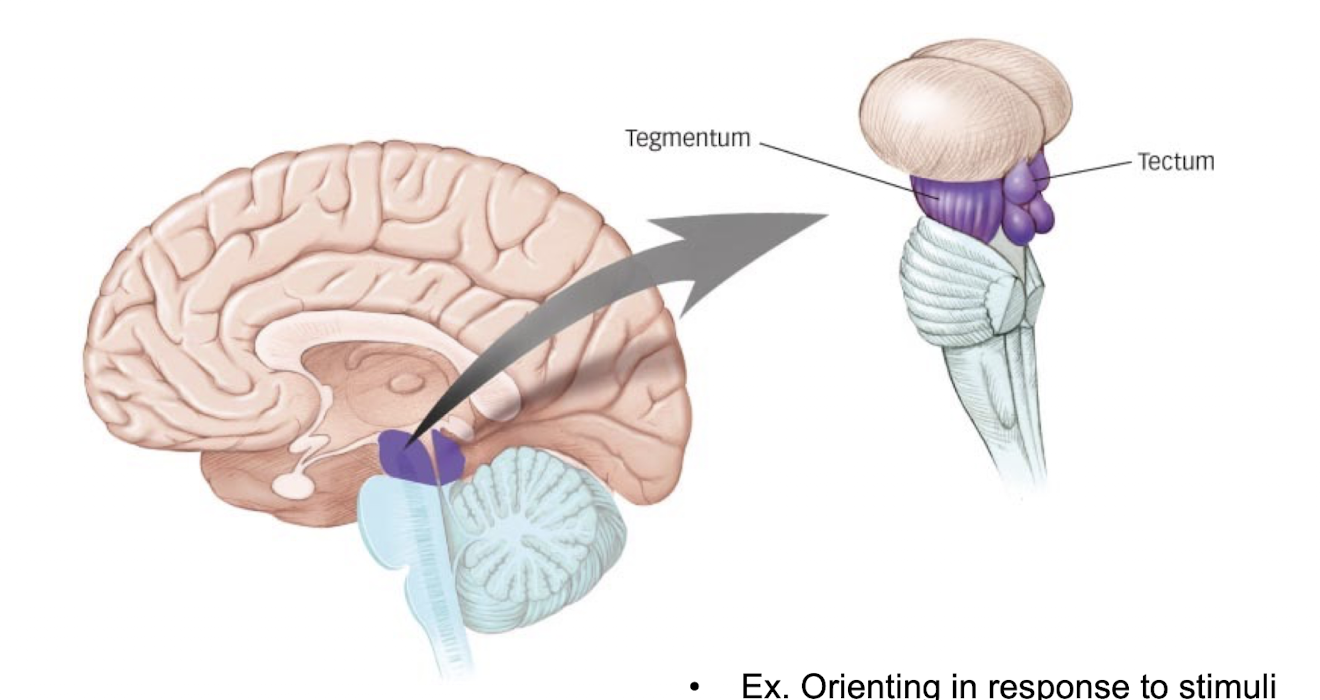
What is the tectum responsible for?
orients an organism to the environment by receiving stimulus input from the eyes, ears,and. skin → if you hear a click sound behind you, you’ll whip your head around to look (midbrain)
What is the tegmentum responsible for?
involved in movement and arousal (midbrain)
What part of the brain is the central location of neurotransmitters involved in arousal, mood, and motivation and the brain structures that rely on them?
the midbrain
What is the forebrain?
it is the highest level of the brain that controls complex cognitive, emotional, sensory and motor functions
What are the two main parts of the forebrain?
cerebral cortex and subcortical structures
What is the cerebral cortex?
outermost layer of brain, visible to naked eye divided into two hemispheres
What is the subcortical structures?
areas of the forebrain housed under the cerebral cortex near the center of the brain
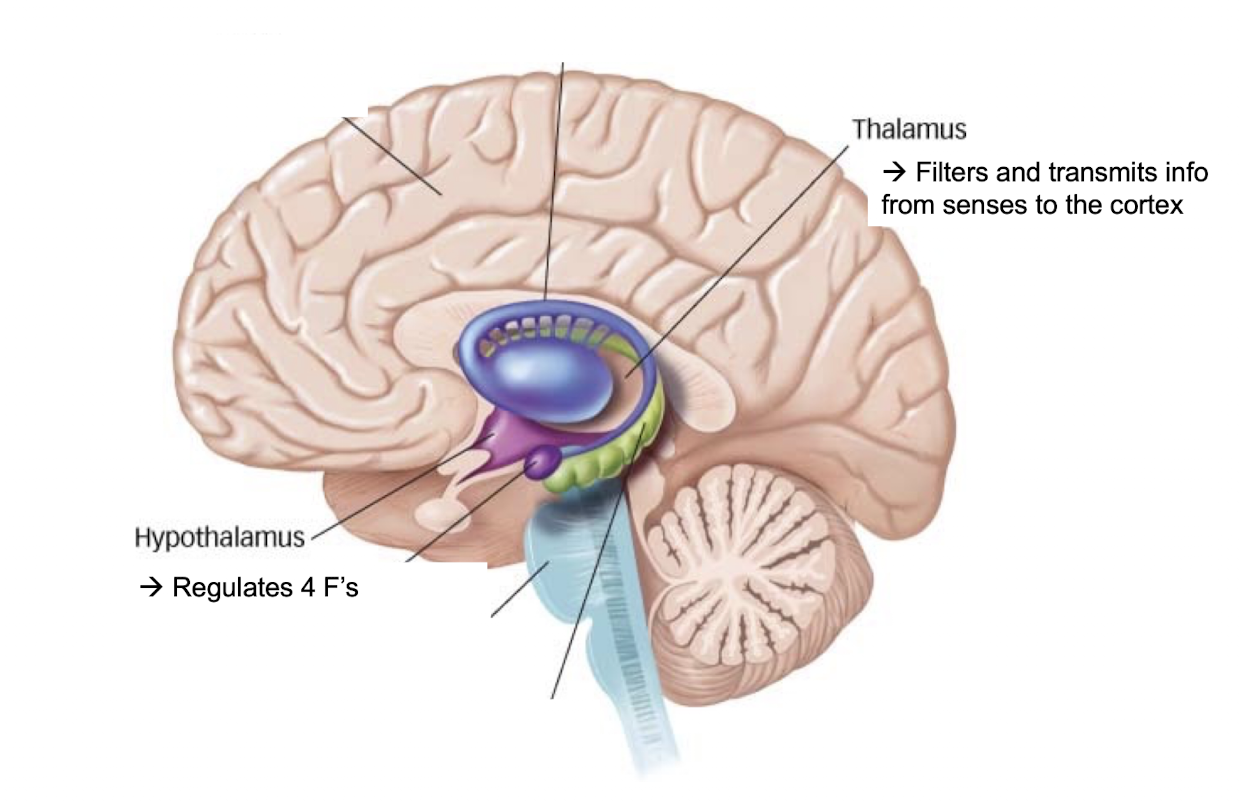
What is the thalamus responsible for?
processes info for cortex → thalamus sends info where to go like a train for all senses EXCEPT FOR SMELL (subcortical structures)

What is the hypothalamus responsible for?
controls needs like a sim → 4 F’s = fighting, fleeing, feeding, fucking (subcortical structures) ; limbic system
What can happen if you stimulate one part of hypothalamus for too long?
it can starve an animal because it is basically an on/off switch
What is the amygdala?
role in emotional processing → amy is emotional (subcortical structures) ; limbic system
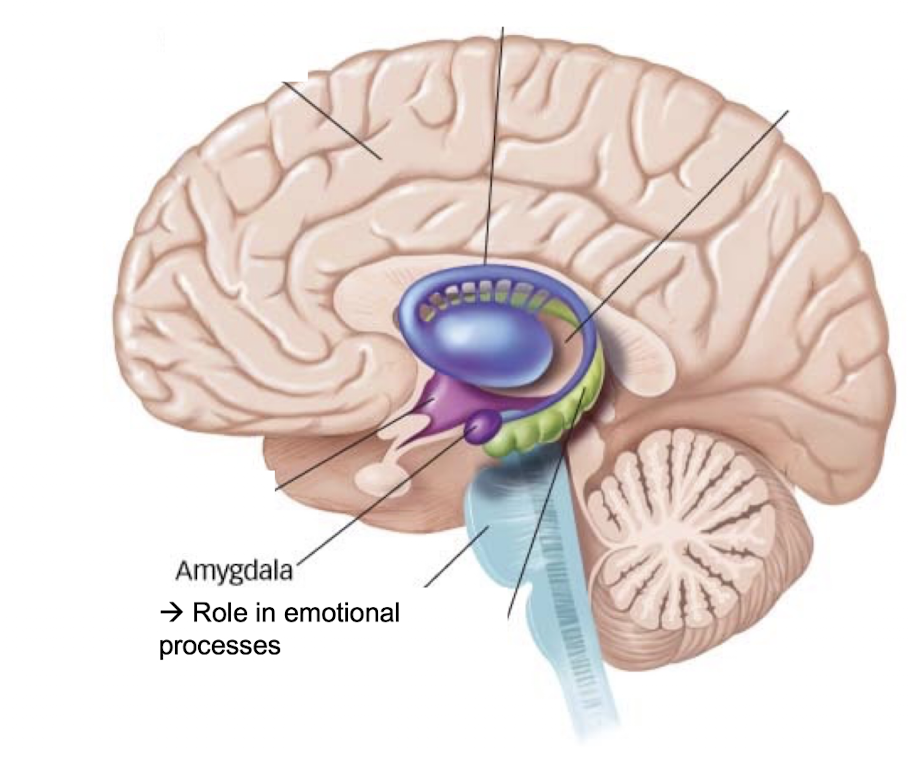
What is the hippocampus responsible for?
responsible for creating and integrating new memories (subcortical structures) ; limbic system
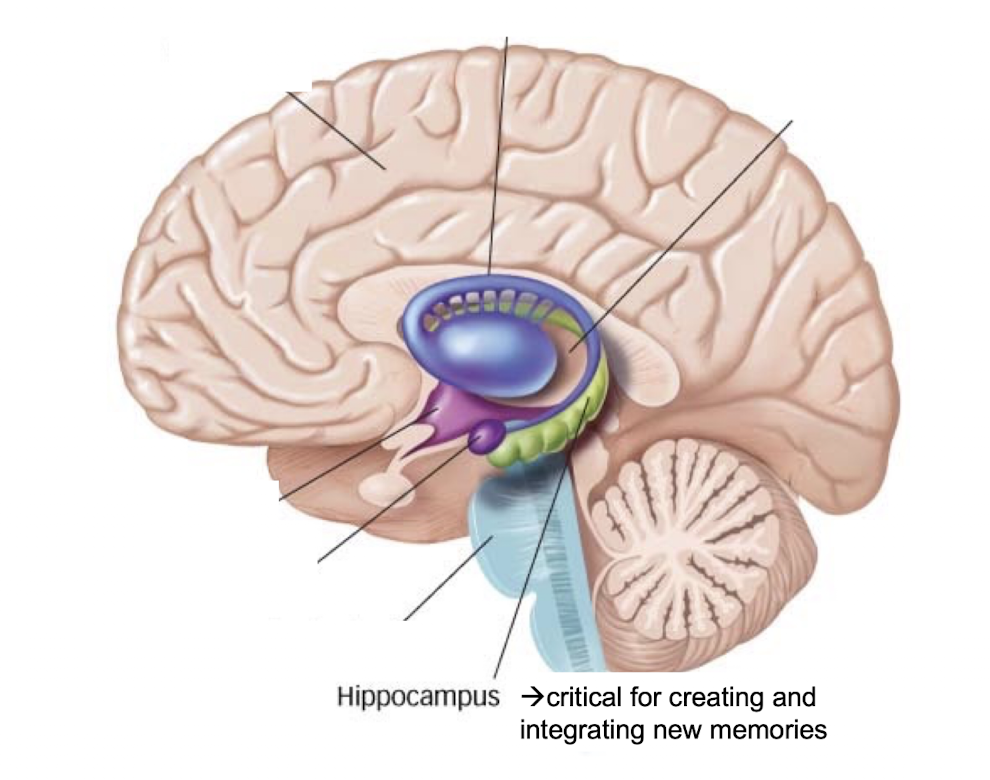
What can happen if the hippocampus is removed?
you would have a 20 second memory and cannot form memories anymore
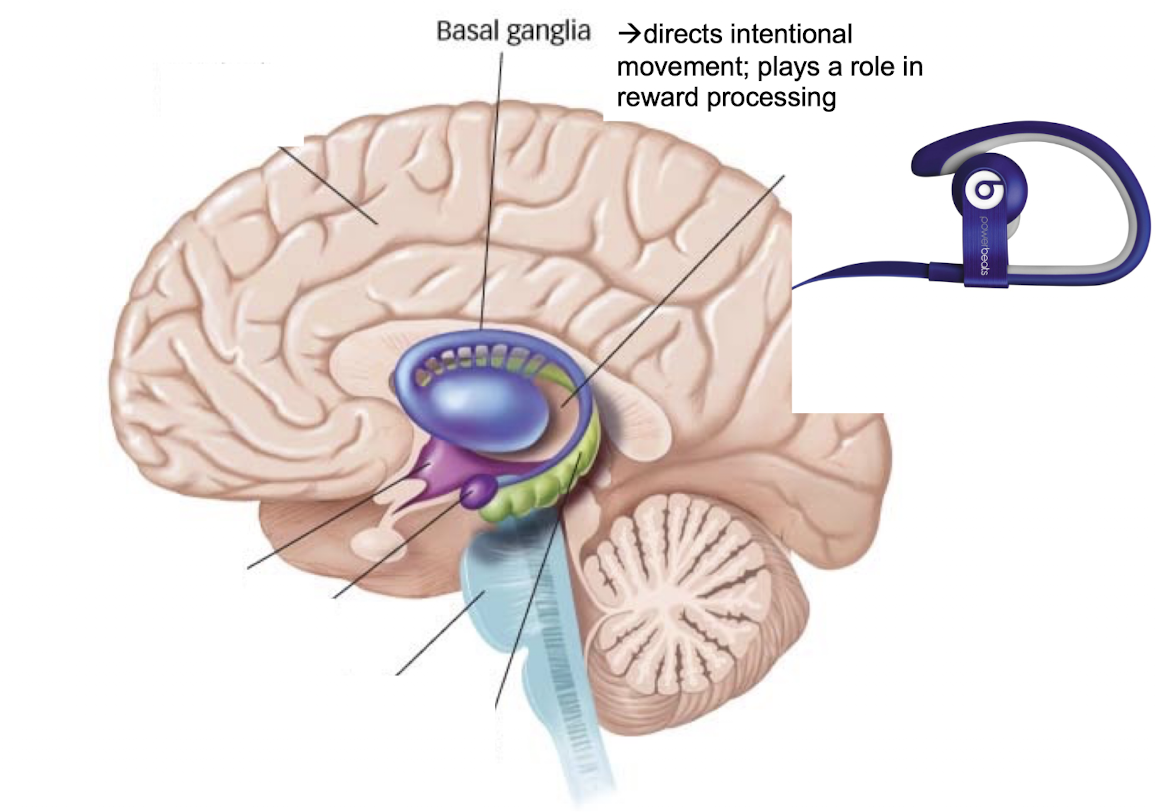
What is the basal gangalia responsible for?
directs intentional movement and plays a role in reward processing → turn up the bass so we can dance!
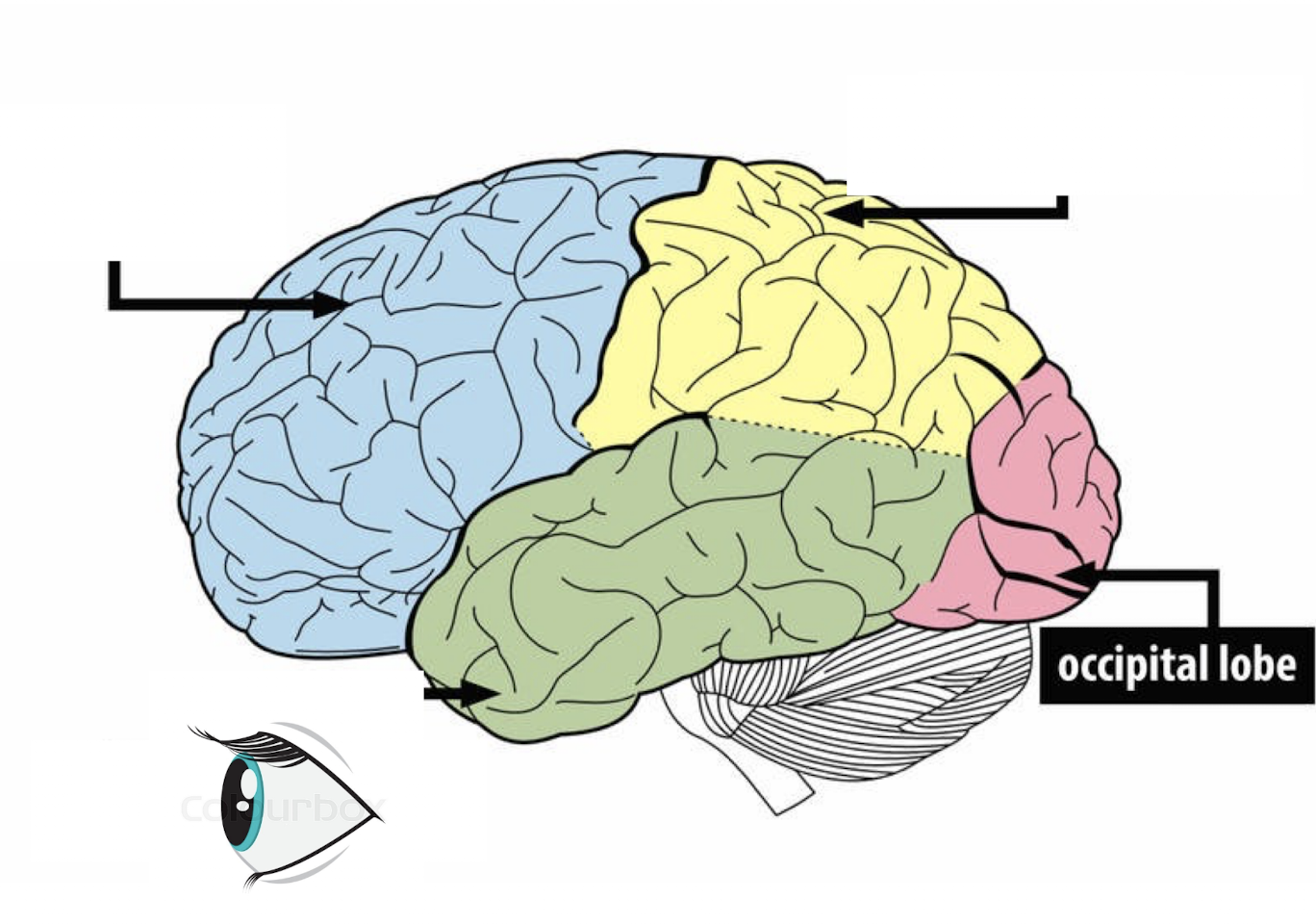
What is the occipital lobe responsible for?
processing visual information → optometrist in the optical
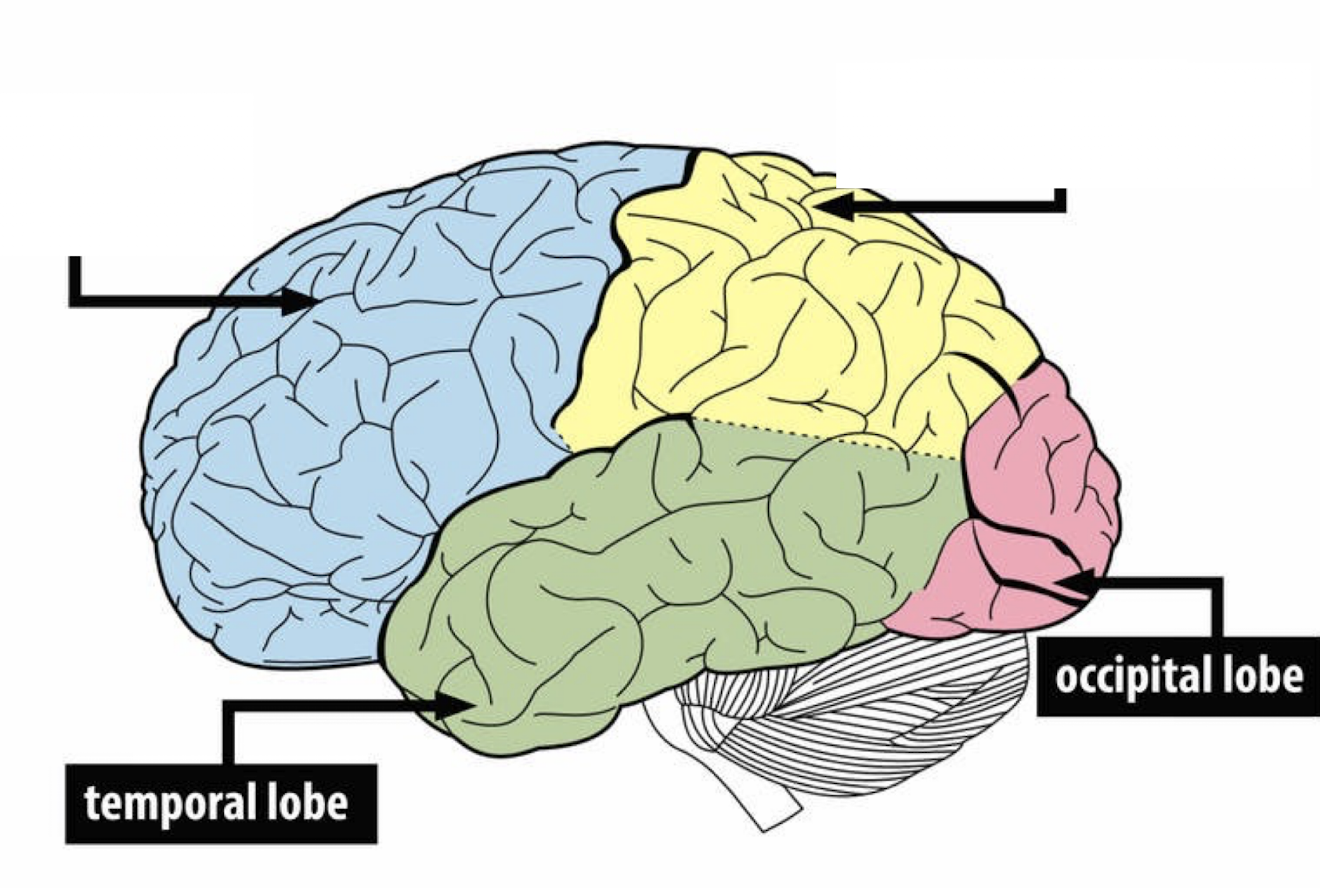
What is the temporal lobe responsible for?
primary auditory process, also helps us identify faces
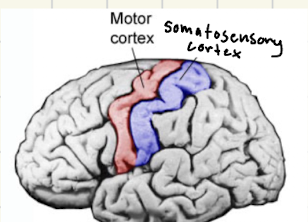
What is the somatosensory cortext?
if an area is more sensitive (lips), it’ll take up more space in the cortex → two point test (touching fat and lips) helps detect what is more sensitive

What is the motor cortex?
areas with more fine motor control will take up more space → tms testing shows that when you stimulate certain areas, motor control is affected
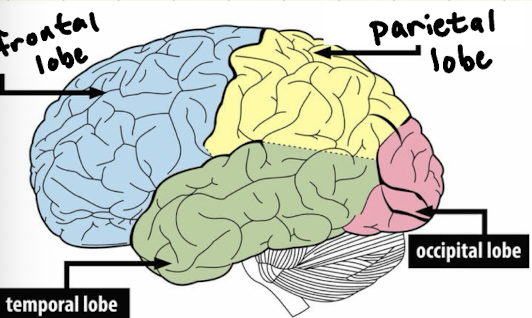
What is the parietal lobe?
allows us to process touch → petting like parietal
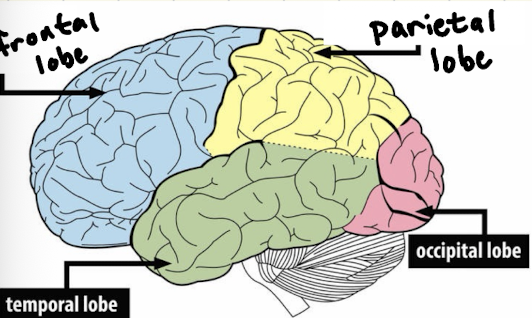
What is the frontal lobe?
impulse control → prefrontal cortex develops last → reason why younger child has trouble making “big decisions”
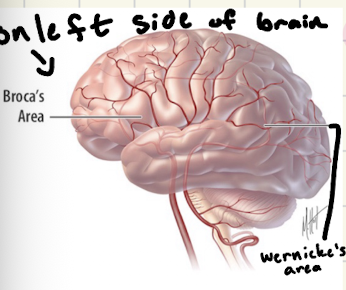
What is broca’s area?
responsible for language/speak → patients who have trouble speaking have damage on the left side of their brain between frontal and temporal → understands what is said but cannot form words
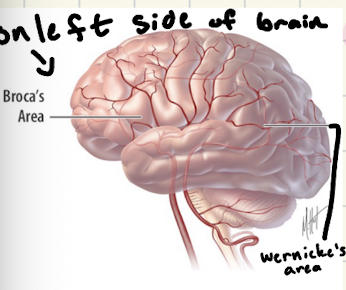
What is wernick’s area?
responsible for speech comprehension → located by parietal area → everything is just word salad
What are broca’s aphasia symptoms?
halting speech, repeat words/phrases, disorder grammar/syntax, comprehension intact
What are Wernicke’s aphasia?
fluent speech, little spontaneous repitition, adequate grammar, comprehension not intact
What are cell bodies?
coordinates info processing tasks and keeps the cell alive
What are axons?
long progression off cell body, carries info to other neurons, muscles, or glands
What are dendrites?
receive info from other neurons and relays info to the cell body
What is the synapse?
region between 2 neurons/dendrites
What is the myelin sheath?
fatty sheath that insulates axons, increases speed + efficency
What can happen if the myelin sheath is damaged?
multiple diseases can occur like multiple selerosis because it’ll impact muscle movement and coordination
What is a neuron?
a cell that specializes in receiving and transmitting information
What is the synaptic cleft?
tiny gap between two neurons where they communicate
What are neuron transmitters?
chemical messengers that transmit signals from one neuron to a muscle cell, gland, or another neuron across a synapse
What is agonist?
drugs that increase the action of a neurotransmitter
What is antagonist?
drugs that diminish the function of neurotransmitter
What is the outside and inside charge of a neuron?
outside “+” charged (NA+, Cl-) → inside “-” charged (K+, A-) → resting potential = -70mV
In action potential, what is repolarization?
after the sodium gates close - potassium moves out
What is depolorazation
When stimulated sodium channels open and + ins rush in
What is sensation?
physical processing of environemntal stimuli by sense organs
What is perception?
psychological process of interpreting sensory information
What is psychophysics?
methods that systematically relate physical characteristics of stimulus to an observers perception
What is absolute threshold?
smallest amount of stimulation needed for detection by a sense 50% of the time
What is the just noticible difference (JND)
minimum difference between two stimuli to detect a difference 50% of the time
What is top-down processing
when our perceptions are influenced by our expectations or by our prior knowledge
What is bottom up processing?
when we perceive individual bits of sensory information (sound) and use them to construct a more complex message
What is signal detection theory?
response to stimulus depends on person’s sensitivity on a person’s decision criteria
What is sensory adaption?
diminished sensitivity as a result of constant or recurring stimuli
What is selective attention?
focusing on one particular task or event
What is inattentional blindness?
failure to perceive objects that are not focus of attention (gorilla coming into scene)
What is change blindness?
failure to detect changes to visual details of scene (curtain changing colors)