[L2] - Cell: The Basic Unit of Life
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Prokaryotes
The simplest organism.
Capsule
Gel-like coating outside the cell wall
Nucleoid
Location of the bacterial chromosome
Where the DNA is located in a single circular.
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis
Many proteins specified by bacterial DNA are synthesized on tiny structures.
Plasma Membrane
Sheet that surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates entrance and exit of molecules.
Cell wall
Structure that provides support and shapes the cell
Cytoplasm
Semi-fluid solution surrounded by the plasma membrane; contains nucleoid and ribosomes.
Flagellum
Rotating filament that propels the cell
Protruding from the surface of a cell that are used in locomotion.
Peptidoglycan
The cell wall is composed of (blank) which consists of a carbohydrate matrix that is cross-linked by short polypeptide units.
Compartmentalization
What is the hallmark of the eukaryotic cell?
Endomembrane System
This is achieved through a combination of an (blank) that weaves through the cell interior and by numerous organelles.
Nucleus
The largest and most easily seen organelle within a eukaryotic cell.
Nucleolus
Many nuclei exhibit a dark-staining zone called (blank), which is a region where intensive synthesis of ribosomal RNA is taking place.
Chromatin
DNA is divided into multi linear chromosomes.
These are organized with proteins into a complex structure.
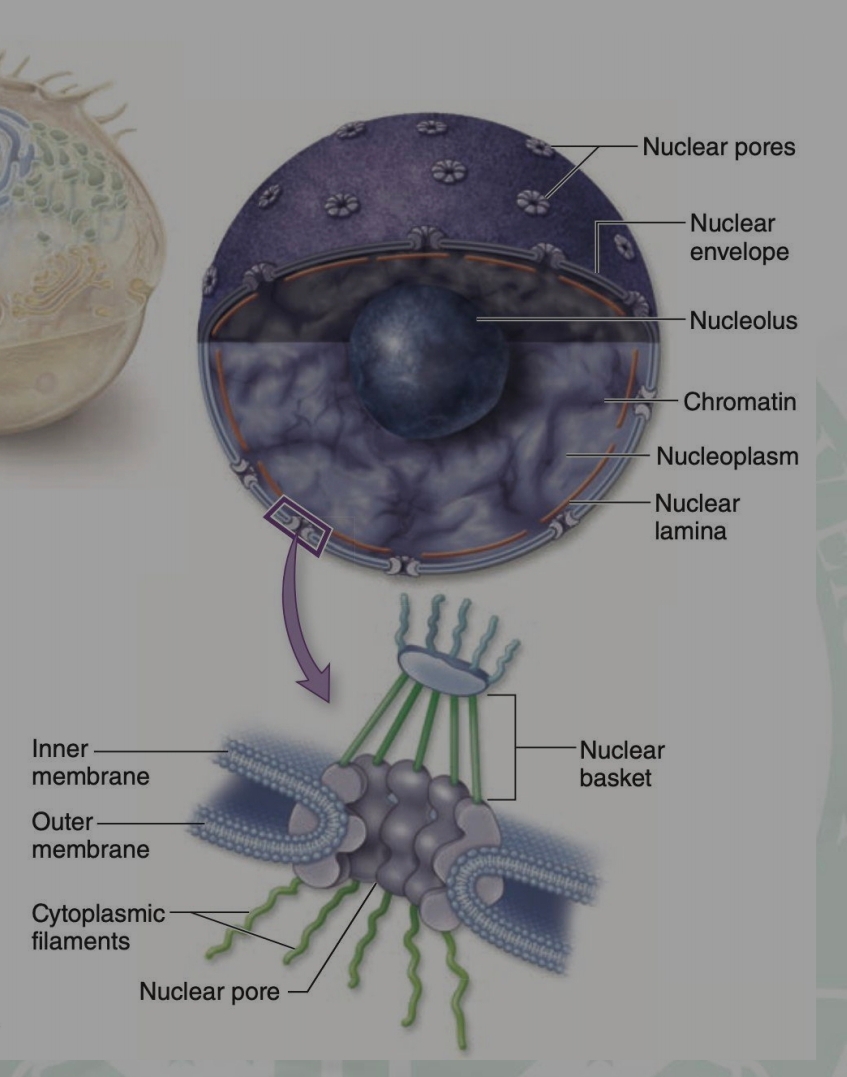
Nuclear Pores
Nuclear Envelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nucleoplasm
Nuclear Lamina
Nuclear Basket
Inner Membrane
Outer Membrane
Cytoplasmic Filaments
Nuclear pore
Enumerate the parts of nuclei.
Ribosomal RNA
Each ribosome is composed of two subunits and is composed of what?
Universal Organelles
Ribosomes can be thought of (blank) because they are found in all cell types from all three domains of life.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The largest of the internal membranes is called.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
It appears to be composed primarily of flattened sacs, the surfaces of which are bumpy with ribosomes.
Proteins synthesized are destined to be exported from the cell.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
It is a region of the ER with relatively few bound of ribosomes.
It store intracellular Ca²+
It modify the foreign substances to make them less toxic.
Cisternae
The individual stacks of membrane are called (blank), and they vary in number within the Golgi body.
Golgi Apparatus
It functions as collection, packaging, and distribution of molecules synthesized at one location.
Cis face
Trans face
What are the two faces of the Golgi apparatus?
Lysosomes
They contain high levels of hydrolytic degrading enzymes.
These enzymes break down old organelles or broken parts of a cell.
Peroxisome
It contains enzymes involved in the oxidation of fatty acids.
Hydrogen peroxide
It is produced as a by-product of the activities of oxidative enzymes.
Enzyme Catalase
It is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
Vacuoles
Plant cells have specialized membrane-boundef structures and it's called?
Tonoplast
It contains channels for water that are used to help the cell maintain its tonicity, or osmotic balance.
Mitochondria
It metabolize sugar to generate ATP
They are typically tubular or sausage-shaped organelles about the size of bacteria that are found in all types of eukaryotic cells.
Known as power house of the cell.
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Mitochondria are bounded by two membranes.
Cristae
The inner membrane with numerous contiguous layers are what?
Matrix
It is lying inside the inner membrane
Intermembrane space
It is lying between the two mitochondrial membranes.
Chloroplasts
Uses light to generate ATP and sugars.
It contains the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll that gives most plants their green color.
Granum
Chloroplasts have closed compartments of stacked membranes called (blank), which lie inside the inner membrane.
Thylakoid disk
Each granum may contain from a few to several dozen disk-shaped structures called (blank).
Stroma
It is a fluid matrix that surrounds the thylakoid.
Plastids
Collectively term for chloroplasts, leucoplasts, and amyloplasts.
Actin Filaments
Long fibers about 7 nm in diameter.
Each filament is composed of two protein chains loosely twined together like two strands of pearls.
Microtubules
The largest of the cytoskeletal elements, are hollow tubes about 25 nm in diameter, each composed of a ring of 13 protein protofilaments.
Intermediate filaments
The most durable element of the cytoskeleton in animal cells.
A system of tough, fibrous protein molecules twined together in an overlapping arrangement.
Centrioles
These are barrel-shaped organelles found in the cells of animals and most protists.
Centrosome
It is the region that surrounds the pair in almost all animal cells.
Cilia
These are short cellular projections that are often organized in rows.
Primary walls
These are laid down when the cell is still growing.
Middle lamella
Between the walls of adjacent cells a sticky substance glues the cells together.
Secondary walls
They are deposited inside the primary walls of fully expanded cells