Chapter 16 reactions & terms
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
need to know all mechanisms except imine & enamine
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
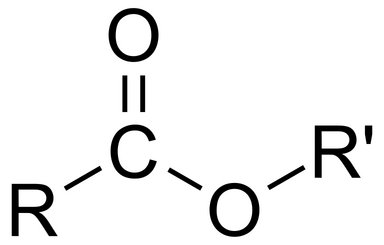
Ester
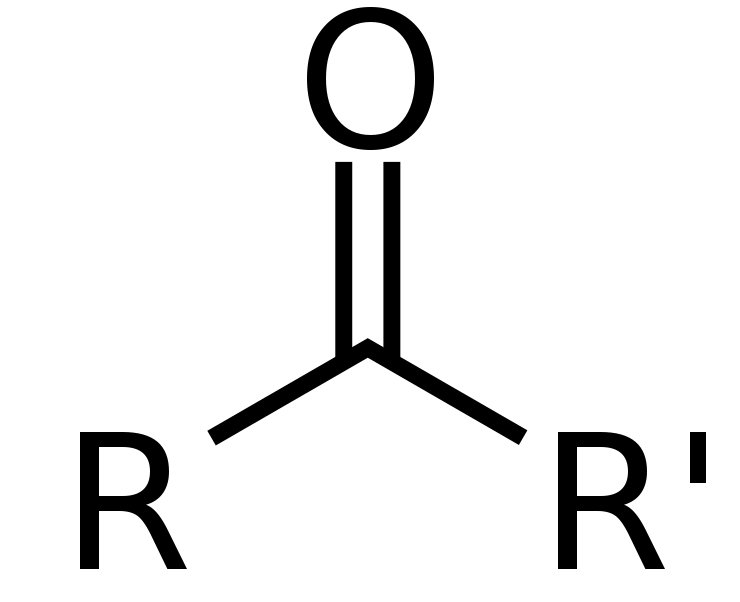
Ketone
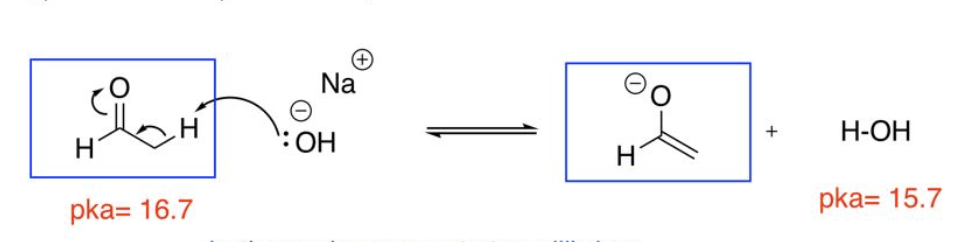
uses weaker bases ex. NaOH, NaOEt
Reversible enolate formation
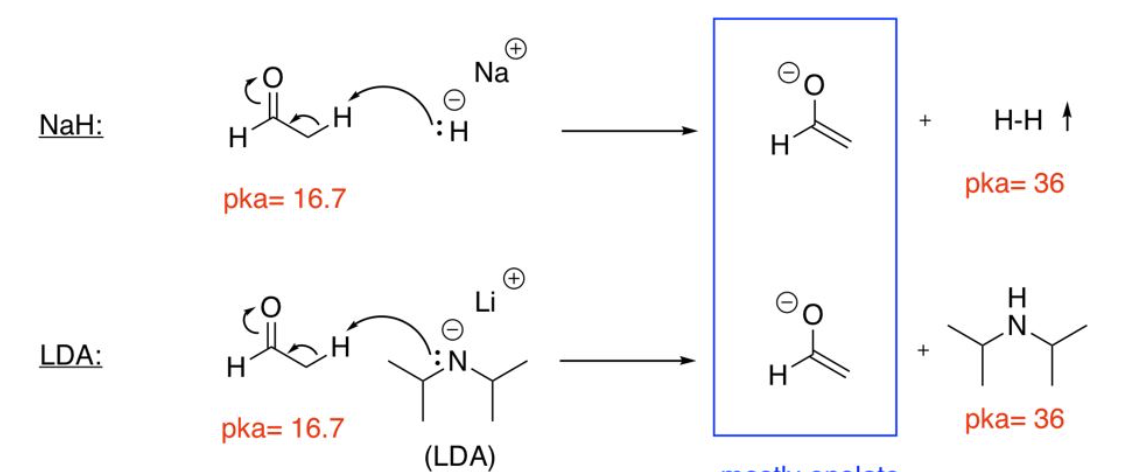
uses strongest bases ex. LDA, NaH
Irreversible enolate formation
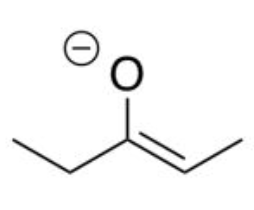
enolate (base)
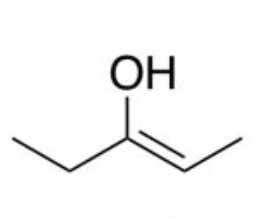
enol (conjugate base of acid)
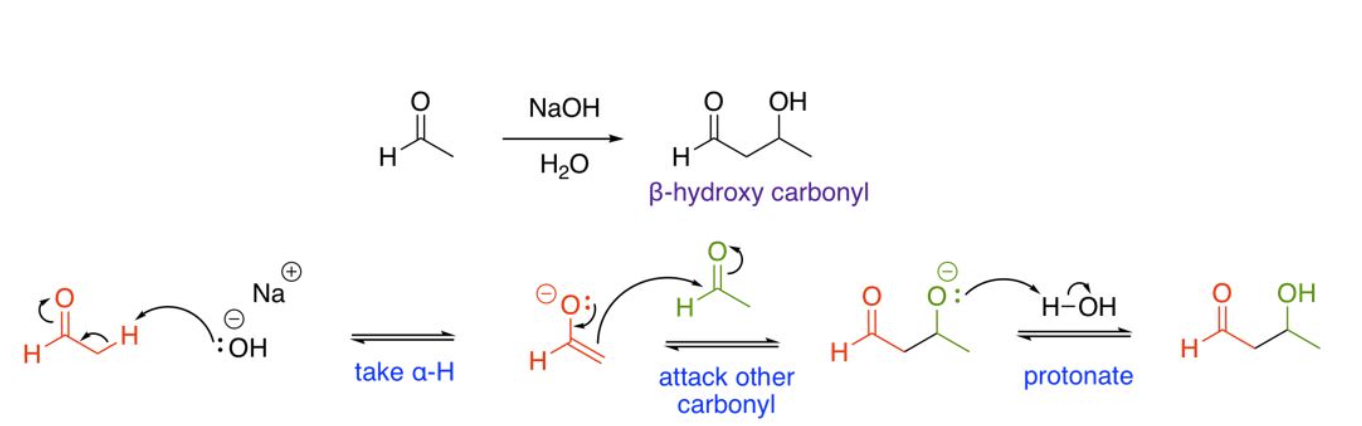
Self Aldol Addition
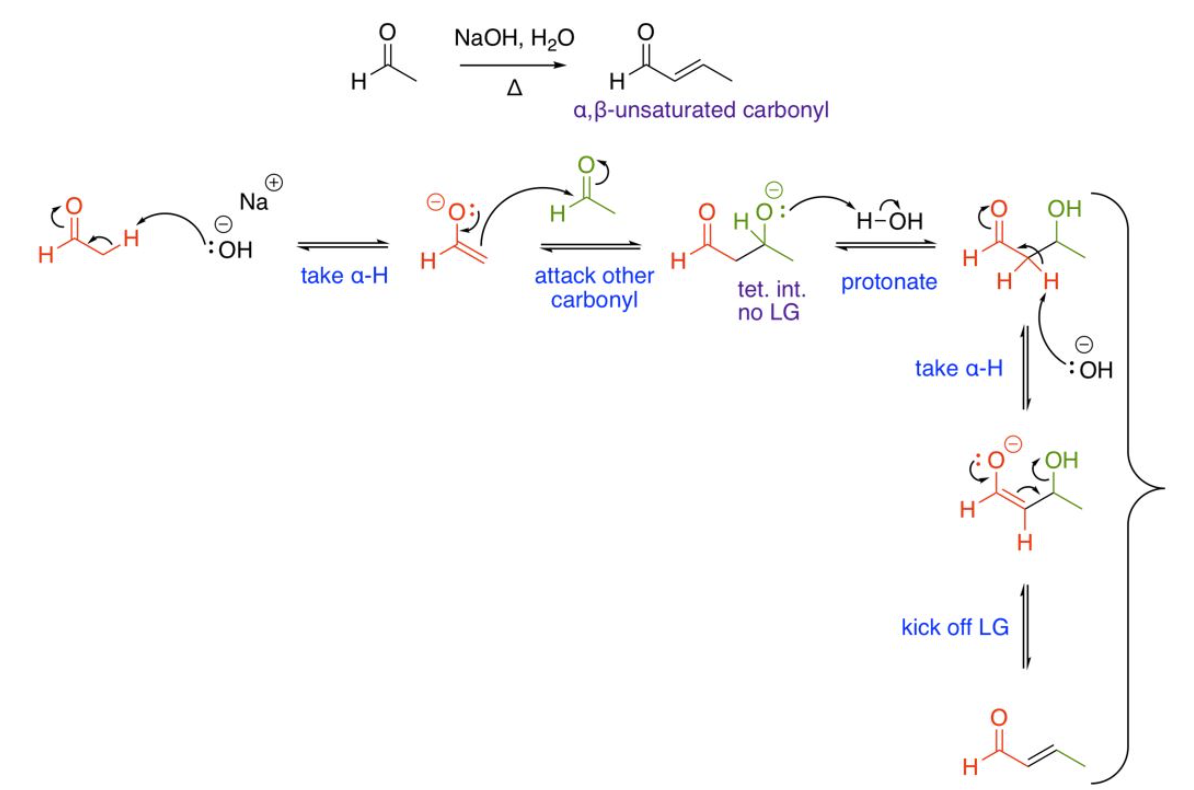
Self Aldol Condensation (one unique aldehyde or ketone with HEAT)
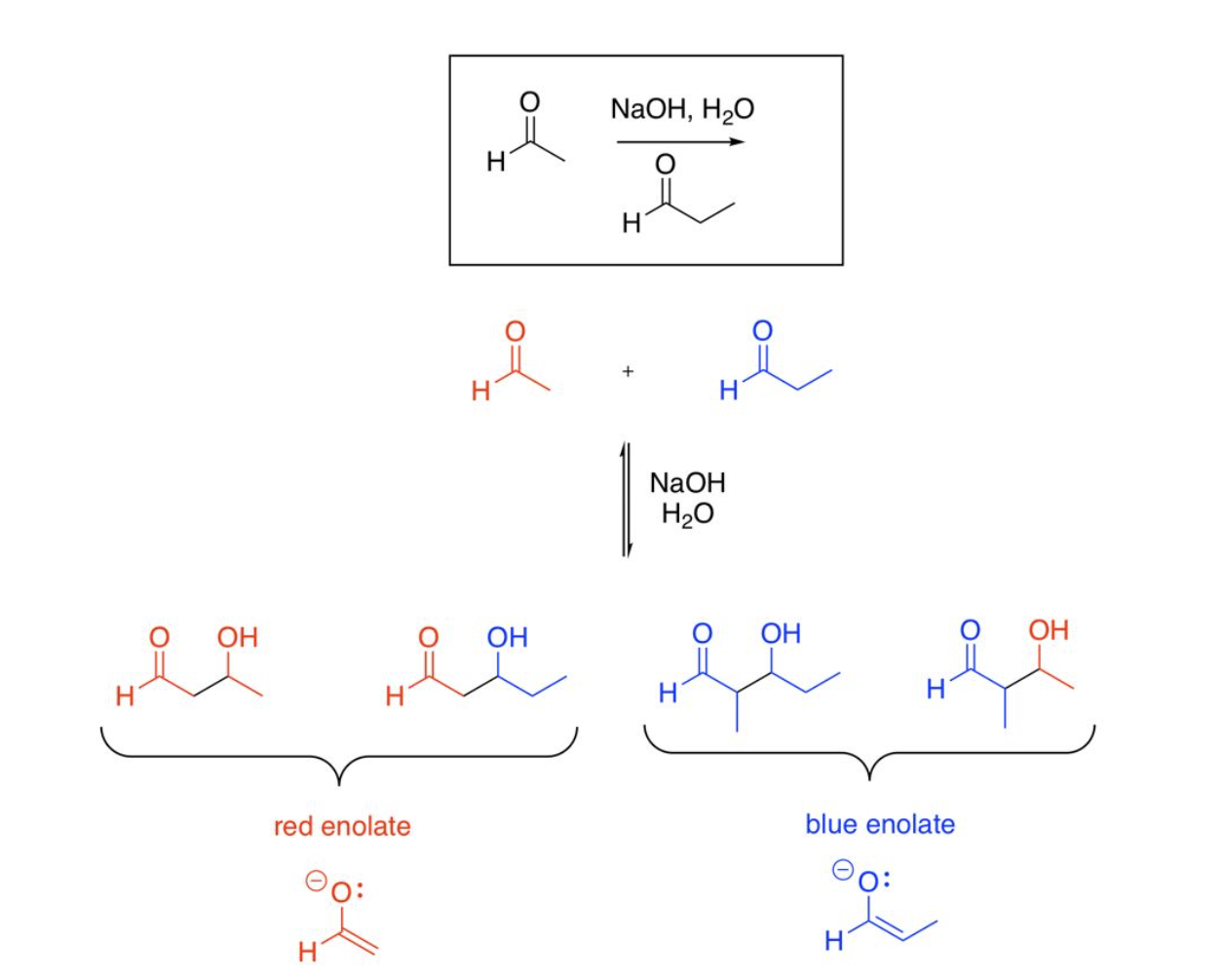
Crossed Aldol Reactions (two unique aldehydes or ketones); (control number of products using irreversible base & no water OR using one carbonyl without an α-hydrogen)
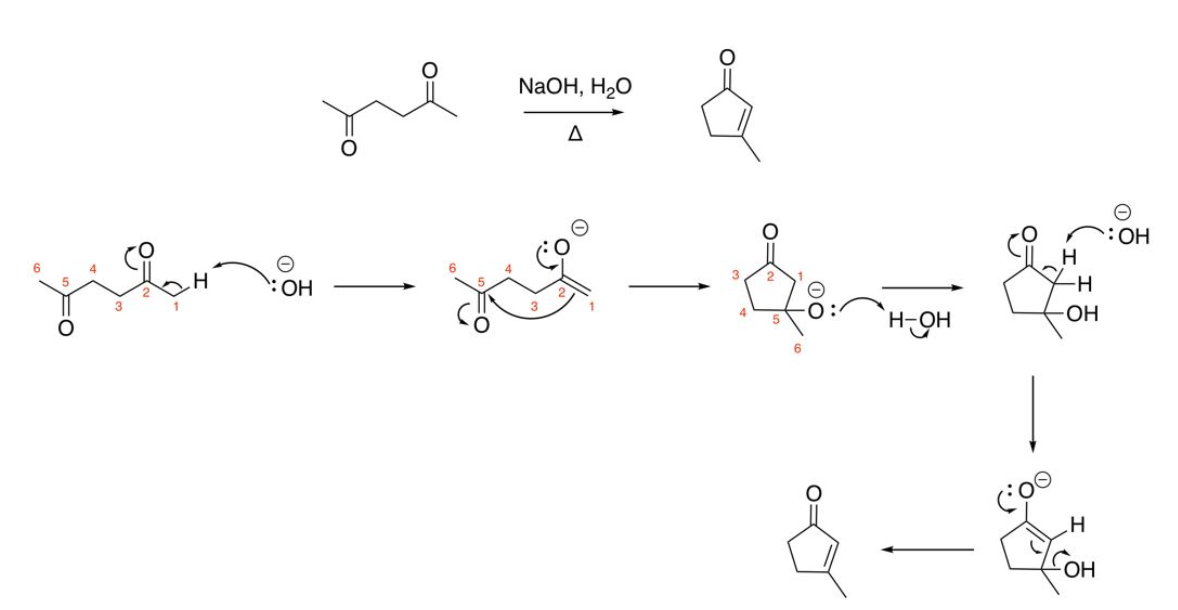
Intramolecular Aldol reaction (2 or more carbonyls on same aldehyde/ketone molecule)
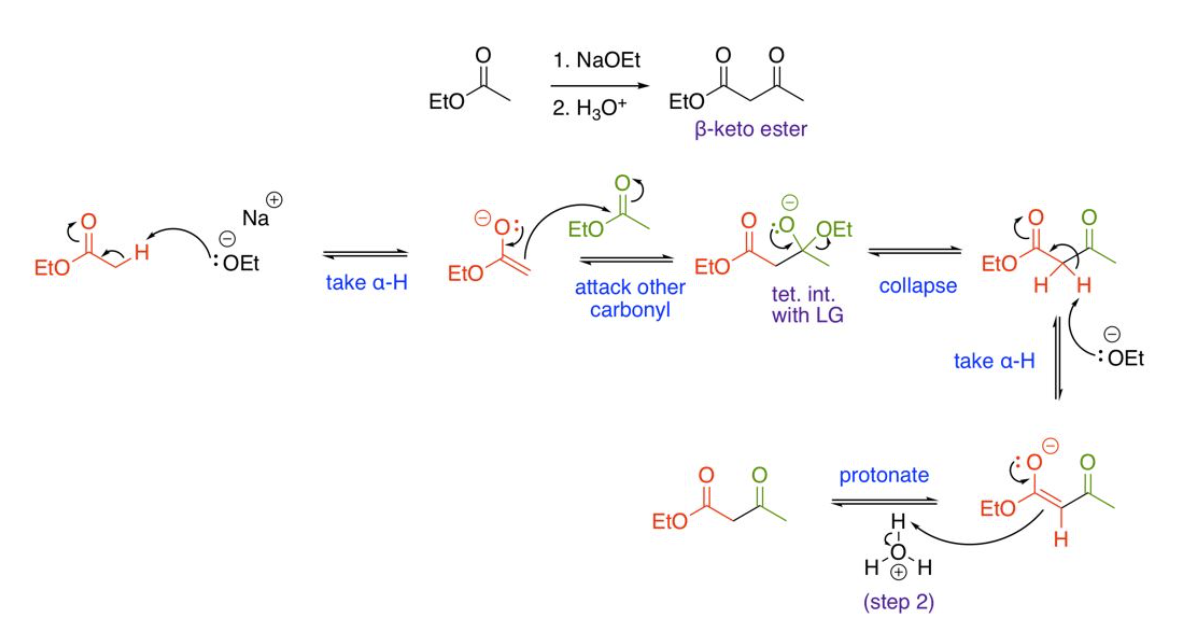
Self Claisen Condensations (one unique ester molecule), using acid or bases avoiding NaOH or non-matching Alkoxide bases
types of Crossed Claisen Condensations (two unique ester molecules)
direct Claisen condensation (order of addition, irreversible base) and use of an ester without alpha-H’s
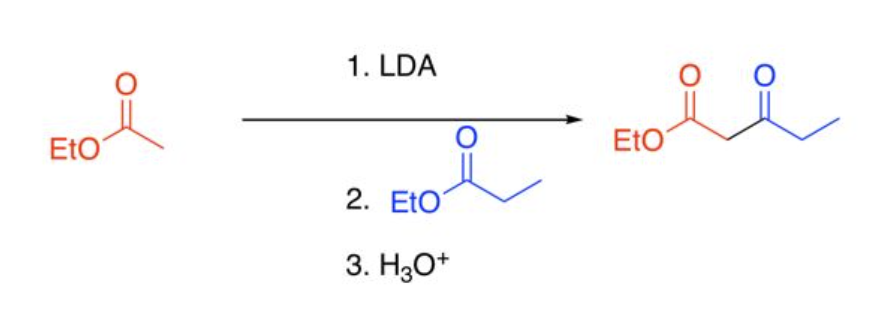
Direct Claisen
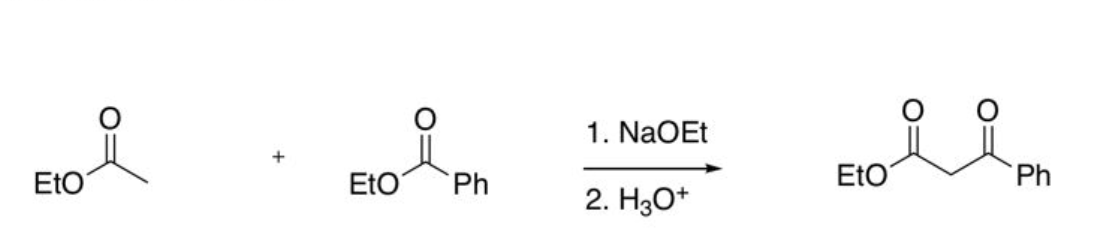
Claisen using one ester with no alpha-H’s
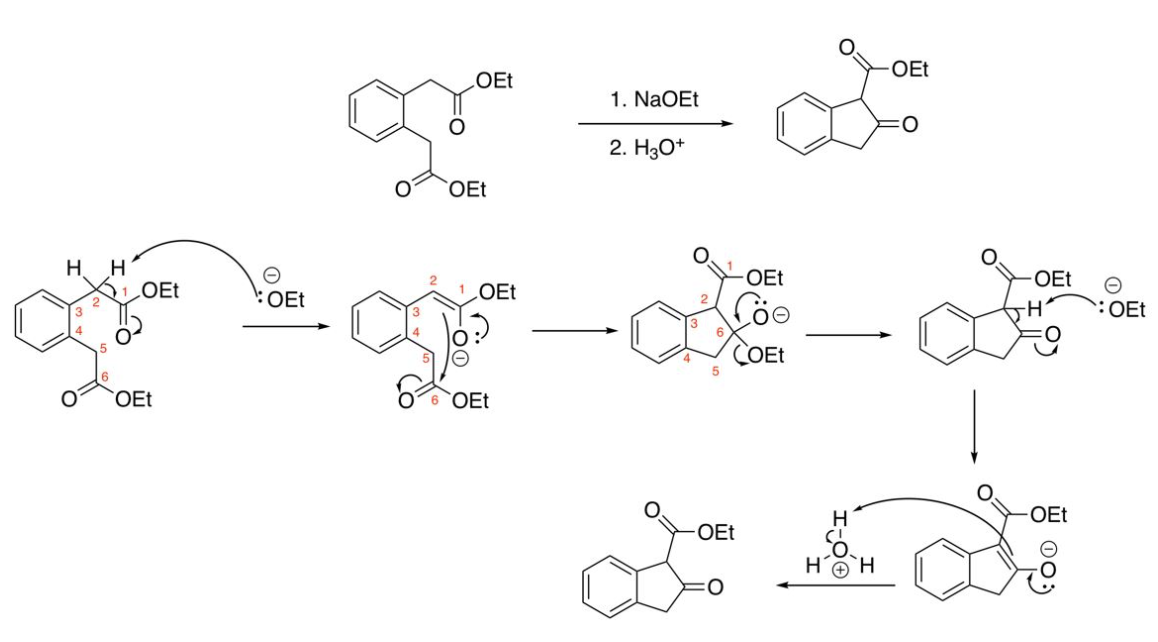
Dieckmann Condensations (two ester groups on the same molecule)
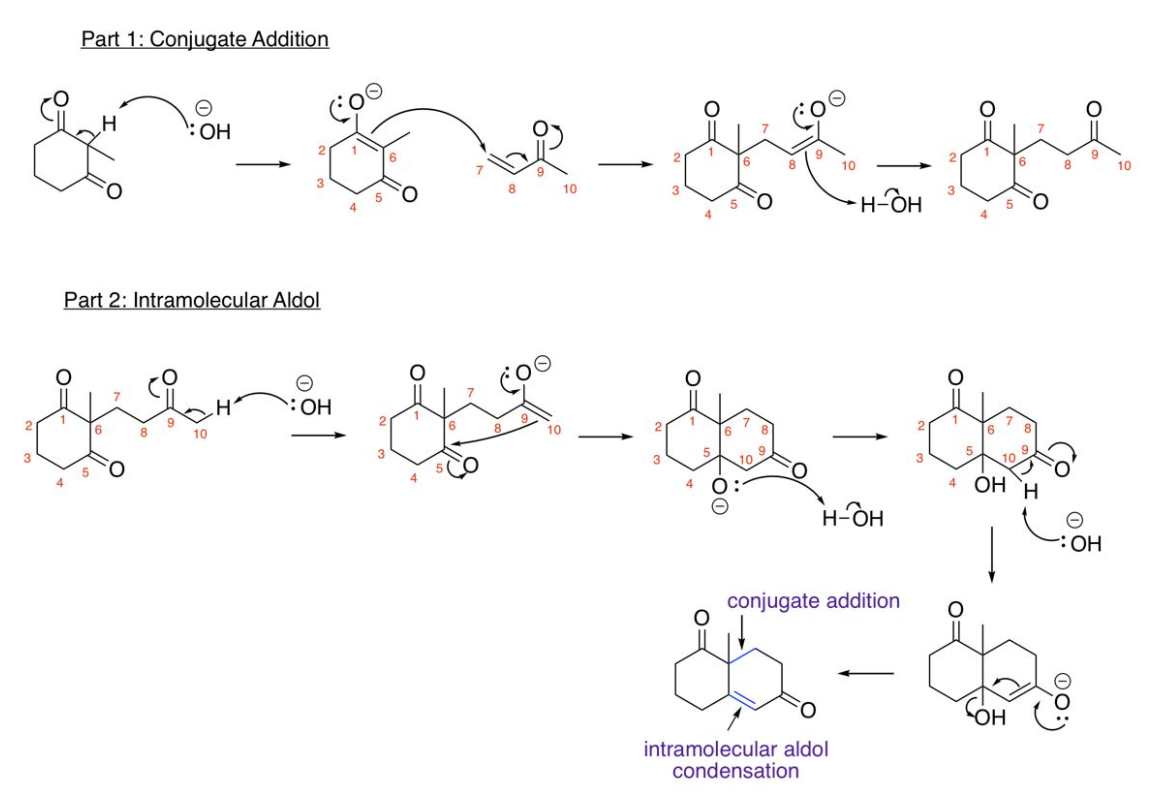
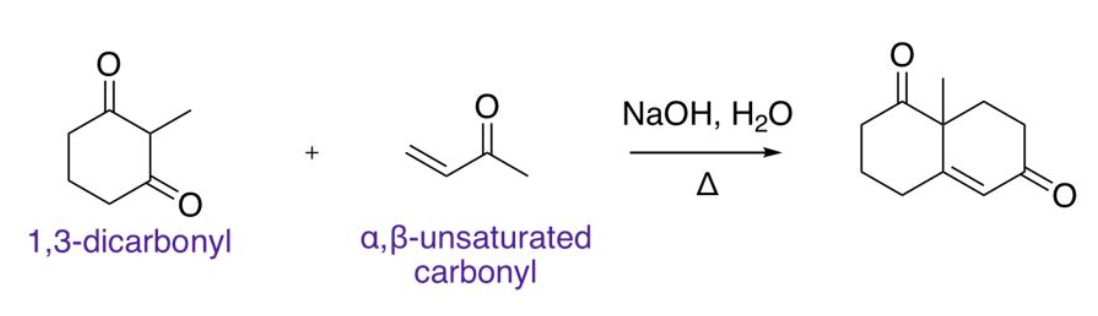
Robinson Annulation
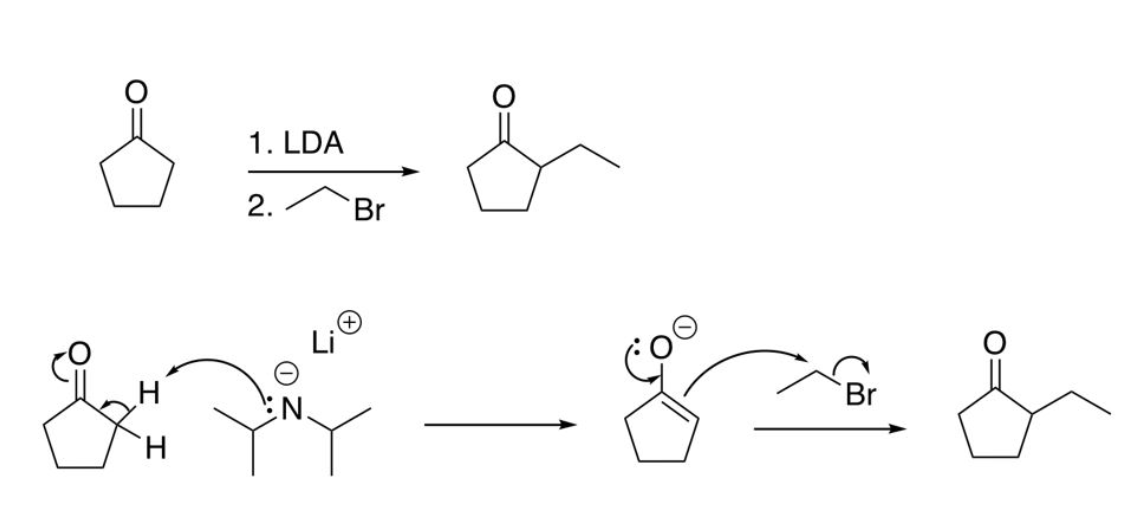
Enolate Alkylation (must use irreversible base to avoid undesired products)
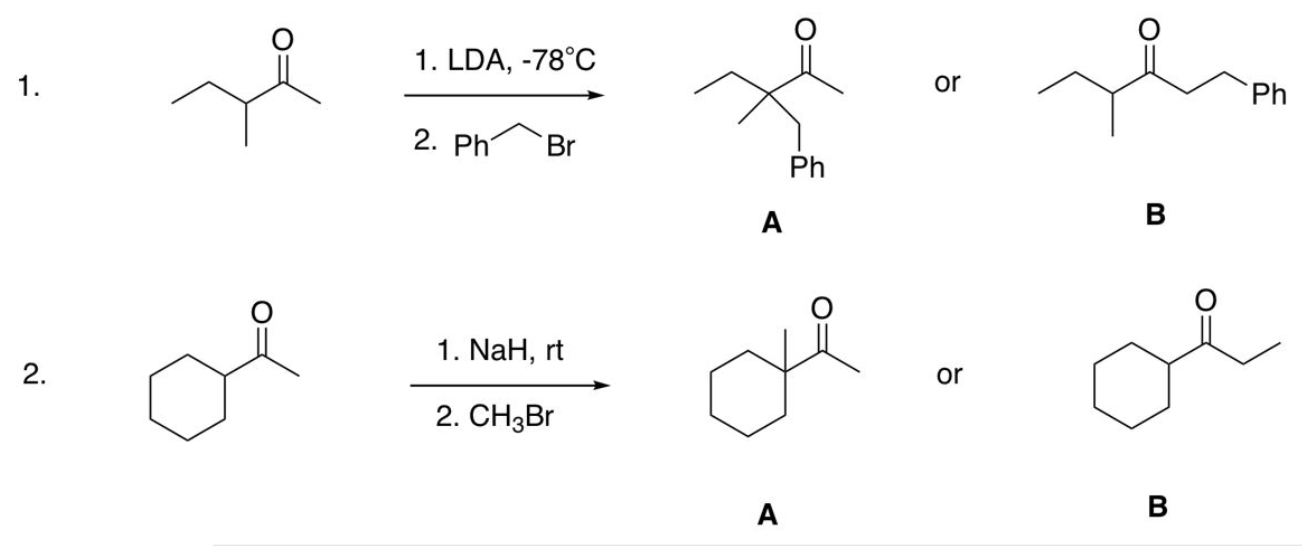
Asymmetrical Enolate Alkylation (kinetic is less stable low temp, thermo is more stable high temp product)
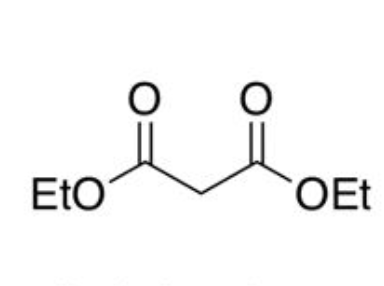
diethyl malonate
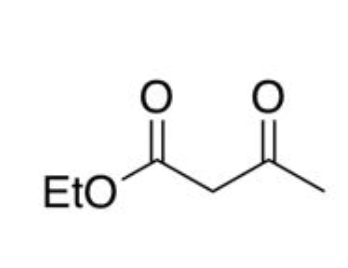
ethyl acetoacetate
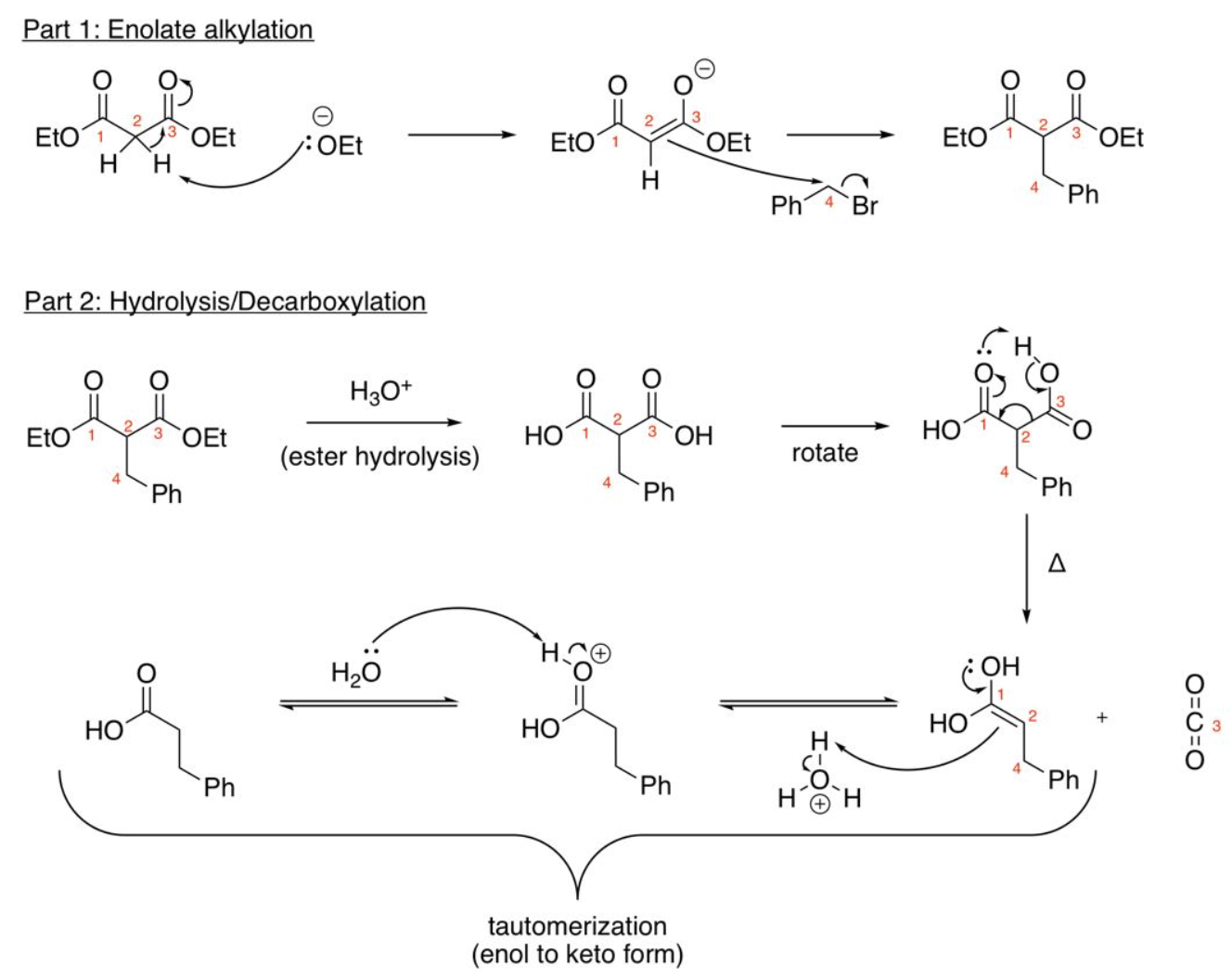
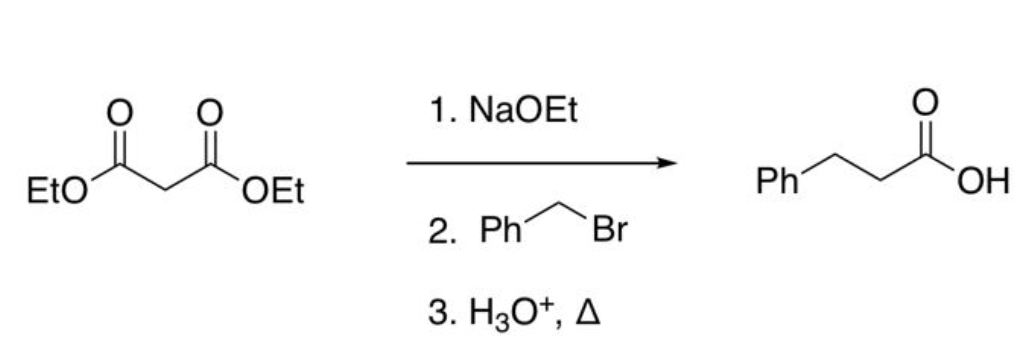
Malonic ester Synthesis (1 alkyl group added)
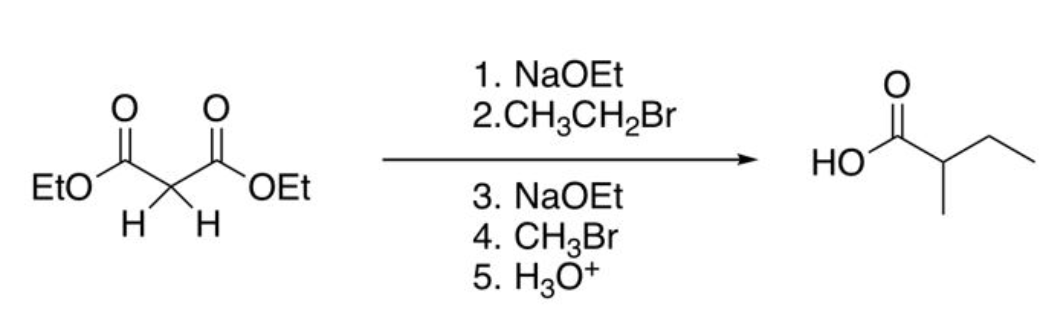
Malonic ester Synthesis (2 alkyl groups added)
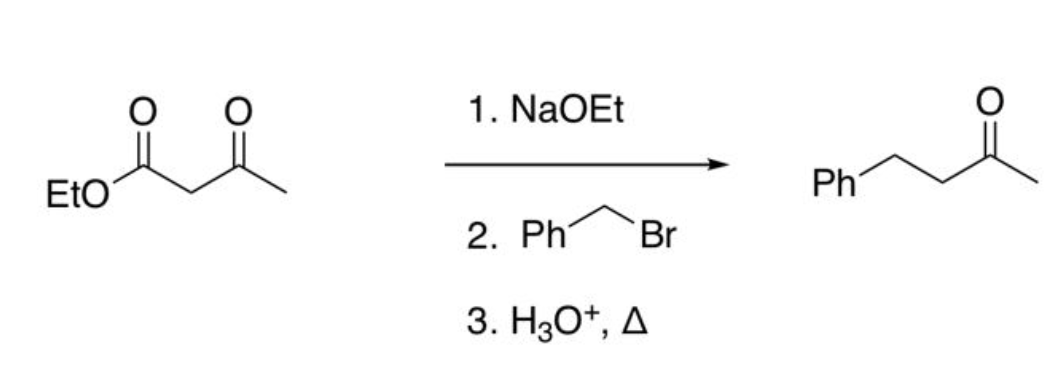
Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
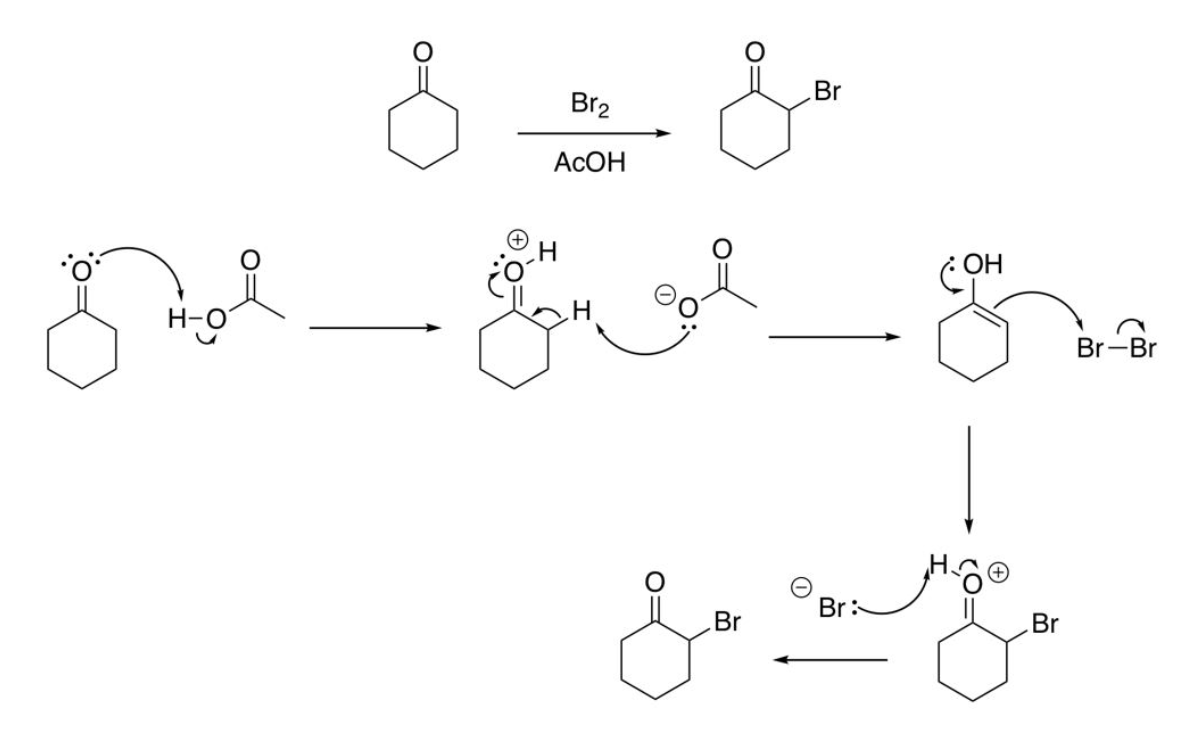
Halogenation of Enols
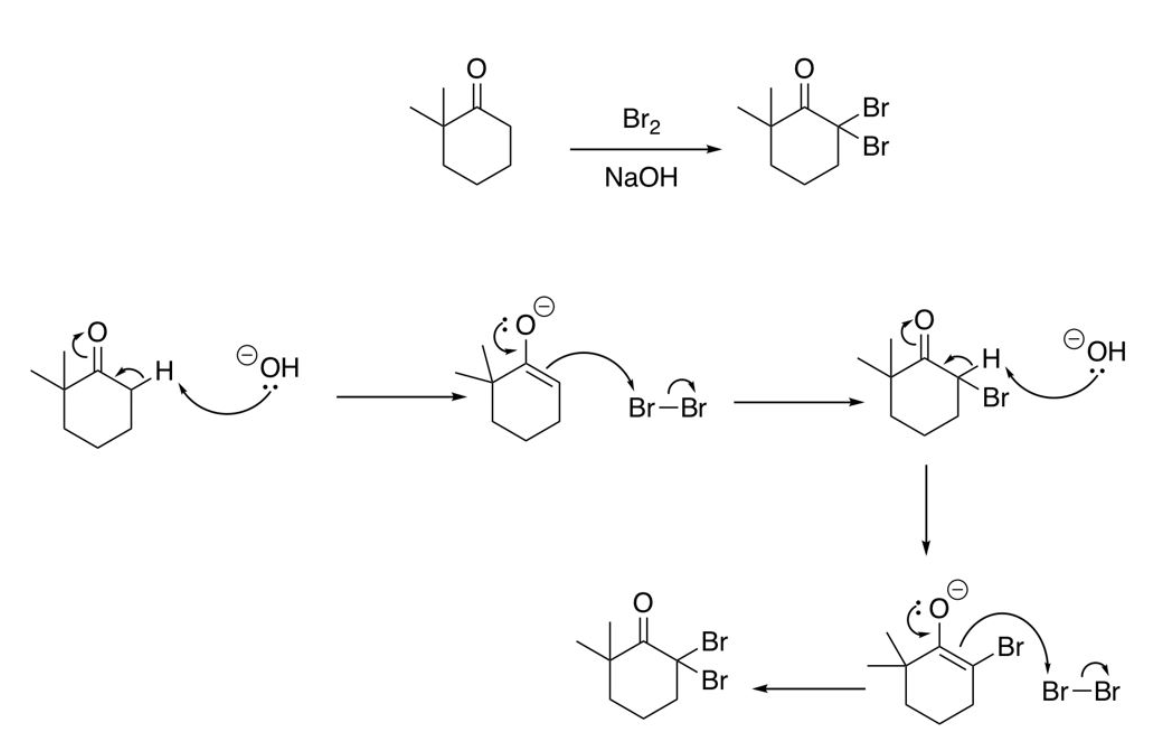
Halogenation of Enolates; Overhalogenation
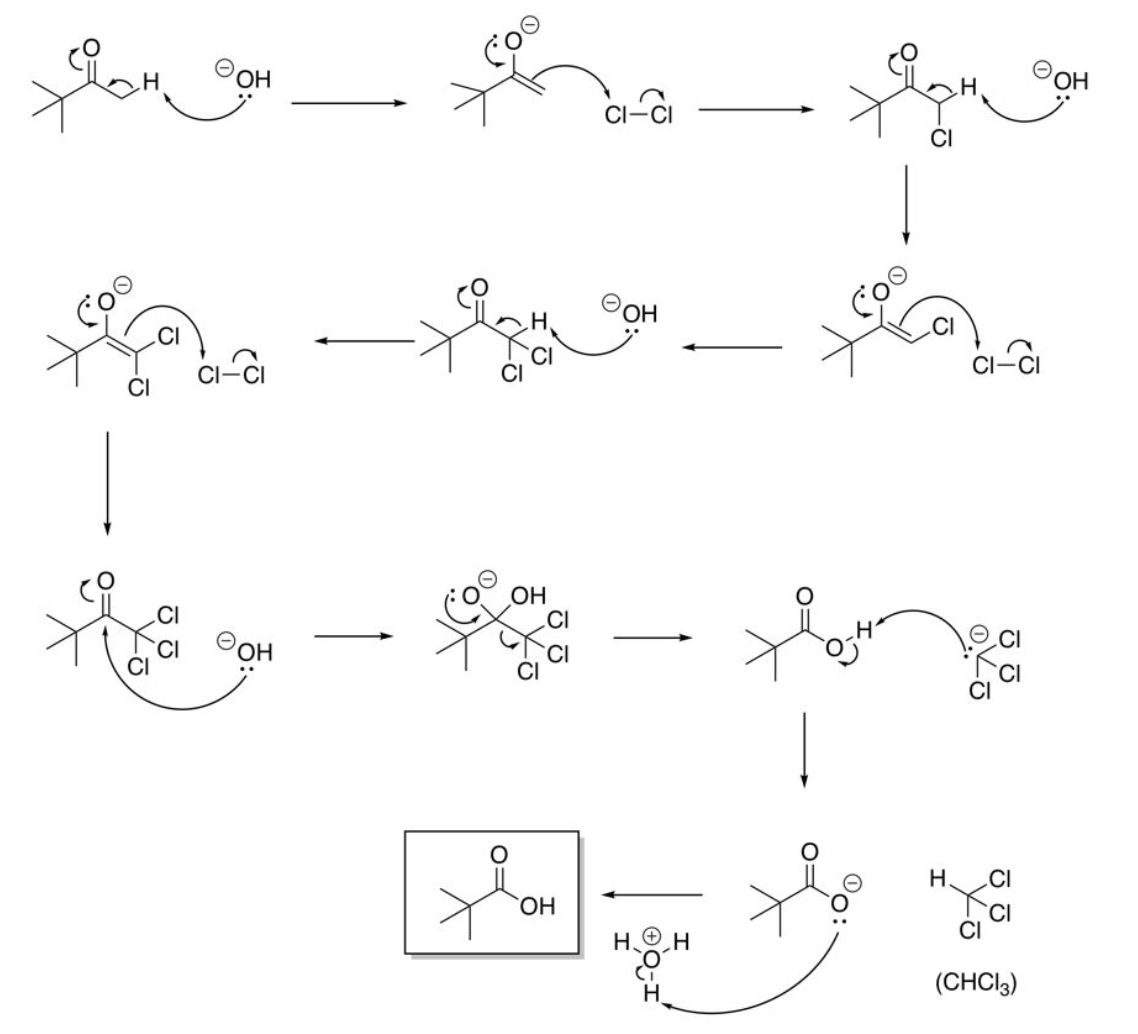
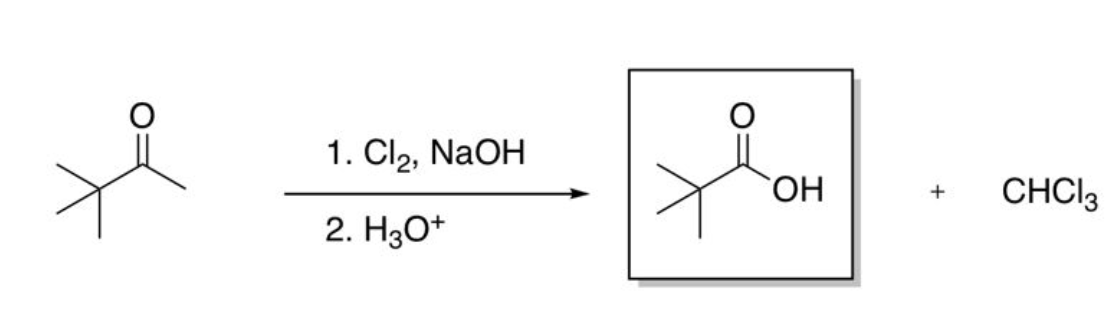
involves methyl ketone and NaOH
Haloform reaction
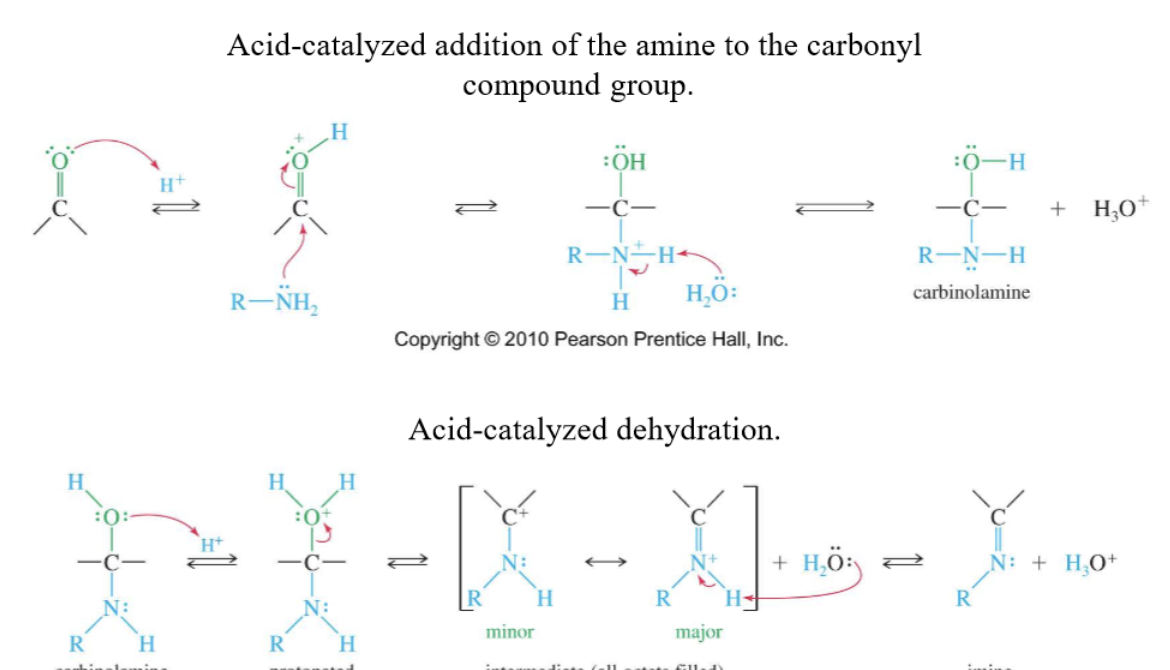
Imine formation
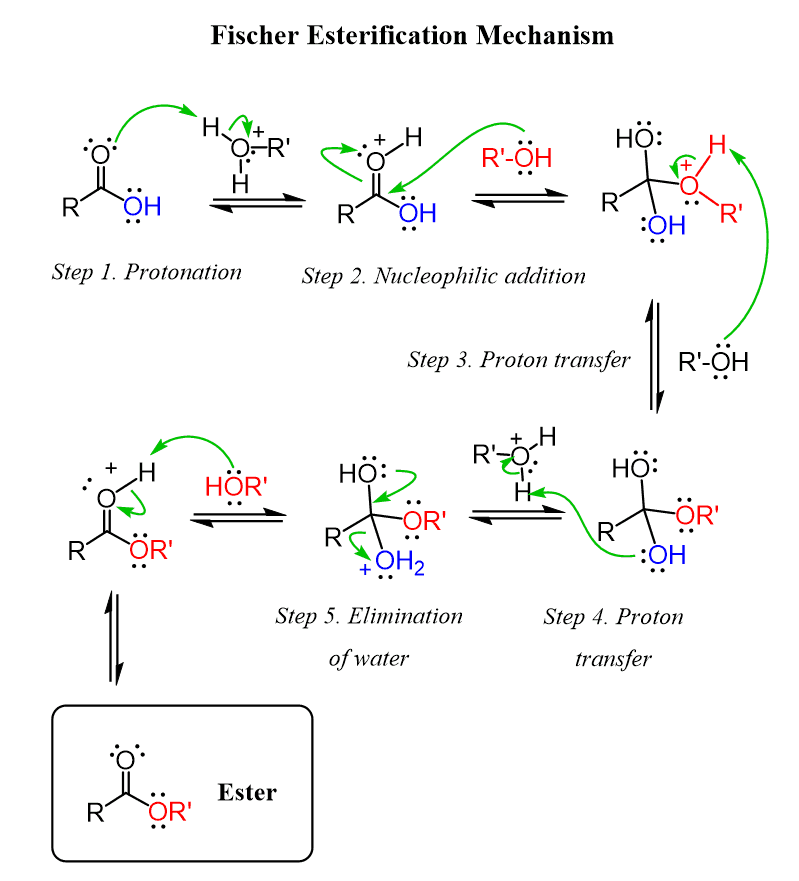
Fischer esterification
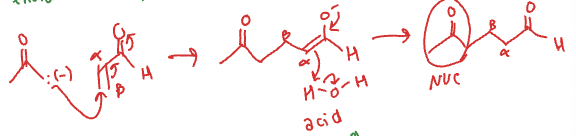
NUC + alpha, beta unsaturated ketone/aldehyde
(1,4) Michael addition (Conjugate addition)
Beta carboxylic acid to carbonyl
Decarboxylation
Enolate chirality
forms racemic mixture
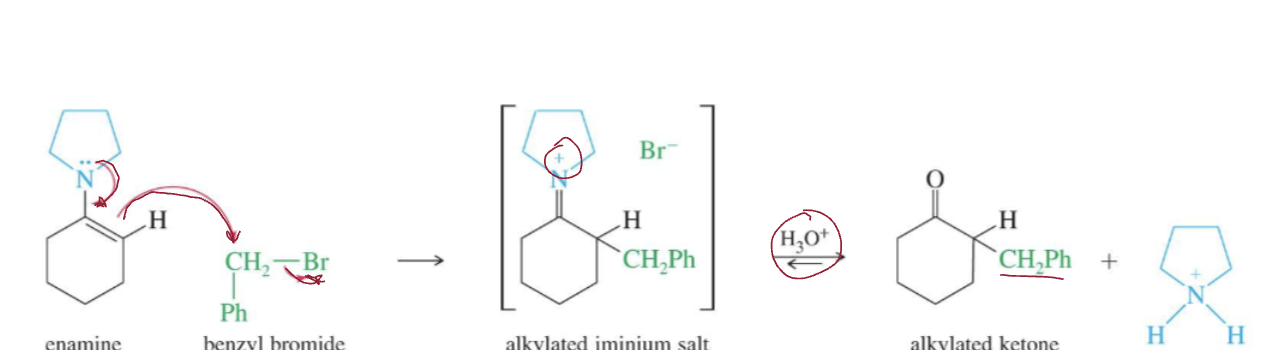
Enamine alkylation
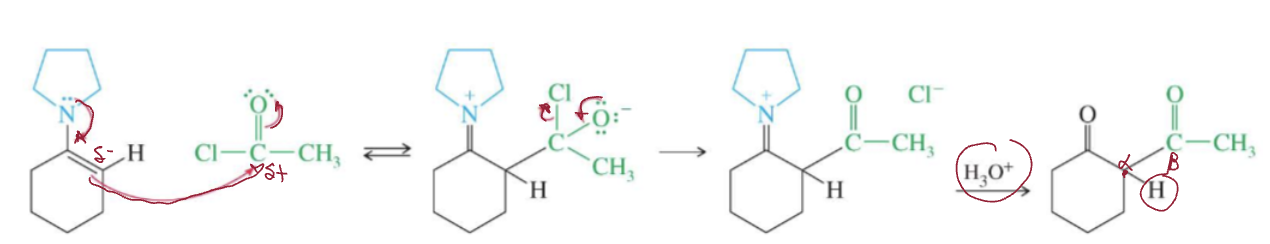
forms beta-diketone
Enamine acylation
Acid/base (deprotonation)
SN2 (diesterbromide)
Acid/base (deprotonation)
SN2
Hydrolysis (NaOH + H+; H3O+) (cleaves molecule into 2 fragments)
Decarboxylation (remove 1 carboxylic acid)
Amino acid synthesis
Amino acid (components)
amine (H2N) and (carboxylic) acid
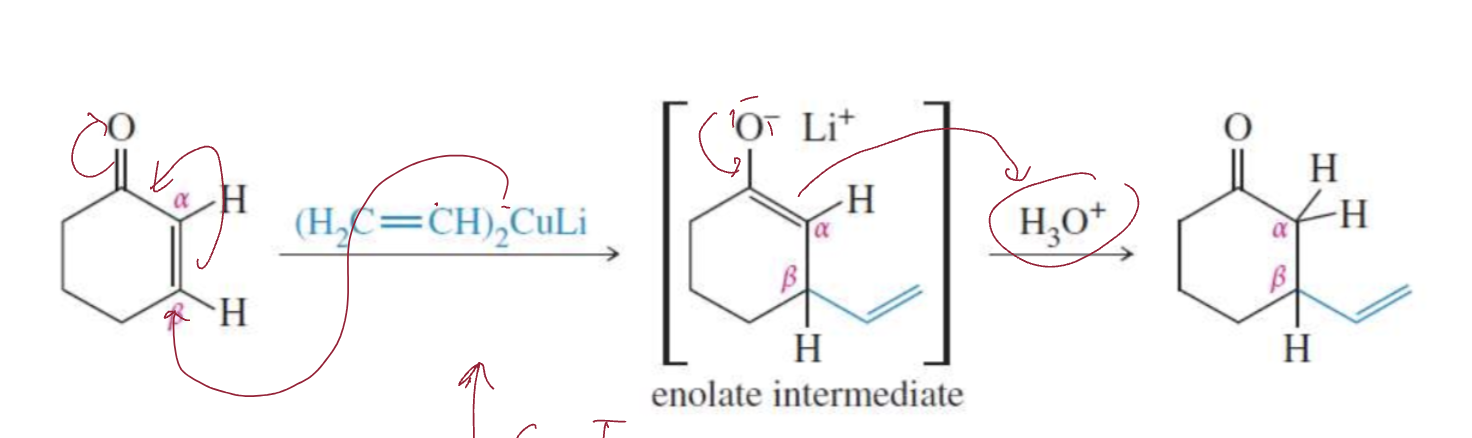
Gilman reagents (1,4 addition)
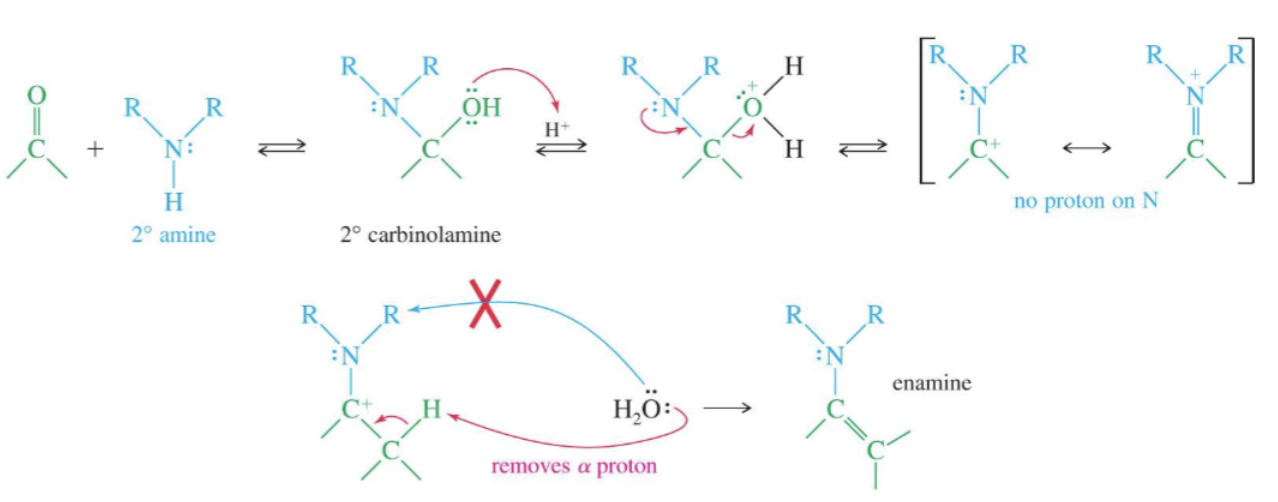
Enamine formation
Lactam (cyclic amide)
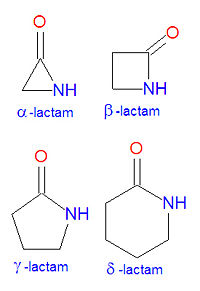
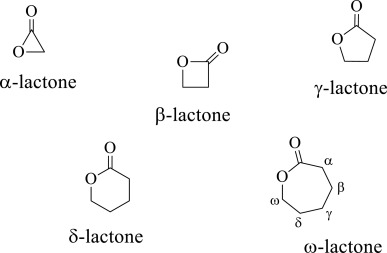
Lactone (cyclic ester)