Final Review A&P Lab
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
How many homeostatic factors are there?
seven (nutrient concentrations, oxygen/carbon dioxide, waste products(NH4, acids, cell debris), pH, water/salt/electrolytes, temperature, fluid volume/pressure)
When blood glucose levels rise, what hormone is released to help cell absorb glucose, returning levels to normal?
insulin
the primary functions of ___ tissues are protection, secretion, and absorption
epithelial

What position is the pig lying in?
dorsal recumbency
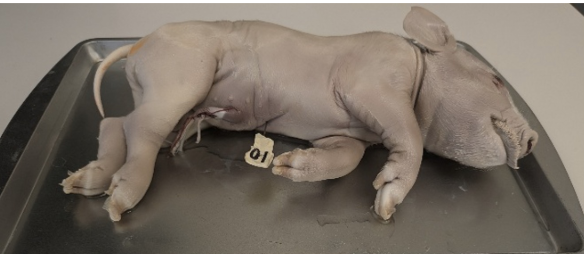
What term best describes the location of the pin?
ventral
What type of bone marrow is responsible for producing red and white blood cells as well as platelets?
red
Name the part of the skeleton that includes the skull, vertebrae, and sternum
axial
Name the correct order of vertebrae from cranial to caudal
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccygeal
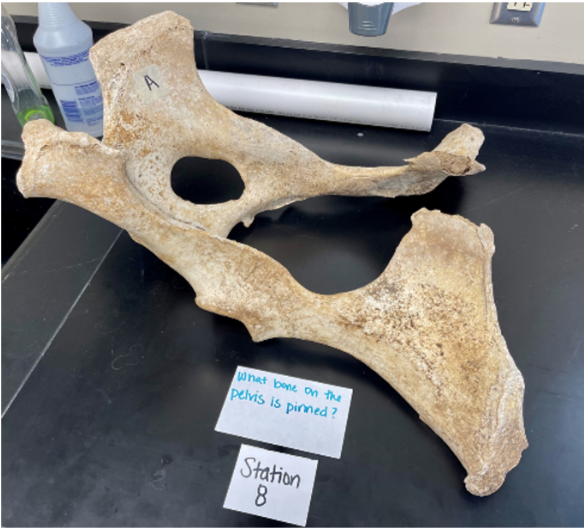

What bone of the pelvis is pinned?
ischium

What vertebrae is this?
cervical
Which two muscle types are striated?
skeletal and cardiac
What is the purpose of intercalated discs?
allow sustained contractions
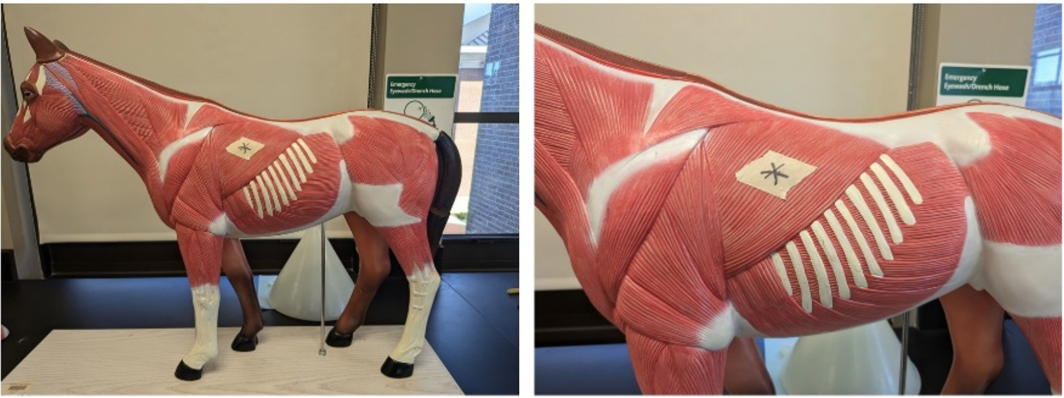
What muscle is denoted with a star?
latissimus dorsi
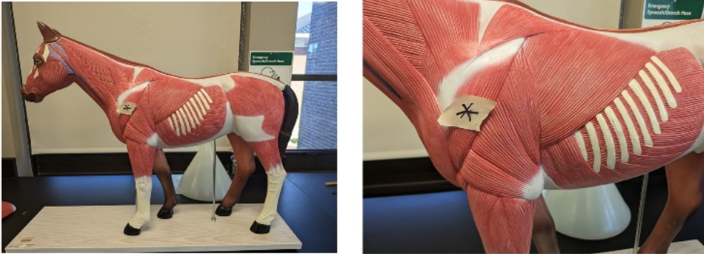
What muscle is denoted with a star?
deltoid

What muscle is denoted with a star?
biceps femoris
What part of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord?
central nervous system
Which nerves carry signals from sensory organs to the central nervous
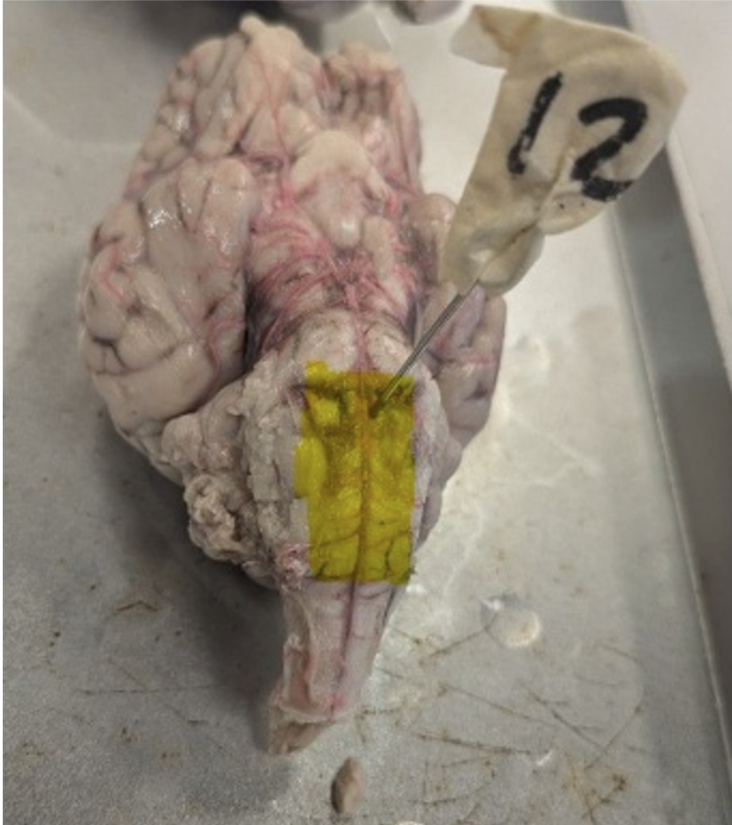
Which part of the brain is highlighted?
medulla oblongata
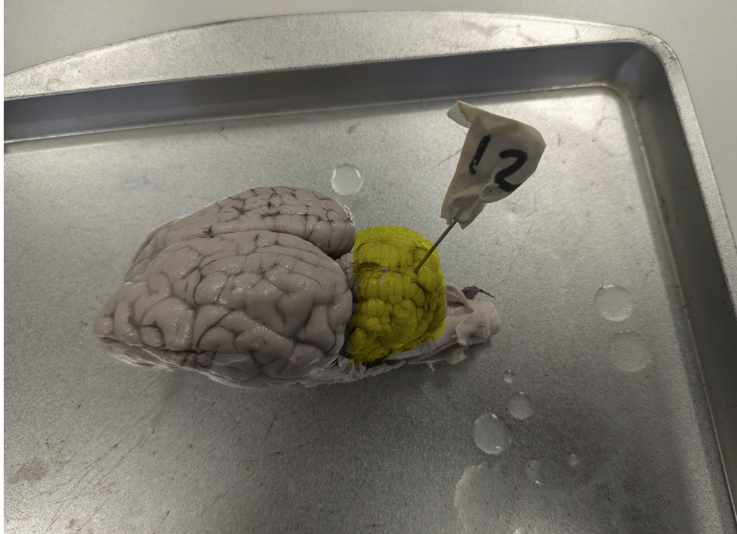
What portion of the brain is highlighted?
cerebellum
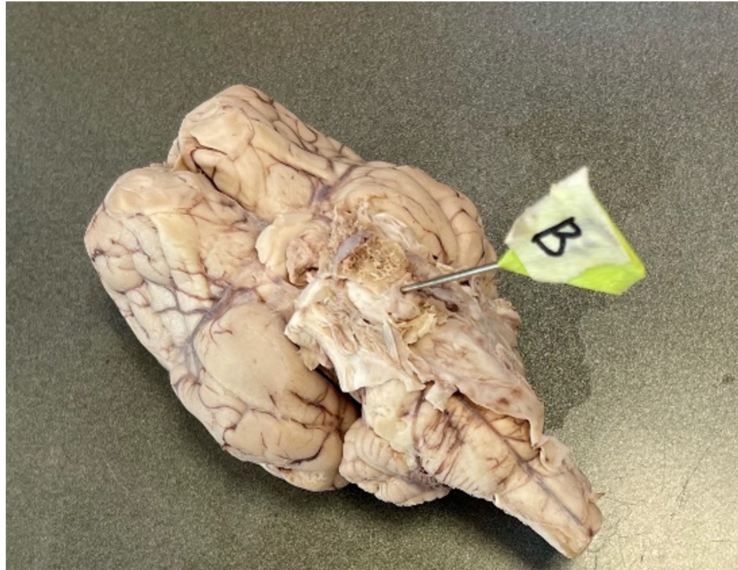
What structure is pinned?
pituitary gland
What are the two large veins returning blood from the body to the heart?
cranial and caudal vena cava
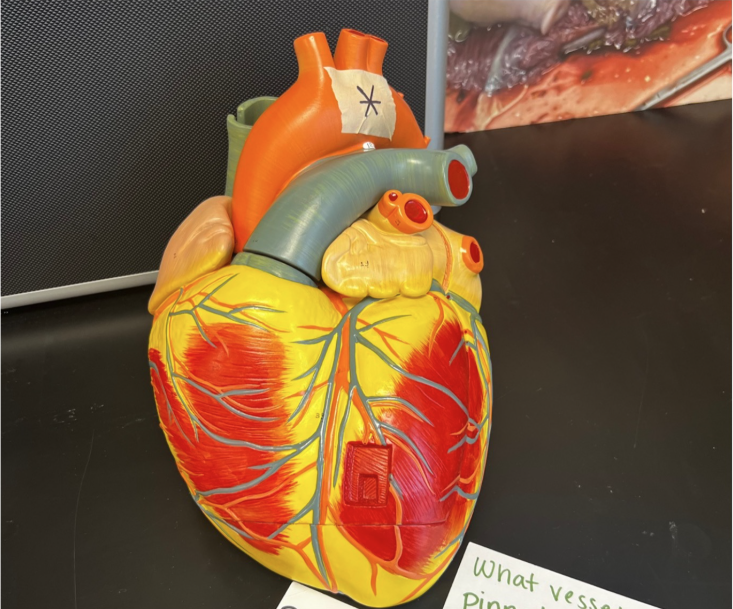
What vessel is pinned?
aorta
Which vessels carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated?
pulmonary arteries
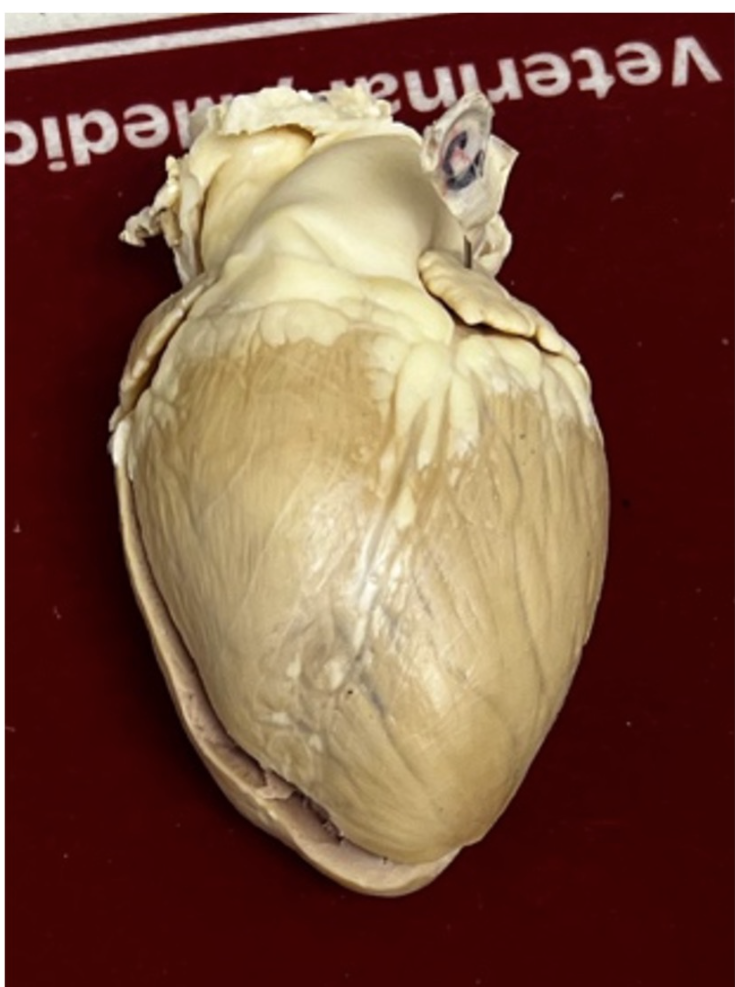
What side and chamber of the heart is pinned (C)?
left atrium
What chamber of the heart does deoxygenated blood from the body enter?
right atrium
What are the primary muscles of respiration?
diaphragm and intercostal
List the portions of the respiratory tract from uppermost to lowermost
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, primary bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
What muscles serve as secondary respiratory muscles?
abdominal
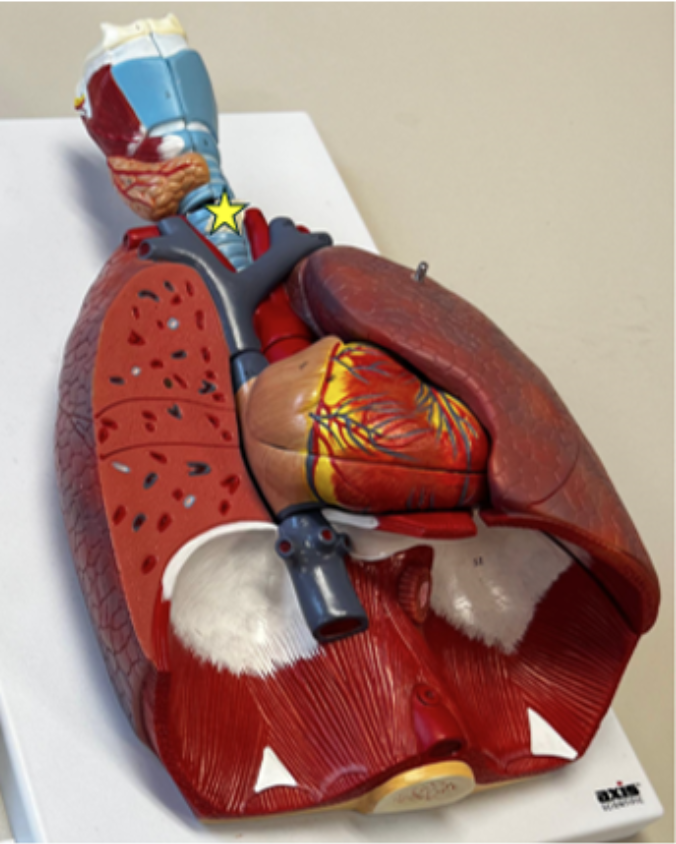
What structure is denoted with a star?
trachea

What structure of the lungs is pinned?
secondary bronchi
What are the three types of digestion?
physical, chemical, and enzymatic
List the compartments in the ruminant stomach in the order that food passes through them
rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum
List the three sections of the small intestine in order from cranial to caudal
duodenum, jejunum, ileum

What compartment of the ruminant stomach is this tissue from?
rumen
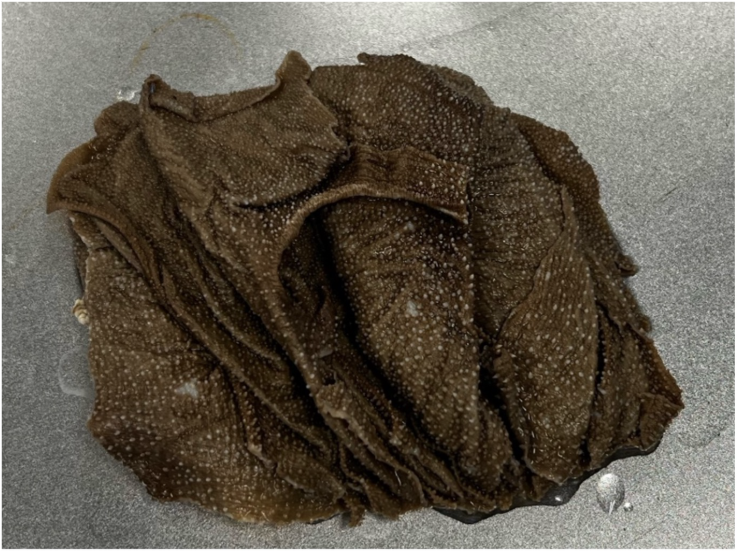

What compartment of the ruminant stomach is this tissue from?
omasum
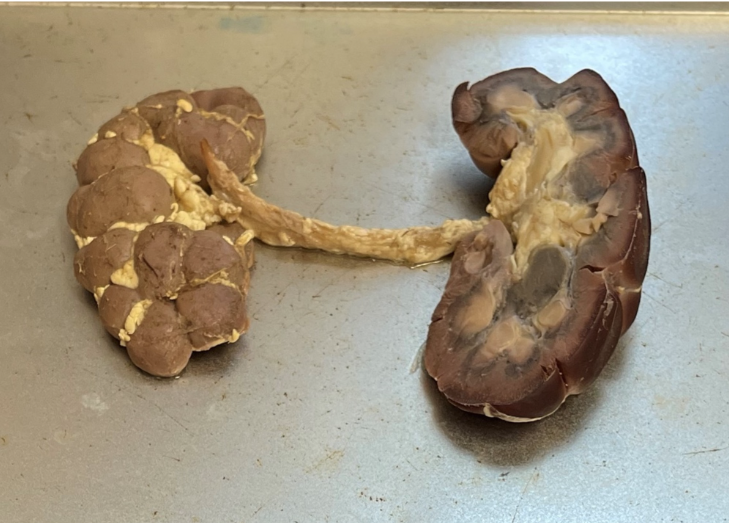
What species is this kidney from?
bovine (cow)
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
nephron
Name one species that has externally fused kidney lobes
dog, pig, rabbit, goat, cat, sheep
What specific part of the kidney is responsible for filtering blood? (hint: it is found within the nephron)
glomerulus
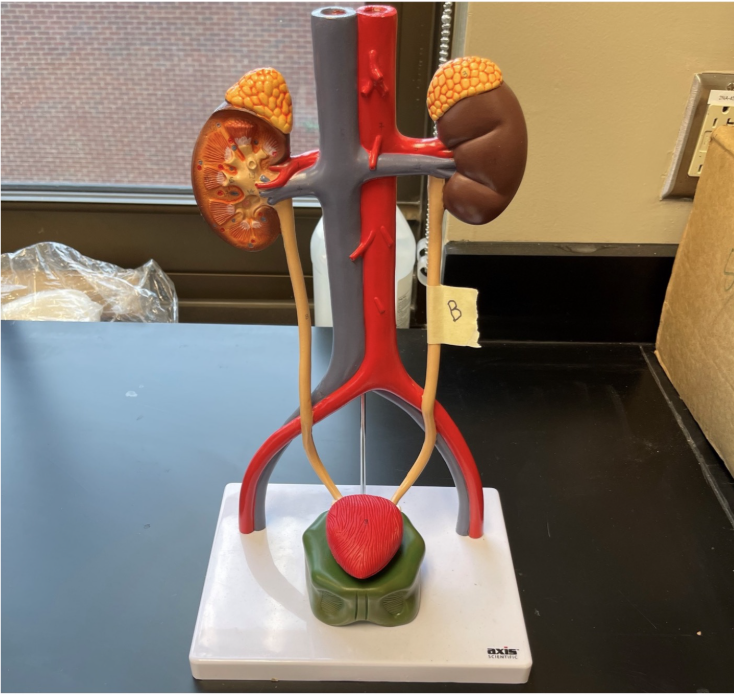
What structure is labeled B?
ureter
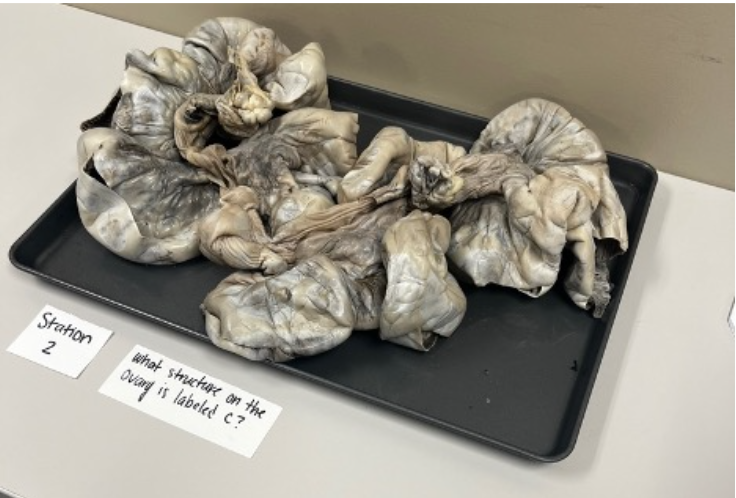

What structure is the on the ovary is the arrow pointing to?
corpus luteum
What portion of the sperm is responsible for movement?
tail
What is the site of fertilization in livestock species?
ampullary-isthmic junction
What placental type does the sheep have?
cotyledonary
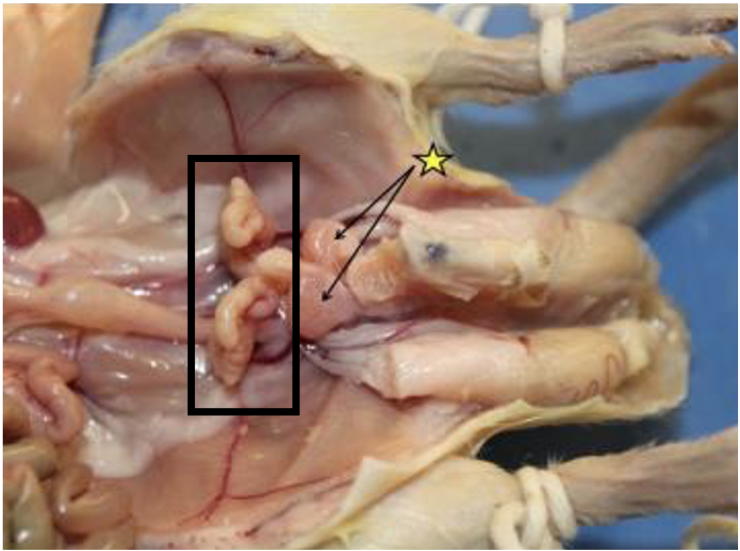
What structure in the male reproductive tract is outlined in the black box?
seminal vesicles
Maintaining internal stability due to coordinated responses of parts of the body to any situation or stimulus that would disrupt normal conditions or functions is called what?
homeostasis
How many phases of the cell cycle are there?
six (interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis)
___ aids growth and development and endocrine functions
pituitary gland
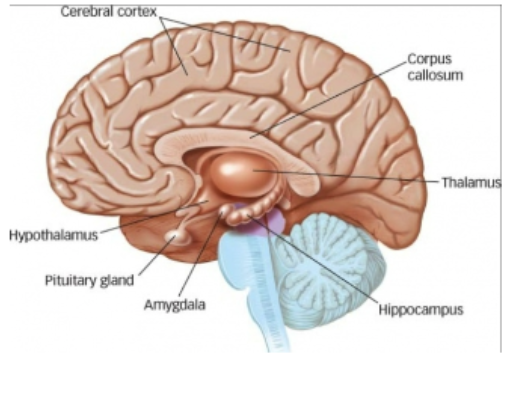
Is the autonomic nervous system voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary (sympathetic - fight/flight, parasympathetic - rest/digest)
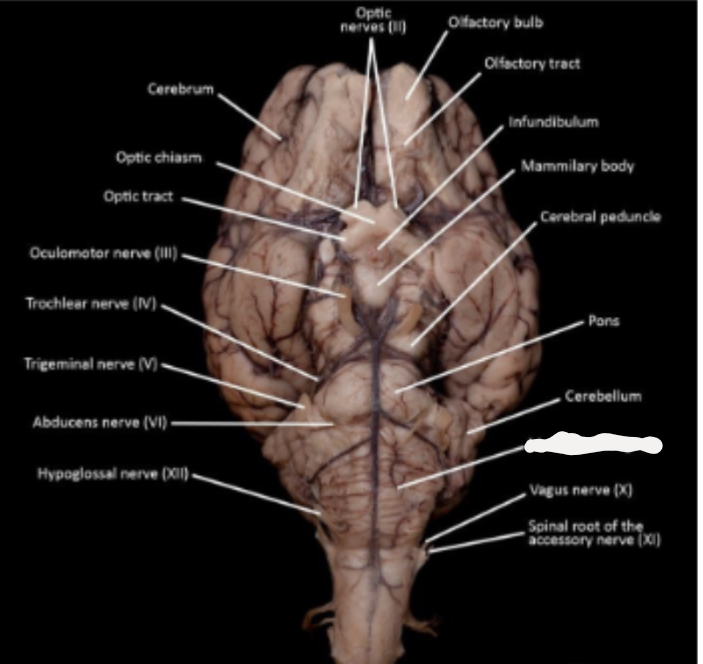
What part of the brain is marked out?
medulla oblongata
The central nervous system is comprised of ___
brain and spinal cord
____ travel from sensory organs to the CNS
afferent nerves (sensory)
what are the two nerves of the somatic (voluntary) system?
afferent (sensory) nerves and efferent (motor) nerves
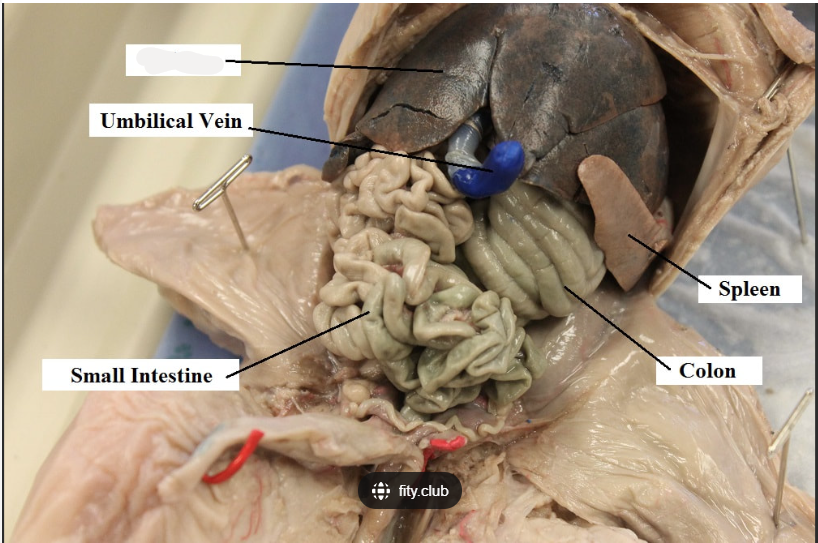
What is marked out on the fetal pig?
liver

What is marked out on the fetal pig?
(coiled) colon
____ comes from the rumen and breaks up fiber
papillae

What is known as the Butcher’s Bible?
omasum

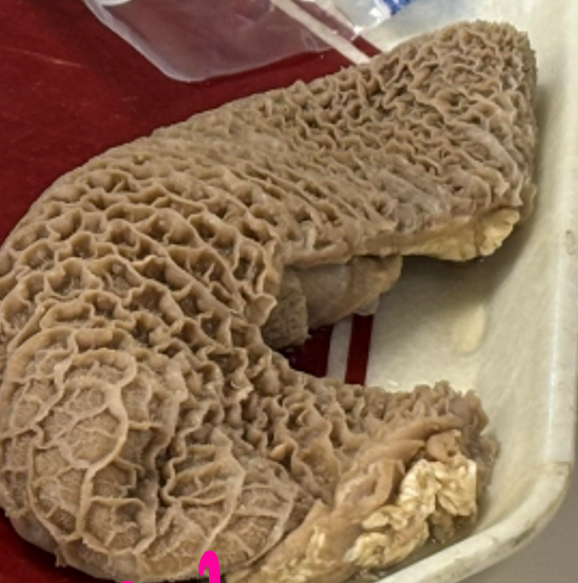
What is pictured?
reticulum

What is pictured?
rumen
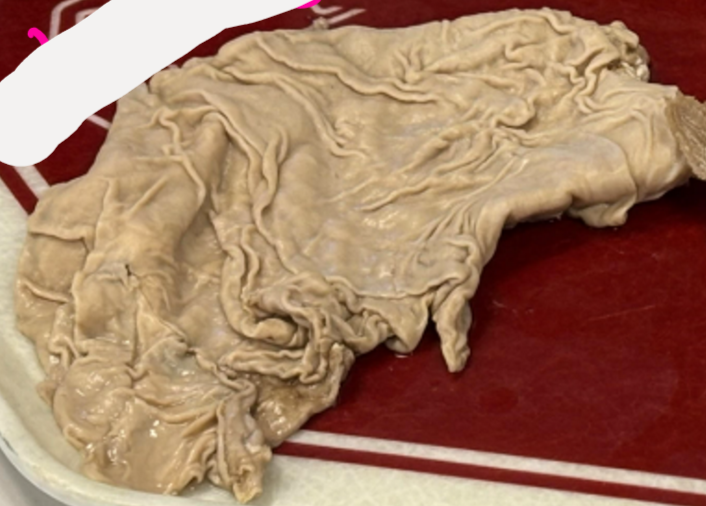

What is pictured?
abomasum
What is the order food travels in the ruminant stomach?
rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum