05.B BIO Carbohydrates BASICS (PART B)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Organic compound
Compound that contains carbon bonded to hydrogen and is found in living things
Macromolecule (Description)
A large molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules called monomers.
Carbohydrate (Function)
Provides short-term energy and helps to make up cell structures such as the cell membrane, cell wall and exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans.
Carbohydrate (Elements)
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; ratio 2H:1O
-ose
common suffix for sugars
sacch-
common prefix meaning sugar
-mer
suffix meaning unit
mono-
prefix for one
di-
prefix for two
poly-
prefix meaning many
Monomer
Simplest building block of a macromolecule
Polymer
Large molecule made up of smaller building blocks or monomers
Monosaccharide (Description)
Building block (monomer) of carbohydrates; chemical formula is C6H12O6
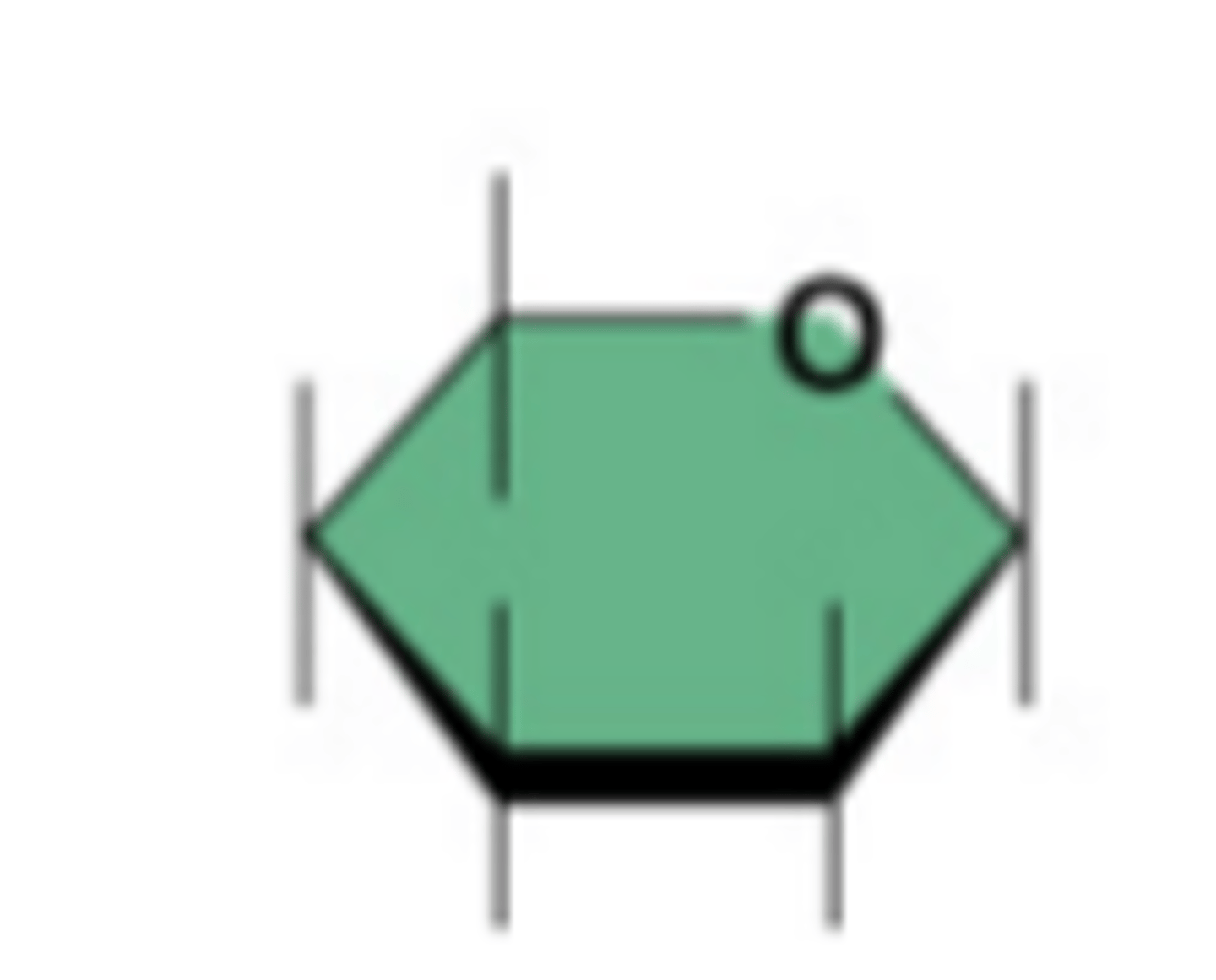
Monosaccharide (Examples)
Examples include:
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
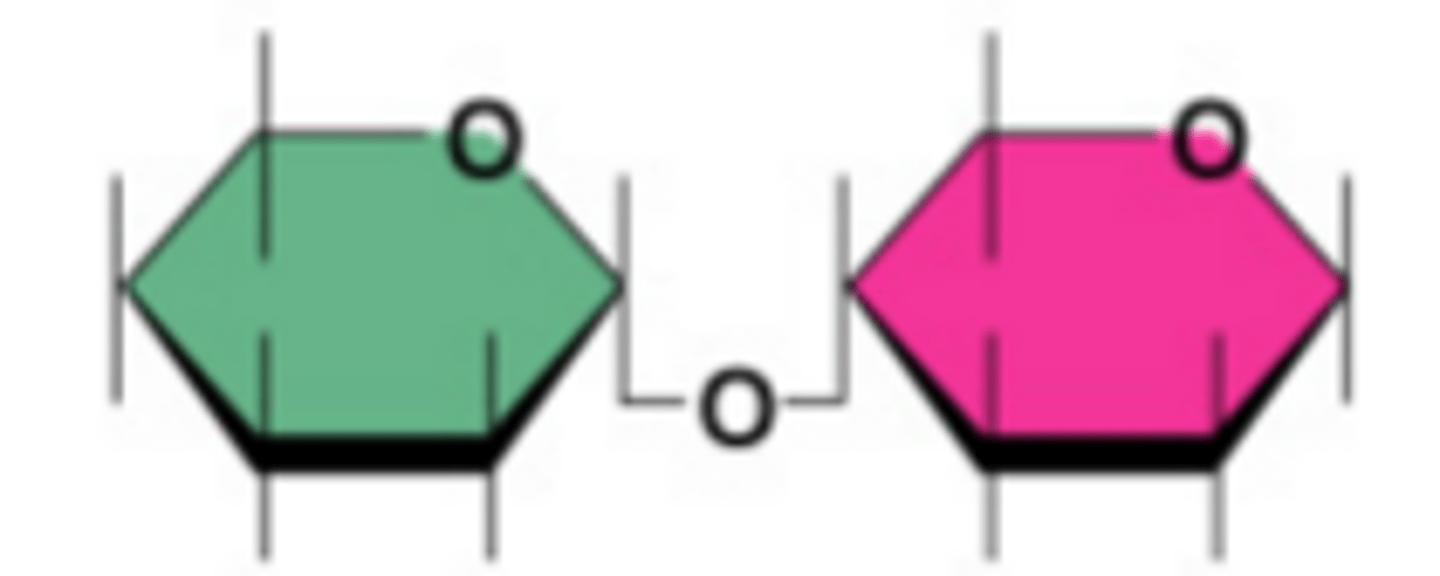
Disaccharides (Description)
A carbohydrate made up of two monosaccharides
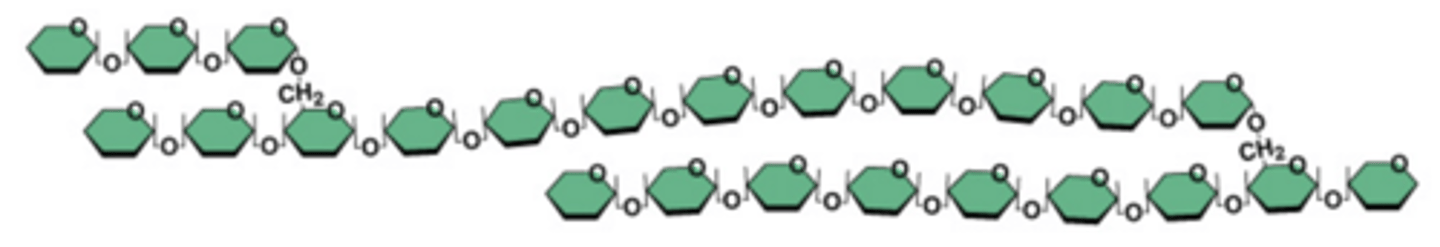
Polysaccharide (Description)
Large carbohydrate made up of many monosaccharides
Disaccharide (Examples)
Examples include:
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Polysaccharide (Examples)
Examples include:
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Chitin
Starch
A polysaccharide found in plants that is used for food storage
Glycogen
A polysaccharide found in animals that is used to store carbohydrates in the liver and skeletal muscles
Cellulose
A polysaccharide found in the cell wall of plants that provides structure and support that can't be digested by humans
Hydrolysis
A chemical reactions in which water is added to break bonds
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which a water molecule is removed to form a bond
Macromolecule (Examples)
Examples include -
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids