AP Biology - Cell Organelles
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
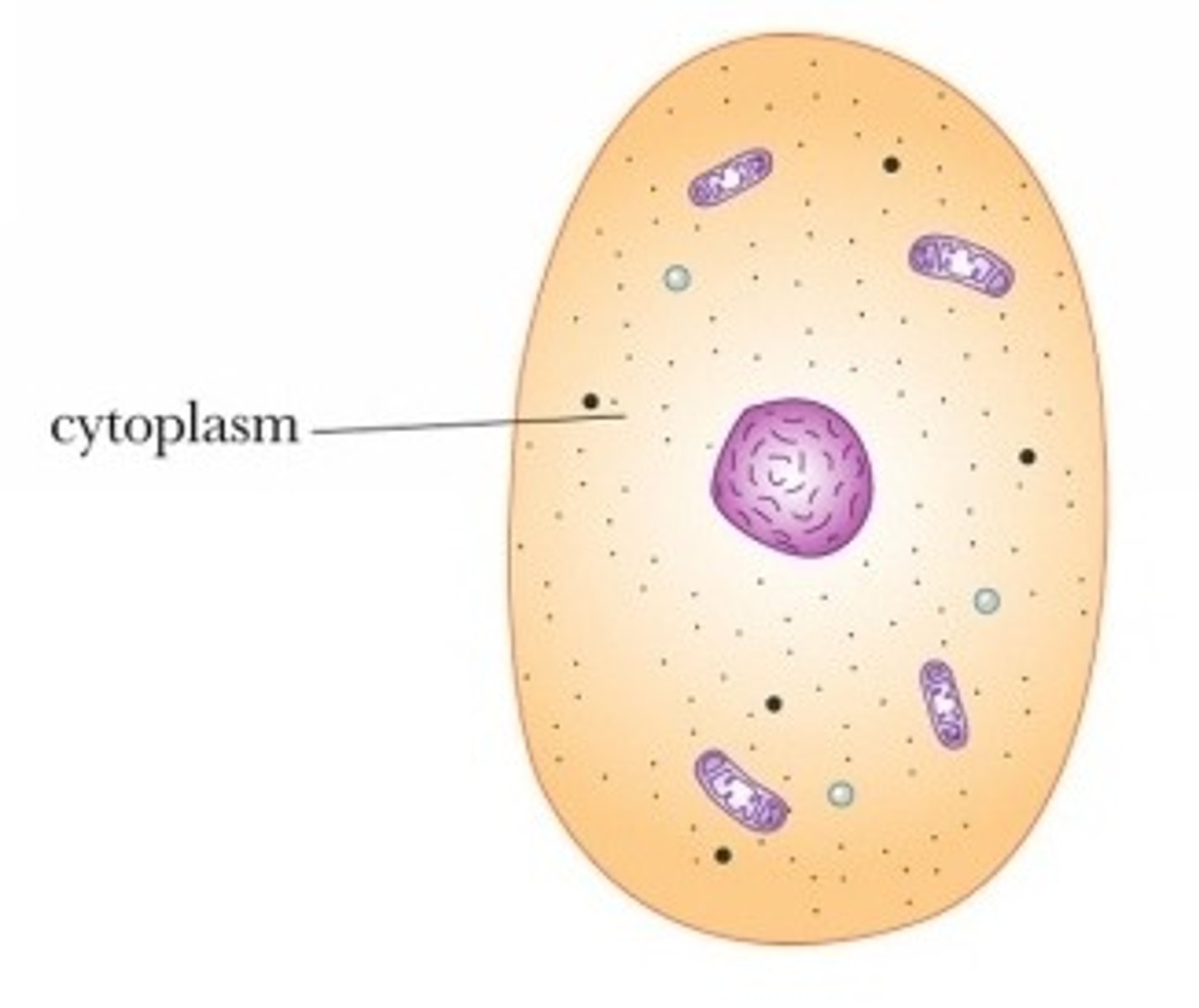
Cytoplasm
Jelly- like substance found in cells where the organelles float.
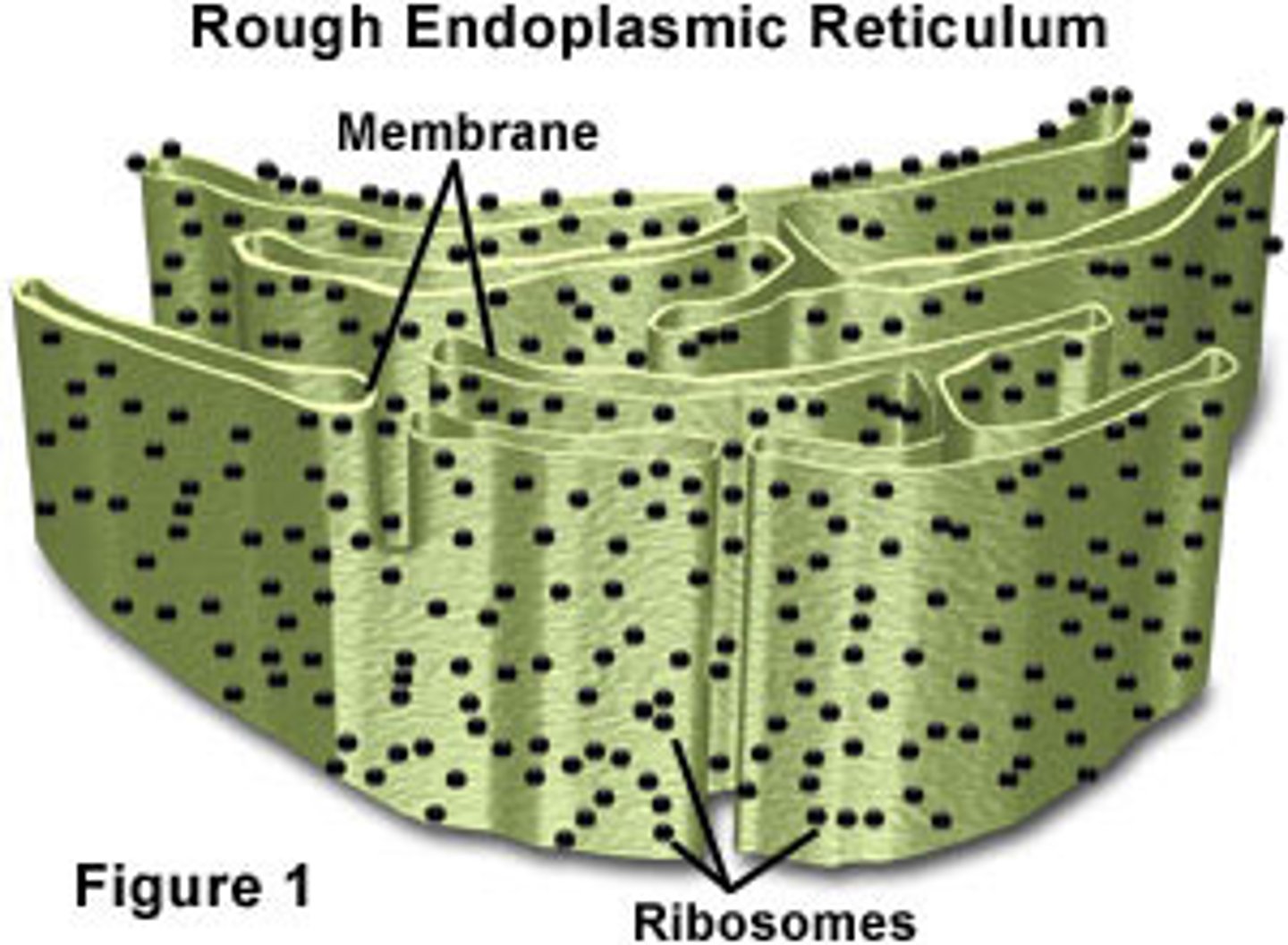
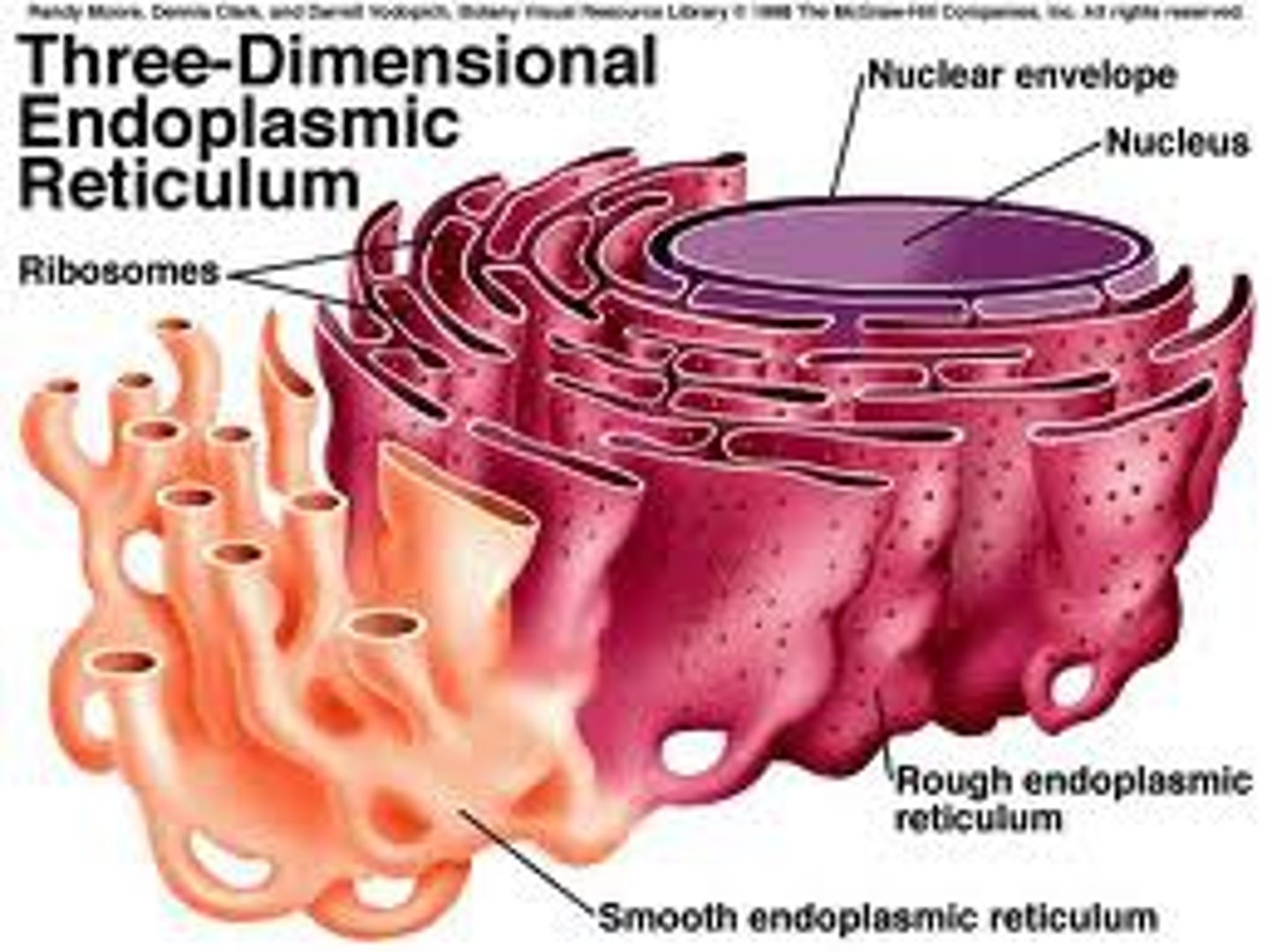
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER)
Ribosomes are attached to the surface of this organelle. It allows materials to travel around the cell. Known as the "highway" of the cell.
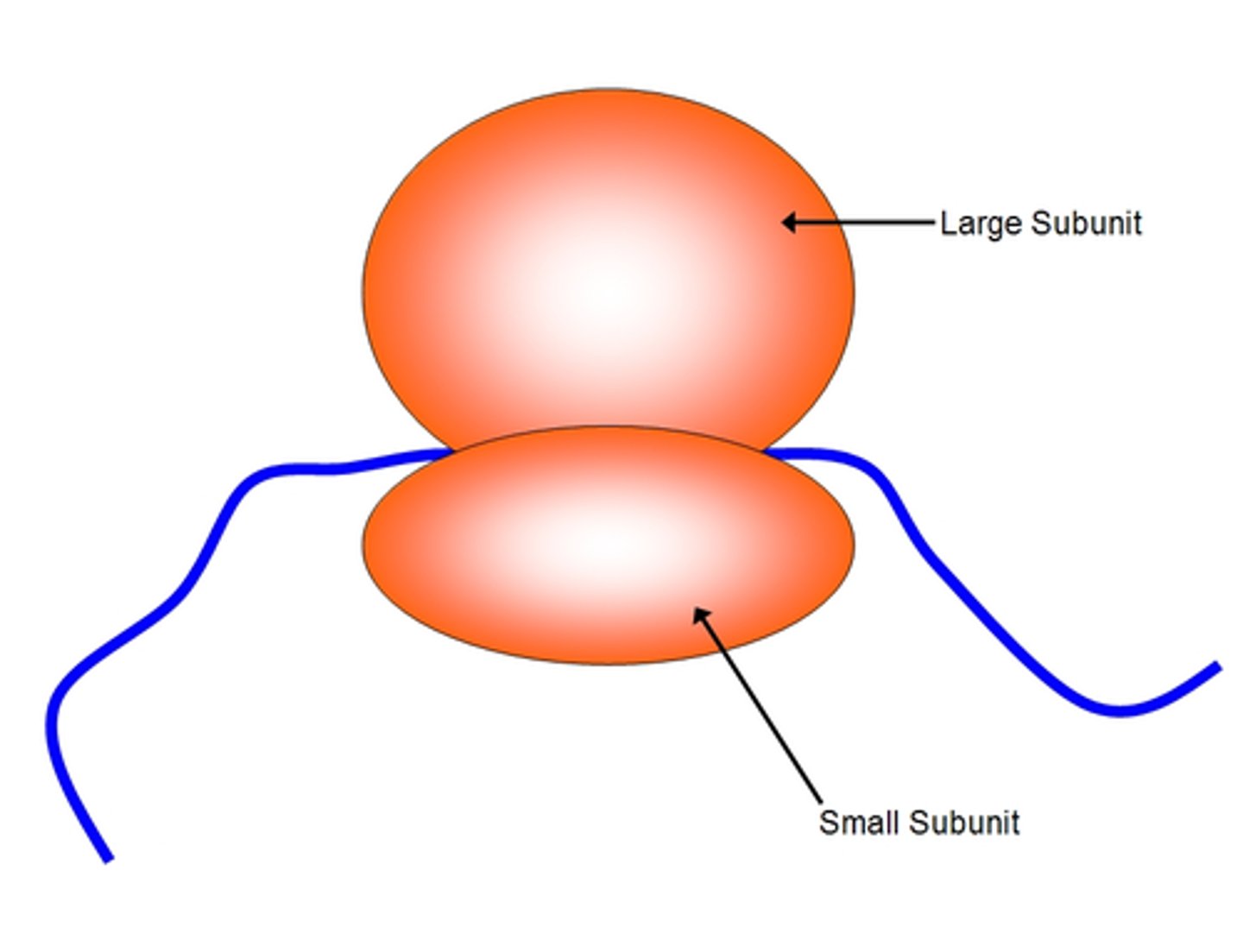
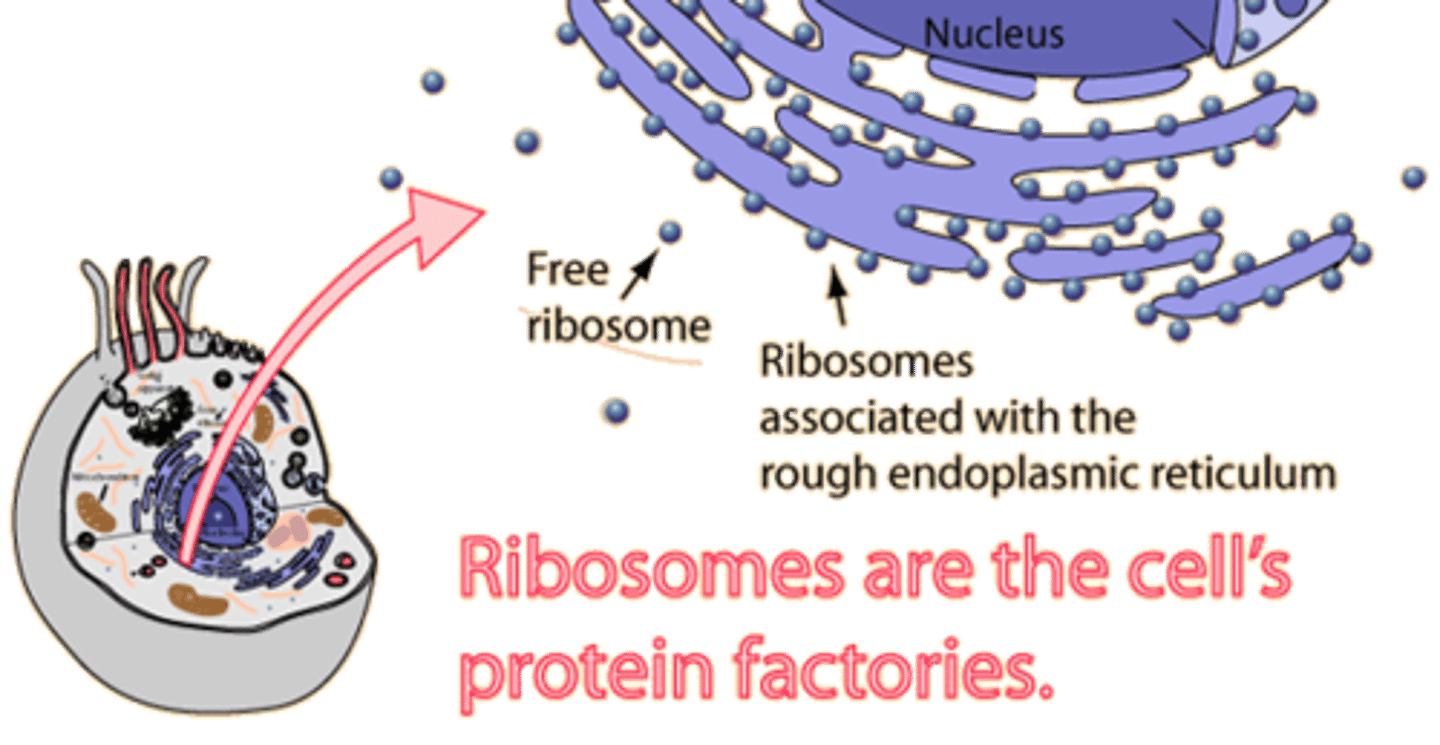
Ribosome(responsibility)
Responsible for making proteins.
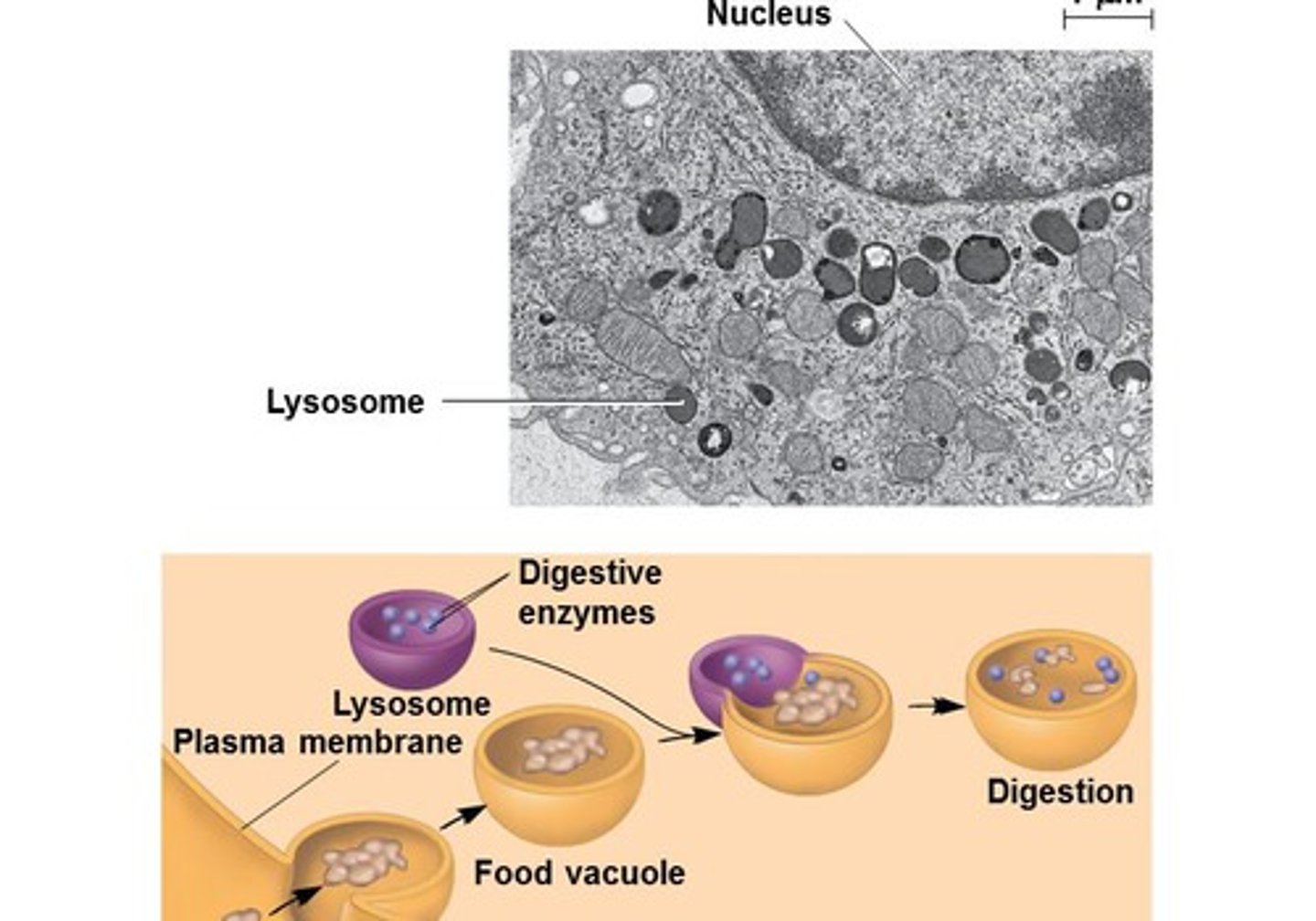
Lysosome
Organelle that engulfs dead organelles or foreign matter and is basically a recycling center.
Vacuoles
Storage unit of the cell; stores water, nutrients, and waste.
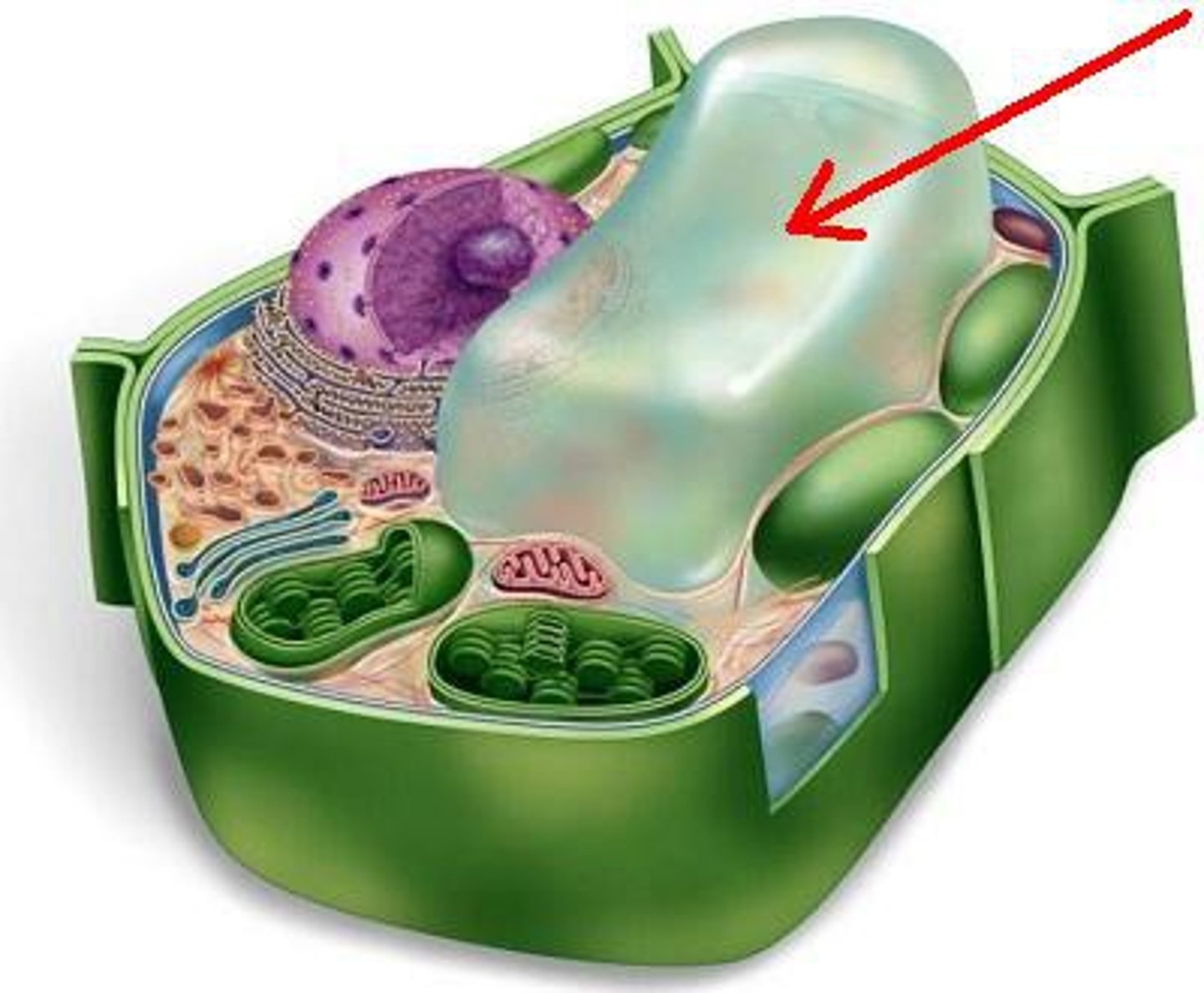
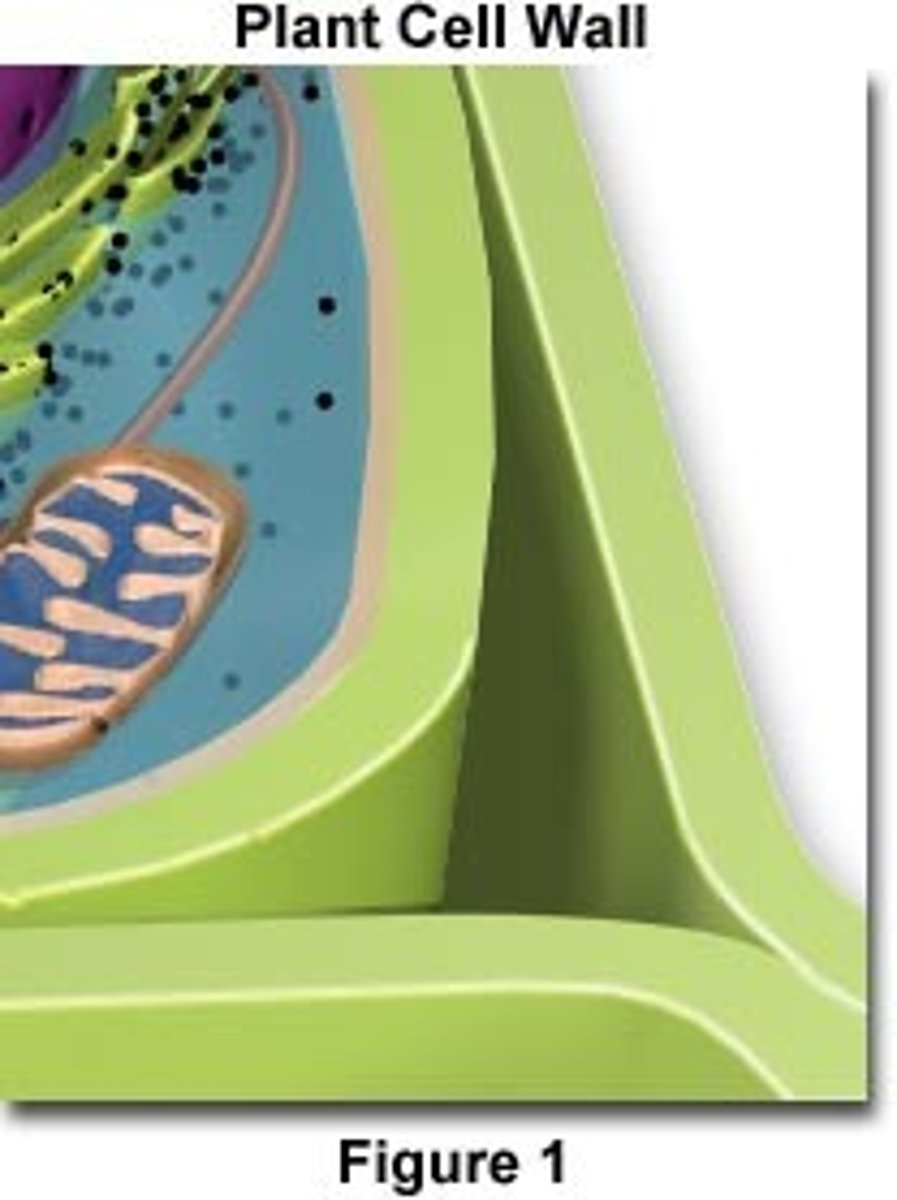
Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell; found only in plant cells.
Eukaryotic
________ cells have a nucleus and other organelles are enclosed by a plasma membrane.
lipids
Smooth ER is used to synthesis _____.
Prokararyotic
small; lack a nucleus.
Examples of Prokaryotic cells
E. Coil, Archea, Bacteria, Salmonella
Examples of Eukaryotic cells
Grass, Pine trees, Moles, Fruit flies.
What surrounds all cells?
cell membrane
Animal cells
Centrioles are found where?
Rough ER has ribosomes and smooth ER does not.
How does rough ER and smooth ER differ?
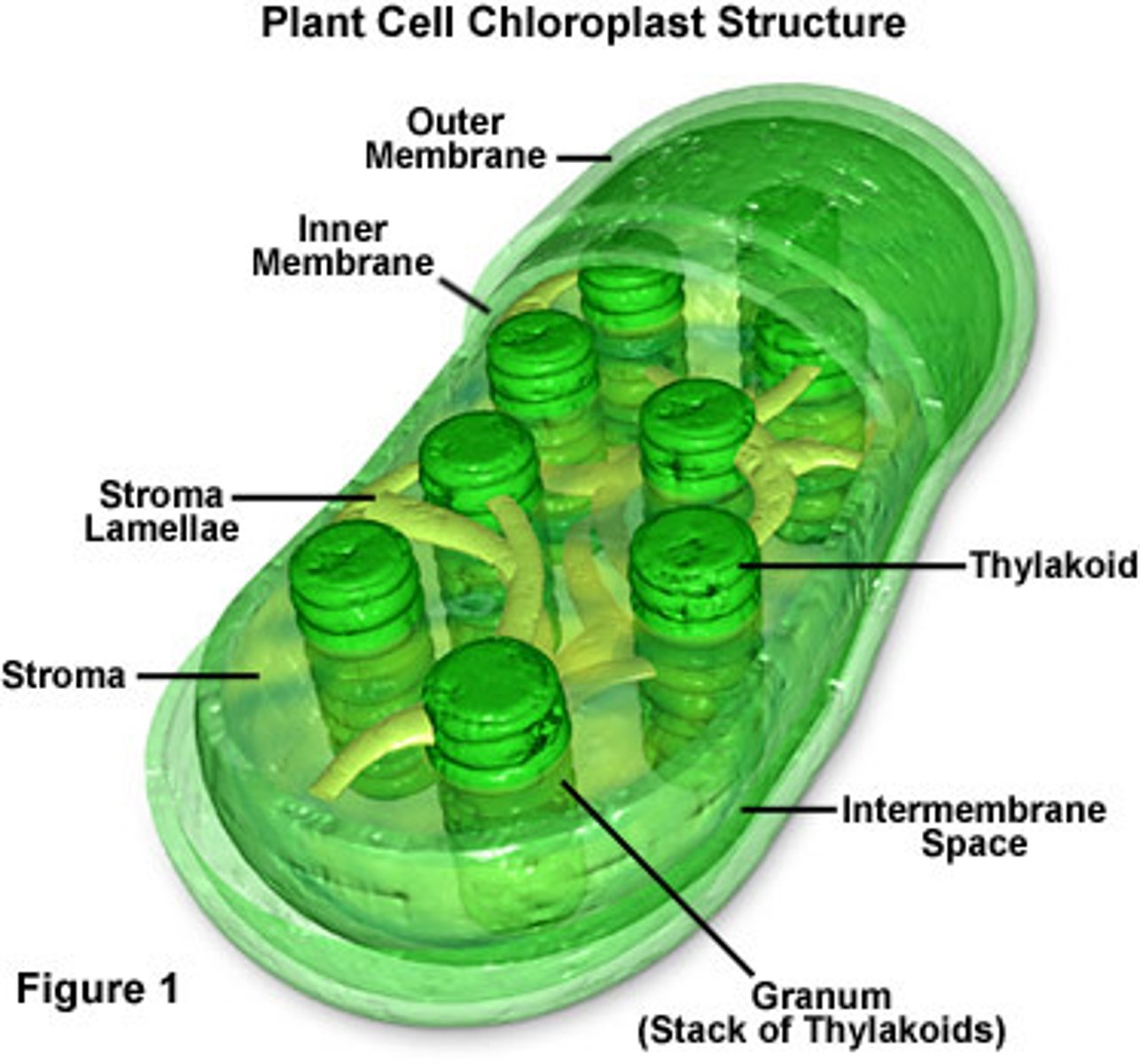
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
Converts solar energy into potential energy in the glucose molecule
plant cells only
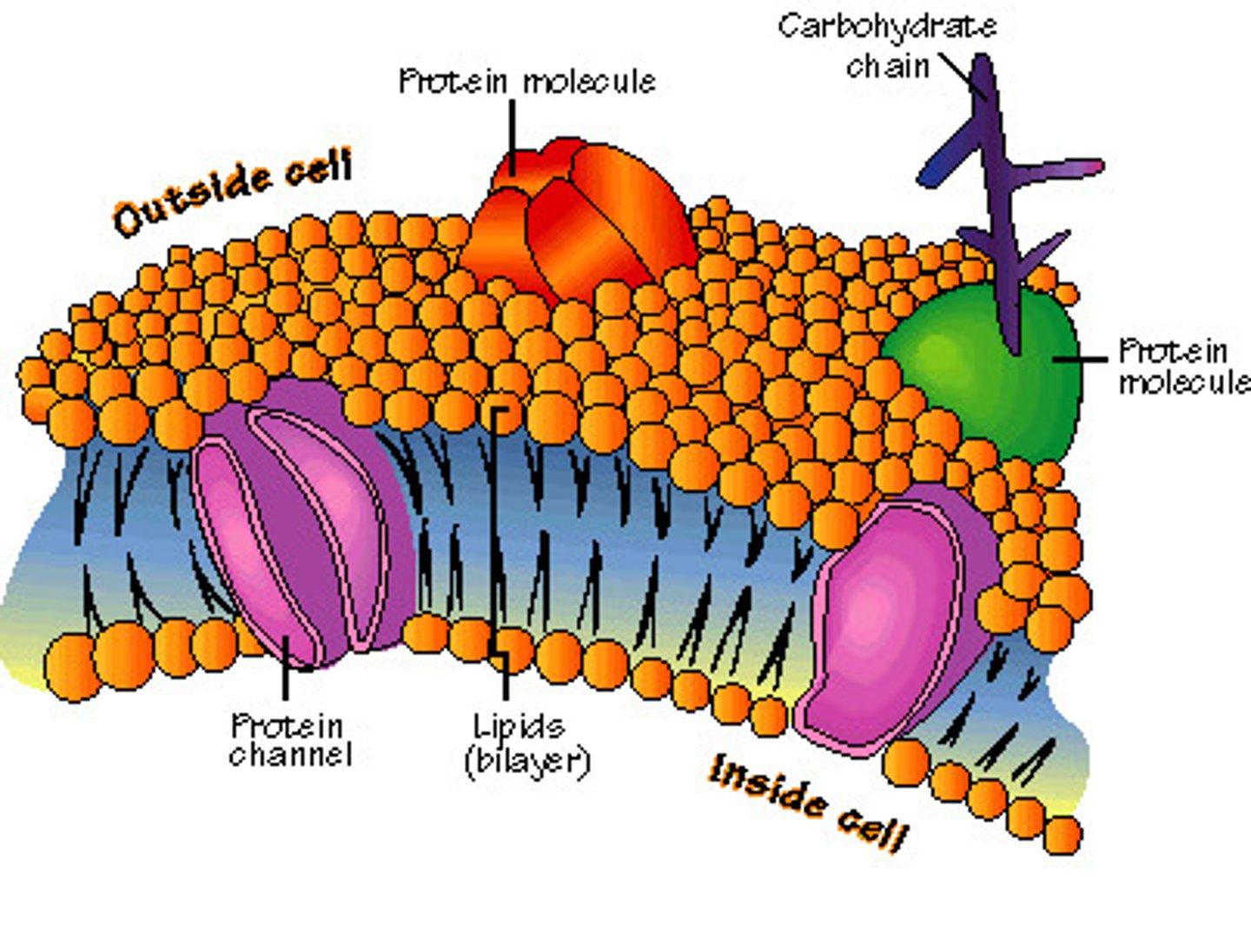
Cell Membrane
Protects cell from surroundings
Allows certain substances in, keeps others out
Phospholipid bilayer with proteins
plant and animal
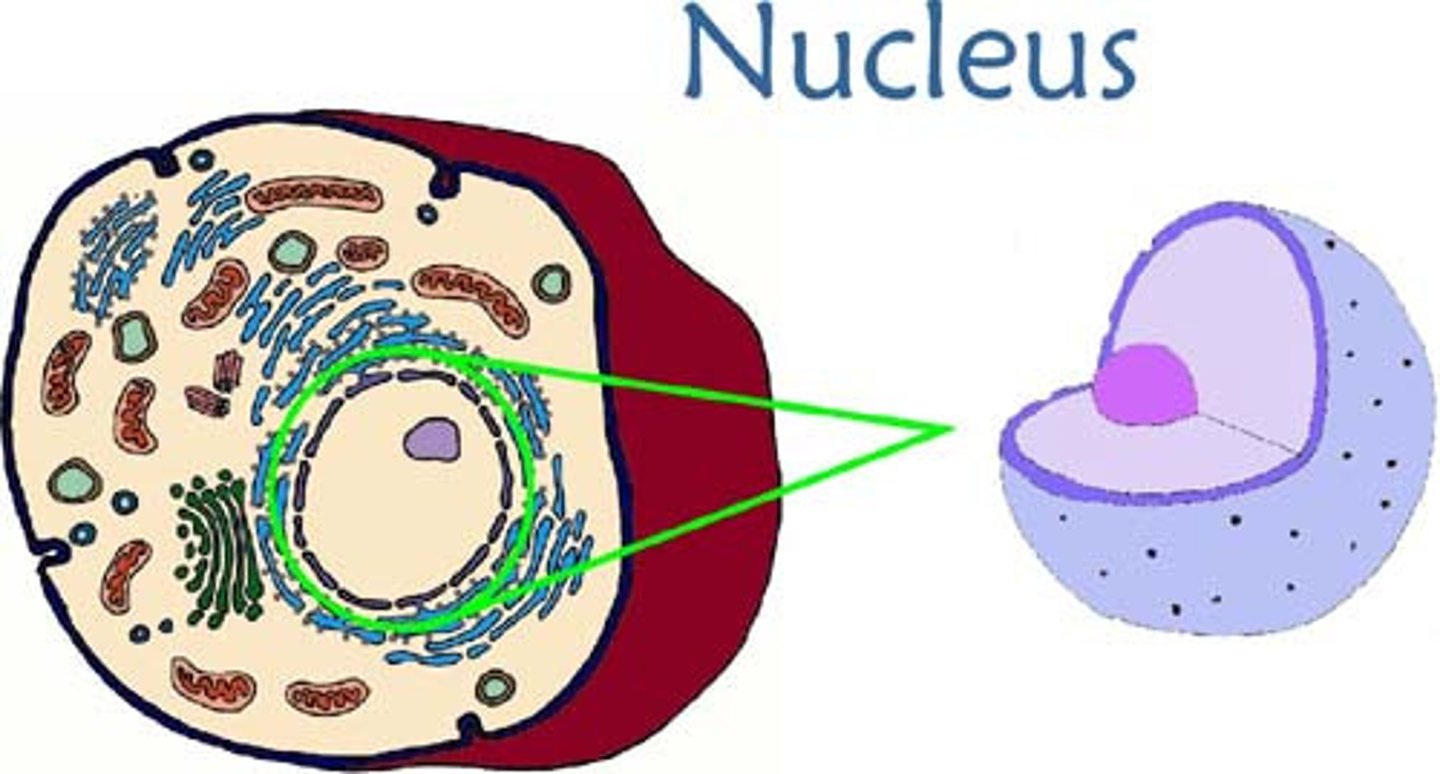
Nucleus
Brain of cell
contains dna
plant and animal
Nucleolus
Non-membranus structure involved in production of ribosomes; located in the nucleus
plant and animal
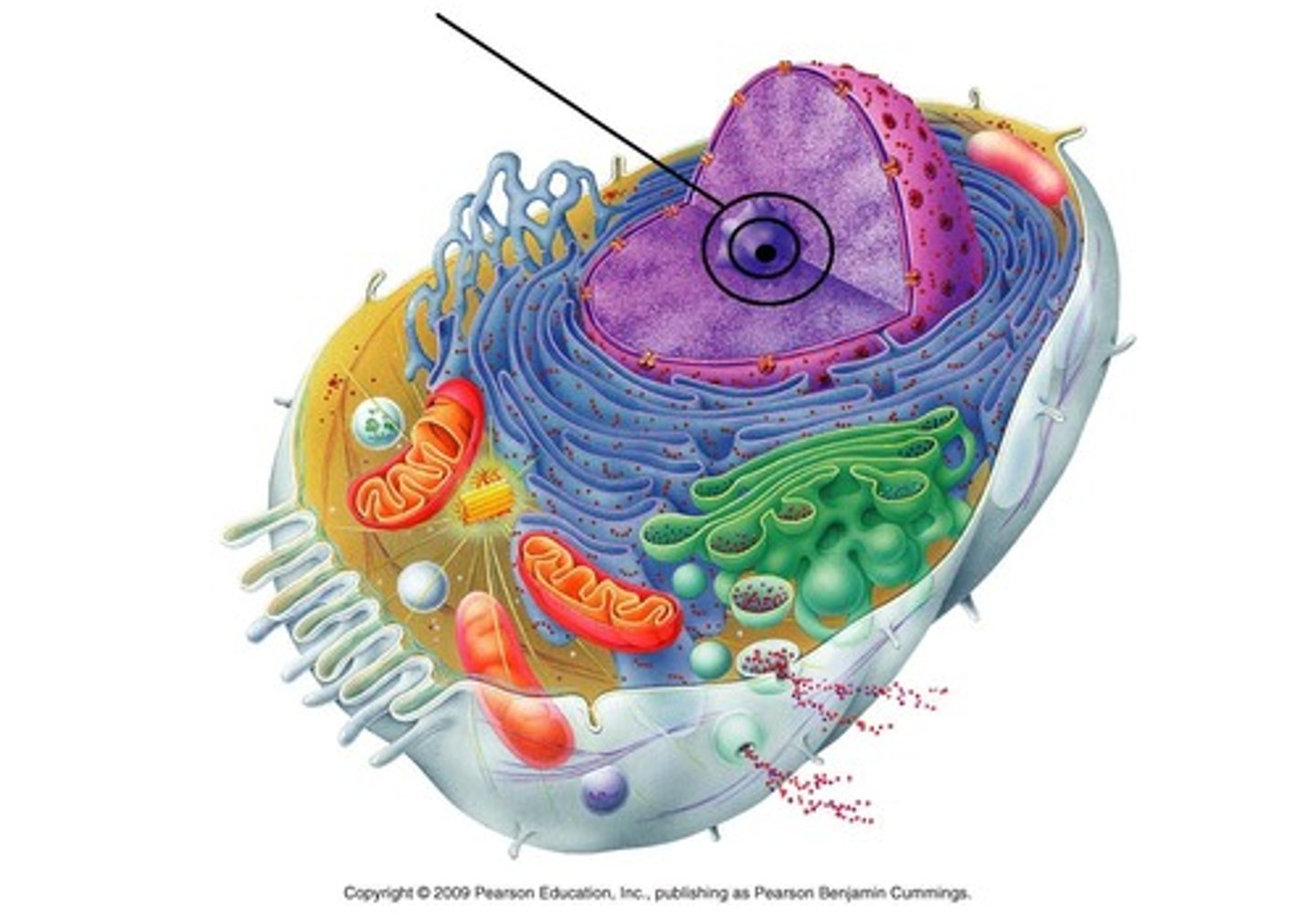
Centrioles
Small microtubles arranged in specific ways
aids in cell division
Animal only
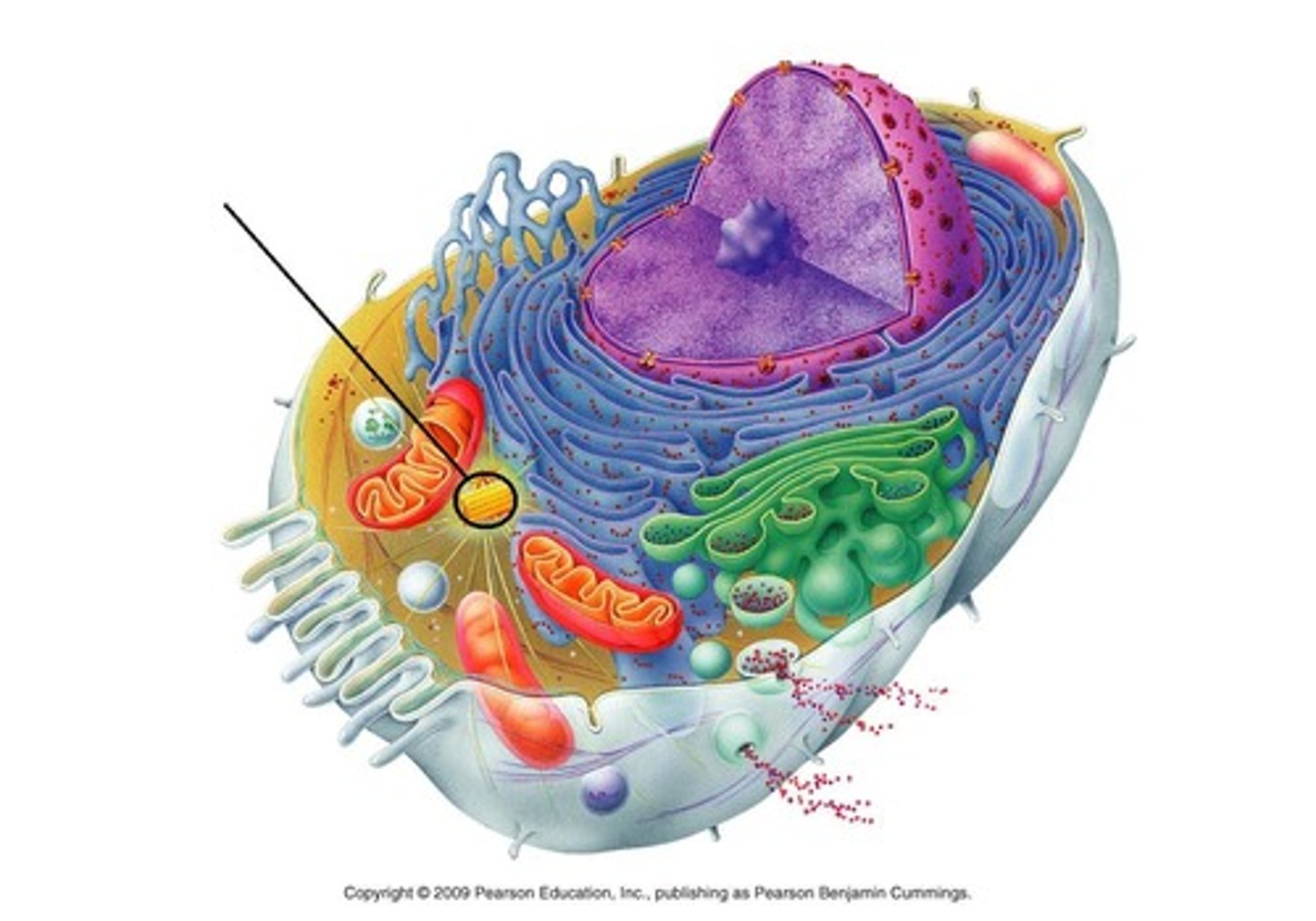
Ribosomes
complexes that makes proteins; free in cytosol or bound to rough ER or nuclear envelope
plant and animal
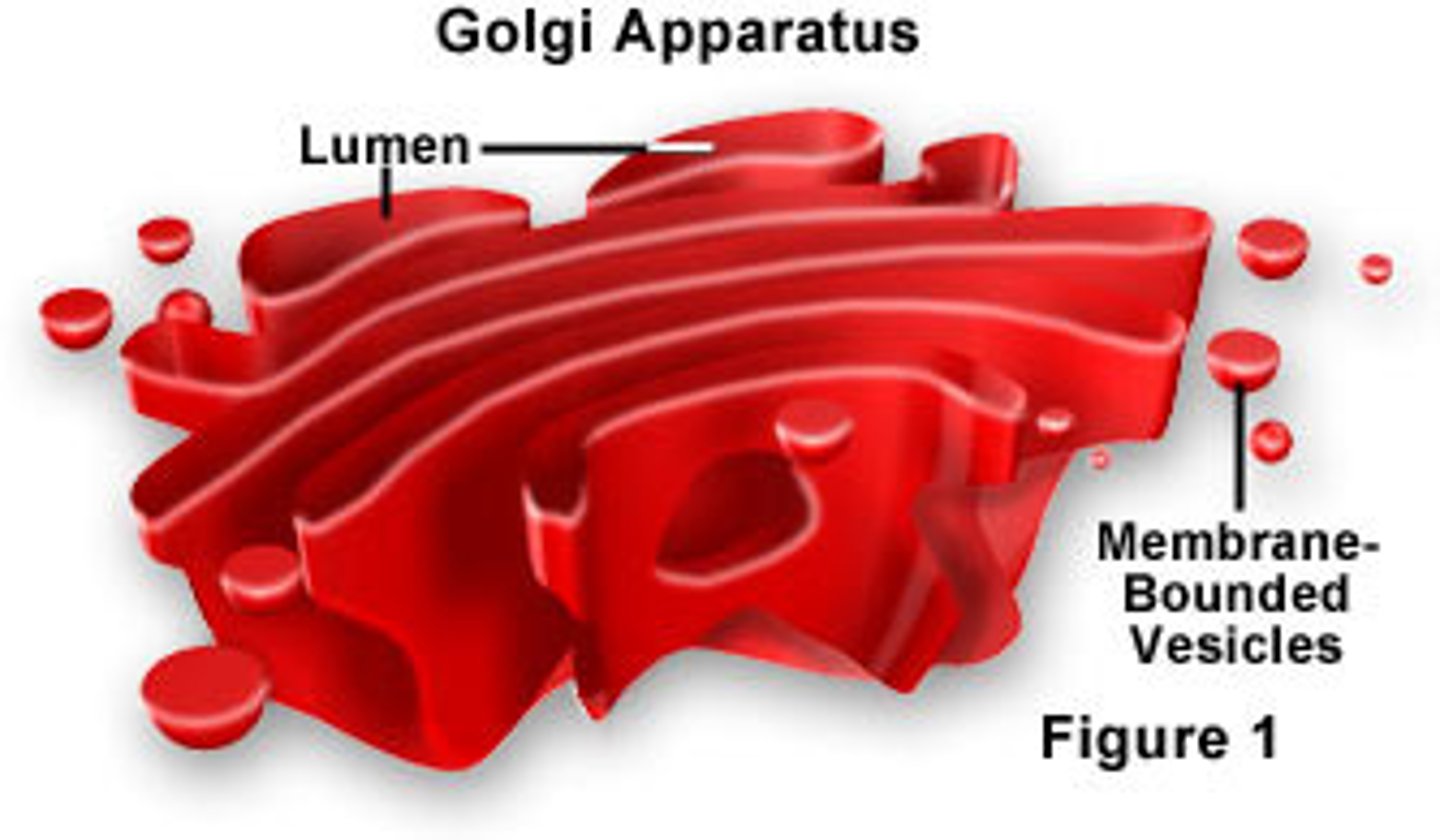
Golgi Apparatus
organelle active in synthesis, modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products
Plant and animal
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough+Smooth
network of membranous sacs and tubes active in making and transporting proteins and lipids
Plant and animal
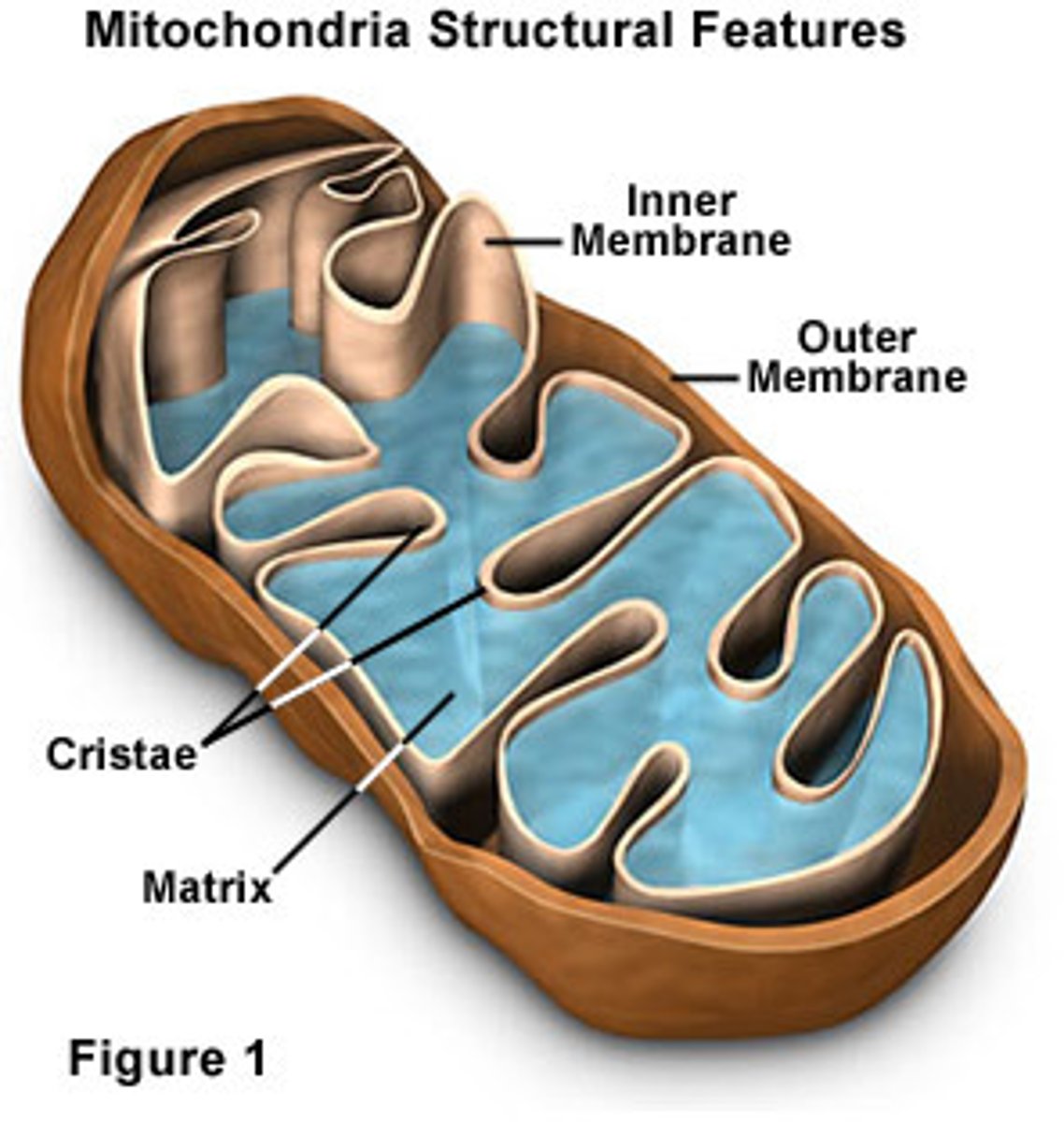
Mitochondria
organelle where cellular resperation occurs and most ATP is generated
plant and animal
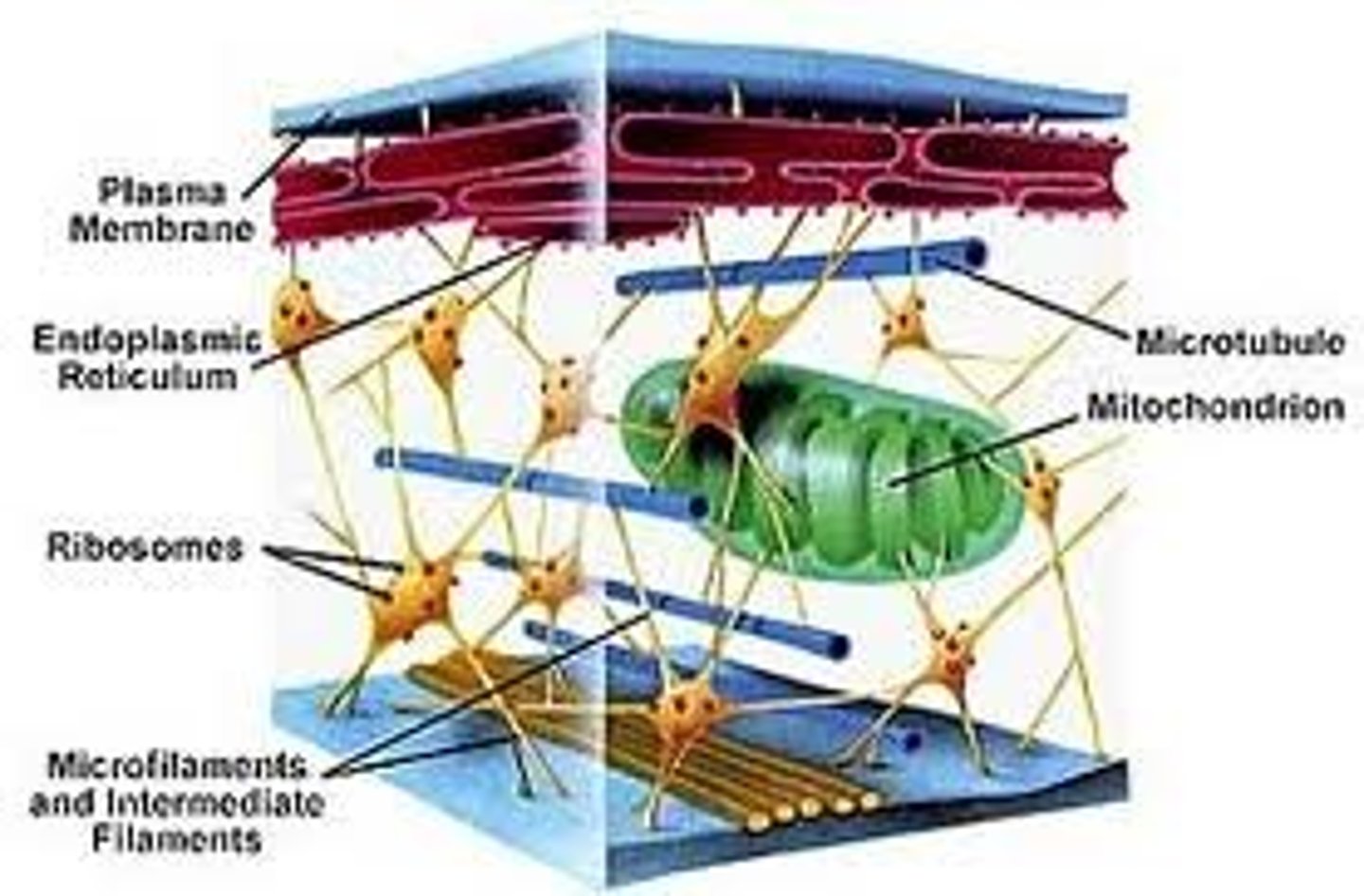
Cytoskeleton
reinforces cell's shape;functions in cell movement; components are made of protein
plant and animal
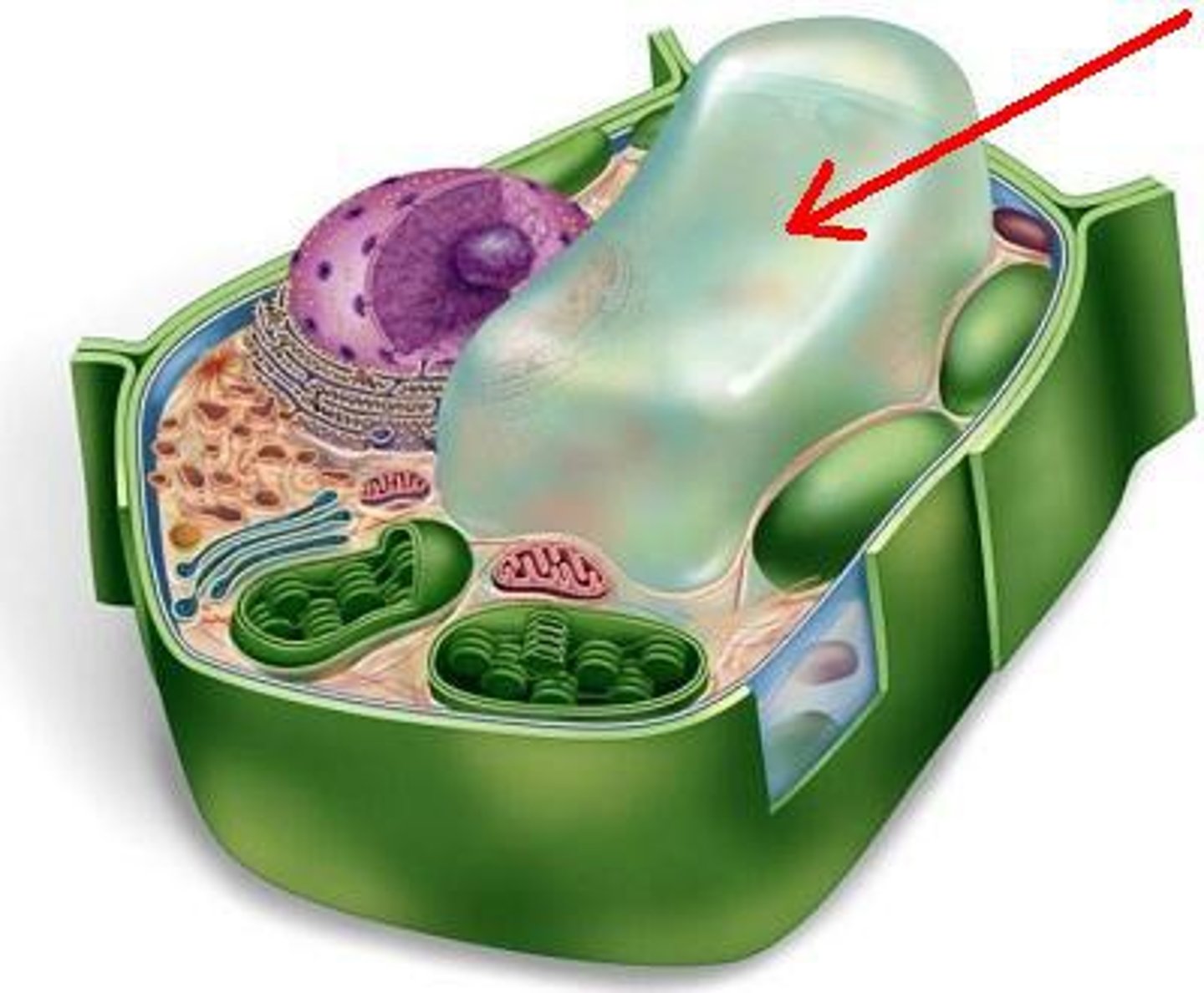
Central Vacuole
Largest organelle in plant cell; maintains turgor pressure because it is inflated with water.
plant only
Cell Wall
outer layer that maintains cell's shape and protects from damage
made of cellulose and other polysachrides, and proteins
Plant only
Cilia
located on outside of cell. pushes cell forward; short, numerous, and hair-like
plant and animal
how proteins are produced, transported and released
1. DNA in nucleus is code for protein
2. Ribosomes on rough endoplasmic reticulum produce protein
3. Mitochondria produce ATP for protein synthesis
4. Golgi apparatus package and modify the protein
5. Vesicles transport protein
and fuse with cell membrane;
flagellum (flagella)
long, tail-like projection with whiplike or propeller motion that helps a cell move
surface area to volume ratio
a variable that decreases as cells grow, so that it sets a limit to the size of cells.
Mitochondial DNA
DNA contributed to the fertilized egg (thus to the child) only by the mother.
endosymbiotic theory
a theory that states that certain kinds of prokaryotes began living inside of larger cells and evolved into the organelles of modern-day eukaryotes