Marine Biology - Lectures 7 - 9
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are identifying characteristics of coccolithophores?
Deposits form chalk
Made up of several overlapping scales or plates
Made of calcium carbonate
A lot of diversity
What are common habitats of coccolithophores?
Epipelagic
Open water
Which shows an image of a coccolithophore
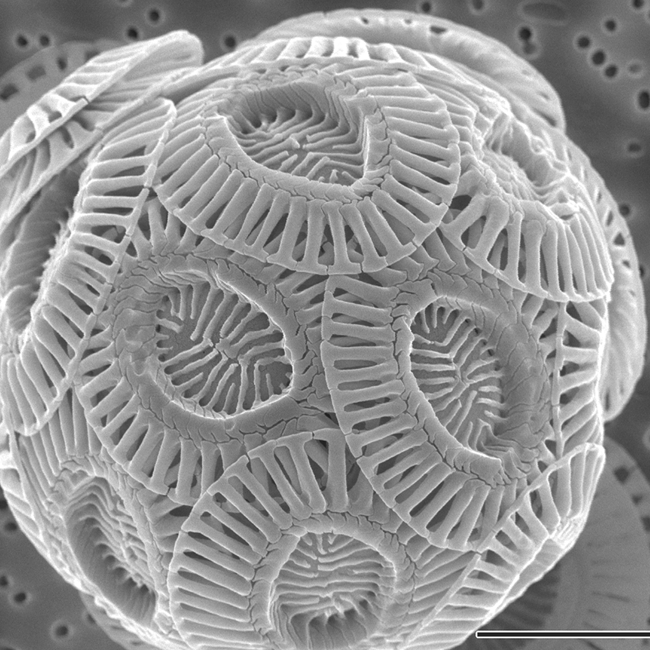
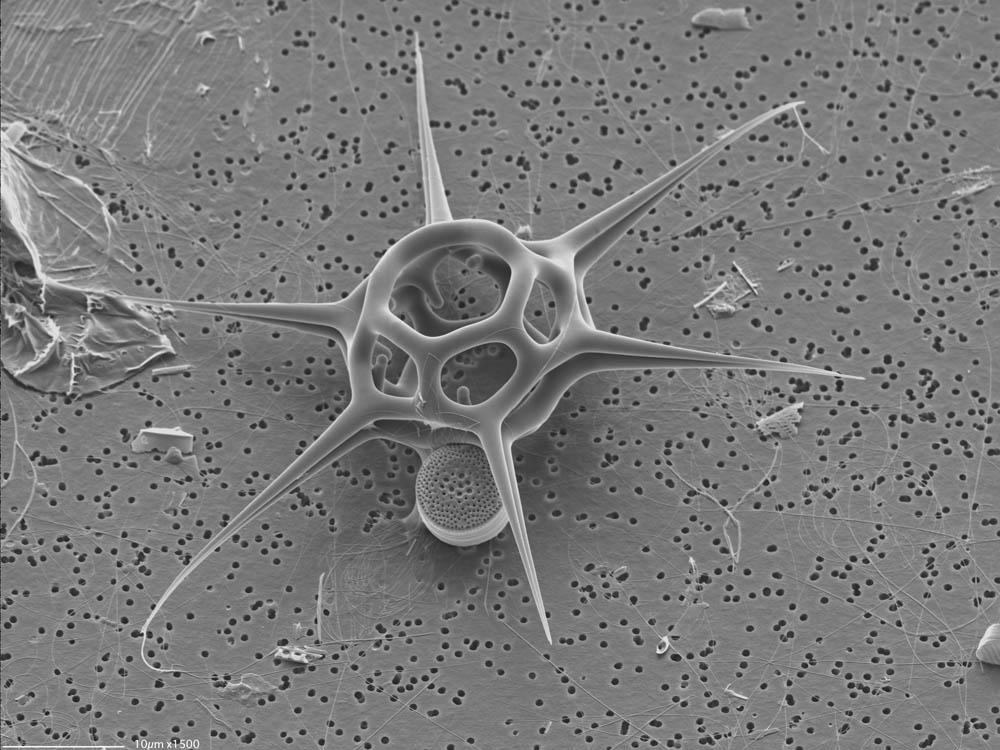
What are identifying characteristics of silicoflagellates?
Internal star shaped skeleton
Photosynthetic
Made of silica
Have flagella
Contain Fucoxanthin
2 pieces that hook together
What are common habitats of silicoflagellates?
Epipelagic region
Which image shows a silicoflagellate
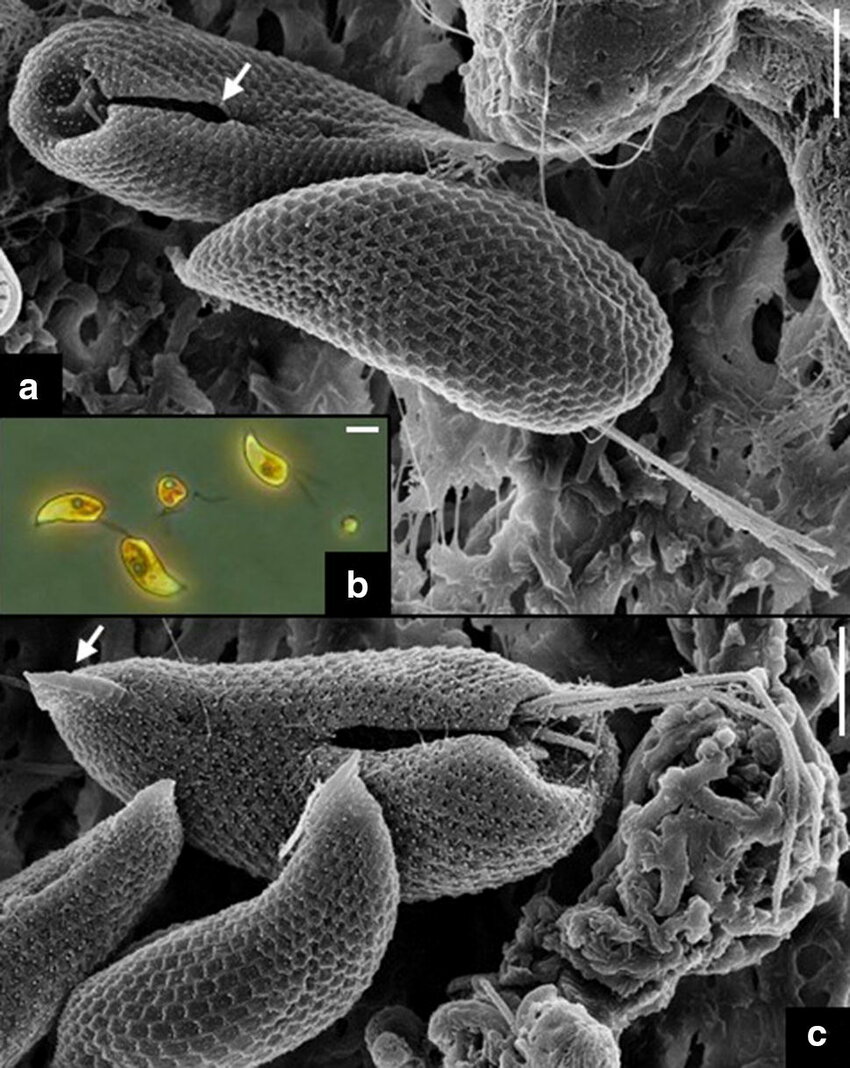
What are identifying characteristics of cryptophytes?
single celled
multiple flagella
scales look knitted on
live deep, and absorb dead organic material (carbon)
What are common habitats of cryptophytes?
deeper water
Which image is a cryptophyte?
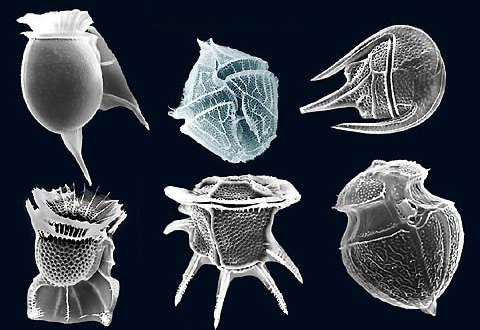
What are identifying characteristics of dinoflagellates?
Have flagella
Fucoxanthin
Made up of cellulose plates
Can produce toxins (red tide)
What are common habitats of dinoflagellates?
Mostly marine but sometimes freshwater environments
Warmer marine water
Which image is a dinoflagellate?
What are zooxanthellae?
Dinoflagellates that live symbiotically with other organisms.
Related to jellies
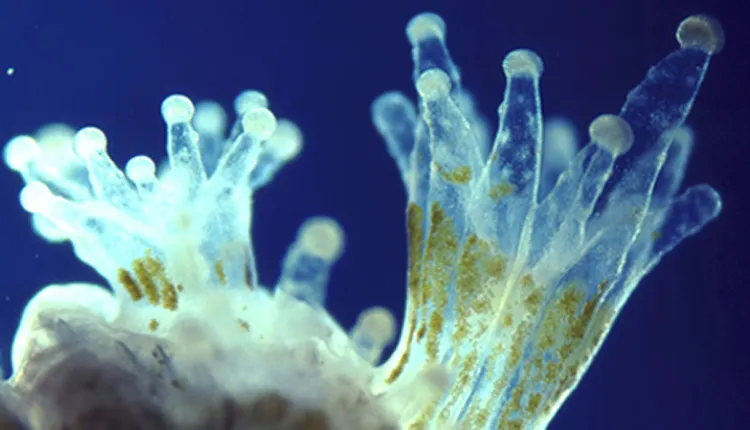
What is red tide?
Harmful dinoflagellate
harmful toxic bloom
What are identifying characteristics of diatoms?
Fucoxanthin
Silica walls
Photosynthetic, mobile organisms
What are common habitats of diatoms?
Mostly in euphotic epipelagic zone
can also be in deep and coastal
Sand, on plants or algae, on animals, on rocks, in mud, on/in ice
Which image shows a diatom?
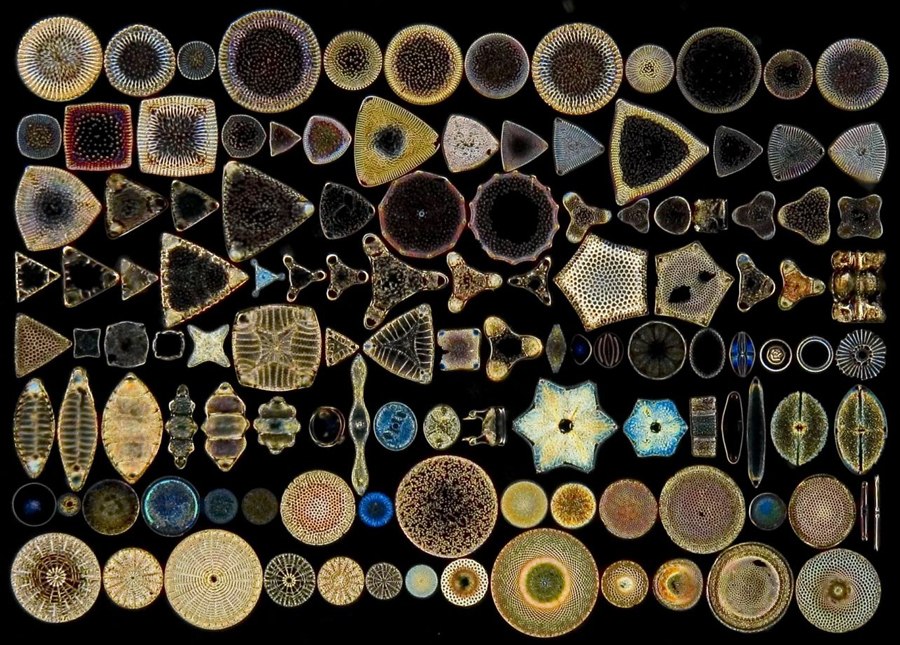
Why are diatoms ecologically important?
They produce 30% of Earth’s oxygen
What are identifying characteristics of ciliate protozoa?
Move by cilia
What are common habitats of ciliate protozoa?
Water
Some parasitic ones can live on other organisms
Which image shows a ciliate protozoa?
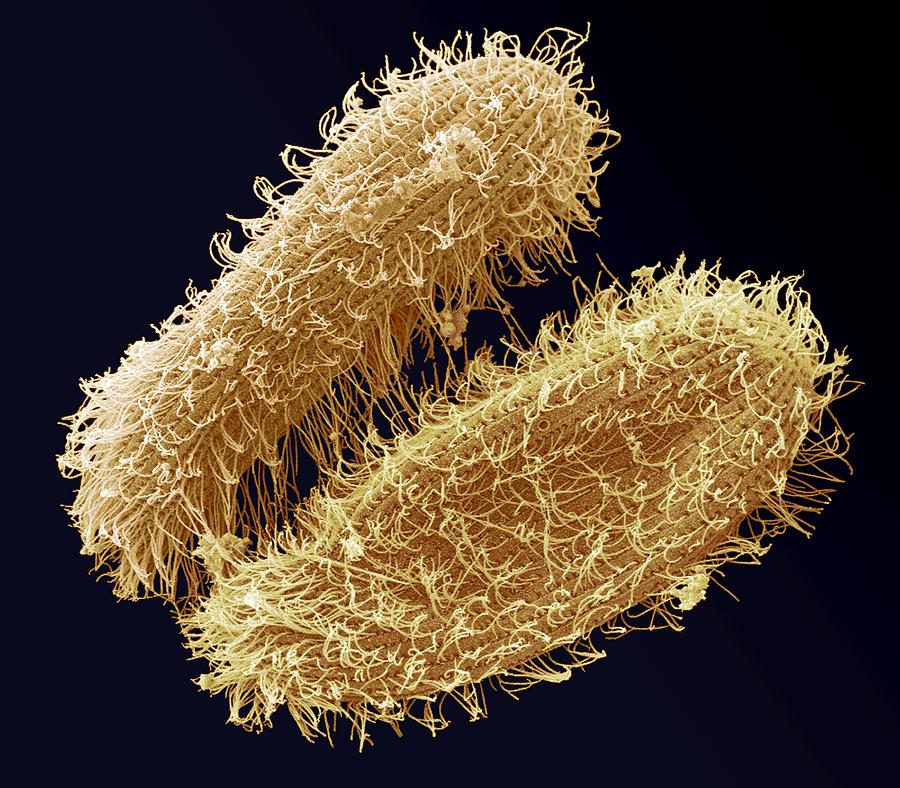
What are identifying characteristics of foraminifera?
multi chambered cells
lead to sand and coral reefs building up
responsible for pink sand
made up of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
What are common habitats of foraminifera?
Shallow coastal waters, pink sandy regions
Which image is a foraminiferan?
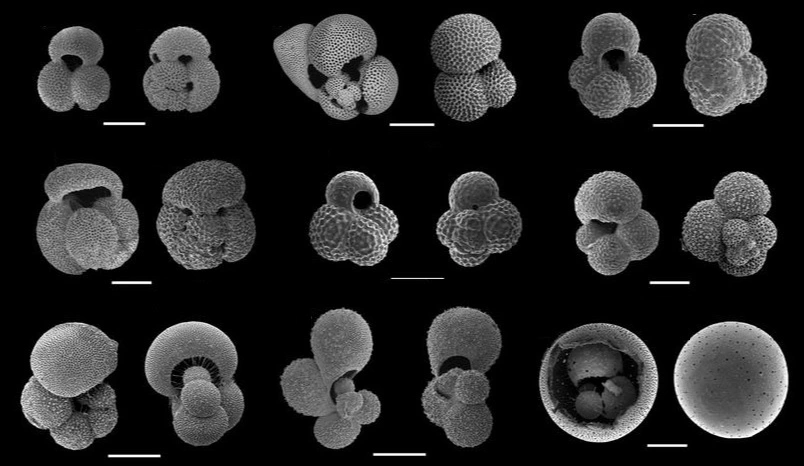
What are identifying characteristics of radiolaria?
Silica skeleton
Spiny skeletons
What are common habitats of radiolarian?
Deep ocean
Which is an image of radiolarians?
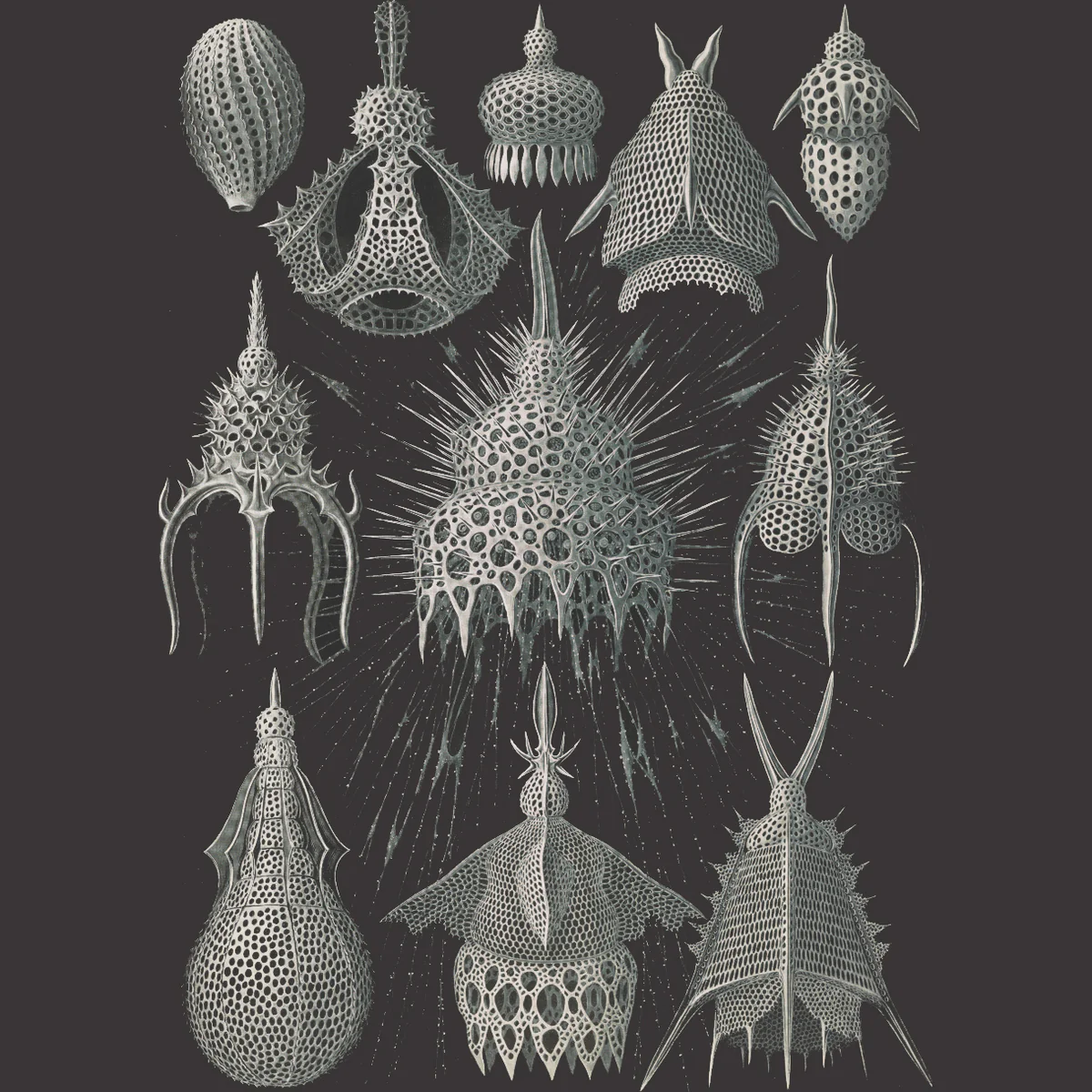

How are forams and radiolarians used in geology and paleoclimate studies?
Petroleum
People use the to determine if they are close to an area with oil underground
In what forms are marine fungi commonly found?
Majority are microscopic
In what marine habitats are marine fungi commonly found?
Shallow coastal areas
Splash zone on the coast, especially rocky areas
How do aquatic photosynthetic organisms adapt to low light conditions in water?
By increasing their light-absorbing pigments like chlorophyll
Which light wavelengths disappear first in surface water?
Red, orange, and yellow
What accessory pigments are common in aquatic algae?
Fucoxanthin
What is the name of the morphological structure of seaweed that are gas-filled bladders that buoy up the plant towards sunlight?
Pneumatocysts
Which three types of marine algae have macroscopic forms?
Macroalgae, Macrophytes, Macrocytis
What is a common name for brown algae?
Phaeophyta
What is the largest macroalgae?
Macrocytis (giant kelp)
What is the scientific term for aquatic plants?
Macrophytes
How are seagrasses ecologically important?
Main food source for many animals
In what habitats are seagrasses found?
ONLY marine environments
Why do wetlands have few, endemic species?
The plants there must be adapted to low oxygen levels in water
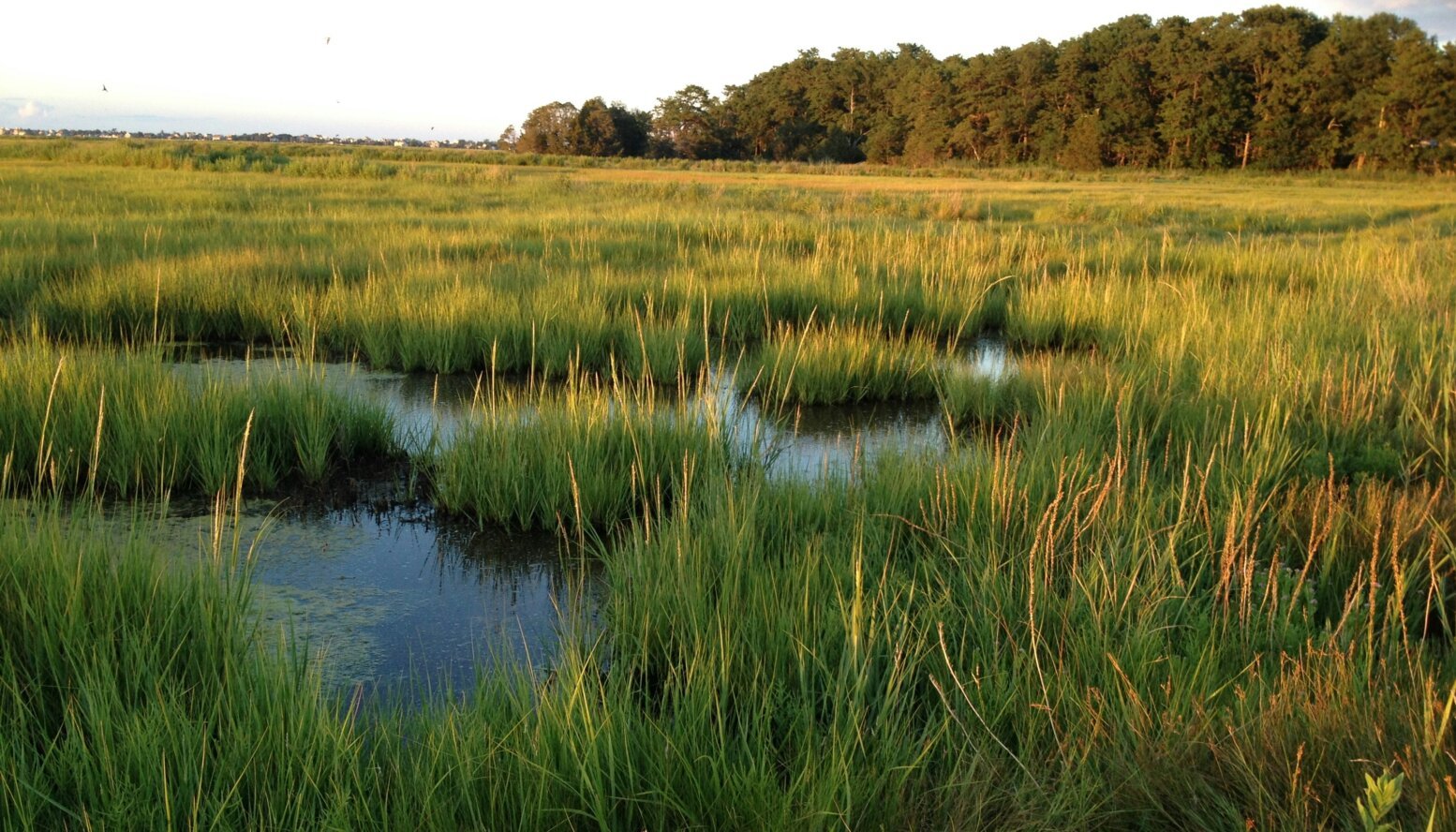
What are identifying characteristics of a salt marsh?
cordgrass
temperate coastal areas
Which image is a salt marsh?

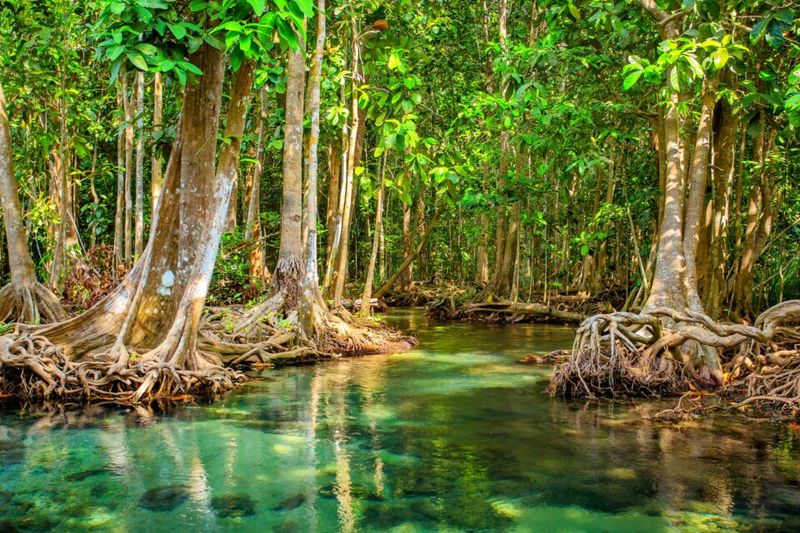
What are identifying characteristics of a mangrove?
Entagled prop roots
Which image is a mangrove?

How are coastal wetlands like marshes and mangroves ecologically important?
Important for habitat
Protecting juvenile species
Good for nutrient cycling
What are conservation threats to coastal marshes like mangroves and marshes? What implications does the loss of these habitats have on people?
These habitats help protect from storm surges, and help keep the young population of select organisms safe.