Biotechnology Lab: GMO Detection, PCR, and ELISA Techniques
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
GMO
Genetically Modified Organism (GMO): An organism in which the genetic material has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally.
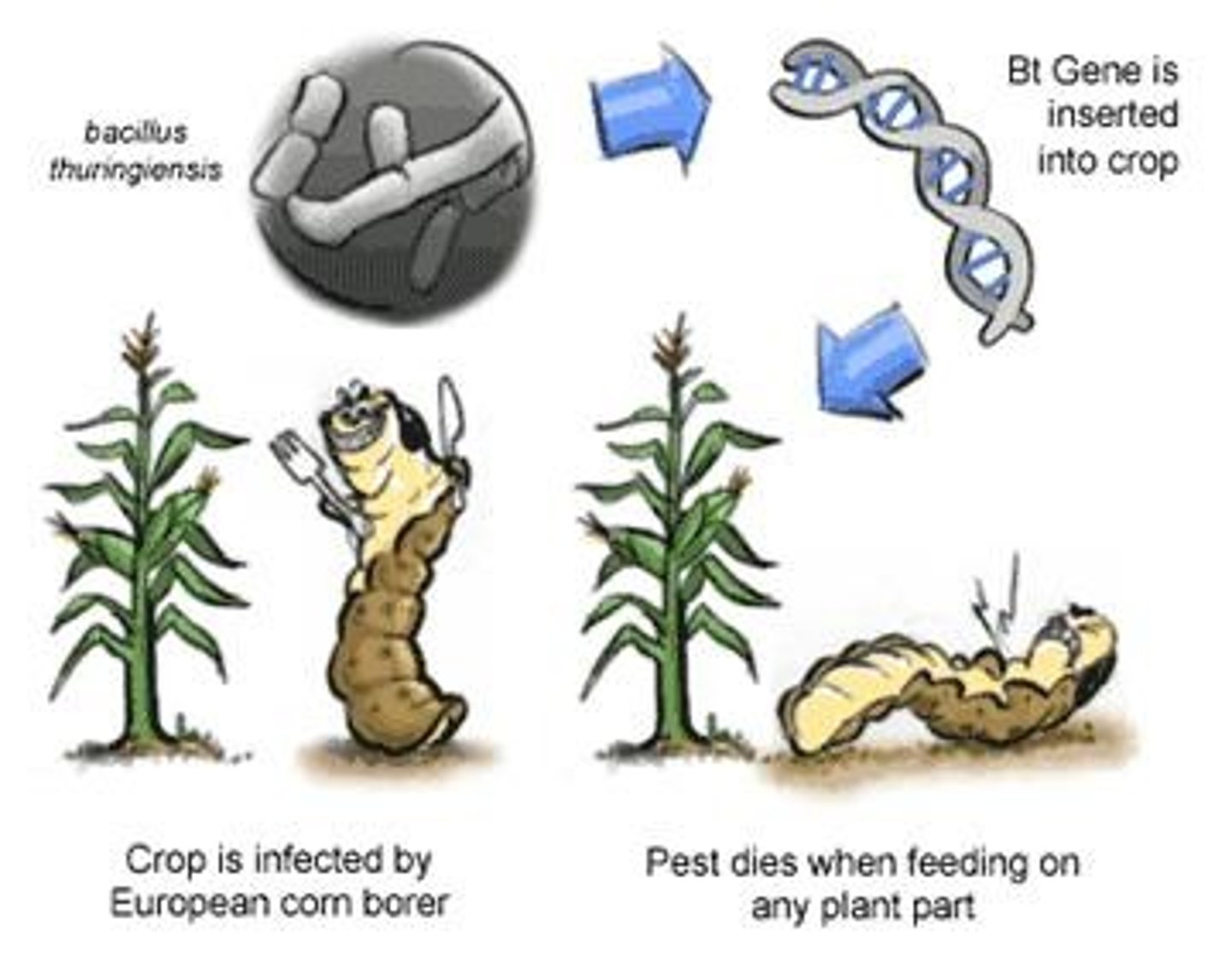
Bt gene
Gene originally from bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis that produces a protein lethal to common insect pests on corn plants.
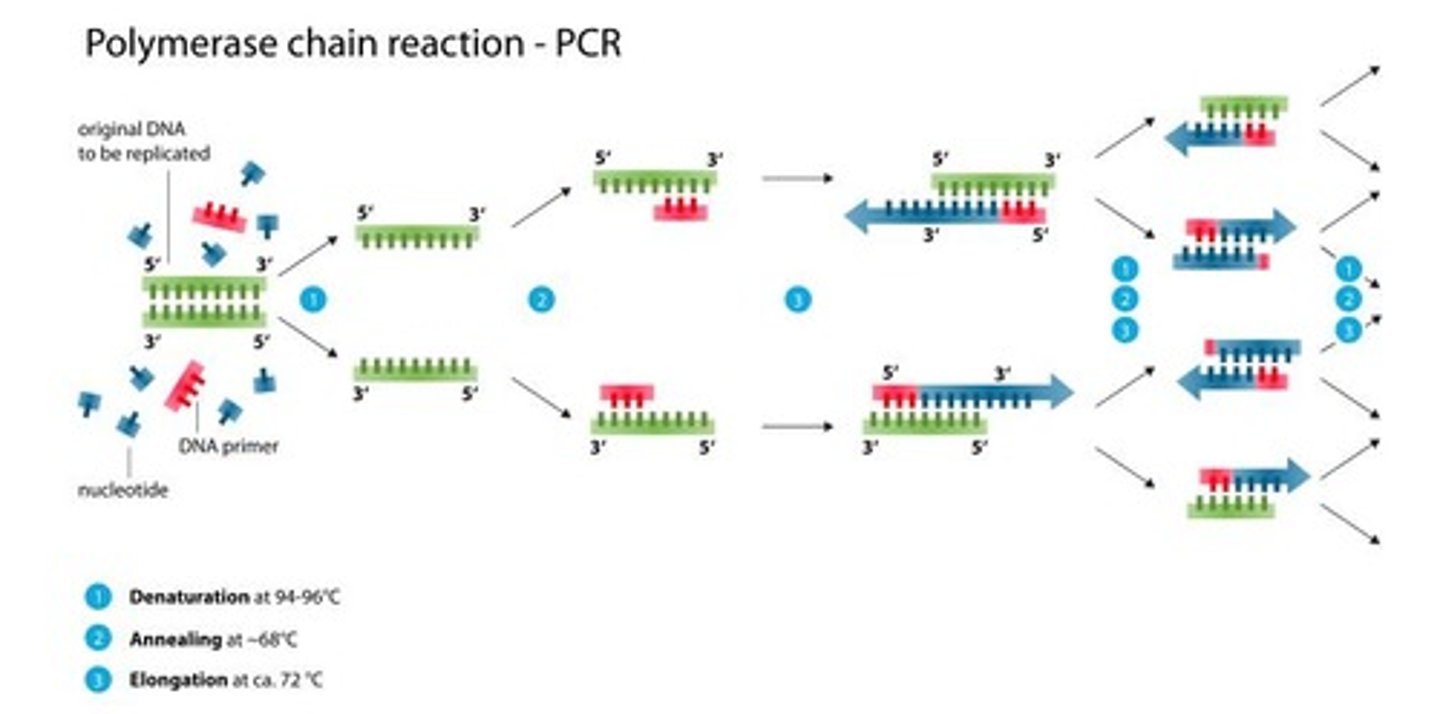
Polymerase Chain Reactions (PCR)
A method to replicate DNA.
What genetic material does PCR amplify
DNA
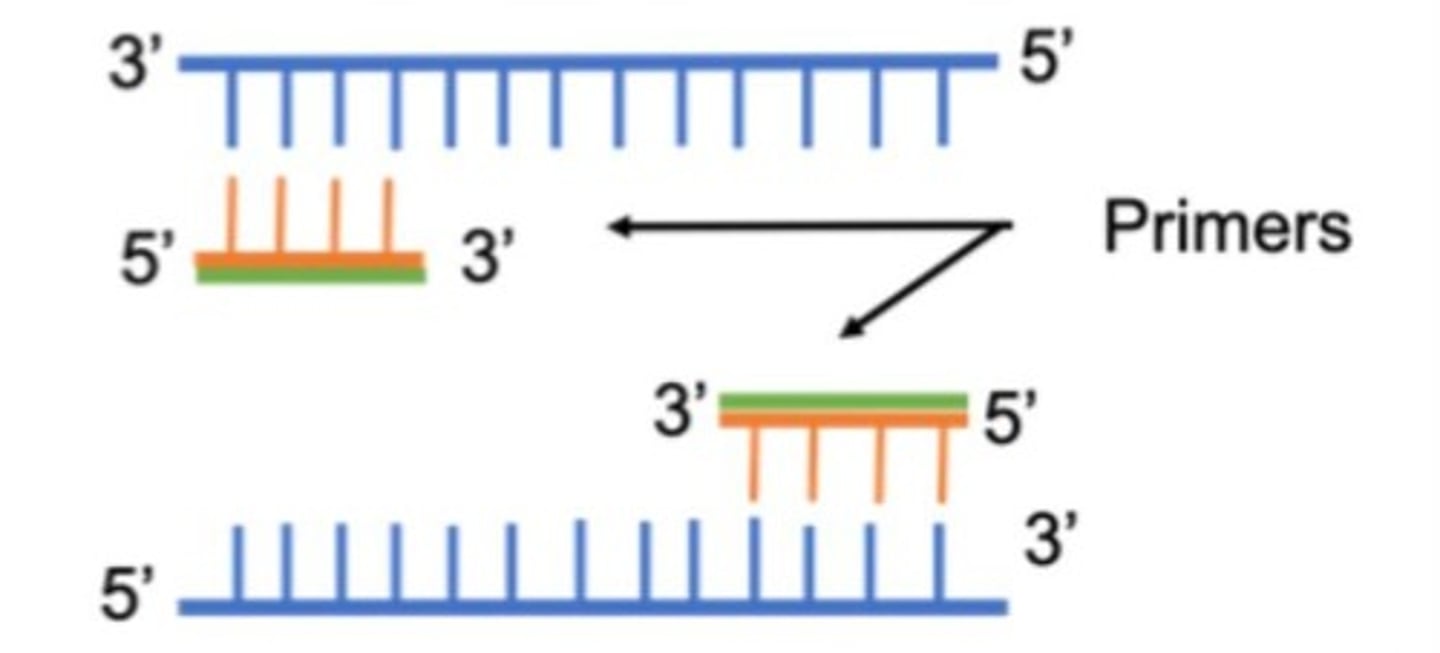
Forward and reverse primers
Short strands of DNA that are complementary to the target DNA and provide a starting point for DNA polymerase for DNA synthesis.
Taq DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase from a thermophilic bacteria that can withstand high temperatures to synthesize new strands of DNA.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA.
Buffers
Provides a stable and neutral environment for DNA synthesis.
Denaturation
The first step of PCR at 94°C, where DNA is denatured.
Purpose of DNA ladder in gel electrophoresis
To serve as a size reference
Annealing
The second step of PCR at 59°C, where primers anneal to template DNA.
Elongation
The third step of PCR at 72°C, where Taq polymerase extends primers and replicates DNA.
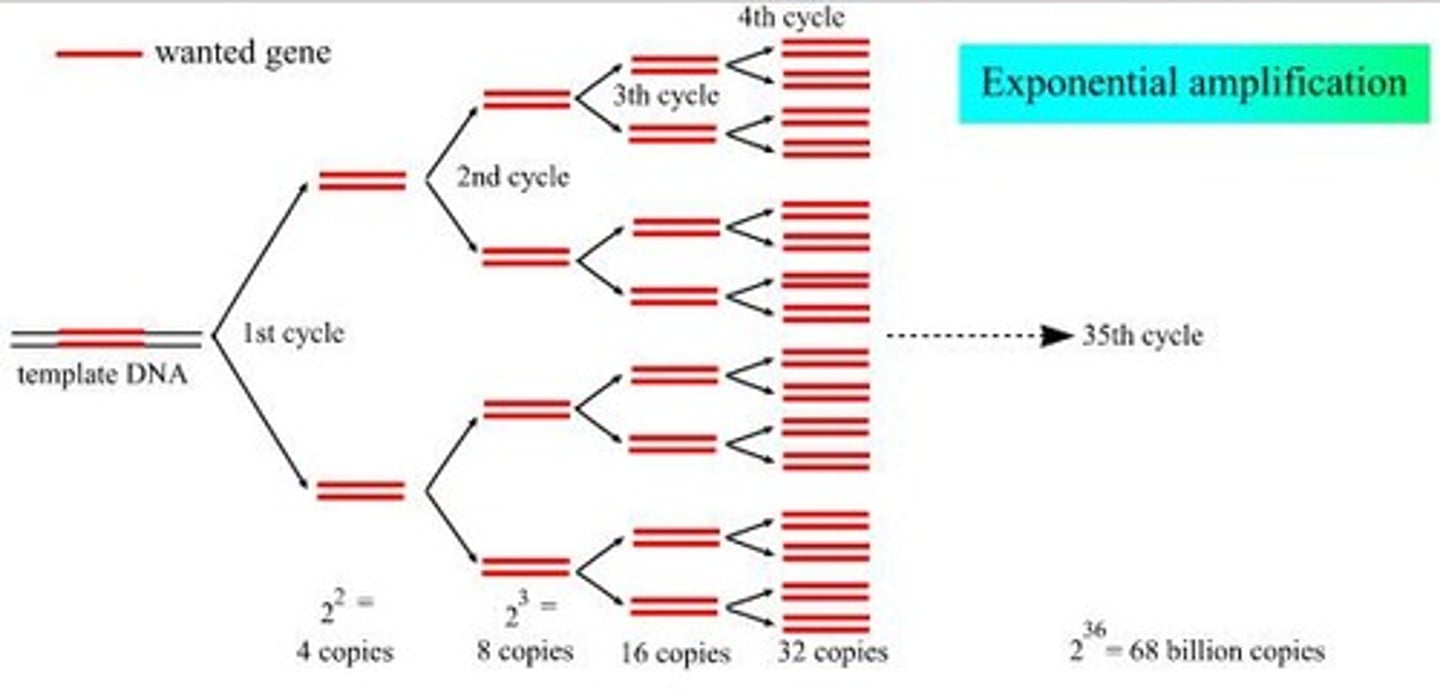
PCR Cycle
The cycle repeats 40 times to continuously produce millions/billions of copies of the original DNA strand.
GMO DNA Extraction
Analyzing food to determine if it contains common GMO genes by using primers.
Plant master mix (PMM)
Primer used to determine if you successfully extracted PLANT DNA, recognizing a DNA sequence common to all plants.
GMO master mix (GMM)
Primer used to determine if your test sample is GM, recognizing a DNA sequence common to most GMOs.
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
A technique using a gel matrix made of agarose to separate DNA.

SYBR Safe
A dye added to agarose gel that fluoresces DNA.
Agarose concentration
Increased to enhance the resolution of DNA separation in gel electrophoresis.
TAE buffer solution
A solution used in gel electrophoresis to conduct electricity and maintain pH.
Orange G loading dye
A dye used to visualize DNA samples in gel electrophoresis. (10uL)
Anode vs cathode
Anode is the positive electrode, while cathode is the negative electrode in an electrochemical cell.
Plant DNA
DNA extracted from plants, typically measured at 455 bp.
GMO DNA
DNA from genetically modified organisms, typically measured at 200 bp.
Bands for larger DNA fragments
Appear closer to the top (closer to the wells) in gel electrophoresis.
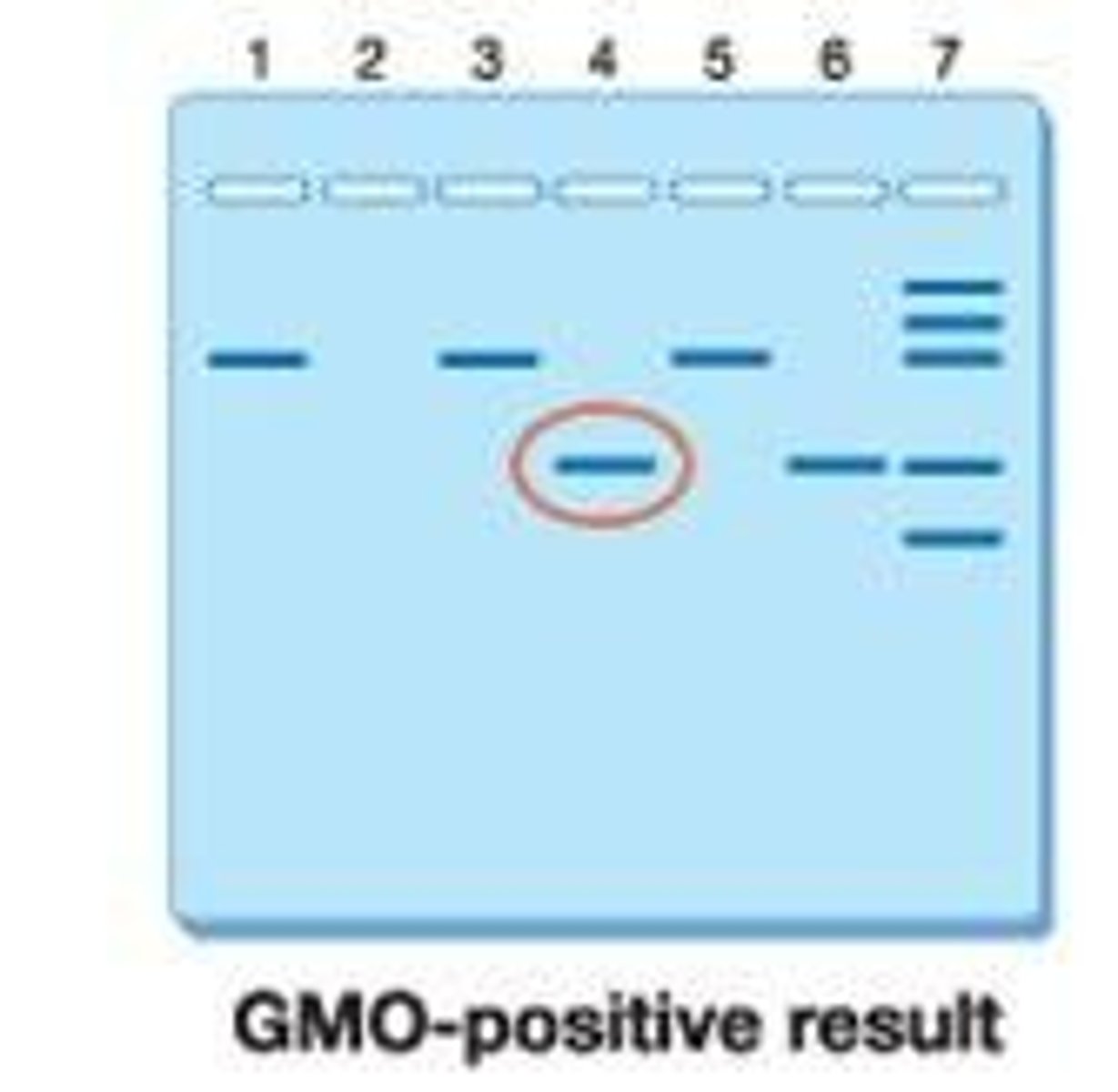
Bands for smaller DNA fragments
Appear closer to the bottom (farther from the wells) in gel electrophoresis.
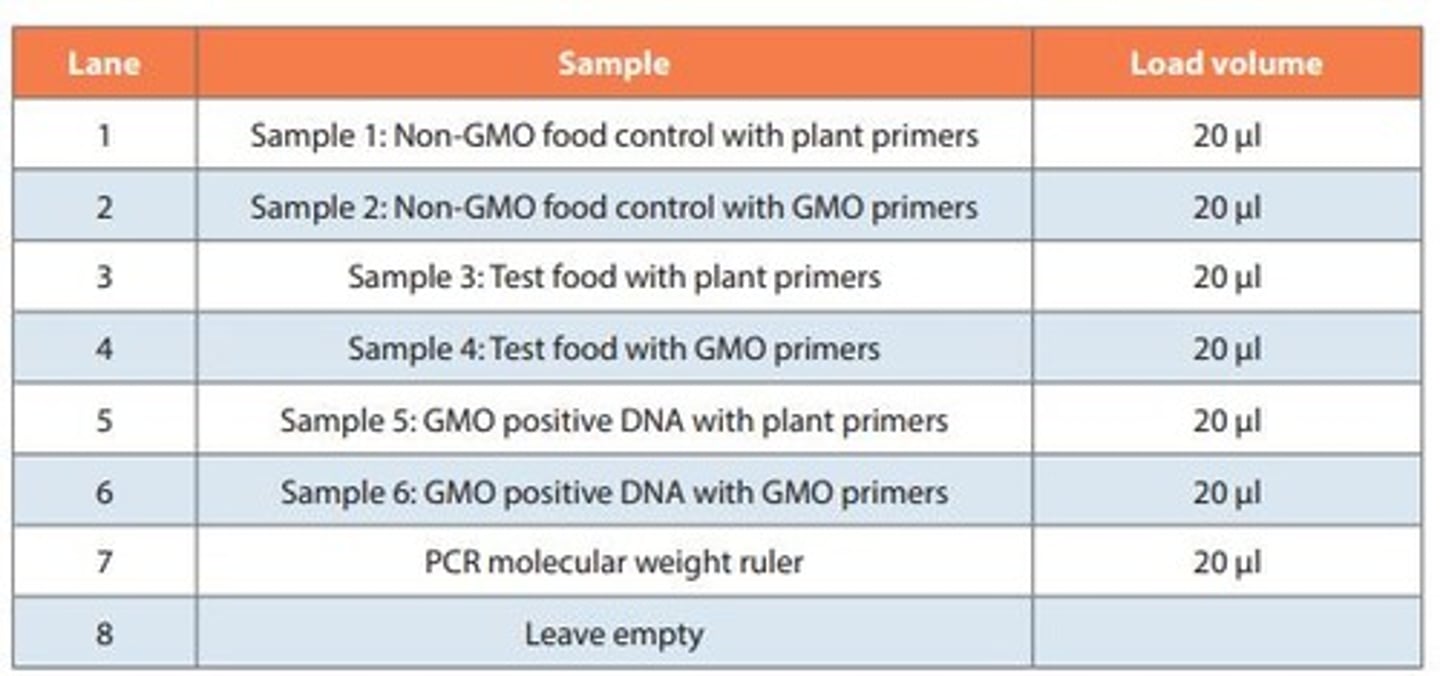
Lane 4
May have a band at 200 bp indicating the presence of GMO food.
Lanes 1, 3, 5
Have a band at 455 bp indicating the presence of plant DNA.
Lane 6
Has a band at 200 bp indicating a positive control for GMO.
Lane 2
Doesn't have a band indicating a negative control, verifying no contamination.
Antigens
Molecules that cause an immune response.
Antibodies
Proteins that recognize and bind to specific antigens.
ELISA
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay, a test that uses antibodies to detect specific antigens.
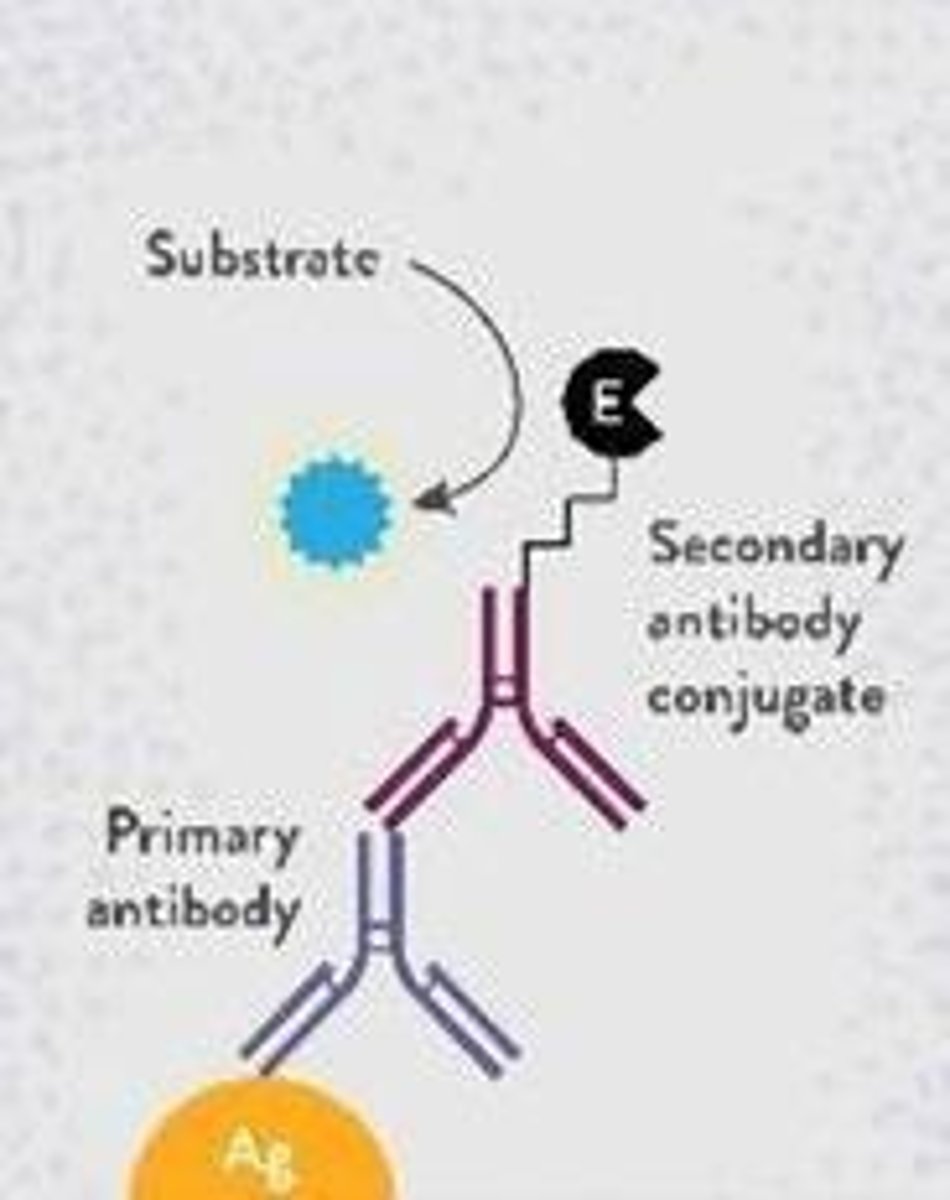
Primary antibody
The first antibody that binds to the antigen in an ELISA experiment.
Secondary antibody
An antibody that binds to the primary antibody and is linked to an enzyme.
Enzyme substrate
A substance that the enzyme acts upon, leading to a color change in the well if the antigen is present.
Positive control
A sample that is known to contain the target antigen, used to validate the experiment.
Negative control
A sample that is known not to contain the target antigen, used to verify no contamination.
Washing wells
The process of cleaning the wells in an ELISA to remove unbound substances.
hCG
An antigen found in the urine of pregnant women that binds to primary antibodies in pregnancy tests.
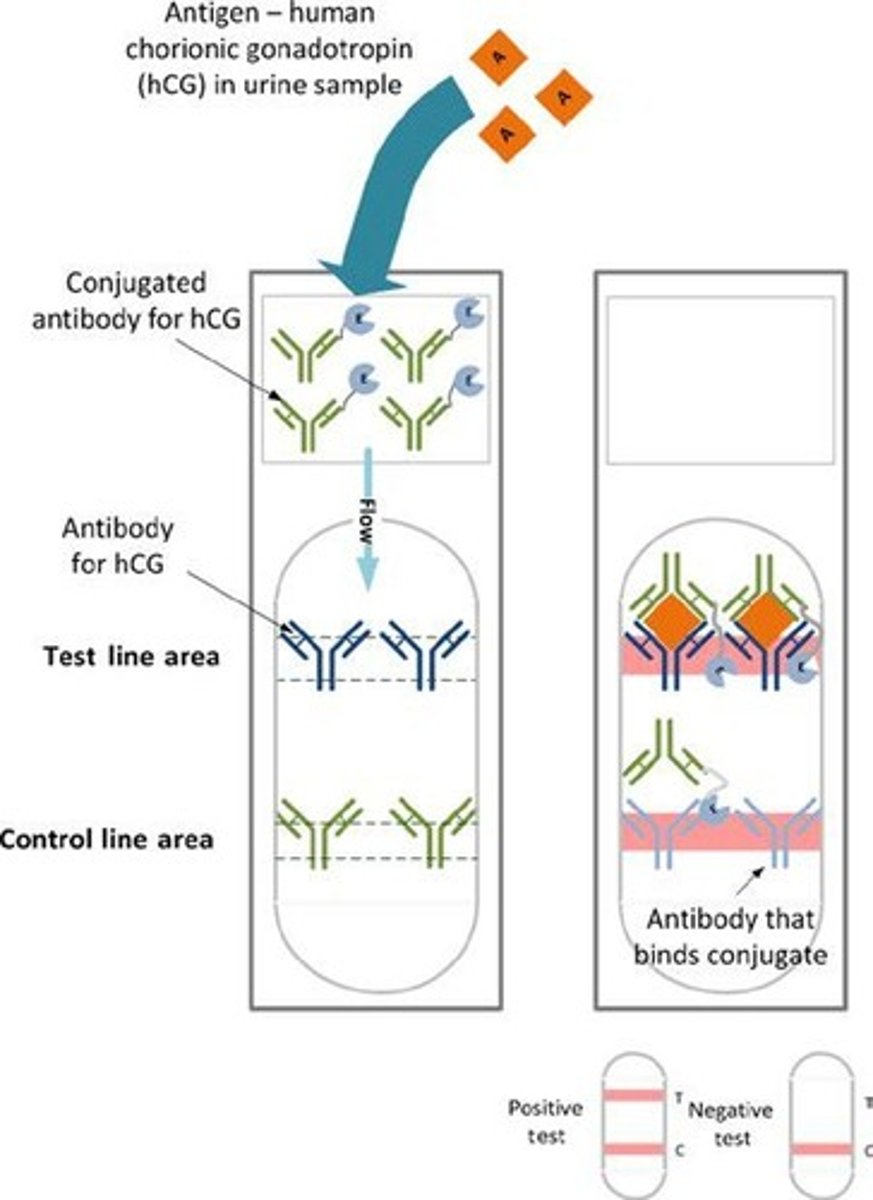
Control Line
The line in a test that indicates the presence of the primary antibody through a secondary antibody binding.
PCR
A method that amplifies the presence of virus DNA, specifically for detecting COVID virus DNA.
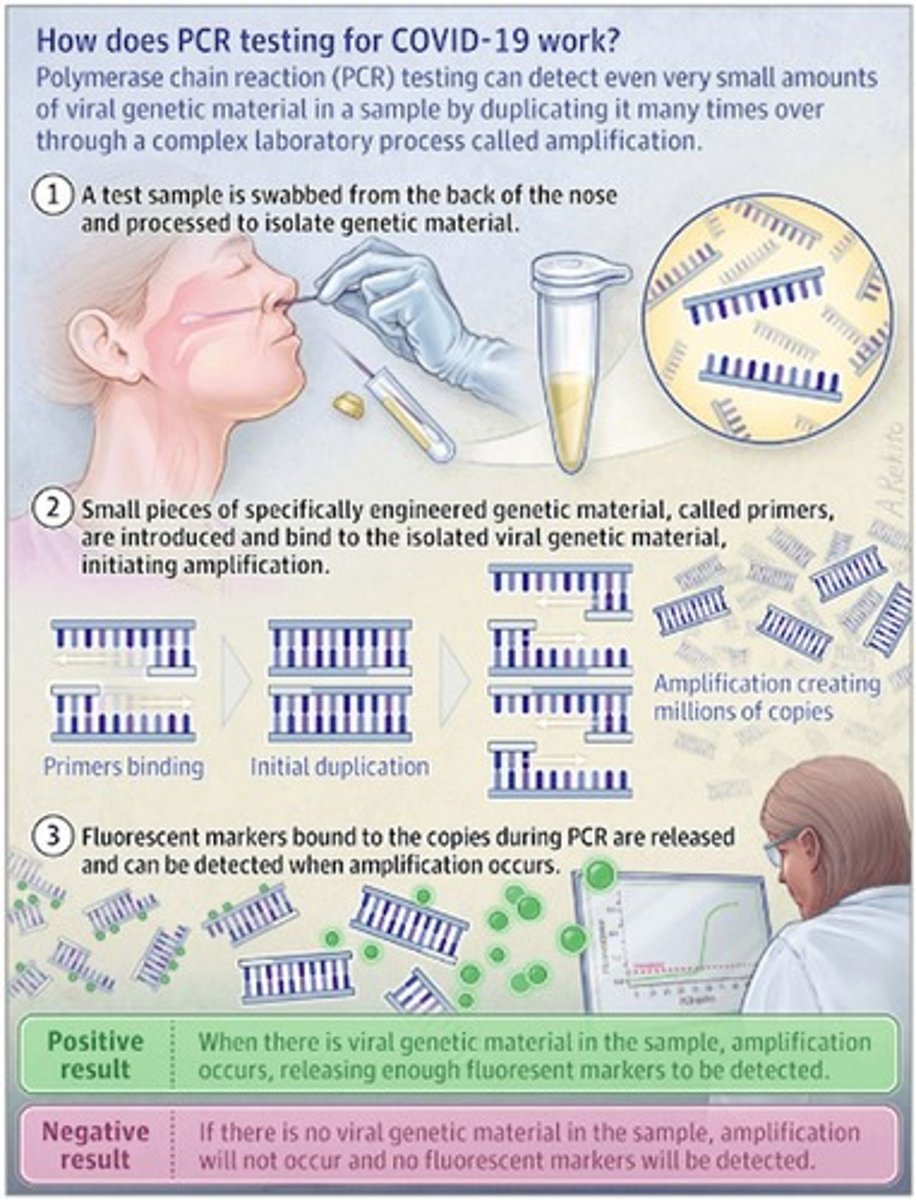
Nasal Swab
A simple method to collect potential COVID virus DNA.
Virus DNA Detection
Testing for the presence of virus DNA instead of just protein markers on the outside of the cell.
Amplification
The process by which PCR creates many copies of the COVID virus DNA if present.
Positive Test Result
A result indicating the presence of numerous copies of a viral DNA (BLUE)
Electrophoresis
A technique used to analyze PCR reactions, such as those for GMO food.
Indirect Detection
A method in ELISA where the presence of an antigen is detected through a secondary antibody.
Enzyme Probe
A component in ELISA that catalyzes a reaction to produce a measurable signal.
Substrate
A substance that reacts with the enzyme probe in ELISA to produce a detectable signal.
Most common regulatory sequences:
355 promoter from cauliflower mosaic virus, nopaline synthase (NOS) terminator
InstaGene Matrix
Composed of negatively charged microscopic beads that chelate or Grab metal ions out of solution. (Mg2+)
What do you need for PCR?
DNA polymerase, 2 DNA primers, 4 dNTPs, and buffer
What were the secondary antibodies in the experiment conjugated to
the enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP) which produces the blue color in presence of its substrate.
What two tests can we use to detect GMOs?
PCR and ELISA
How is DNA from non-GMO plants different from that of GMO plants?
Whole plants = more quantity, less degradation.
GMO = less quantity, more degradation