Concept 12.1: Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells
1/12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
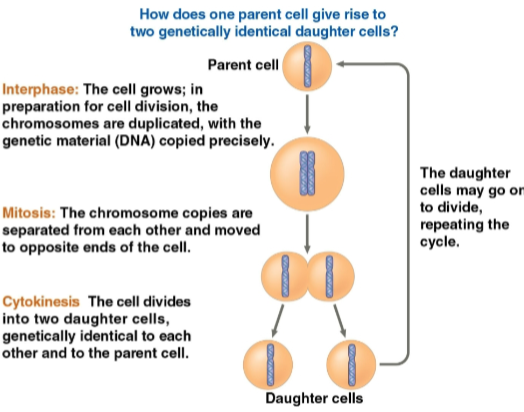
Interphase
Phase of the cell cycle in which the cell grows in preparation for cell division
Chromosomes are duplicated
Genetic material is copied precisely
Mitosis
Phase of the cell cycle where the chromosome copies from interphase are separated from each other and moved to opposite ends of the cell
Cytokinesis
Phrase of the cell cycle where the cell divides into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and the parent cell
Daugher cells may go on to divide after interphase, restarting the cell cycle
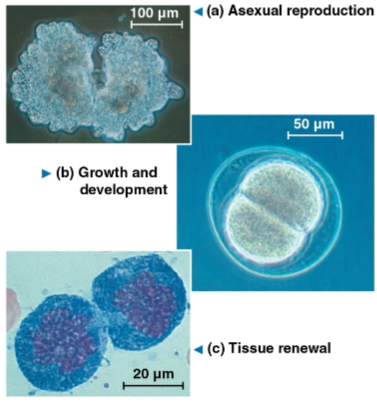
Cell division
The reproduction of cells to ensure the continuity of life
Is the characteristic that distinguishes living things from nonliving matter
Seen in:
Single-celled organisms giving rise to new organisms
Multicellular eukaryotes undergoing embryonic division as well as renewal and repair for the fully grown
Genetic material (DNA)
Instructions for the cell’s function within a eukaryote’s nucelus or prokaryote’s interior
Cell division is remarkably accurate in passing this from one generation to the next
Genome
All the DNA within a cell
Consists of a single DNA molecule (common for prokaryotes) or a number of DNA molecules (common in eukaryotes)
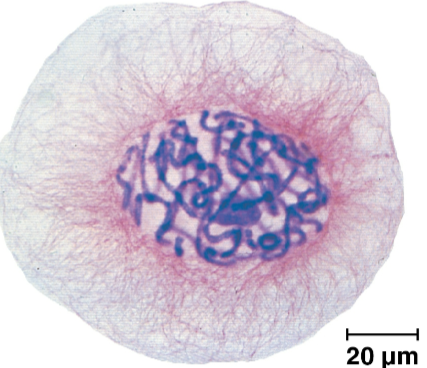
Chromosome
The packaging form for DNA molecules in a eukaryotic cell
Carries several hundred to a few thousand genes
Every eukaryotic species has a characteristic number of these in each cell nucleus
Chromatin
A complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division in eukaryotic chromosomes
Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells)
Cells that have two sets of chromosomes
Gametes (reproductive cells)
Cells that have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells
Produced by a variation of cell division called meiosis
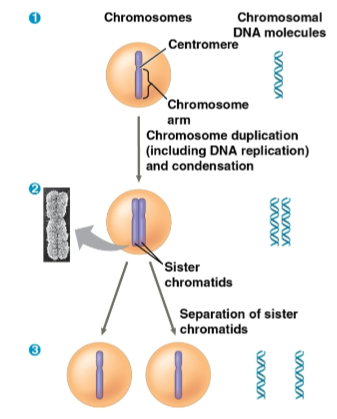
Sister chromatids
Joined copies of the original chromosome created during DNA replication in preparation for cell division
These separate and move into two nuclei during cell division, thus turning into chromosomes
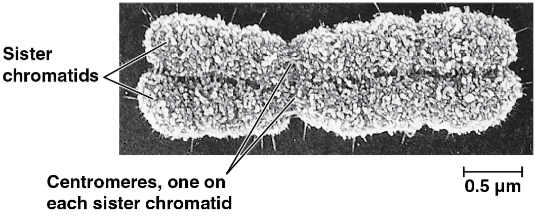
Centromere
The narrow “waist” of the duplicated chromosome where the two chromatids are most closely attached
Meiosis
The variation of cell division that creates gametes
Yields nonidentical daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell