35 Gametogenesis
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Distinguish among somatic cells, germline cells, and gametes in terms of function and whether the cells are diploid or haploid.
Germ cell: diploid cells that are specified early in development, give rise to gametes by meiosis
somatic cells: diploid cells support sexual reproduction
gametes: haploid cells that propagate genetic information to progeny
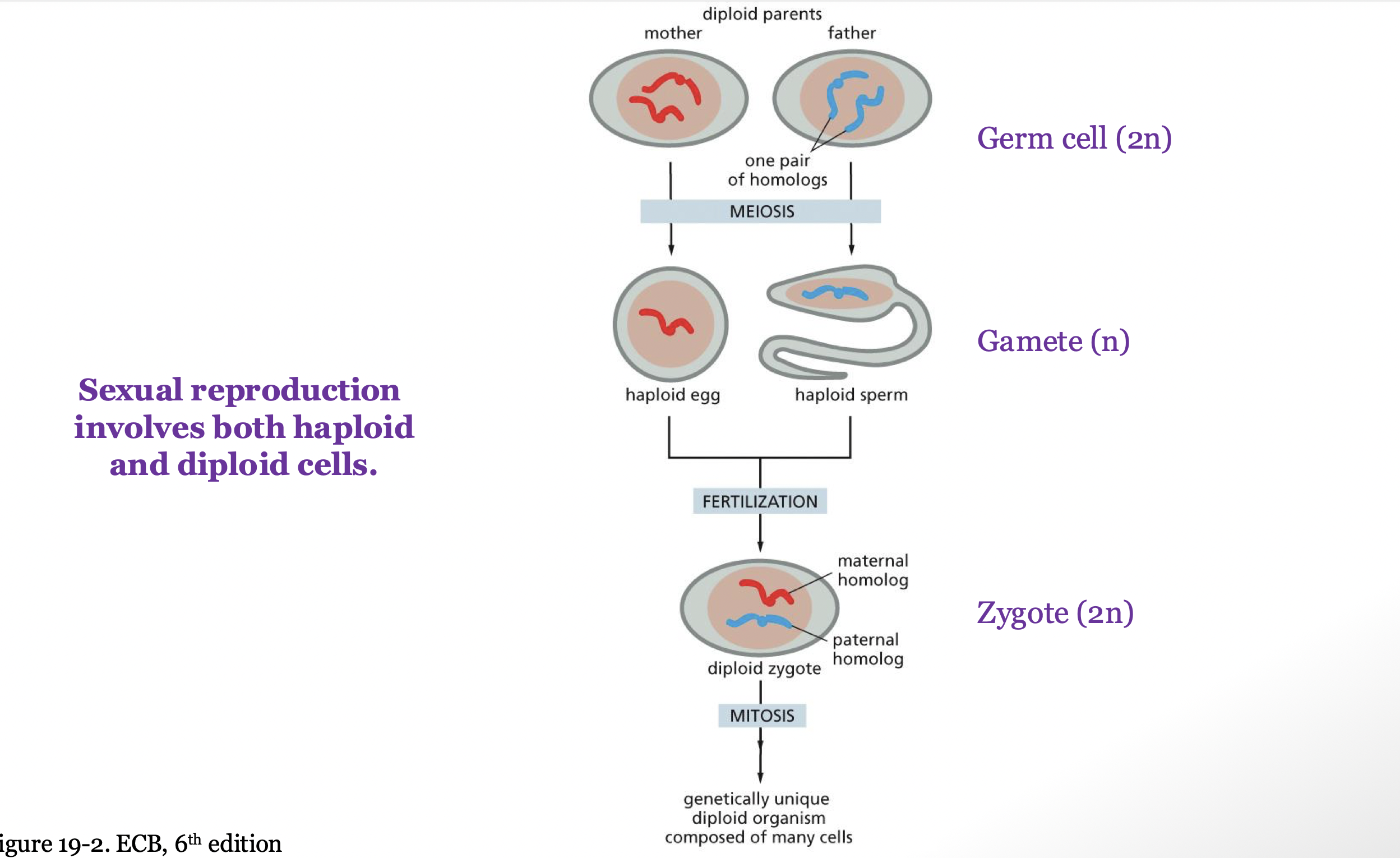
Outline how rounds of DNA replication and division produce a haploid nucleus from the nucleus of a diploid germline cell.
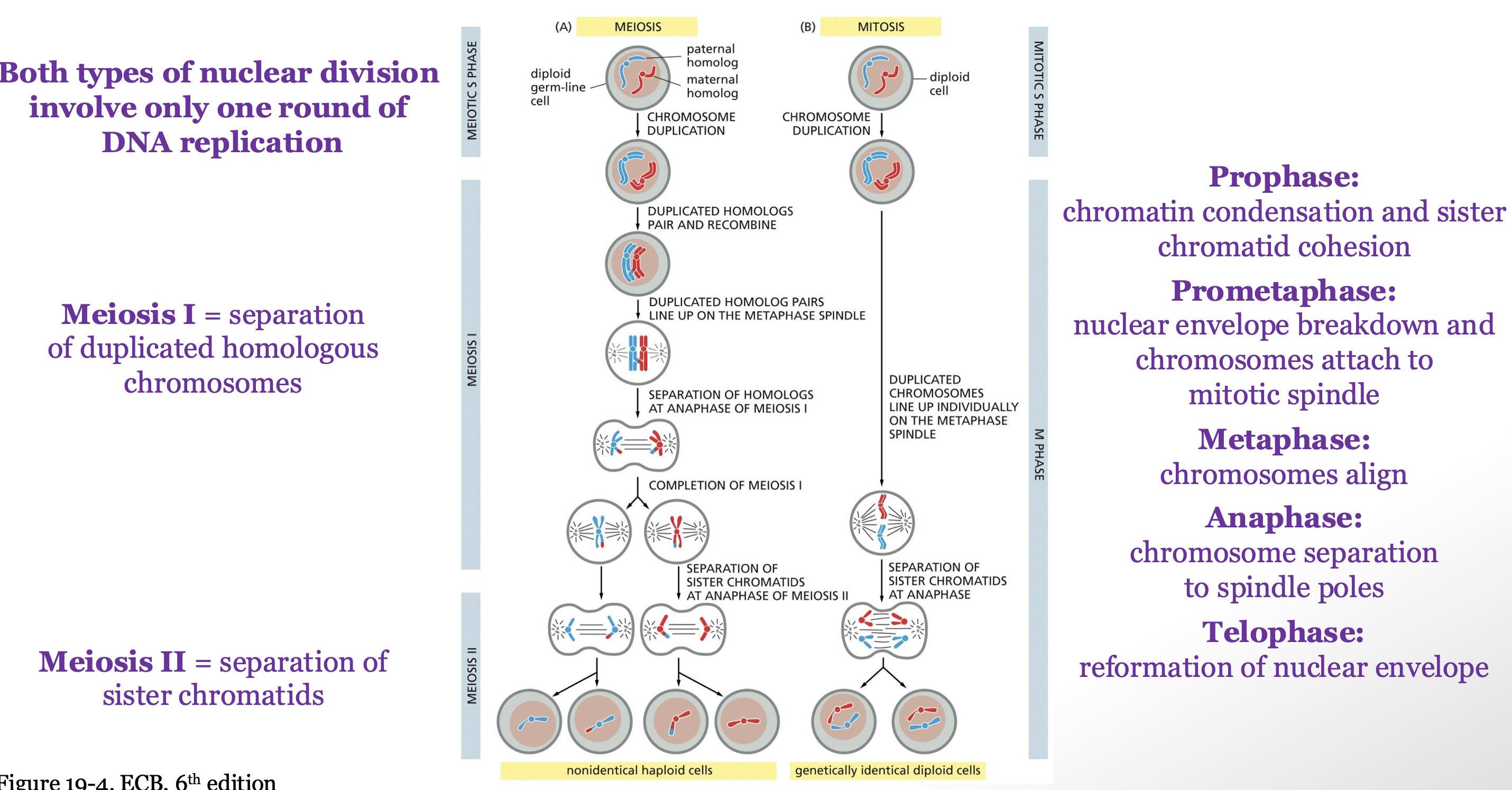
only one round of DNA replication and 2 rounds of division
meiosis I: separation of duplicated homologous chromosomes
meiosis II: separation of sister chromatids
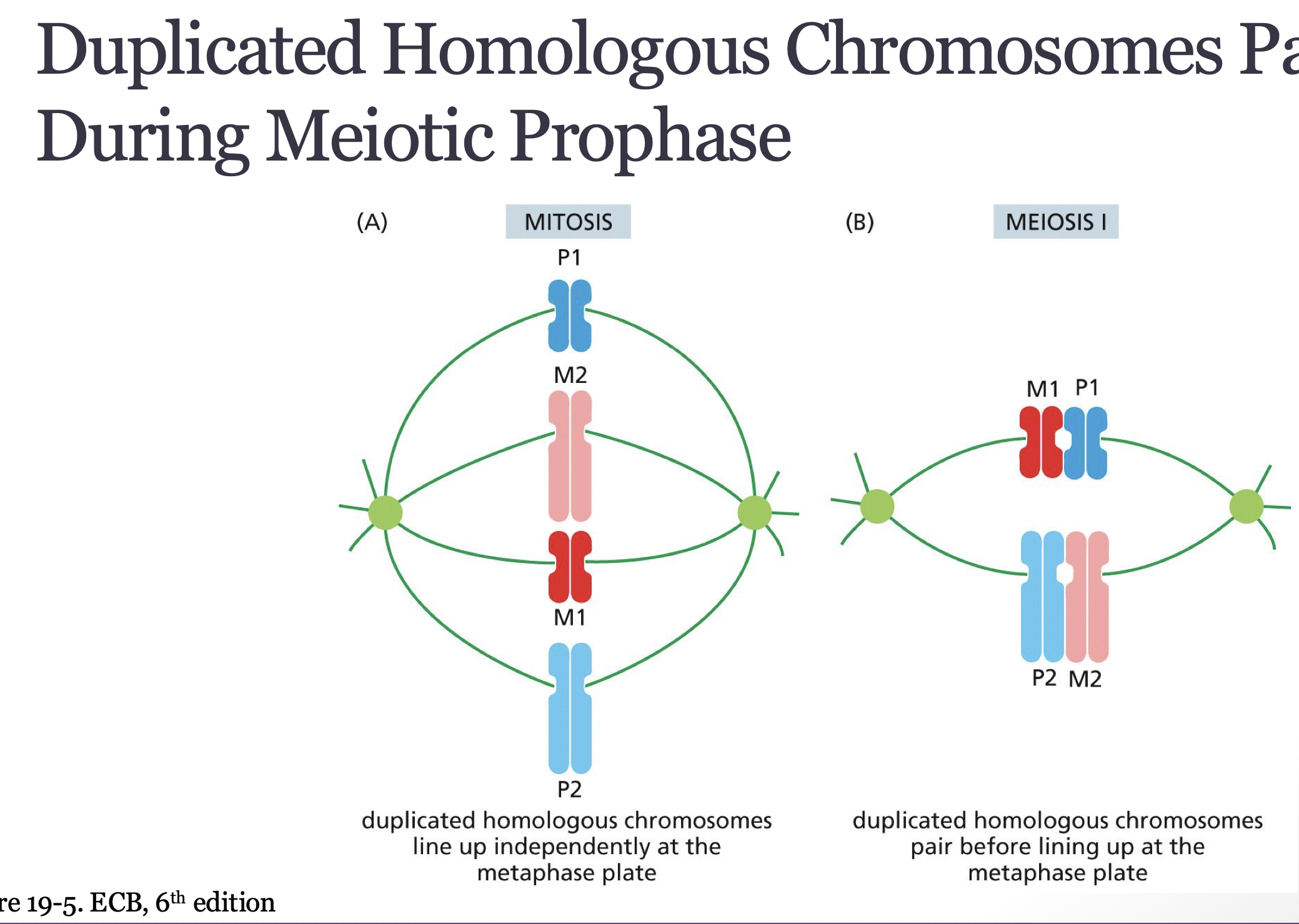
duplicated homologous chromosomes form what structure
bivalent/tetrad
duplicated homologs pair during meiotic prophase
why is homologous pairing and cross over important during prophase of meiosis
it ensures genetic diversity and separation after first meiotic division so each haploid cell has a single sister chromatid / proper segregation of duplicated homologs
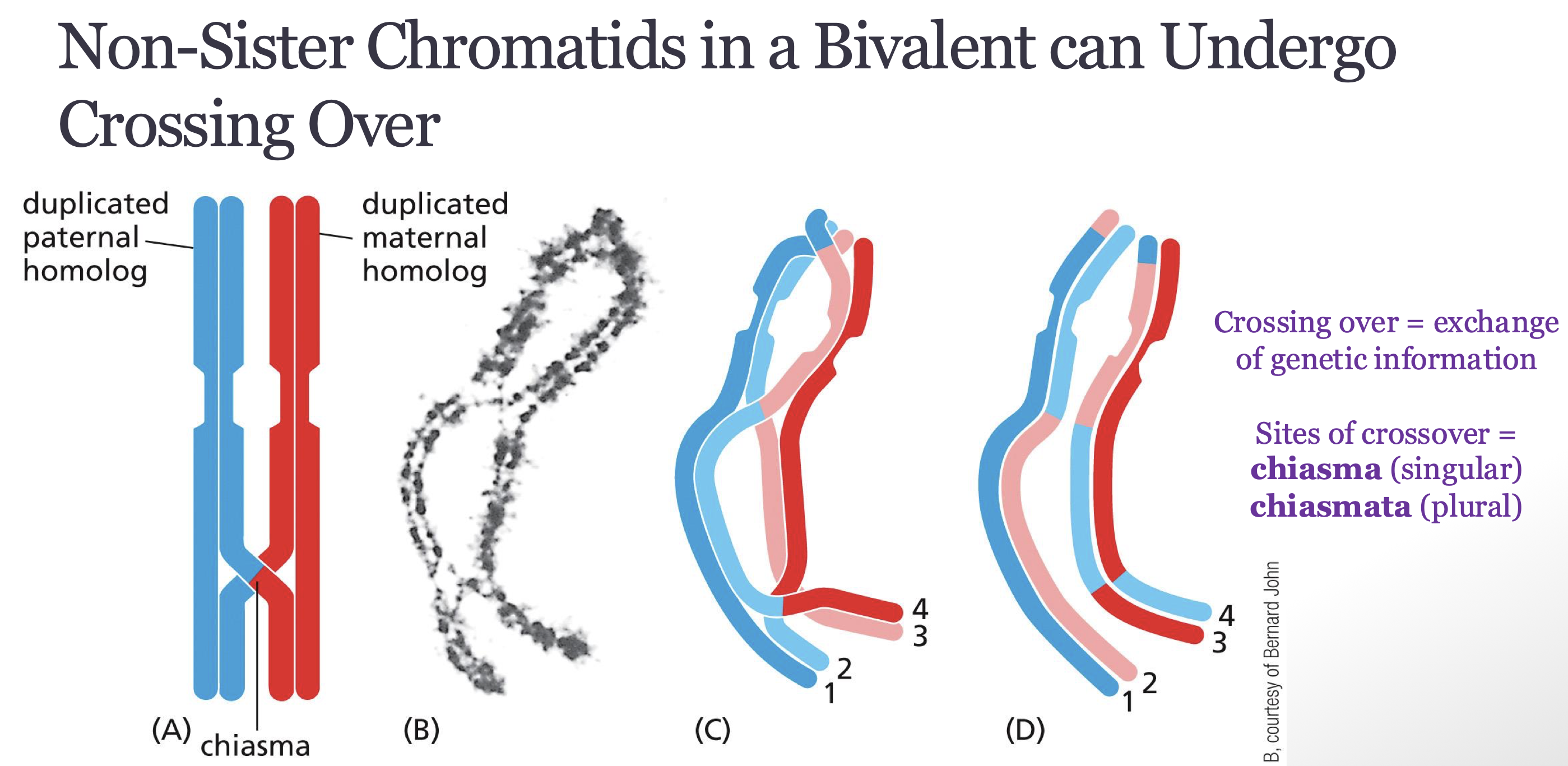
Differentiate how cohesins are degraded during anaphase in meiosis I from their degradation during anaphase in meiosis II.
Meiosis I: cohesins holding the arms of the non-sister chromatids together are suddenly degraded, cohesins at the centromere continue to hold the sister chromatids together
Meiosis II: cohesins holding the sister chromatids together at the centromere are degraded
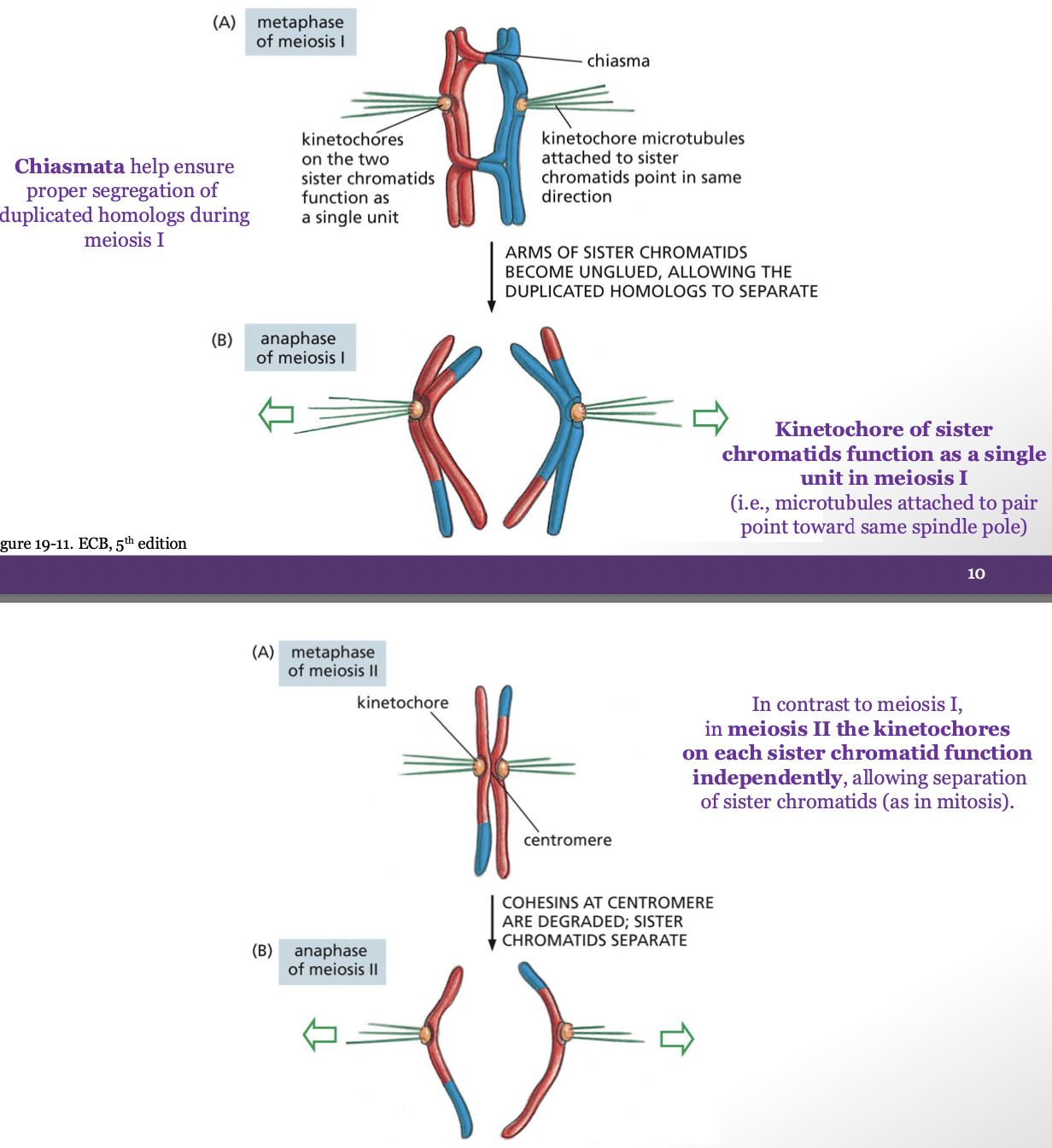
how is the kinetochore different in meiosis I than in meiosis II
kinetochore of sister chromatids function as a single unit in meiosis I and function independently in meiosis II to allow separation of sister chromatids
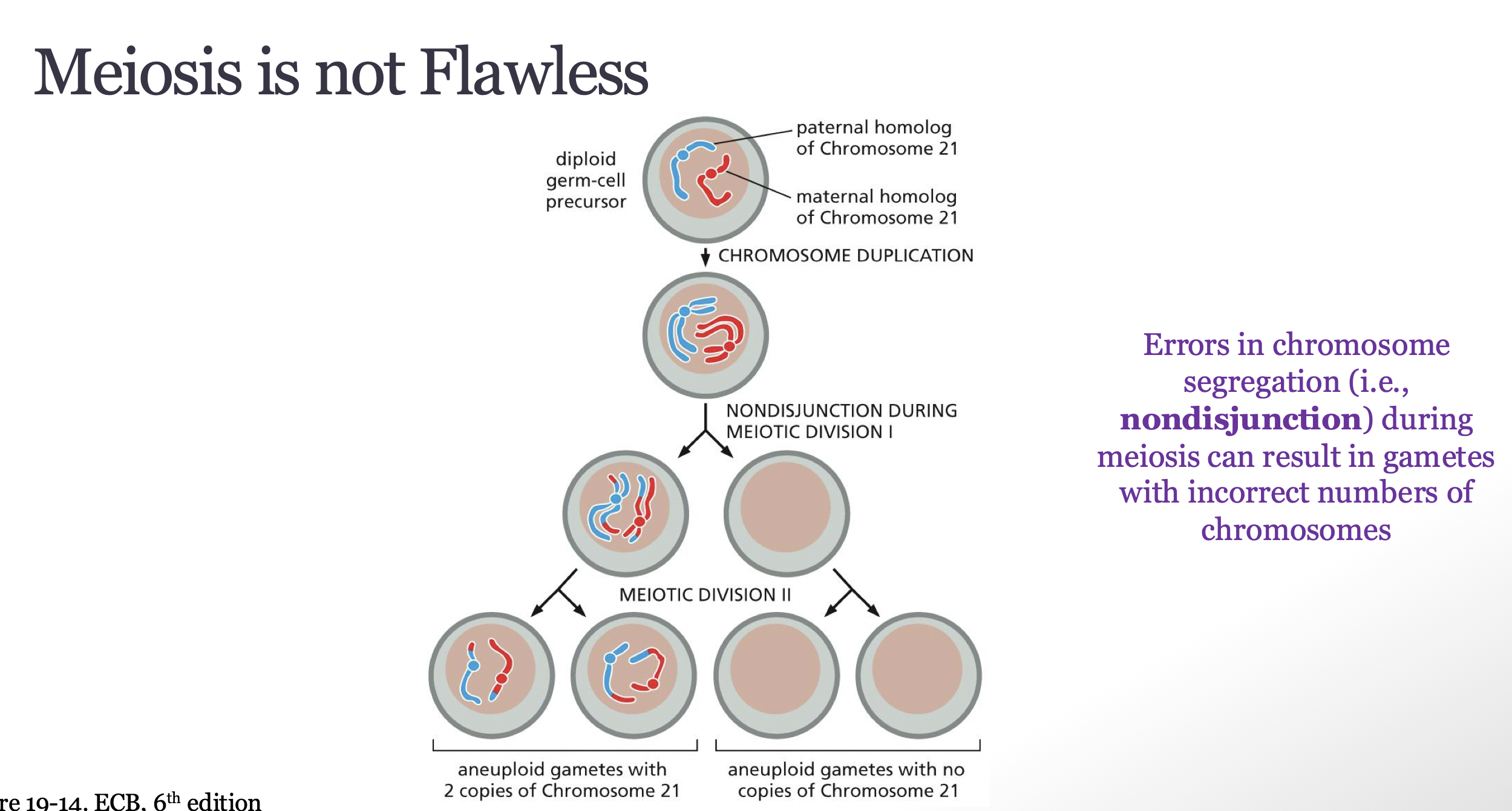
Explain how nondisjunction gives rise to aneuploid gametes, and recall the consequences of this type of genetic error.
nondisjunction occurs due to errors in chromosome segregation which can give rise to disease
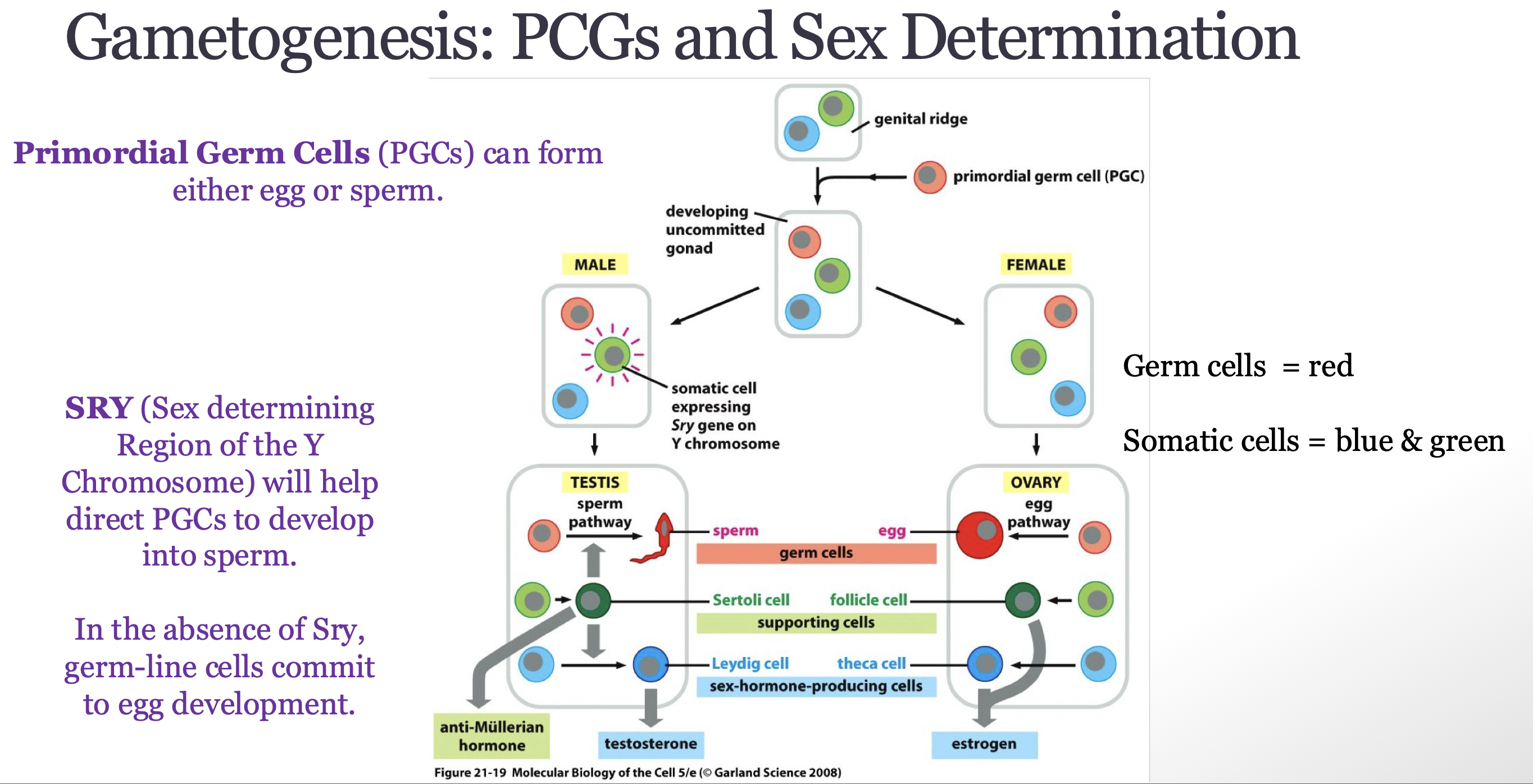
Understand how PGCs give rise to male and female gametes
PCG can form wither egg or sperm
migrate to genital ridge, once they go to developing gonad they undergo mitotic division and eventually choose a path
default path is to become ovary and develop female gametes
some cells in genetical ridge express genes so males can develop male via the Y chromosome
somatic cells express Sry gene on Y chromosome to develop Sertoli cells
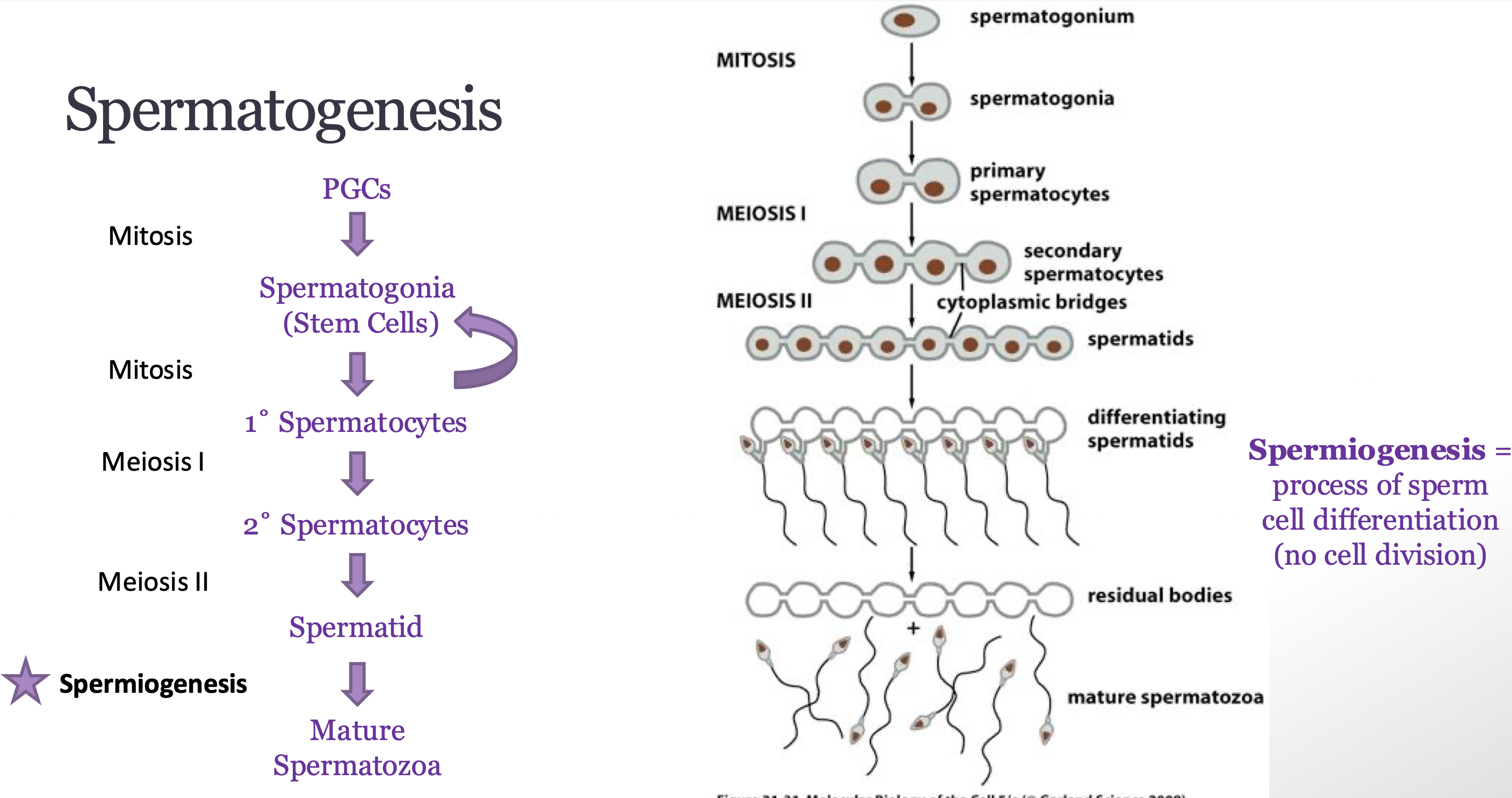
describe spermatogenesis
how many haploid sperm are formed
what is differentiation of sperm called
when does spermatogenesis begin
spermatogenesis:
A spermatocyte undergoing meiosis results in the formation of 4 haploid sperm
Cellular differentiation of a sperm cells is called spermiogenesis
Spermatogenesis begins at puberty and continues through most of the male's life
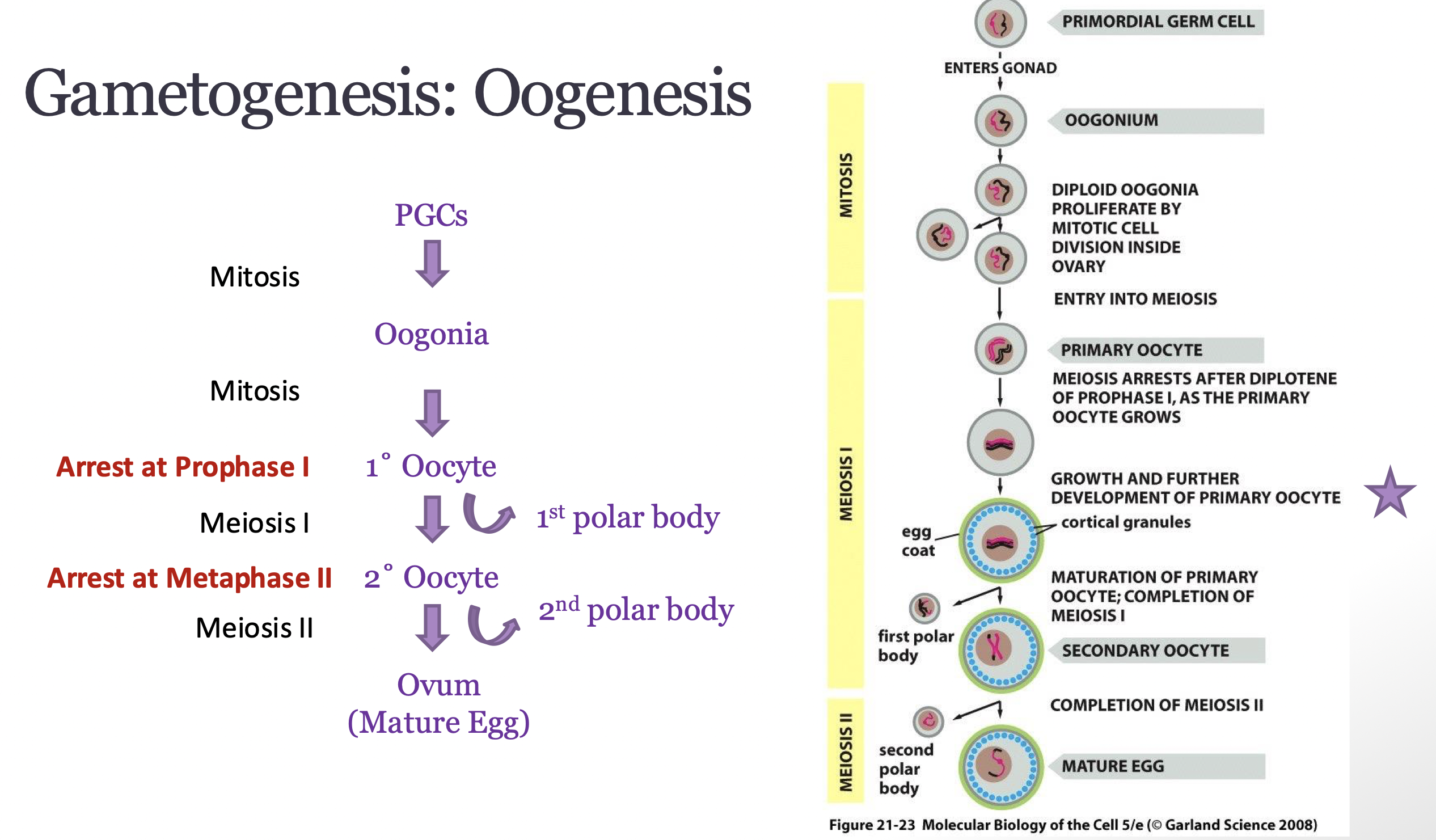
describe oogenesis
describe the 1st arrest
describe the second arrest
how many nuclei form from primary oocyte
when do oocytes undergo differentiation
when does oogenesis begin
oogenesis
Primary oocytes arrest at Prophase I until ovulation
secondary oocyte arrest in metaphase II after ovulation and remains arrested until fertilization
only 1 nuclei will from primary oocyte and will produce functional egg/ovum
Oocytes undergo cellular differentiation prior to the completion of meiosis
Oogenesis begins before a female fetus is born
describe oogenesis arrest in prophase I compared to ovulation in terms of cAMP levels, Wee 1, CDC 45, and M-CDK
prophase I
cAMP high → active PKA
inhibit CDC 25 and activate Wee 1 to inactivate MCDK complex
ovulation
low cAMP → inactive PKA
active CDC 25
active MCDK
Describe where and how sperm and egg unite during fertilization
zona pellucida induces sperm to undergo acrosome reaction to allow penetration and fusion with egg
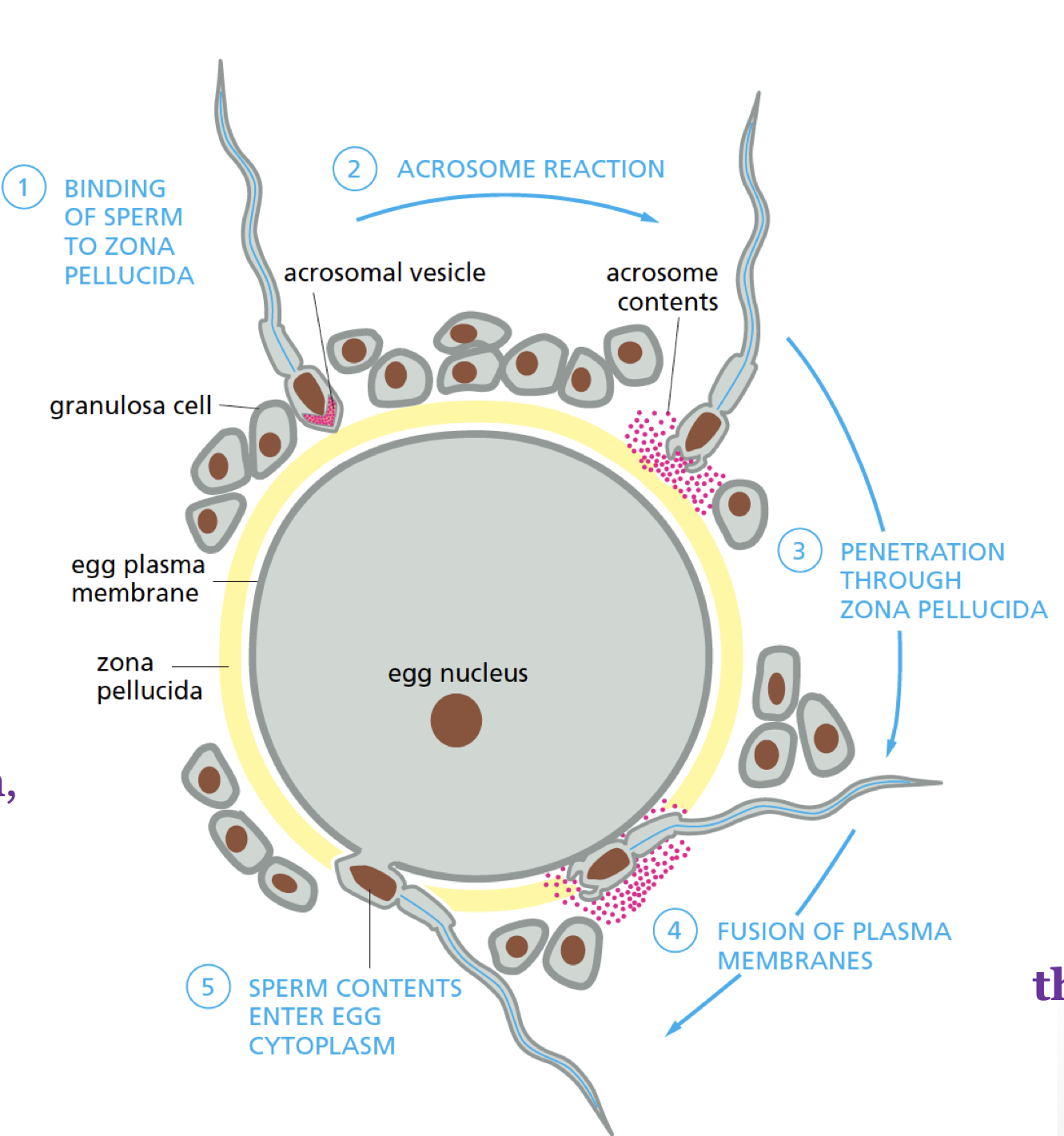
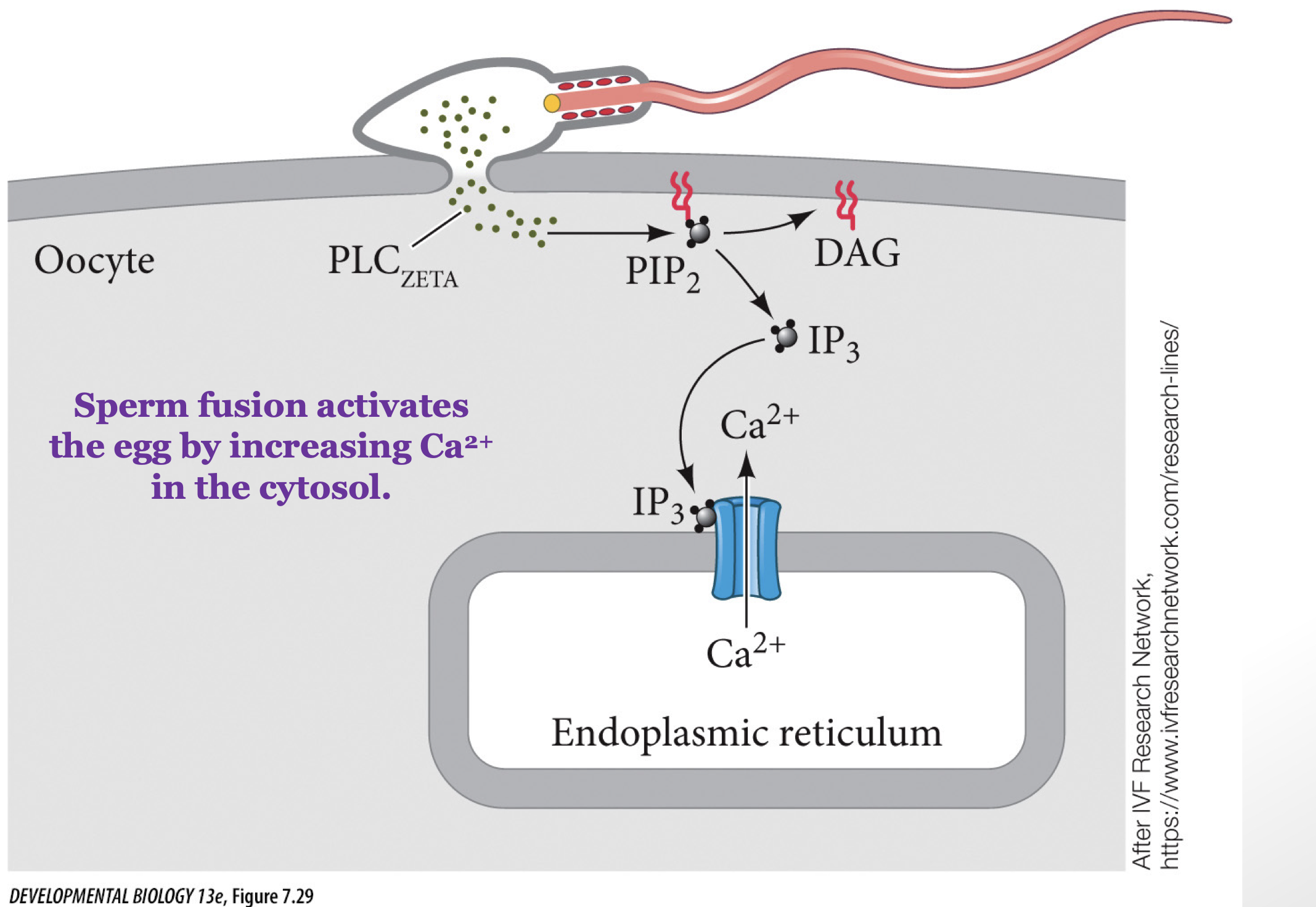
outline the mechanisms that prevent multiple sperm from entering the egg.
sperm fusion activate egg by increasing Ca2+ in cytosol, causing enzymes to be exocytosed changing the conformation of zona pellucid so no other sperm can enter
spermiogenesis
process of cell differentiation
no cell division
spermatid to mature spermatozoa
When are primary oocytes arrested
Diplotene at prophase I
which cells direct sexual differentiation along a male pathway
Sertoli cells
what helps direct PGCs to develop into sperm
the SRY gene of the Y chromosome on a somatic cell that eventually develops into a Sertoli cell
where does fertilization occur
ampulla region of the oviduct