The periodic table: Elements compounds and mixtures: Chemistry: (9:1)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
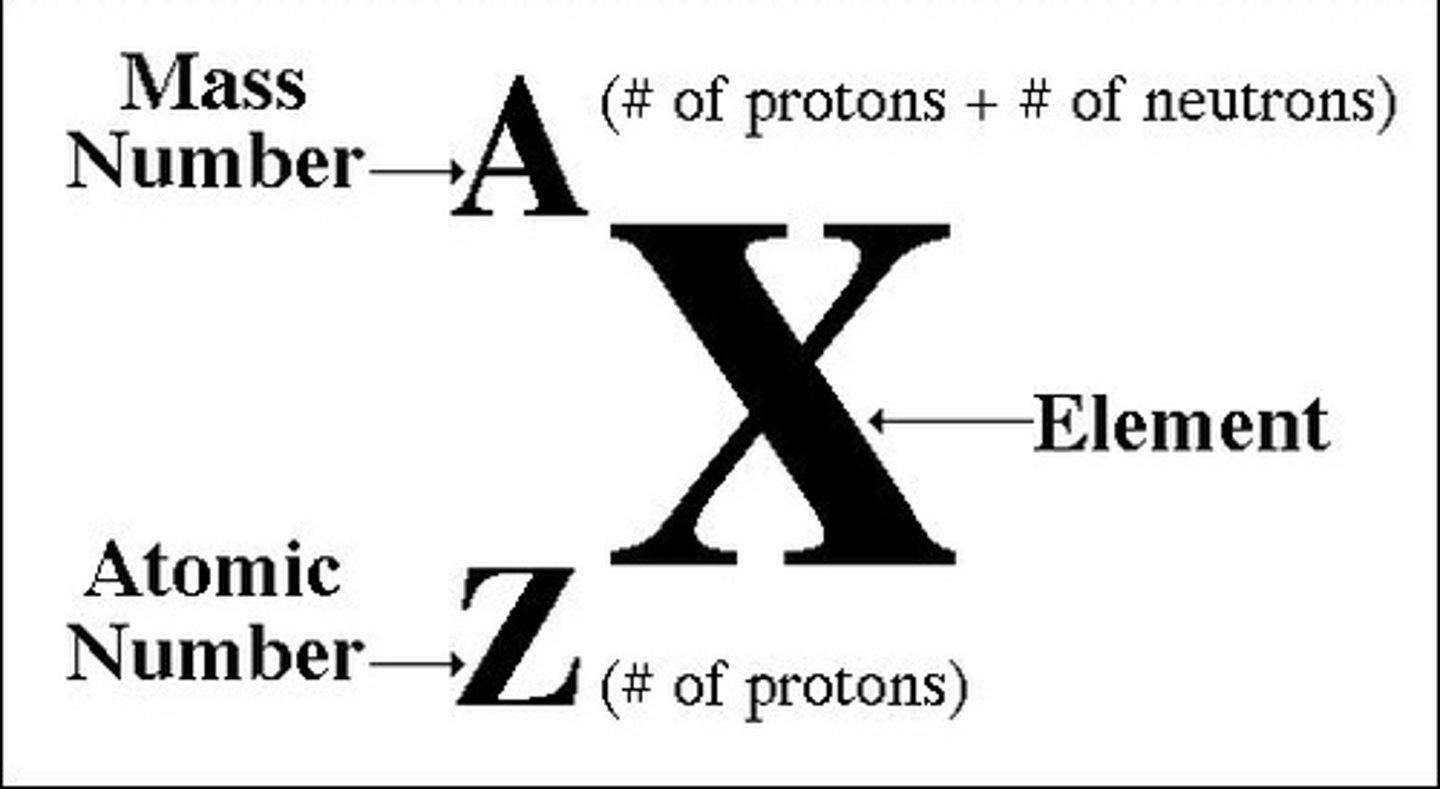
Atomic mass
The average mass of all the isotopes of an element
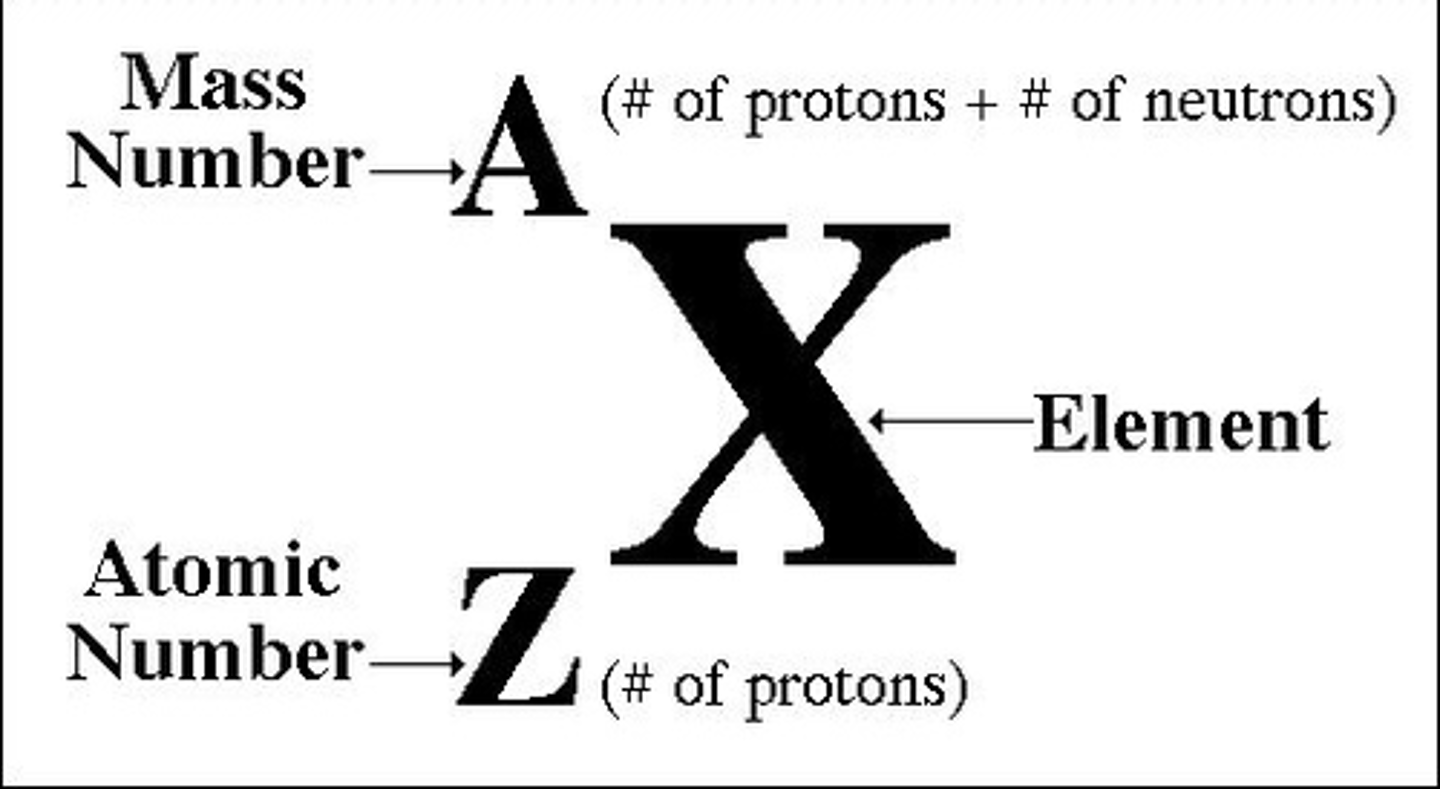
Mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
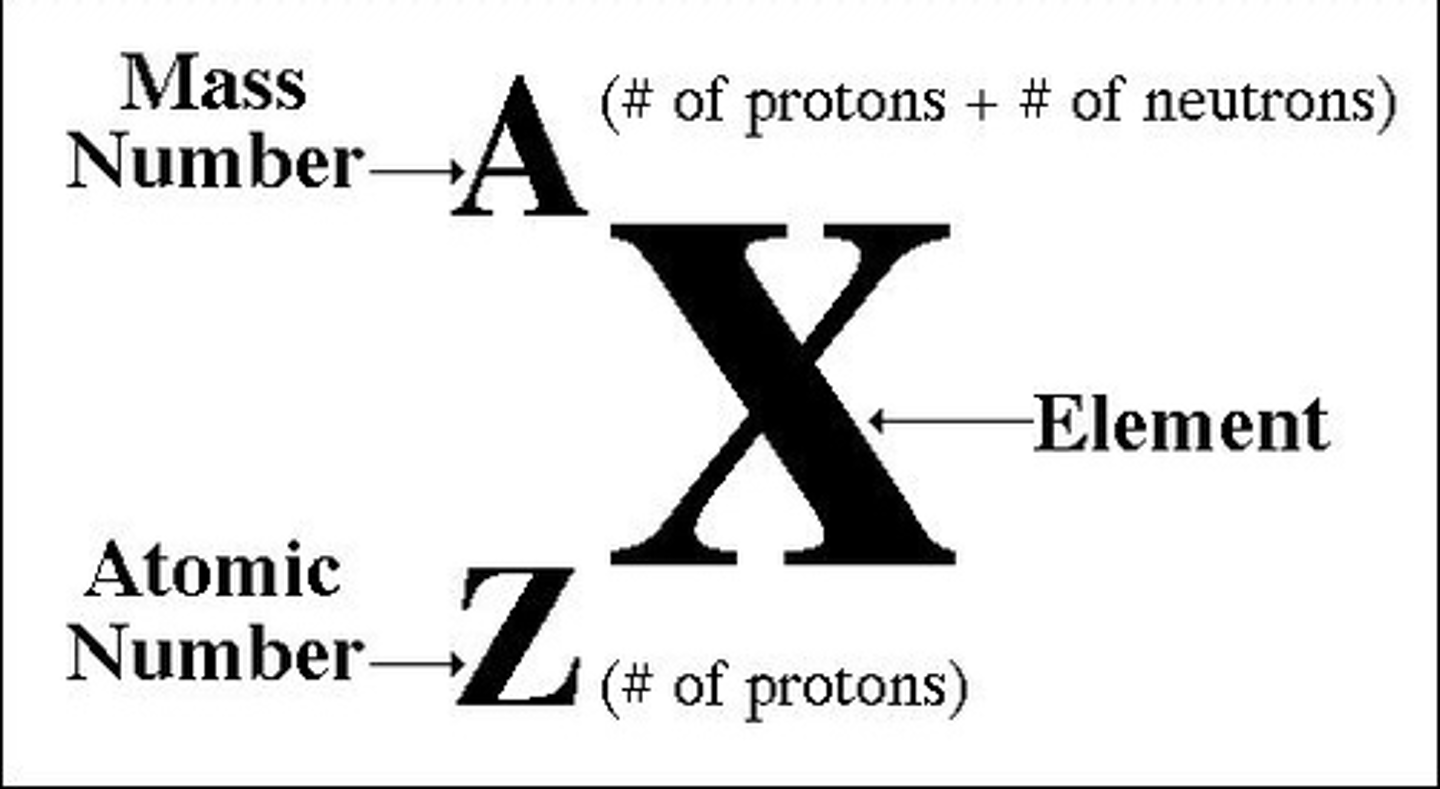
Order of elements on historic periodic table
Elements were ordered by atomic weight
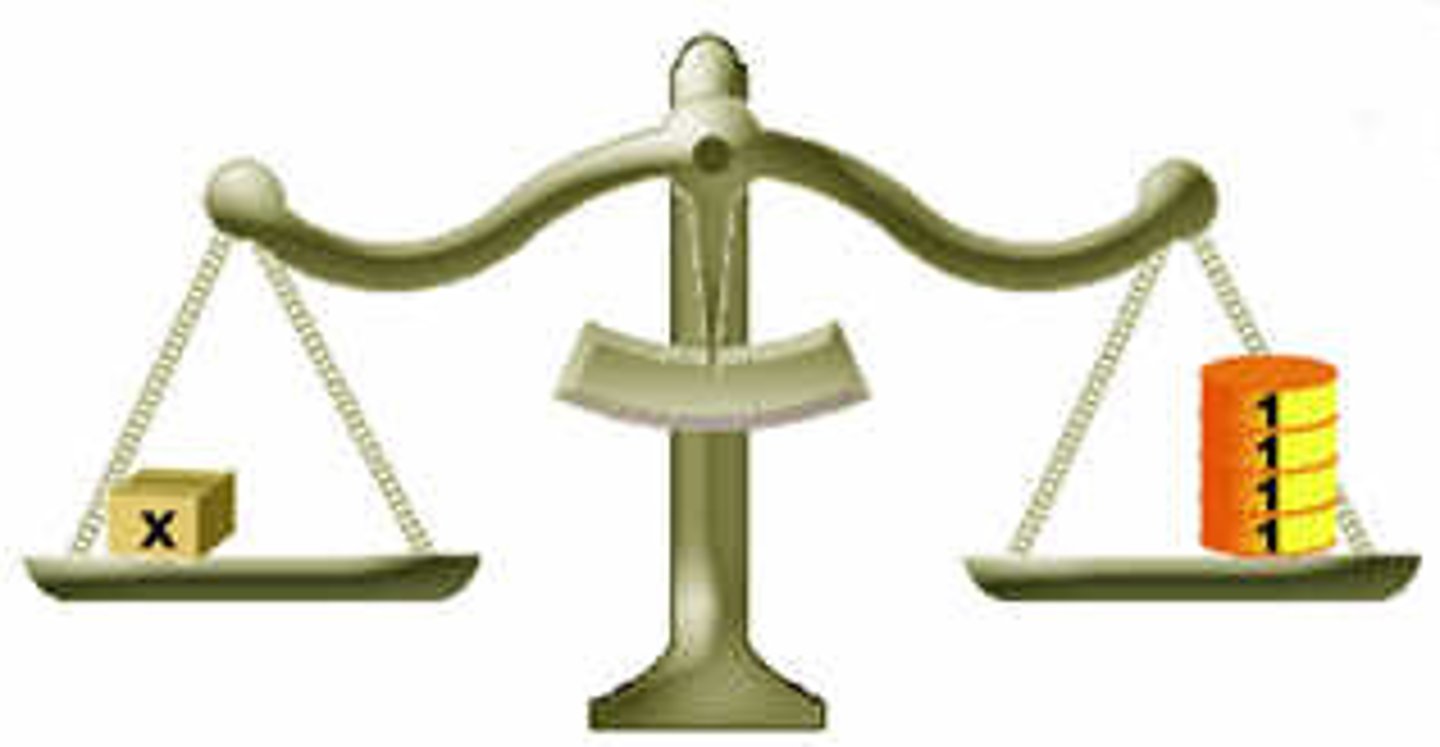

Order of elements on modern periodic table
Elements are ordered by atomic number
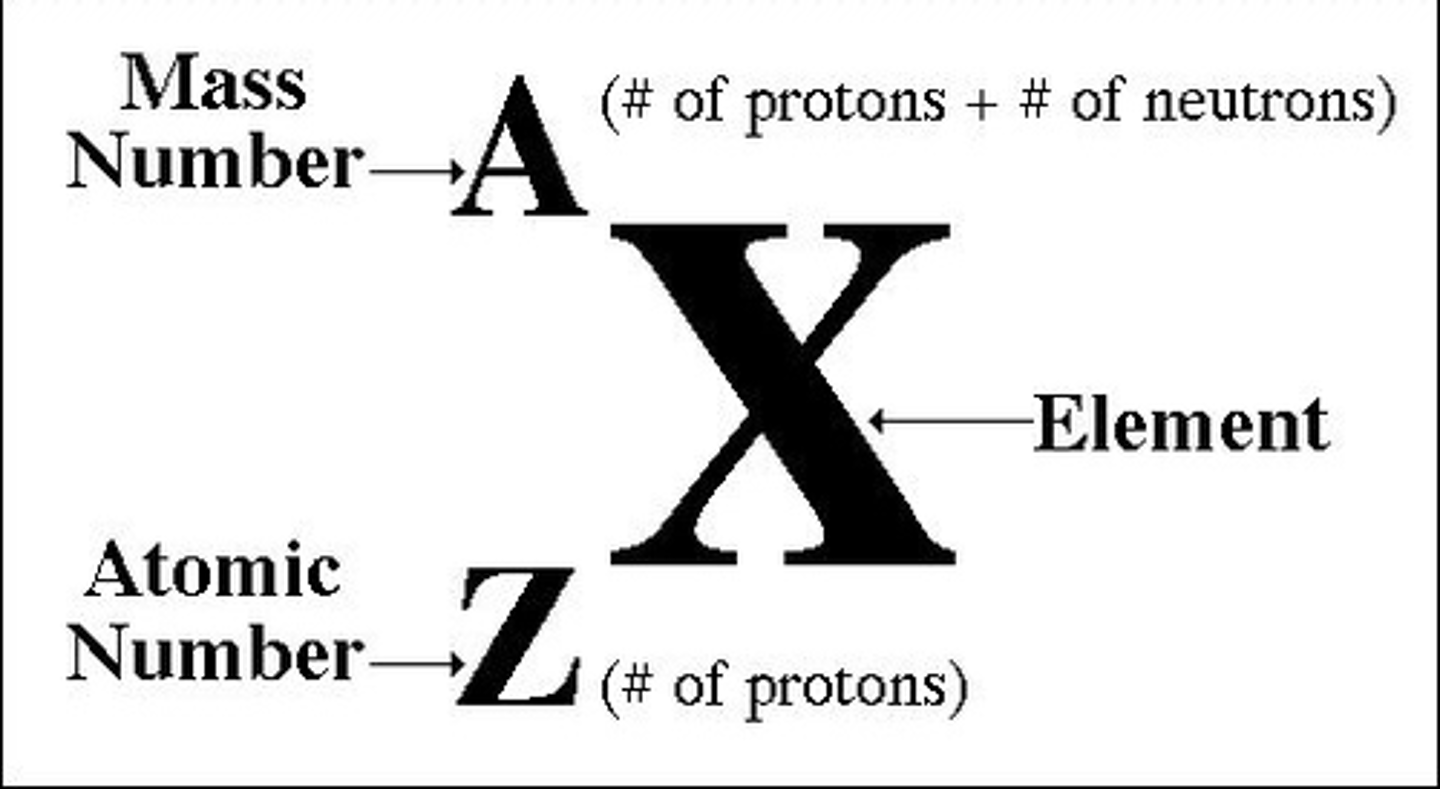
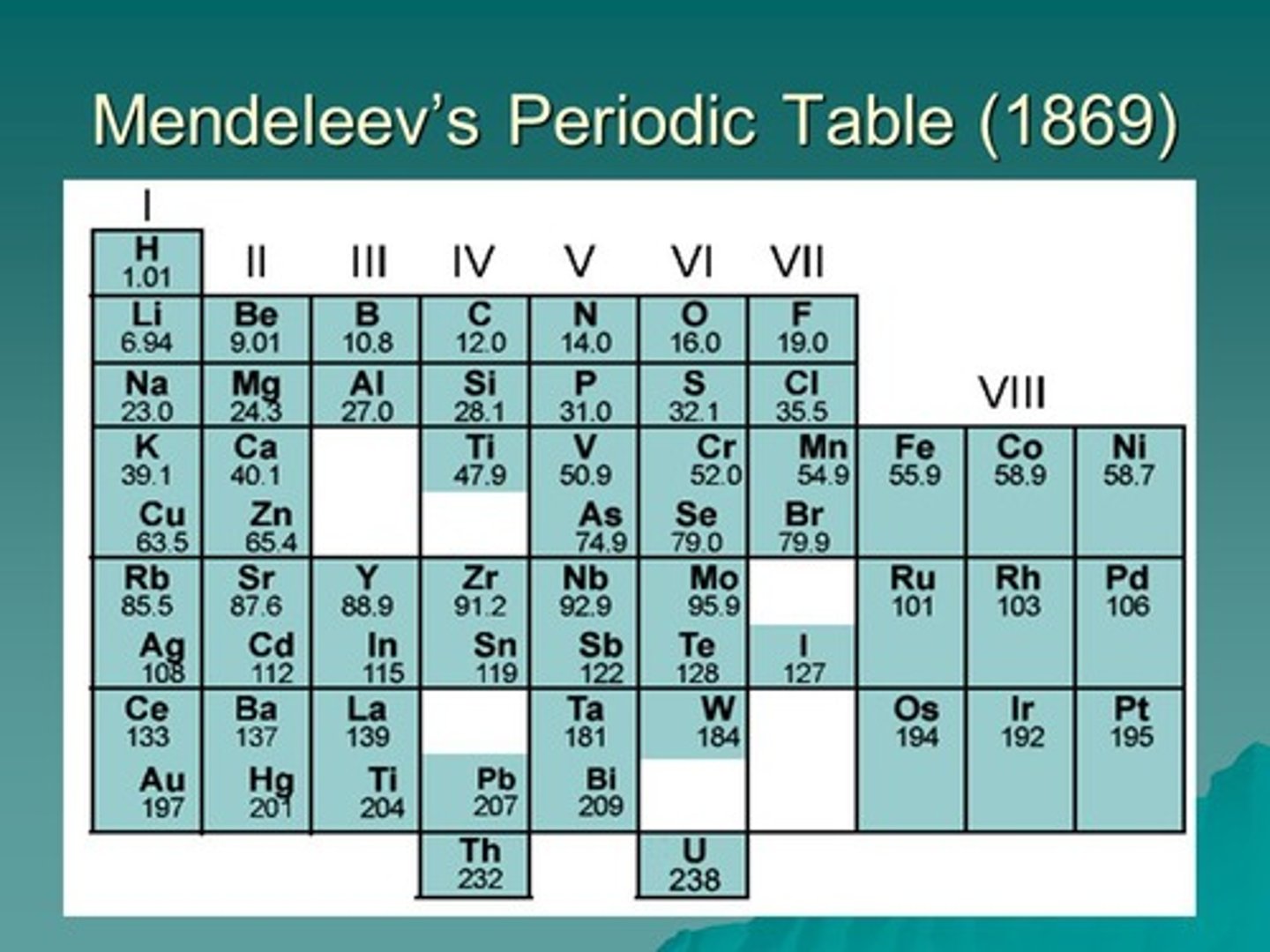
Dmitri Mendeleev's ideas
Ordered elements by atomic weight BUT changed the order/left gaps to keep elements with similar properties in the same collumn

Advantages of Mendeleev's ideas
He was able to predict the properties of elements in the gaps.
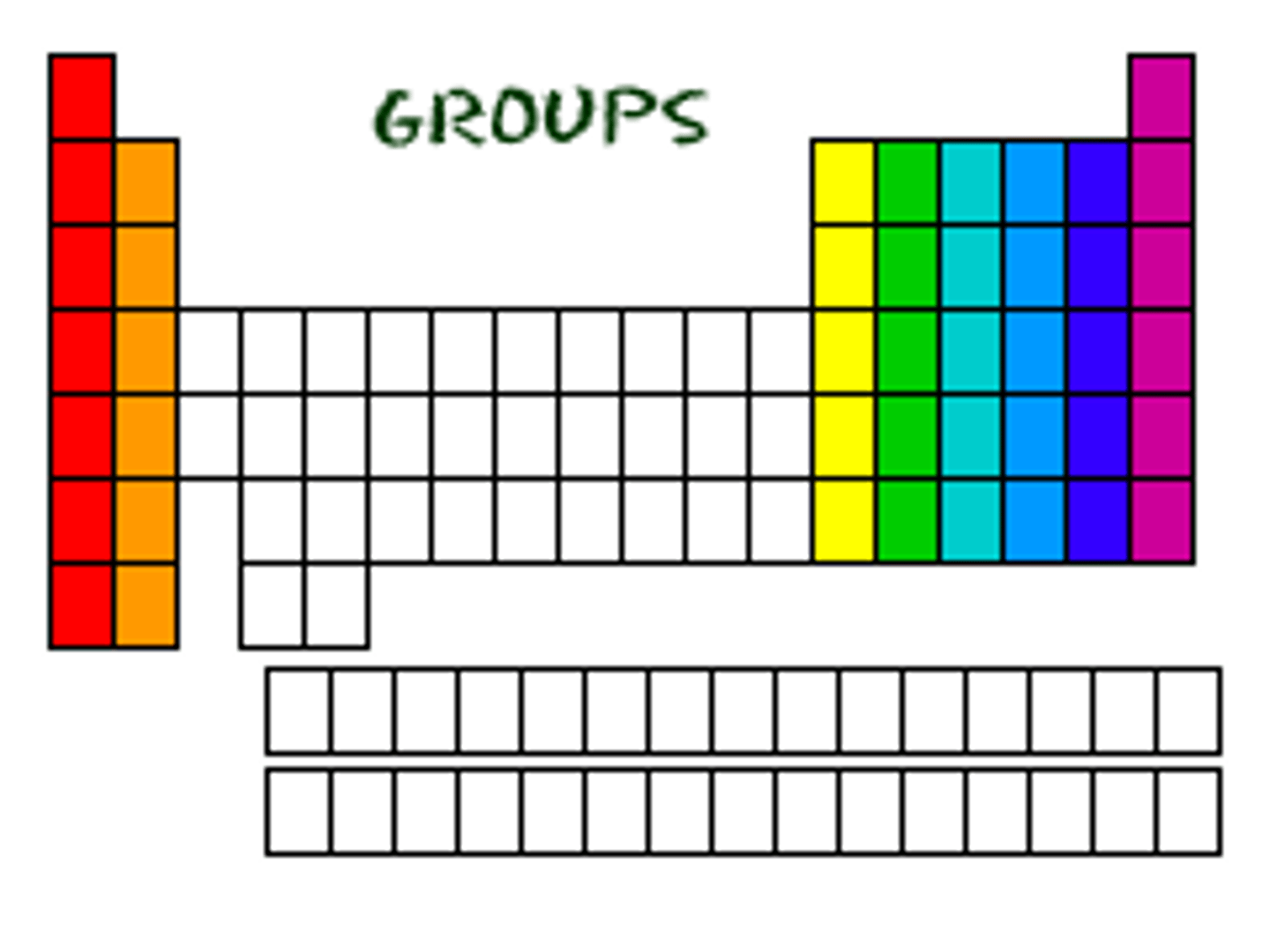
Group
A vertical column of elements with the same number of outer shell electrons
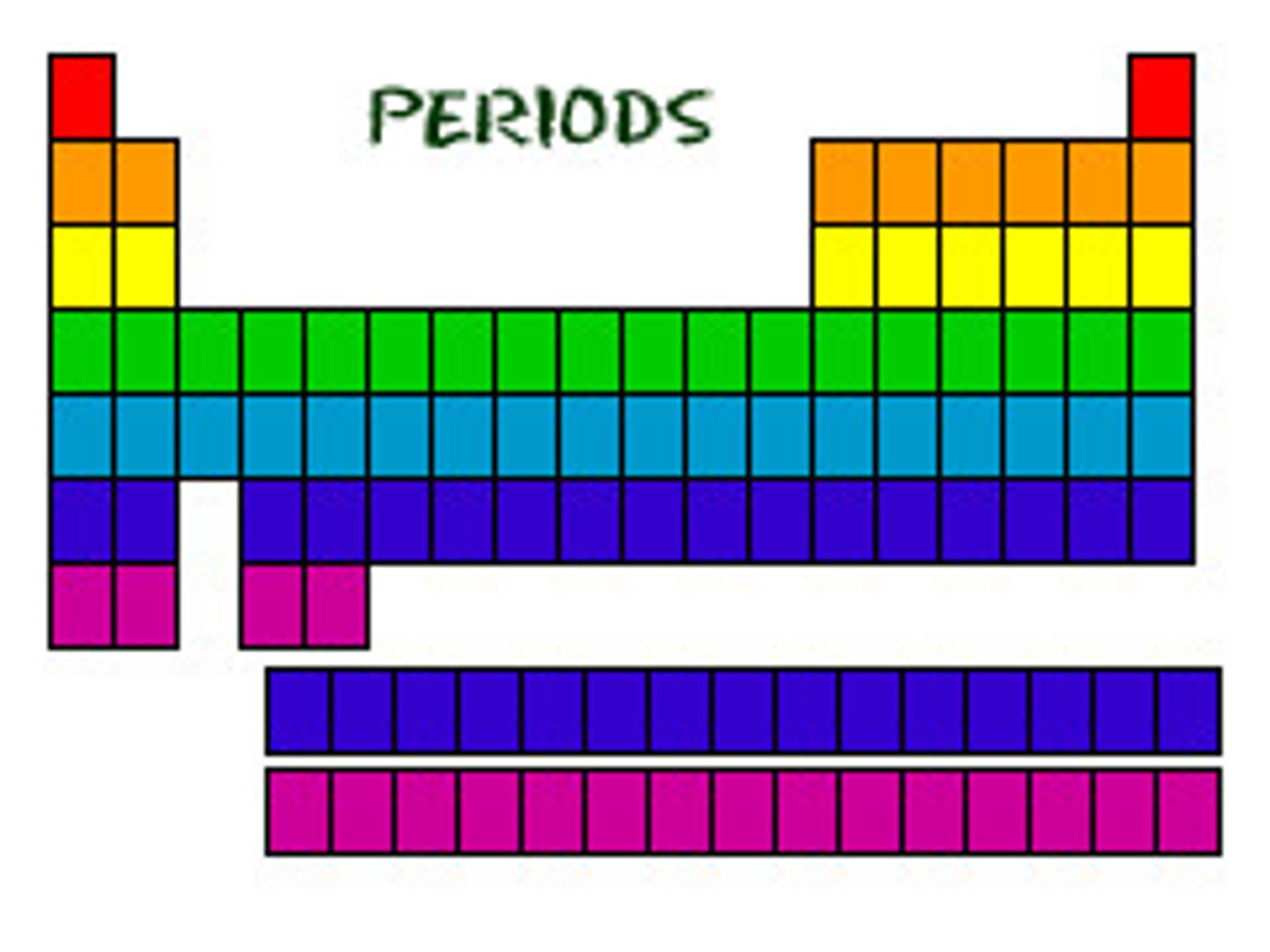
Period
A horizontal row of elements with the same number of electron shells
Physical properties
observed or measured characteristics of a substance. (e.g. colour, density)

Chemical properties
How a substance reacts with other substances.
Example of Mendeleev pair reversal
Tellurium is heavier than Iodine, but Iodine fits best into the halogens
IUPAC Groups
Give numbers to the transition block, so old group 3 is now group 13 and so on