Types of Variables and Data in Political Science Research
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Binary Variables
Variables with two possible values, 0 or 1.
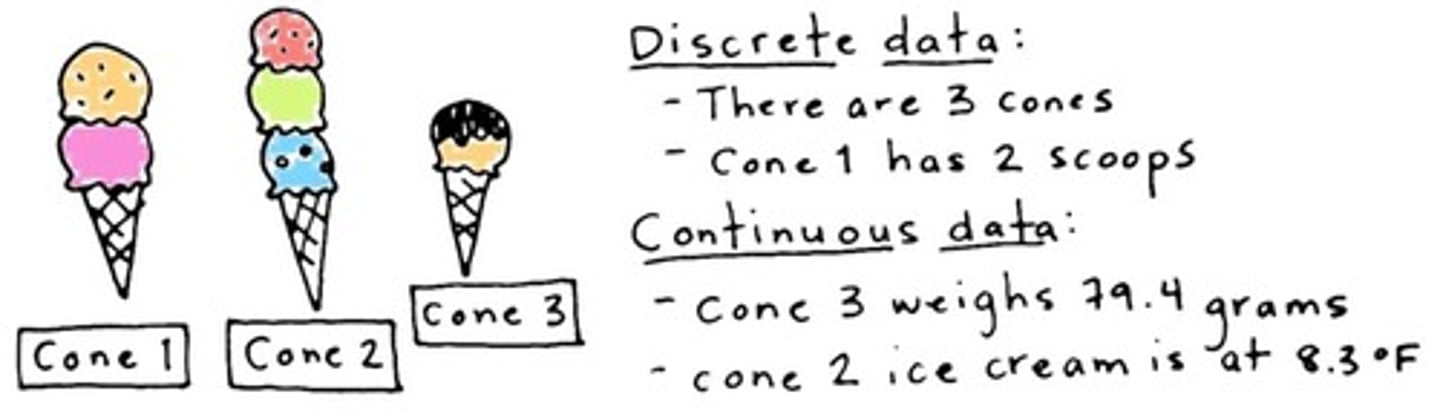
Discrete Variables
Data in distinct categories or groups.
Continuous Variables
Data that can take any value in a range.
Ordinal Variables
Categorical data with a meaningful order.
Nominal Variables
Categorical data without a specific order.
Logged Variables
Transformed variables using logarithmic scale.
Cross-Sectional Data
Data collected at one point in time.
Panel Data
Repeated observations of the same units over time.
Repeated Cross-Sectional Data
Different samples from the same population over time.
Average Treatment Effects
Difference in means between treated and control groups.
Factors in R
Categorical variables treated as factors in analysis.
Fixed Effects Models
Control for unit-specific and time-specific effects.

Causal Relationships
Identifying cause-effect links through repeated measures.
Transforming Data
Changing data types for analysis, e.g., categorical to binary.
Polity Score
Example of discrete data on political systems.
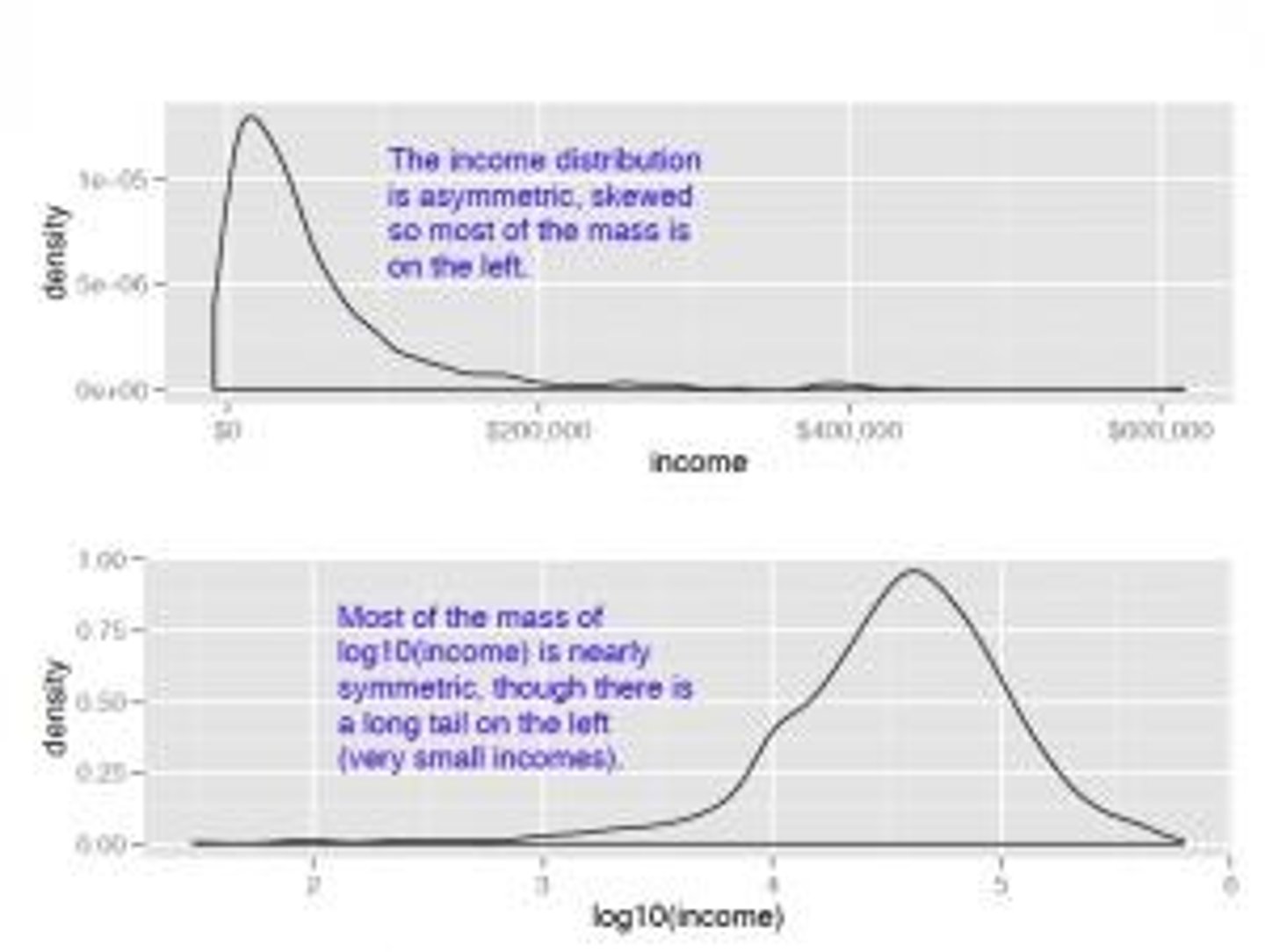
Income Data
Often skewed, may require logarithmic transformation.
Qualitative Research
Research methods focusing on non-numeric data.
Case Studies
In-depth analysis of specific instances or events.
Process Tracing
Method to examine causal mechanisms in qualitative research.

Dummy Variables
Binary variables used in regression analysis.
Regression Analysis
Statistical method for estimating relationships among variables.
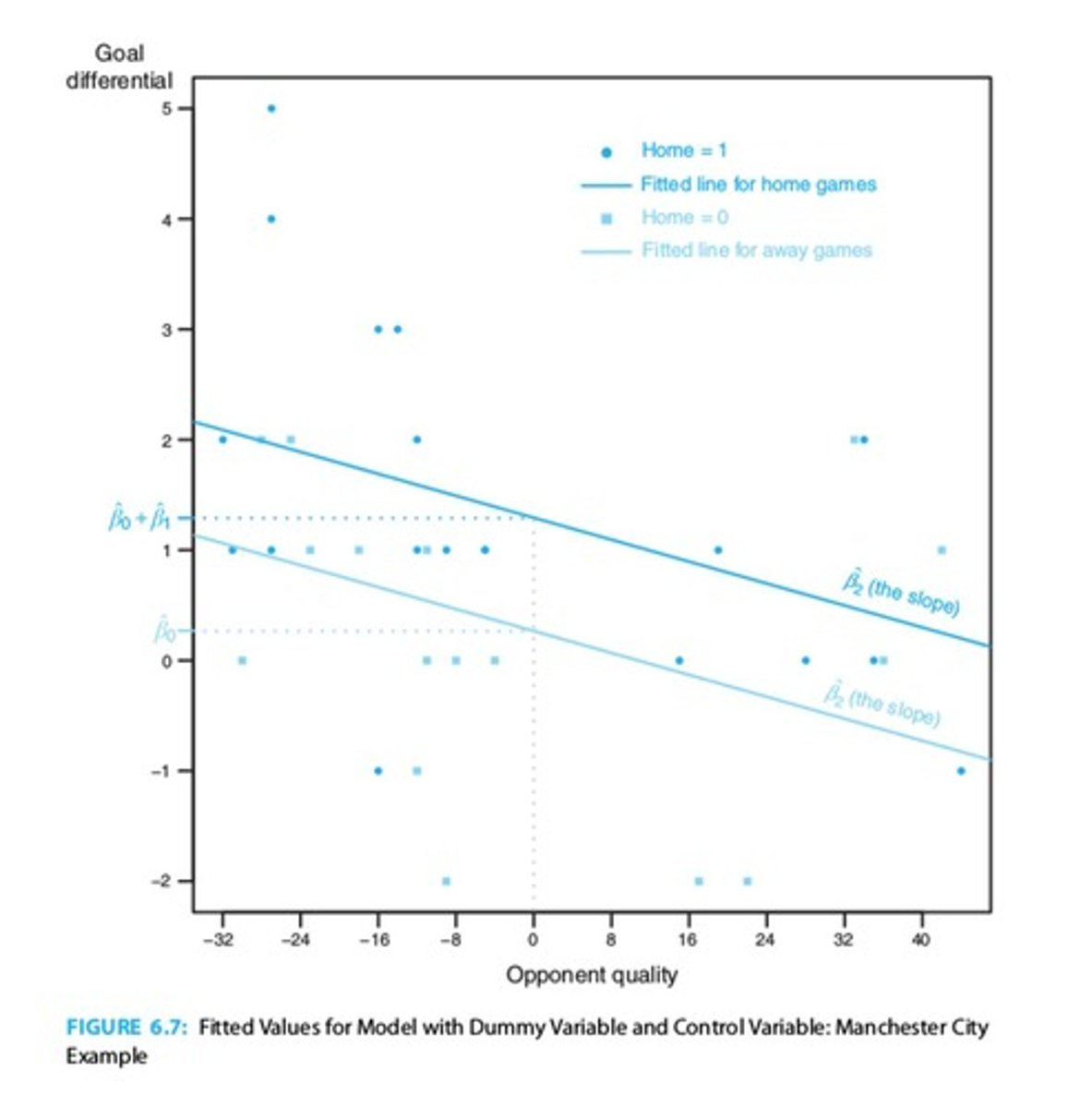
Unit Specific Effects
Unique characteristics affecting a specific unit over time.
Time Period Effects
Common influences affecting all units in a given period.
Covariates
Additional variables included in a regression model.