AP Human Geo
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the topic of this question: Why are there more people 👱👲👳👴👵👦👧 in China and India than anywhere else in the world?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Population
What is the topic of this question: Why are some countries wealthy 💰💲 while many others are not?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Economic Development
What is the topic of this question: Why do so many migrants 🚶 come from Africa and the Middle East?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Migration
What is the topic of this question: Why is the English language 🗣 and Christianity ⛪ so dominant throughout the world?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Culture
What is the topic of this question: Why does globalization—the increasing interconnectedness 🔗 of the world 🗺—serve as a strength and threat to people groups?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Culture/Industry
What is the topic of this question: Why does the European Union exist, and why did Great Britain leave the EU?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Political
What is the topic of this question: Why have Americans become obsessed with organic foods 🍅🍇🍉🍌🍏🍑🍓🌾🌿 in recent years?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Food & Agrictulture
What is the topic of this question: Why are our clothes, smartphones 📱, and cars 🚙 made in factories 🏭 outside the US?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Industry
What is the topic of this question: Why are the largest cities 🌆 in the world in some of the poorest countries?
Population
Economic Development
Migration
Culture
Culture/Industry
Political
Food & Agrictulture
Industry
Urbanization
Urbanization
What is ABSOLUTE LOCATION?
Absolute location refers to the specific coordinates of a place on the earth's surface, such as its latitude and longitude. Absolute location is fixed and does not change
What is RELATIVE LOCATION?
Relative location refers to the location of a place in relation to other places. It is often described using terms like "north of," "south of," "near," or "far from." Relative location is subjective and can vary depending on the context and the perspective of the person describing it
For example, the _______ location of New York City is 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W. Its _______ location could be described as being on the east coast of the United States, north of Washington D.C. and south of Boston.
What is DENSITY and DISTRIBUTION?
Density is simply the number of something in a defined area (the population of Brooklyn, New York), while distribution is the way something is spread out over an area (where different types of people live in neighborhoods throughout Brooklyn).
What are CHOROPLETH MAPS?
These maps use color or patterns to show the distribution of a particular variable or data set.
What are PROPORTIONAL / GRADUATES SYMBOL MAPS
These maps use symbols, such as circles or squares, to represent the size or quantity of a particular variable or data set
What are DOT DENSITY MAPS?
These maps use a dot symbol to represent a quantity of a particular variable or data set. The size and spacing of the dots reflect the density of the data
What are ISARITHMIC MAPS?
These maps use lines to show equal intervals or changes in a particular variable or data set
What are FLOW MAPS?
These maps show the movement of people or goods from one place to another over time
What are CARTOGRAMS?
These maps use a particular variable, such as population, to distort the size or shape of geographic areas in order to better represent the distribution of the data
What is REGIONALIZATION?
Regionalization refers to the process of dividing a large area into smaller regions or territories, often based on shared characteristics or common interests
What is ADMINISTRATIVE regionalization?
Refers to dividing a country or other large area into smaller regions for the purpose of local governance and decision-making
What is ECONOMIC regionalization?
Refers to creating regional economic development programs or trade agreements to promote economic cooperation within a specific region
What is CULTURAL regionalization?
Refers to identifying and preserving regional cultural traditions and identities within a larger national or global context
What is ENVIRONMENTAL regionalization?
Refers to defining regional boundaries for the purpose of resource management or conservation. Regions are important in the process of spatial analysis because they allow geographs to lean about patterns, processes and connections between places at different scales
What is ABSOLUTE DISTANCE?
Distance in measurements (feet, miles, kilometers) Ex. Boston and New York are about 215 miles apart
What is RELATIVE DISTANCE?
Refers to the measure of distance between two locations based on factors like time, effort, or cost rather than just physical space (basically compares two locations) Ex. A flight between Boston and New York takes about an hour, while driving could take 4+ hours depending on traffic
What is ABSOLUTE DIRECTION?
Cardinal Directions such as North, South, East, West
What is RELATIVE DIRECTION?
Refers to directions based on a person’s perspective or a specific point of reference. For example: The lunchroom is to the right of the library
What is CLUSTERING & DISPERSAL
They show how different phenomena are organized across an area.
Clustering - houses in New York City
Dispersed - farms in the midwest
What is ELEVATION?
Refers to the measure of the height of geographic features relative to sea level
How is direction represented on a map
Via COMPASS ROSE, which indicates cardinal directions and someimtes intermediate directions
Scales tells us how much of the world we’re seeing on the map.
Large scale map = ___ buildings (zoomed in)
Small scale map = ___ buildings (zoomed out)
Large scale map - Large buildings (zoomed in)
Small scale map - Small buildings (zoomed out)
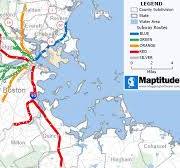
What Map is this?
Reference Maps - displays specific geographic locations (e.g. a road map)
What are the types of REFERENCE MAPS and explain what they do?
Reference Maps (Show locations of places and geographic features)
Political Map – Shows boundaries like countries, states, and cities.
Physical Map – Displays natural features like mountains, rivers, and lakes.
Road Map – Highlights highways, roads, and transportation routes.
Topographic Map – Uses contour lines to show elevation changes.
What are the types of THEMATIc MAPS and explain what they do?
Thematic Maps (Show spatial patterns of a specific subject)
Choropleth Map – Uses colors or shading to represent data intensity (e.g., population density).
Dot Density Map – Uses dots to show frequency or distribution of a feature (e.g., number of farms).
Graduated Symbol Map – Uses differently sized symbols to represent numerical values (e.g., larger circles for higher populations).
Cartogram – Distorts land area to represent a variable (e.g., countries resized by GDP).
Isoline Map – Uses lines to connect points of equal value (e.g., weather maps showing temperature or elevation).
Flow Line Map – Uses arrows or lines to show movement (e.g., migration patterns).
What are the four types of CARTOGRAMS?
Mercator Projection
Peters Projection
Polar Projection
Robinson Projection
What are GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGIES and what are the 3 types?
Geospatial technologies - Technologies that use hardware or software to examine and measure geographical features on teh earth
GPS (Global Positioning System) - Use satellites to communicate with devices on earth to connect an absolute location which is where you currently are to another destination which is where you want to go - FINDING LOCATIONS
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) - Software that can manipulate geospatial data that can be used for research or problem-solving - FINDING ANSWERS TO RESEARCH-BASED PROBLEMS (like figureing where to put a new parking lot)
Remote Sensing - A method of data collection that gathers information about geographic locations through satellite immagery which can help visualize population patterns and other geospatial information
The government needs _____ ___ for urban planning like
______
______
______
______
The government needs CENSUS DATA for ubran planning like
Place of Residence
Race
Gender
Income
What is SPACE referred to as?
Space refers to the physical characteristics of a location and can be measured mathematically (City A is 50 miles away from City B or City B is 30 mi^2)
What is PLACE refferred to as?
Place refers to the meaning people attribute to the locations in which they live which cannot really be measured mathematically
What are FLOWS?
Flows - describe patterns of spatial interaction between different locations (e.g. roads faciliate movement locations, meaning if Place-A has many roads to Place-B, then it has move interaction, more flow)
What is DISTANCE DECAY?
Distance Decay - the further apart two things are, the less connected they will be

What is TIME-SPACE COMPRESSION?
Time-Space Compression - refers to the decreased distance between places measured by the time or cost it taeks to travel between them
How are GEOGRAPHIC PATTERNS used and what are the types?
Geographic Patterns are used by people to try to make sense out of how phenomena are arranged on hte landscape
Random pattern - no order whatsoever
Lineaer pattern - objects under study arranged in a straight line
Dispersed pattern - the phenomena are scattered throughout a large space like farms
What are the types of Natural resources?
Renewable resources - resources that can be used in unlimited measure
Non-Renewable resources - resources that are only available in limited measure
What is ENVIRONMENTAL DETERMINISM?
Environmental Determinism - A theory that flourished in the 19th and early 20th centuries that argues that physical environment determines how a people’s culture develops - “Environment determines Culture”
This was the dominant theory b/c it helped justify europeans to themselves that colonizing lands in tropical regions was just fine b/c if people lived in a tropical region then that means they were lazy b/c they didn’t have to work very hard for their food
What is POSSIBILISM?
The opposite of determinism, arguing that humans are the driving force in shaping their culture and that whatever environment a people finds themselves in offfers many different possibilities for developing a culture (those possibilites change with the level of technological advancement that is present within a culture
For cultures with access to many technologies, environment plays less of a role in how their culture is formed
What are the types of SCALES OF ANALYSIS?
Global
Regional
National
Local
Changing the scale of analysis reveals the different ______ of patterns and processes
variations
Global Map = ___ Scale Map | City Map = ___ Scale Map
Small, Large
Scales of Analysis: Global
Analyses data at the global level - what does this phenomena look like on the whole earth
Scales of Analysis: Regional
Analyses data at the continental level - the point is to draw comparaisions between two or more regions (e.g. life exspectancy in Africa compared to North America)
Scales of Analysis: National
Studies phenomena in a particular country (e.g. median household income in Germany compared to median household in the Czech Republic)
Scales of Analysis: Local
Analyzing data at the state or city level (e.g. graduation rate of one state vs another)
A region is some geographical unit which shares some ____ principle. And that unifying principle can be ______, like a shared language, _____, like a treaty that binds states together into an economic unit, a _____ or activity, like farming, or anything else that helps bind people _____
A region is some geographical unit which shares some unifying principle. And that unifying principle can be cultural, like a shared language, economic, like a treaty that binds states together into an economic unit, a pattern or activity, like farming, or anything else that helps bind people together
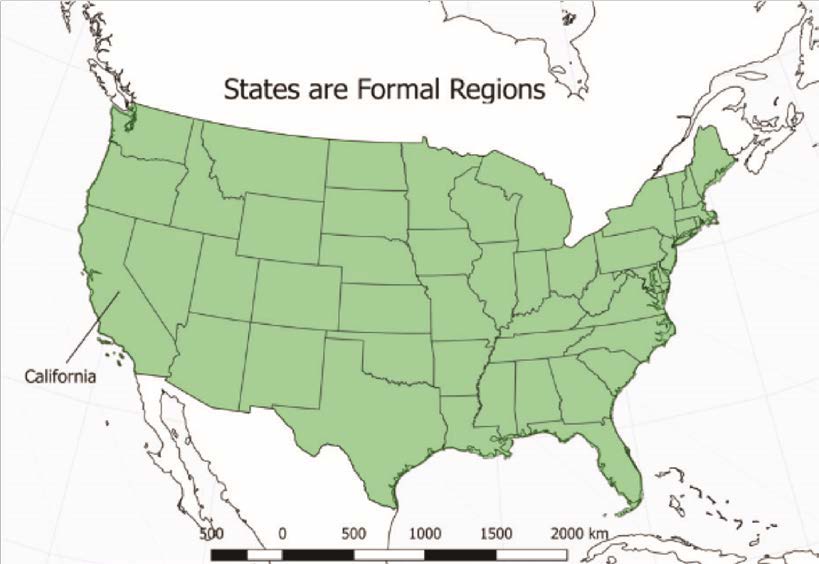
What is Formal Region / Uniform Region / Homogenous Region?
Is linked by common traits like language, religion, or economic prosperity - Its the geographer that defines the region based on the shared traits that they want to analyse
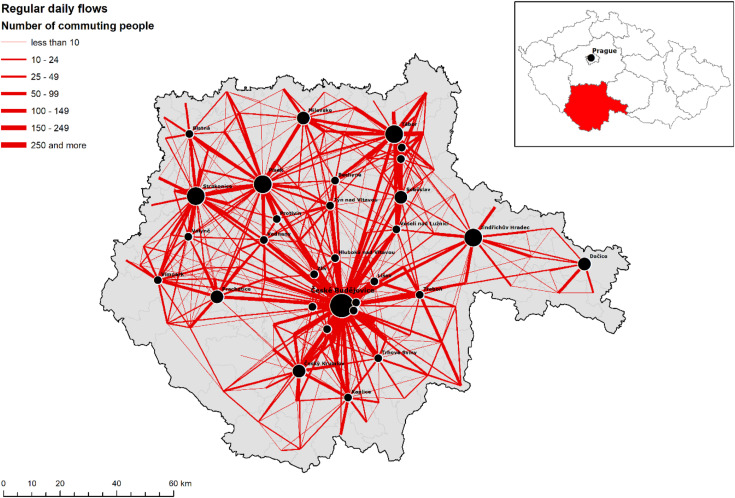
What is Functional Region / Nodal Region?
A region organized not based on shared traits but on shared function
How this works - one entity serves as the node or the center point of the region and this Center Point defines the activity in a region
REMEMBER: Formal and Functional regions can ____ but often don’t take up the same space
Overlap
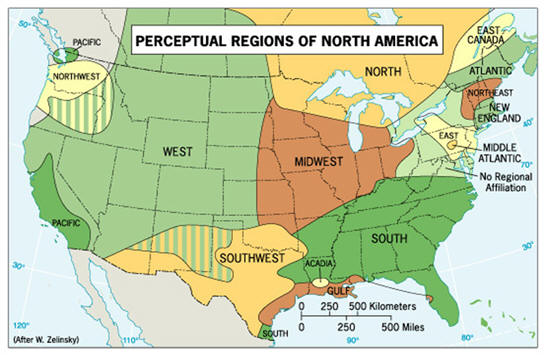
What is Perceptual Region / Vernacular Region?
Defined by people’es shared beliefs and feelings about themselves (e.g. the american south think of themeslves as hospitable and they walk slowly and are very religious), but the borders of perceptual regions are vague
But even with Formal And Functional Regions, ______ can be ______ - since boundaries have no distinct end and start, they are often the subject of ______ known as contested boundaries
But even with Formal And Functional Regions, Borders can be transitional - since boundaries have no distinct end and start, they are often the subject of disputes known as contested boundaries
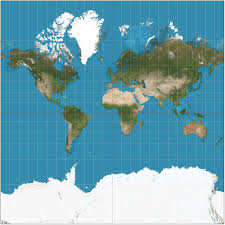
What is the MERCATOR PROJECTION?
Mercator Projection - Latitude and Longitude lines meet at right angles
The farther south/north you get the more distorted the land masses become
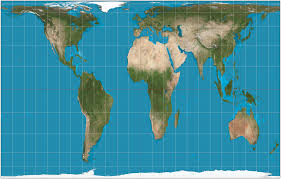
What is the PETERS PROJECTION?
Peters Projection - Challenges Eurocentric Mercator Projection by depitcing continents according to the true size of their landmass
While size-landmasses are accurate, the shapes are distorted
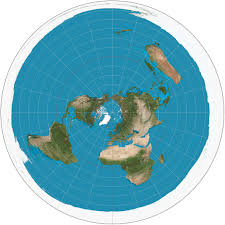
What is the POLAR PROJECTION?
Polar Projection - Views the world from the noth or south pole
While directions are true, distortion occrus at the edges of map
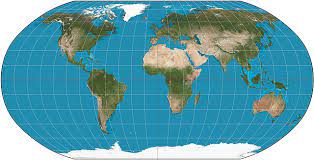
What is the ROBINSON PROJECTION?
Robinson Projection - A comprimise between Peters and Mercator Map Projections
Distributes all kinds of distortions to all parts of the map equally