rate of reaction quiz
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
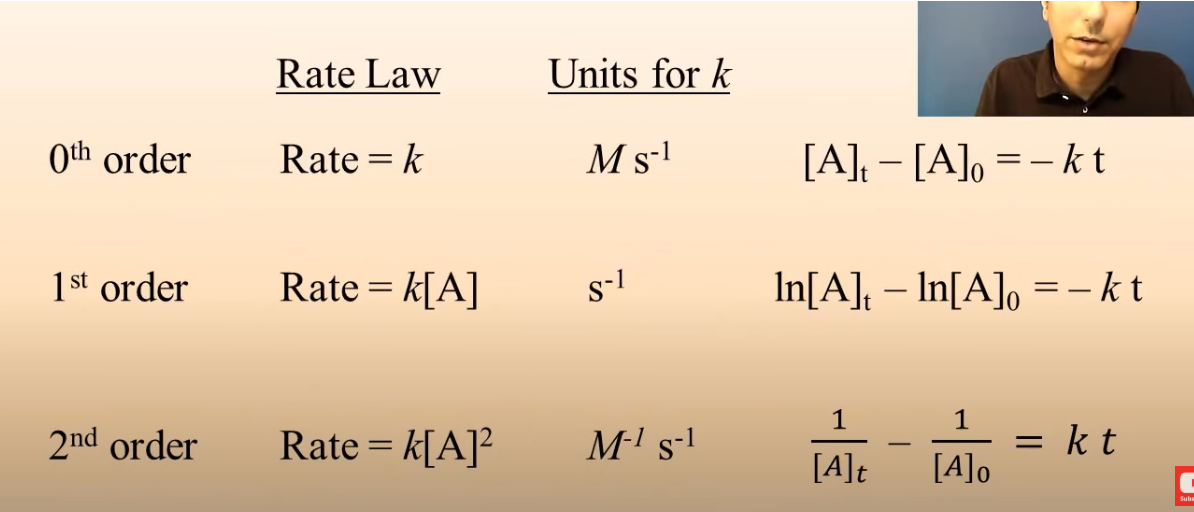
zero order rate laws
r = k (concentration does not affect rate)
if something is only on one side of the reaction can it be a catalyst
no
explain this
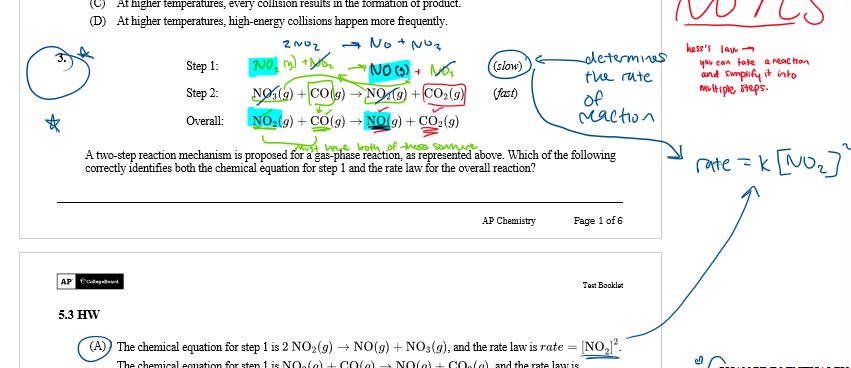
first order rate laws
r = k [A]
second order rate laws
r = k[A]²
0 order, 1 order, and 2 order integrated concentration-time relationship
these are on the equations sheet!
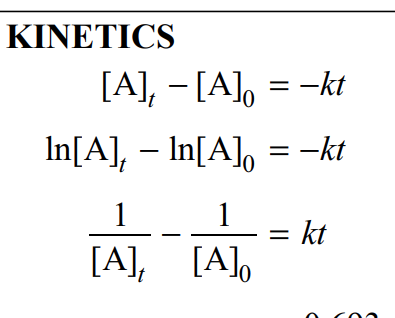
0 order linear slope
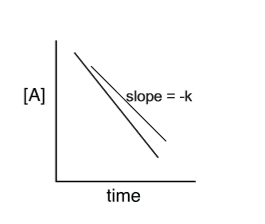
1 order slope
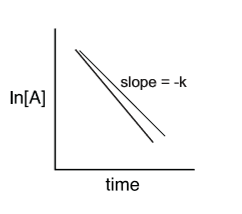
2nd order slope

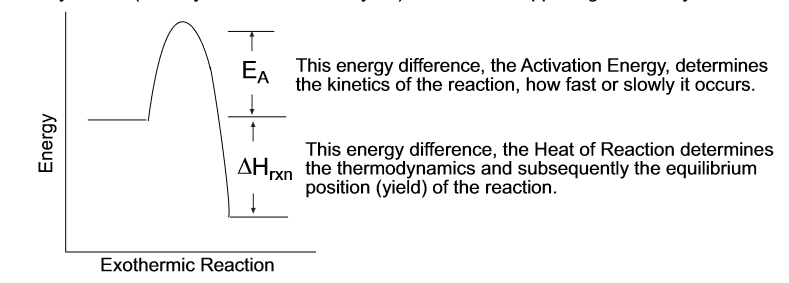
kinetics graph
the heat of reaction is also the change in enthalpy and can show you if you have an endo or exothermic reaction
what affects the rate of reaction
how much contact they have
temperature (higher temp means more speed and less stability which is a good thing for the reaction to go)
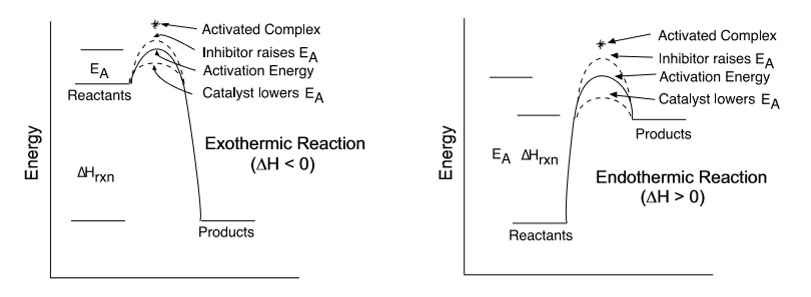
catalyst (increase rates of reaction and lowers activation energy
concentration of reactants
collision theory graph
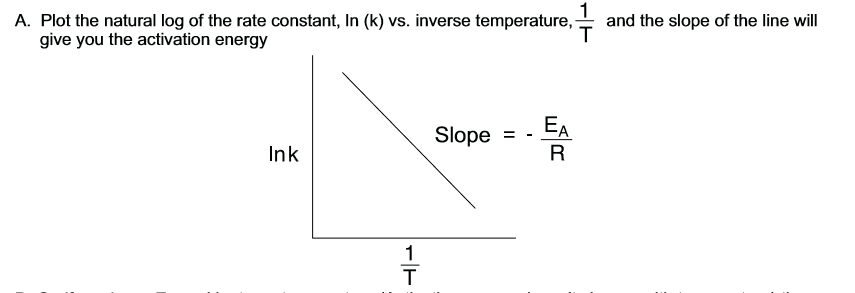
to get activation energy on a graph…
R is the universal gas constant 8.314 J/mol K
rules for reaction mechanisms

rate law with multiple products
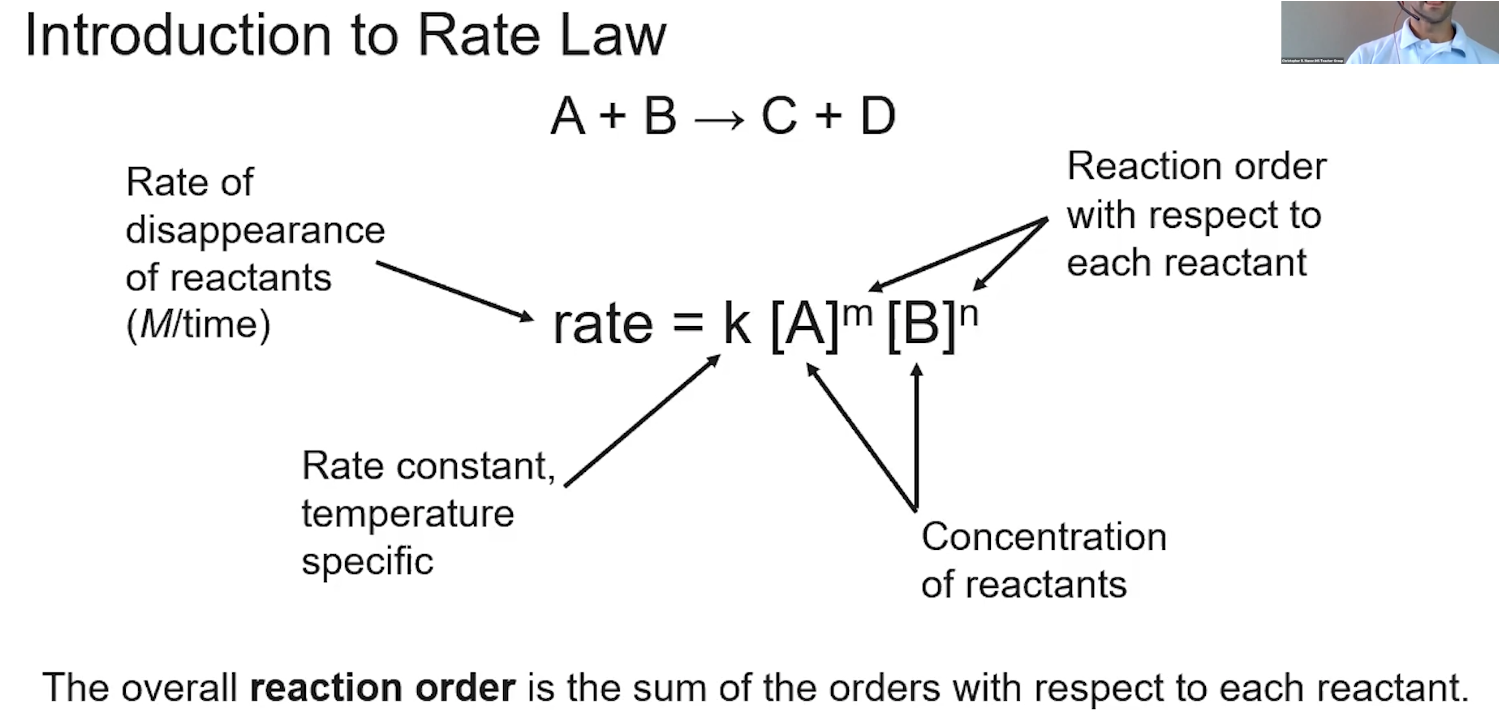
units for k
remember that the order matters!!
elementary reaction
a process that occurs in a single event, an overall chemical reaction usually has more than one elementary reaction
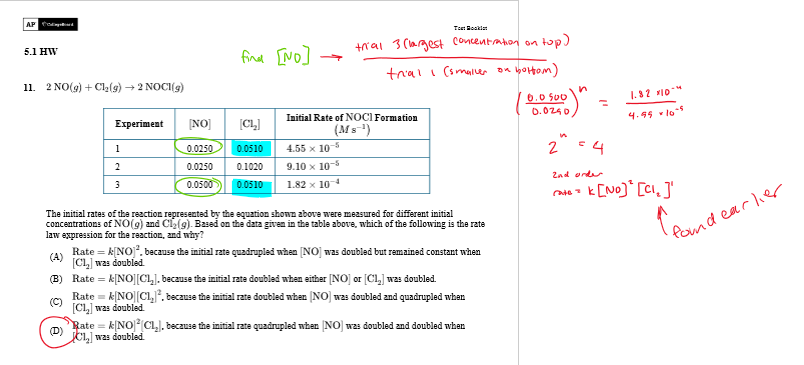
practice problem

practice problem

practice problem cont.
k=230 1/M²s
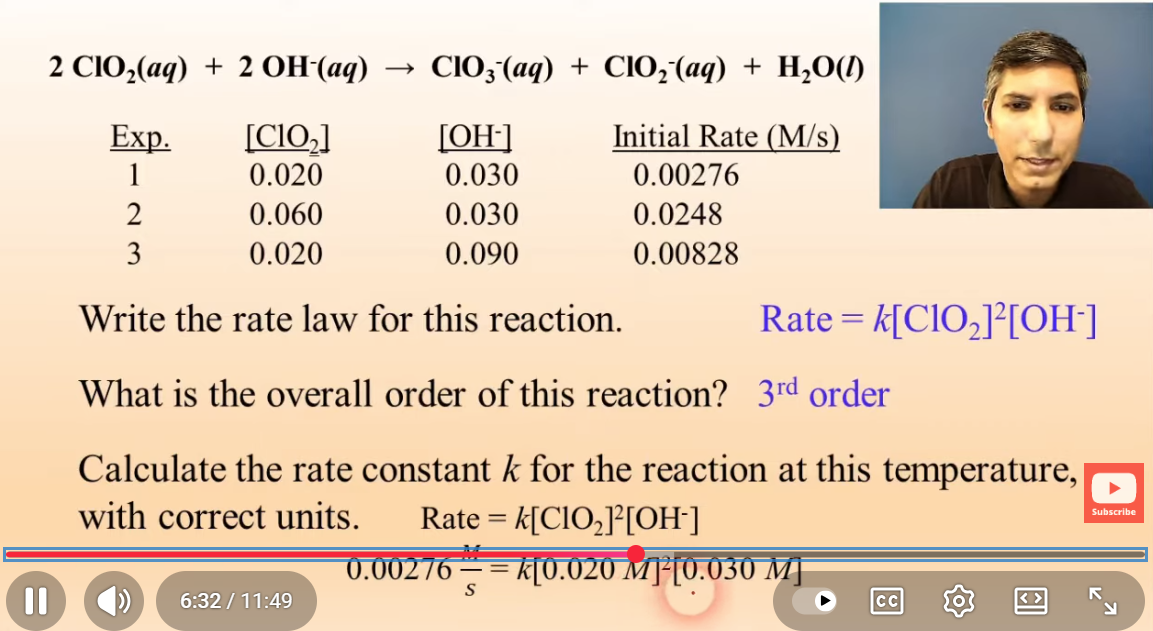
practice problem

activated complex
an unstable, high-energy transition state molecule temporarily formed after the reactant state but before the product state
practice problem

practice problem