Ch 20 Pt 1: Phylogenies and the History of Life
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
phylogeny
the evolutionary history of a species and its relationship to other species
2 types of phylogenetic trees
rooted
unrooted
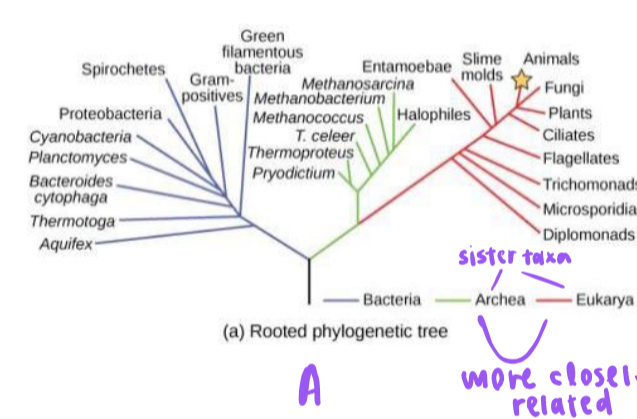
rooted phylogenetic trees
single lineage (at base) represents common ancestor
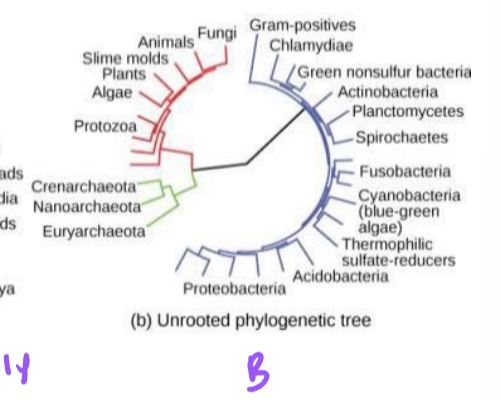
unrooted phylogenetic tree
shows relationships but not a common ancestor
bacteria
do not contain a nucleus
archaea
do not contain a nucleus, have a different cell wall from bacteria
eukarya
cells do contain a nucleus. includes plants, animals, fungi, and protists
true or false. archaea are more closely related to eukarya than bacteria.
true
true or false. bacteria are more closely related to eukarya than archaea.
false
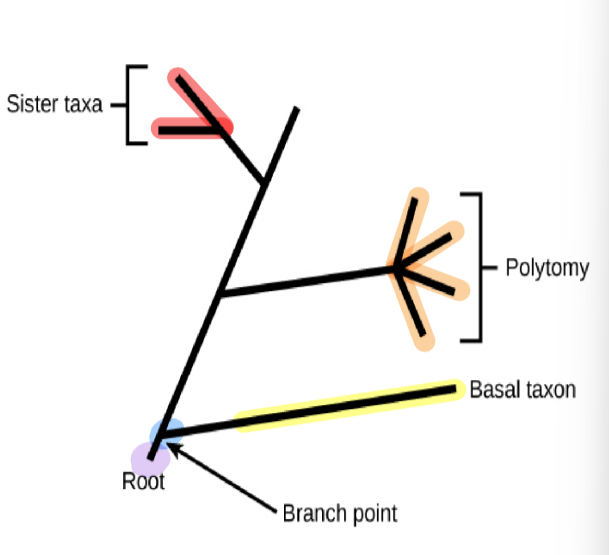
phylogenetic tree: root
indicates than an ancestral lineage gave rise to all organisms on the tree
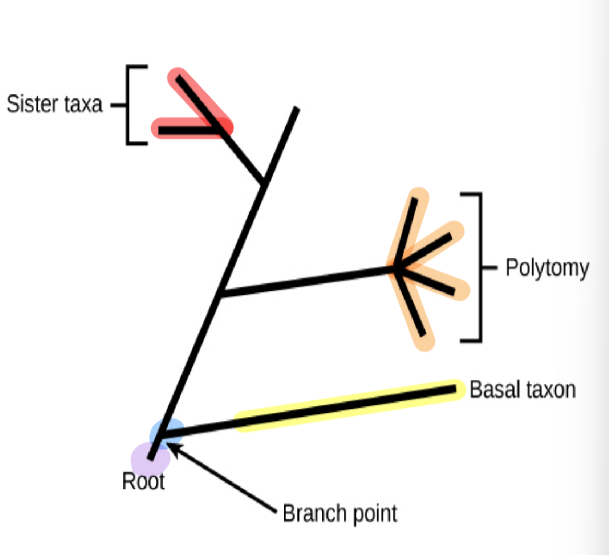
phylogenetic tree: branch point/node
indicates where two lineages diverged
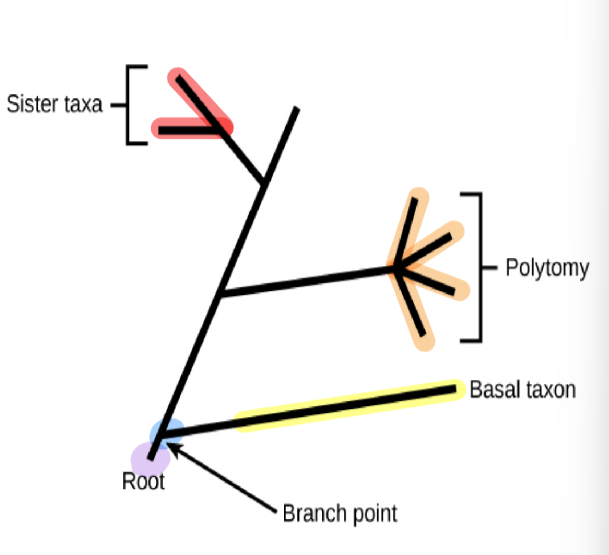
phylogenetic tree: basal taxon
a lineage that evolved early and remains unbranched
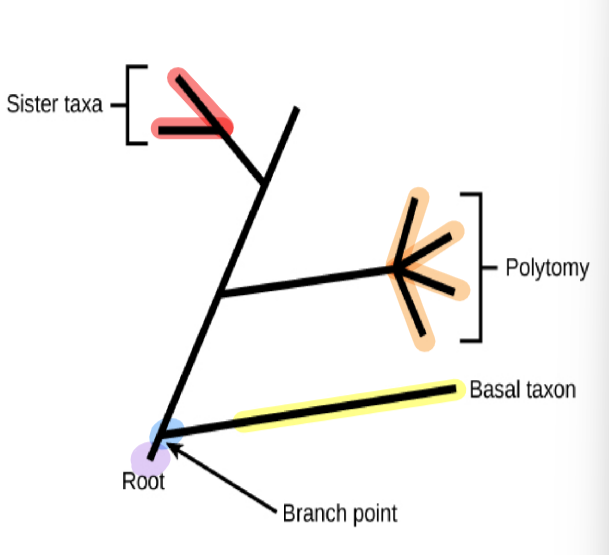
phylogenetic tree: sister taxa
when two lineages stem from the same branch point
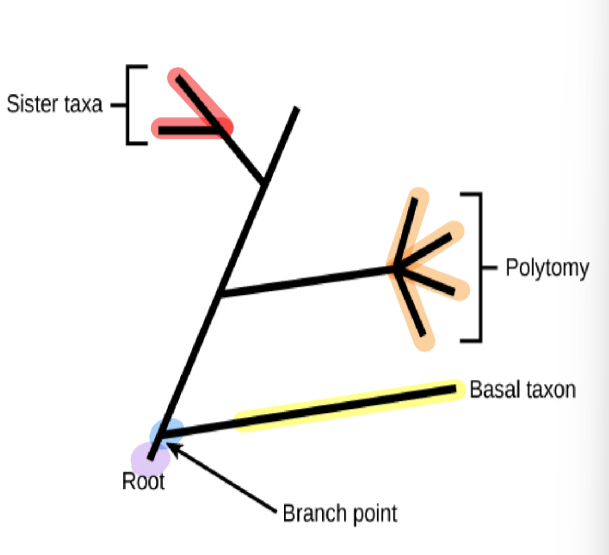
phylogenetic tree: polytomy
a branch w more than two lineages
systematics
study of phylogenetic relationships
taxa that share a more recent ancestor with one another are more ______ related than taxa whose most recent common ancestor is _____
closely, older
clade
a grouping that includes a common ancestors and all the descendants (living and extinct) of that ancestor (monophyletic groups)
cladistic analysis
groupings organisms in a way that reflects their evolutionary relationship
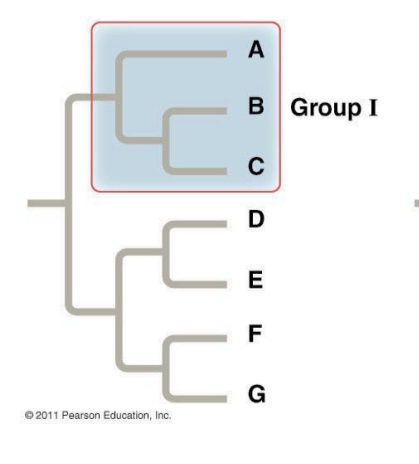
monophyletic group (clade)
consists of ancestral species and all of its descendants
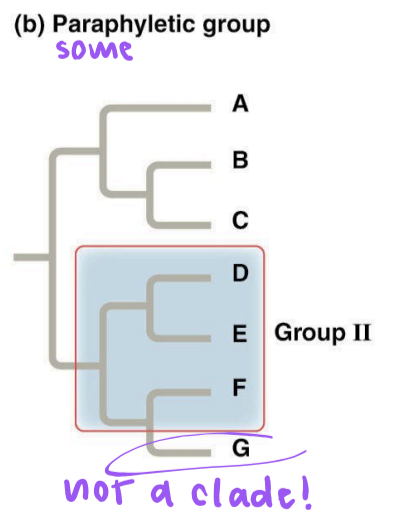
paraphyletic group
consists of an ancestral species and some, but not all, of its descendants
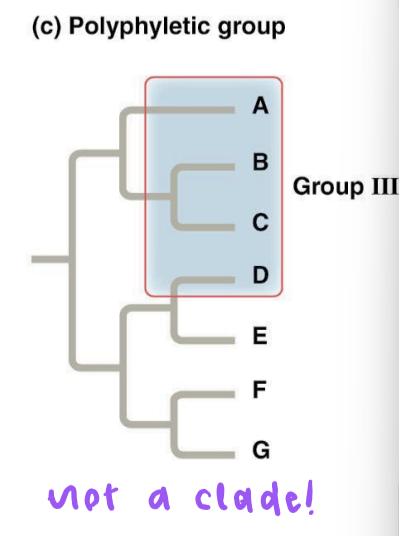
polyphyletic group
includes distantly related species but does not include their most recent common ancestor
true or false. unless specified, the length of the branch does not indicate amount of time passed since the split (node)
true
taxonomy
grouping or classifying species together based on similarities and differences
father of taxonomy
carl linnaeus
who created the binomial nomenclature for species?
Carl Linnaeus
binomial nomenclature
Genus (group) + “specific epithet”
Which is the correct binomial nomenclature for humans?
homo Sapiens
Homo sapiens
Homo Sapiens
homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
Linnaeus’s hierarchical classification system
Doman
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Subspecies
organisms that belong to the same Order should also belong to the same __________.
a) species
b) family
c) genus
d) class
d) class
characteristics of Linnaeus’s hierarchical classification system
consists of a hierarchy of groupings called taxa
organisms that shared obvious phenotypical traits were grouped together
not based on evolutionary characteristics
organisms are divided into three large categories: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
within each domain is a second category called a kingdom
advantages of phylogenetic classificaiton
tells evolutionary history
does not “rank” organisms and does not suggest that 2 identically ranked groups are comparable
Linnaean classification “ranks” groups of organisms artificially into kingdoms, phyla, orders, etc
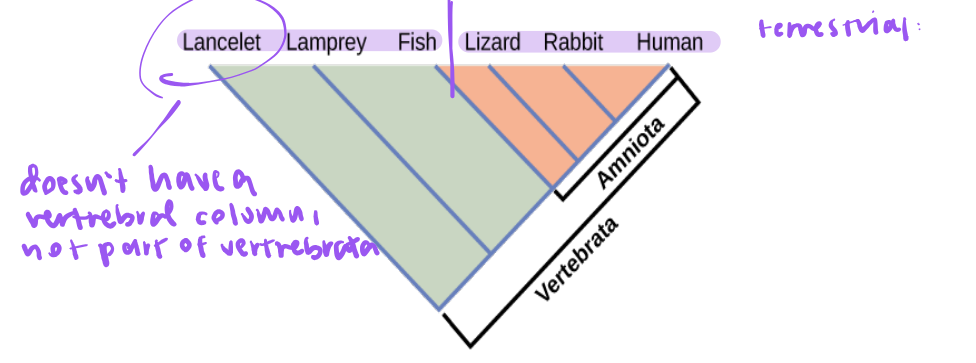
cladistics
a method of determining phylogeny or method of hypothesizing relationships among organisms
analysis depends on characters - anatomical, physiological, behavioral, or genetic sequences
homologous structures
similar due to evolutionary origin (same ancestral source)
based on genetics and developmental origin
divergent evolution
divergent evolution
closely related species develop different traits over time, eventually becoming separate species
analogous structures
similar due to function or ecological pressures
characters can be very similar in appearance due to evolutionary convergence
evolutionary convergence
when unrelated species evolve similar features or behaviors
shared ancestral characteristic
all of the organisms in the taxon or clade have that trait
shared derived character
this characteristic derived at some point but does not include all of the ancestors in the tree
maximum parsimony
fewest evolutionary events
events occurred in the simplest, most obvious way
morphology regarding maximum parsimony
physical characteristics or traits of organisms, such as shape, size, structure, and other anatomical features, that are used to determine evolutionary relationships
as measured by the origin of shared derived morphological characters
DNA regarding maximum parsimony
has the fewest base changed
bioinformatics
the application of the tools of computation and analysis to the interpretation of biological data