IB Bio SL Review
1/300
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
301 Terms
Hydrogen bond
An weak inter-molecular force between oppositely charged poles of separate molecules.
Coolant
A substance that can cool down or regulate the temperature of a system.
Particle
General term for any atom, ion or molecule.
Simple diffusion
The passive movement of a particle from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
Passive transport
Any transport mechanims which does not require energy from the cell
Active transport
Any transport mechanism which requires energy from the cell produced in cellular respiration.
Facilitated diffusion
The passive movement of a particle down its concentration gradient and through a channel protein in the phospholipid bilayer.
Osmosis
The movement of a molecule from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution.
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower solute concentration relative to another solution.
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher solute concentration relative to another solution.
Isotonic
A solution that has the same solute concentration as another solution.
Solution
Solvent + Solute
Solvent
A substance that can dissolve another compound
Solute
A compound that is dissolved by the solvent.
Phospholipid
A type of lipid that contains a hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic tail.
Hydrophobic
Water-hating, non-polar substances
Amphipathic
Containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts
Singer-Nicolson Fluid Mosaic Model
The current model of membrane structure
Davson-Danielli Model of membrane structure
A previous model of membrane structure, shown by evidence to be incorrect.
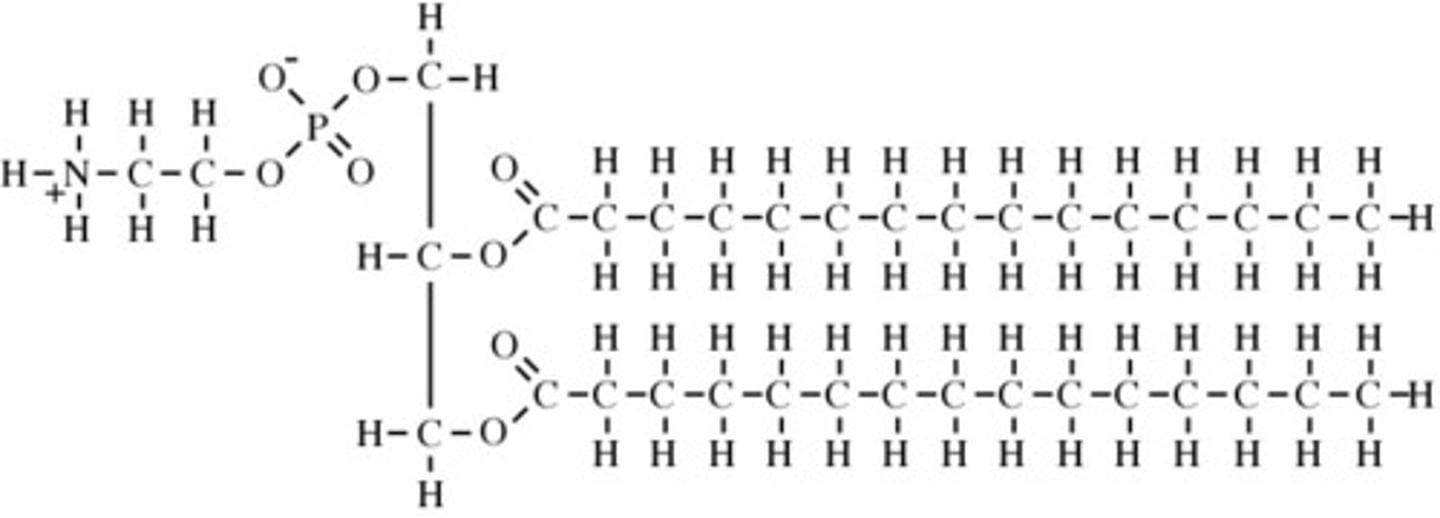
molecular formula of a phospholipid
A cell will lose water to the environment or surrounding medium
if the salt concentration outside the cell is higher then it is inside
A cell will gain water from the environment or surrounding medium
if the salt concentration outside the cell is lower then it is inside
the type of bond that exists between the 2 hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom in a water molecule
polar covalent
Nutrients
substances that provide nourishment essential for the maintenance of life and for growth.
Essential Nutrients
Cannot be made, must be taken in
Non-essential Nutrients
Can be produced or replaced and not required in the diet
- carbohydrates (energy can be from protein or lipids)
- vitamin D & K
- saturated fatty acids
- some amino acids
Appetite control centre
hypothalamus, responsible for making us feel satisfied
Essential Amino Acids
the amino acids that a human cannot synthesize must be obtained through food
Starvation
severe or total lack of nutrients
Malnutrition
lack of proper nutrition can be the result of deficiency, imbalance or excess nutrients
Hypertension
excessively high blood pressure
Cholesterol
steroid that is synthesized in the liver and found mainly in foods of animal origin.
part of the cell membrane, regulates fluidity
High density lipoproteins
"good" cholesterol that carries cholesterol from the cells to the liver for removal from the body
Low density lipoproteins
'bad cholesterol' increases chlotesrol levels in the blood, can clog up arteries, causing blockages, or stroke.
Function of starch in plants
storage of glucose/energy in plants
and storage form that does not draw water
Structure of starch in plants
polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules
ex: amylose which is a linear/helical molecule
and amylopectin which is a branched molecule
saturated fat
carbon atoms all joined by single bonds / have no double bonds / have no increase in number of hydrogen atoms possible; tend to be straight
monounsaturated fat
one double bond in carbon chain of the fatty acid/ could add two hydrogens in the carbon chain; tend to be bent
polyunsaturated fat
two/more double bonds in the carbon chain of the fatty acid, tend to be bent
type 1 diabetes
disorder in which the body cannot produce enough insulin
type 2 diabetes
progressive disorder in which body cells become less responsive to insulin, associated with obesity
Insulin
hormone produced by the pancreas that lovers blood glucose levels
Glucagon
A hormone secreted by the pancreas that increases blood glucose
Environment benefits: of GMO's
*pest-resistant crops can be made
*so less spraying of insecticides/pesticides
*less fuel burned in management of crops
*longer shelf-life for fruits and vegetables so less spoilage
*greater quantity/shorter growing time/less land needed
*increase variety of growing locations / can grow in threatened conditions
Environment risks of GMOs
*non-target organisms can be affected
*genes transferred to crop plants to make them herbicide resistant could spread to wild plants making super-weeds
*GMOs (encourage monoculture which) reduces biodiversity
*GM crops encourage overuse of herbicides
Health benefits of GMOs
*nutritional value of food improved by increasing nutrient content
*crops could be produced that lack toxins or allergens
*crops could be produced to contain edible vaccines to provide natural disease resistance
Health risks of GMOs
*proteins from transferred genes could be toxic or cause allergic reactions
*antibiotic resistance genes used as markers during gene transfer could spread to «pathogenic» bacteria
*transferred genes could cause unexpected/not anticipated problems
OR
health effects of exposure to GMO unclear
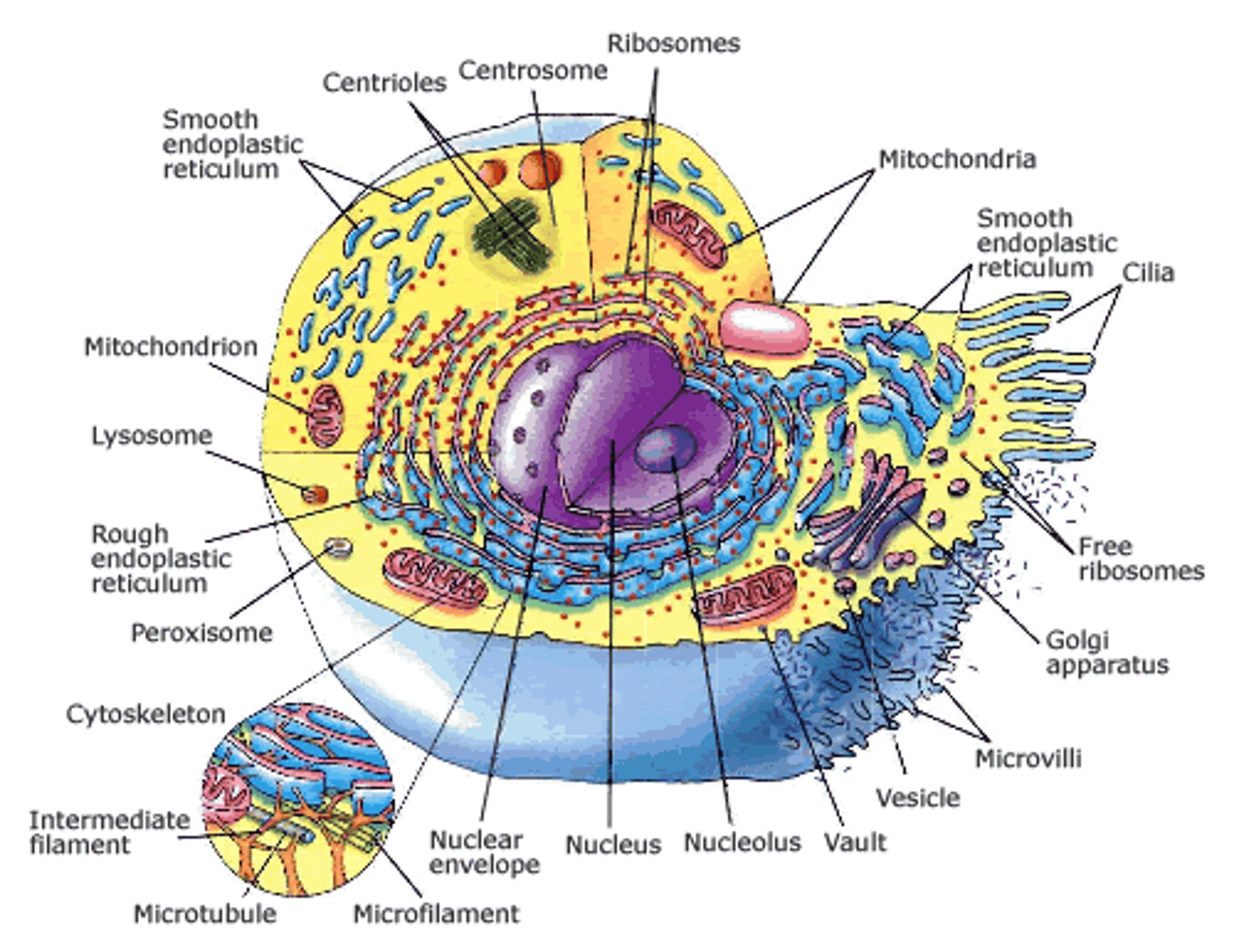
mitochondria
aerobic cellular respiration, ATP production
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum function
synthesis and transport of proteins; (both needed)
plasma membrane function
controls entry and exit of materials/substances in cell
free ribosome function
site of synthesis of proteins for use in the cell
Cell Theory
Idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
Unicellular organism
Organism that consists of one cell that carries all functions of life
Metabolism
Chemical reactions inside a cell, such as cell respiration
Homeostasis
The ability to keep conditions inside the organism within tolerable limits

Scale bar
measure the size of the scale bar and divide by the magnification
Multicellular organisms
Organisms that consist of multiple cells that each have specific functions
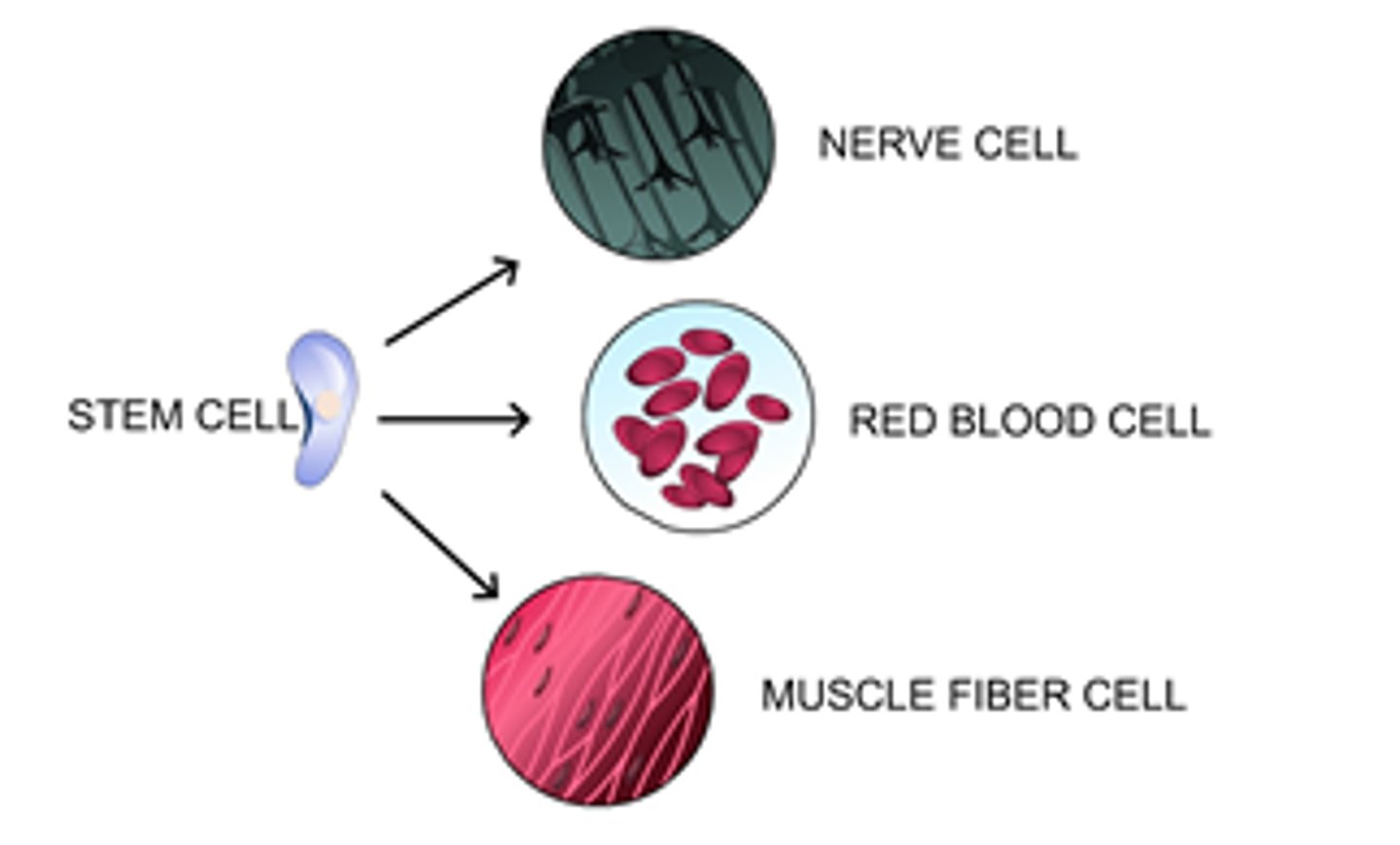
Cell differentiation
Development of cells in different ways to perform different functions
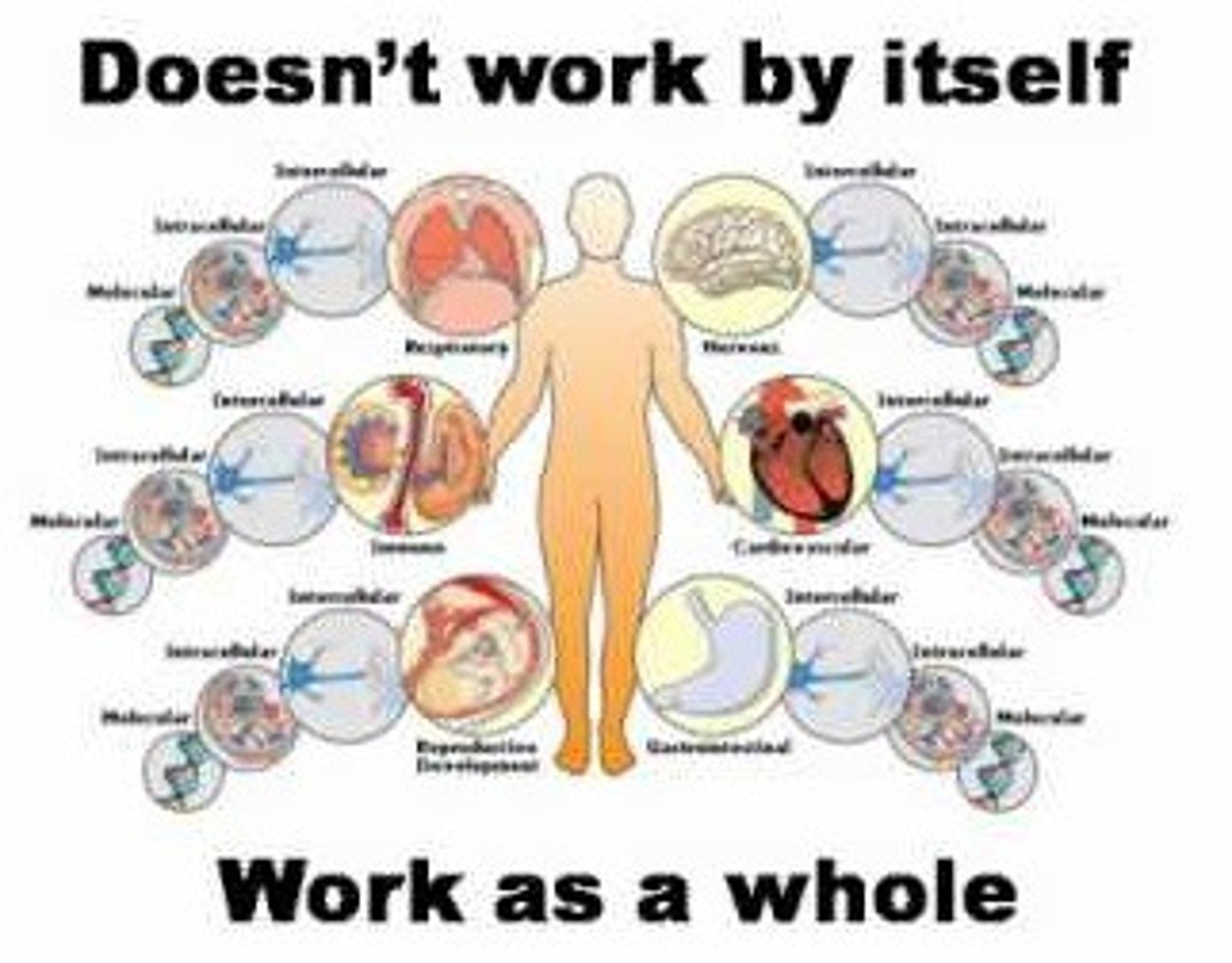
Emergent properties
Properties that arise from the interaction of component parts. "The whole is greater than the sum of its parts."
Eukaryotic cell
Cells for a eukaryotic organism that have complicated, internal structures that are enclosed within membranes
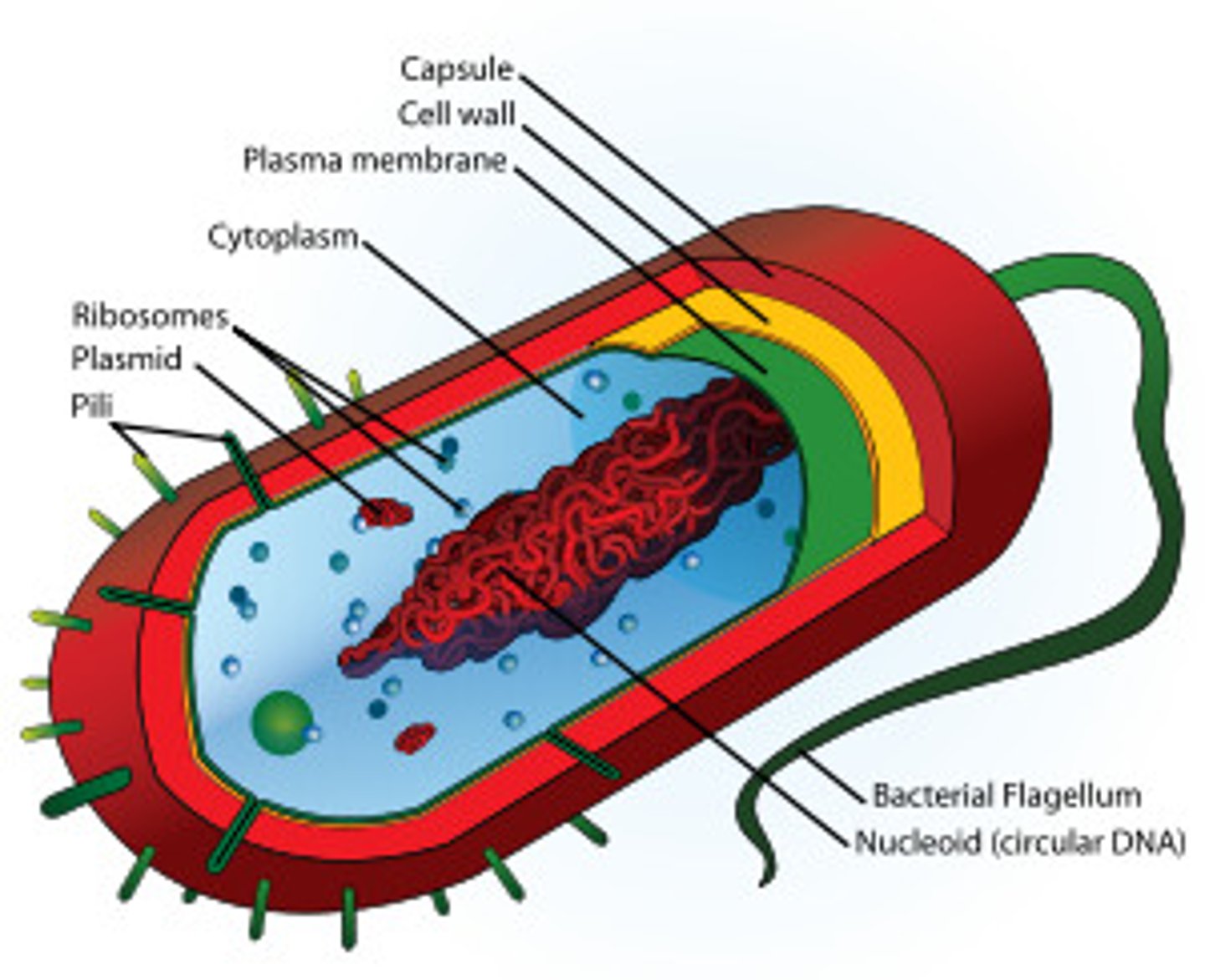
Prokaryotic cell
Cells that do not have nucleus or any membrane-bound organelles
Cell wall
Found in plants, fungi and bacteria, they have an outer layer, are rigid and strong and made of cellulose. They are there for support, protection and allow chemicals to diffuse in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm
Material that contains enzymes that catalyse the chemical reactions of metabolism, it supports and protects cell organelles
Pili
Hair-like structures that project from the cell wall, they can be ratcheted in and out and can by used to pull cells together when connected to another bacterial cell

Flagella
Solid protein structures that protrude from the cell wall, they are used mostly for mobility

Nucleoid
Region of the cytoplasm that contains naked DNA, found only in prokaryotic cells
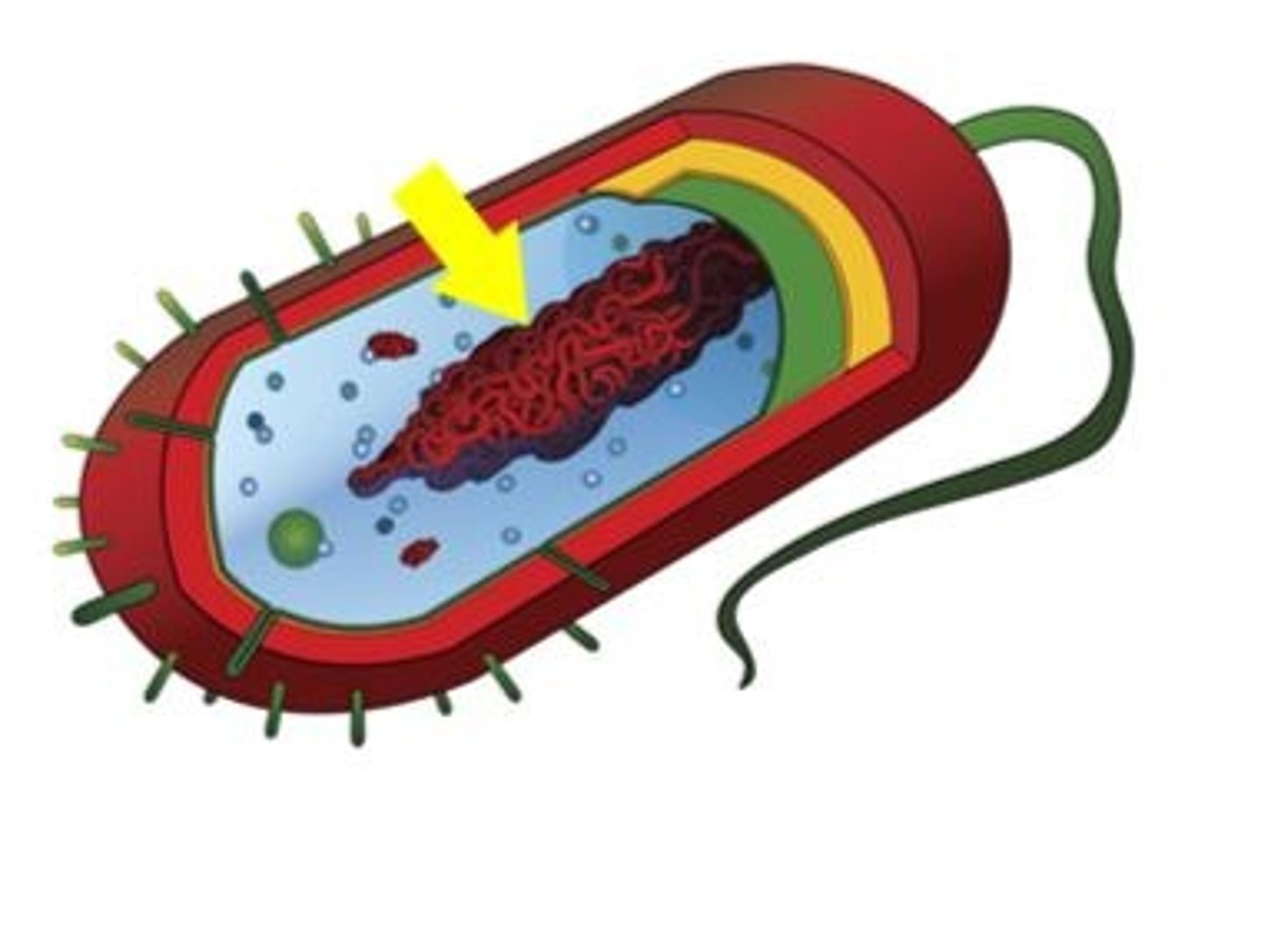
Naked DNA
DNA that does not have a nuclear envelope and 'floats'
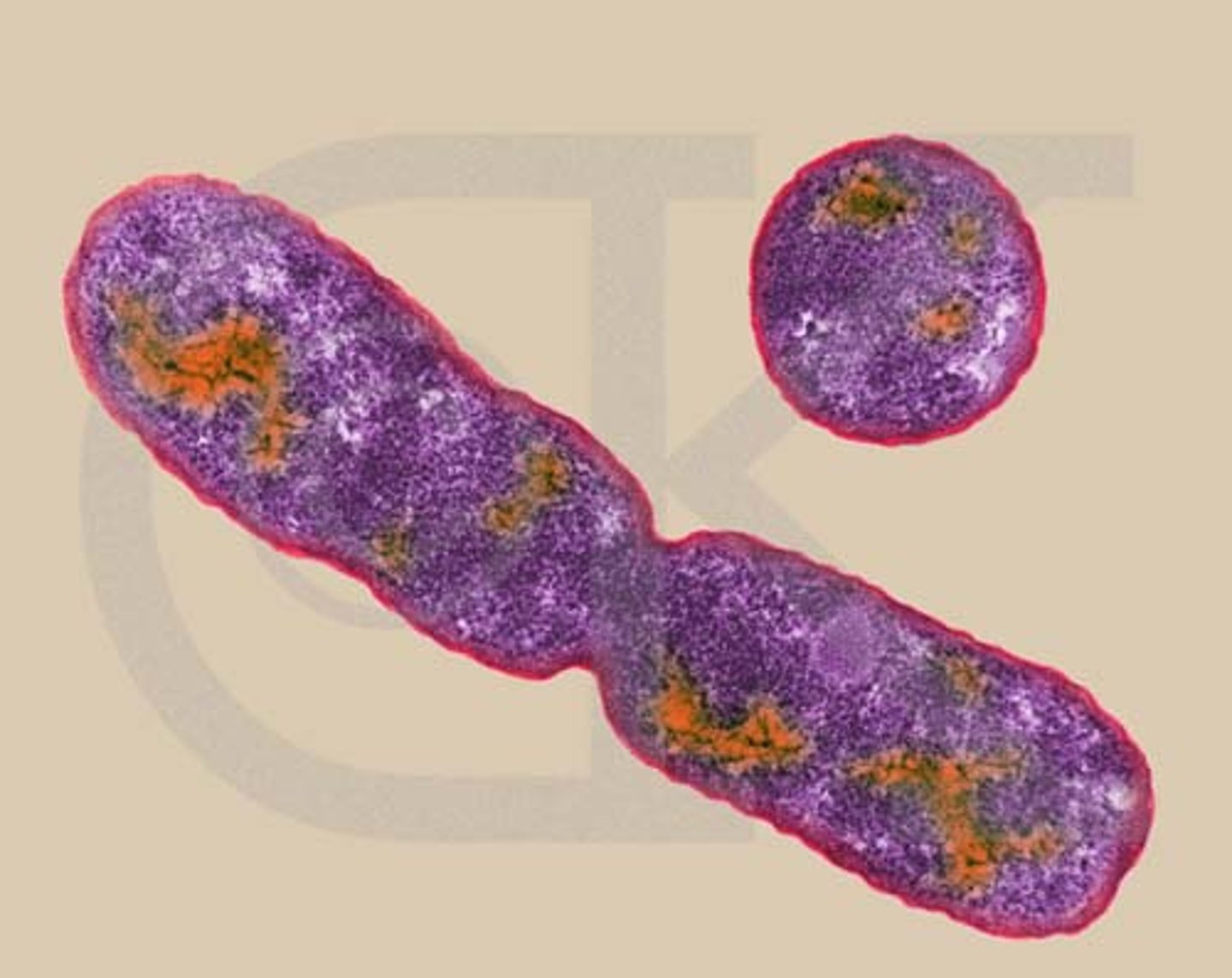
Binary fission
Method of cell division for prokaryotic cells that is used for asexual reproduction
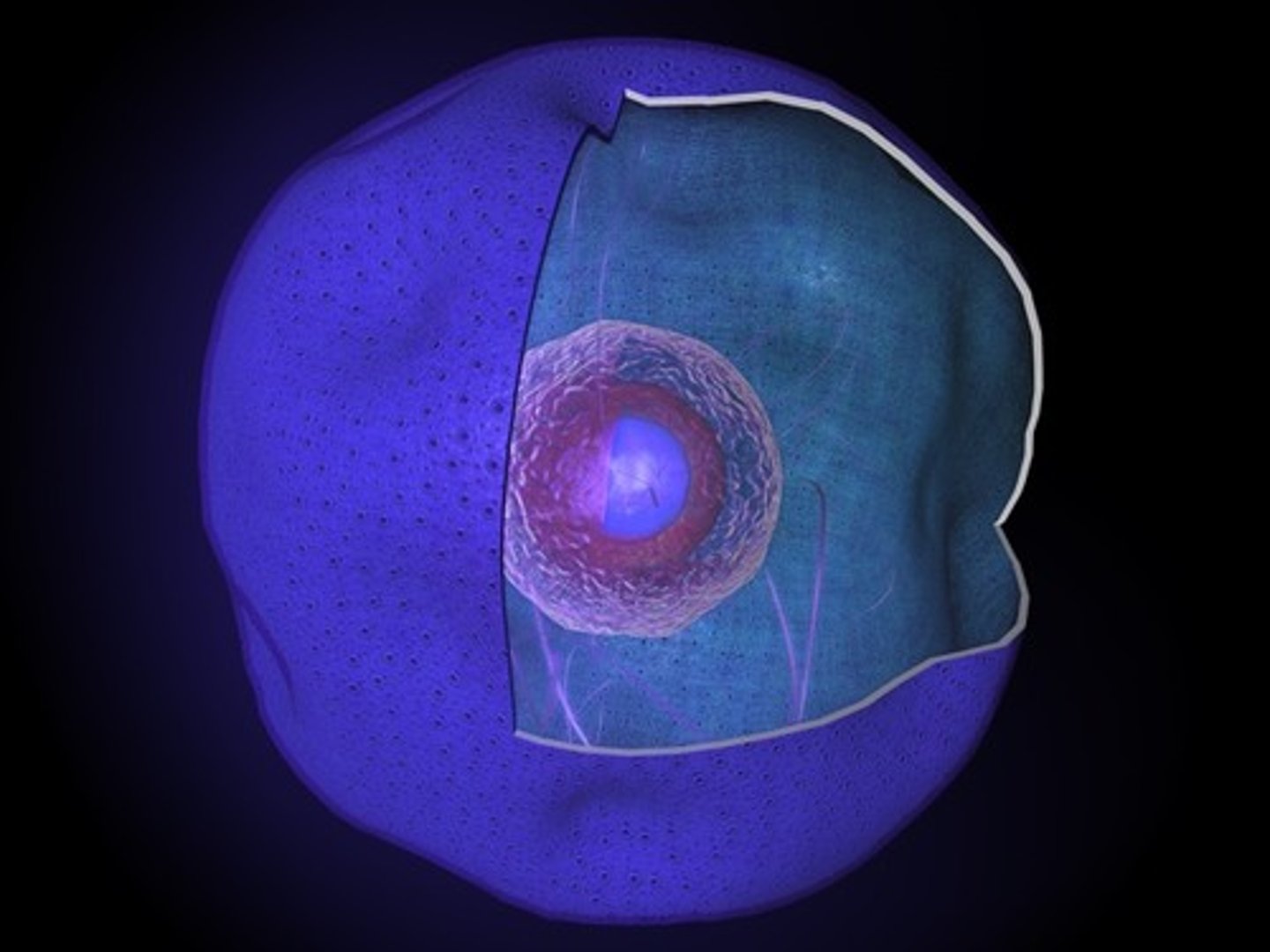
Nucleus
Organelle where cell activity is controlled it contains hereditary information of the cell
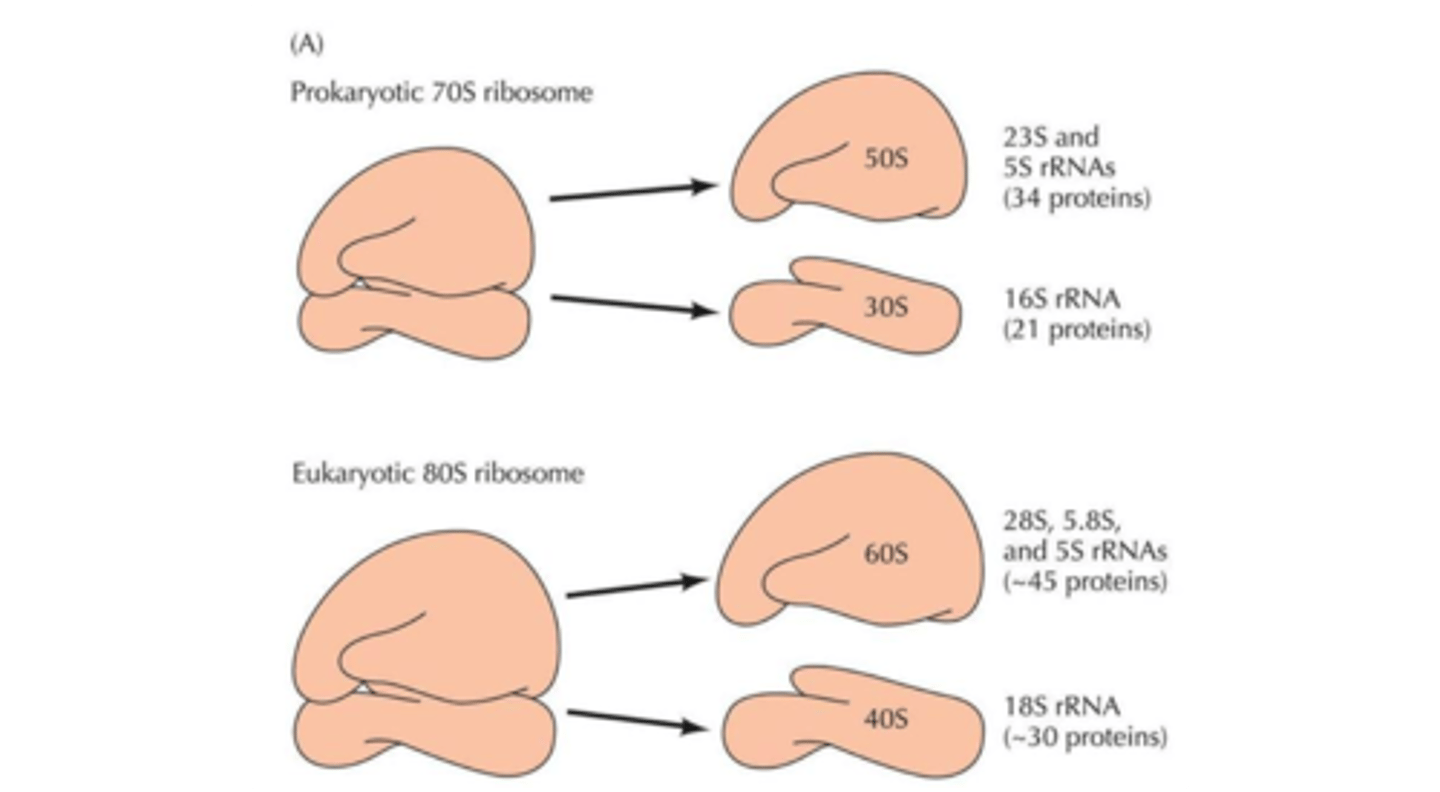
70s vs 80s ribosomes
Prokaryotes have 70s ribosomes, eukaryotes have 80s ribosomes.
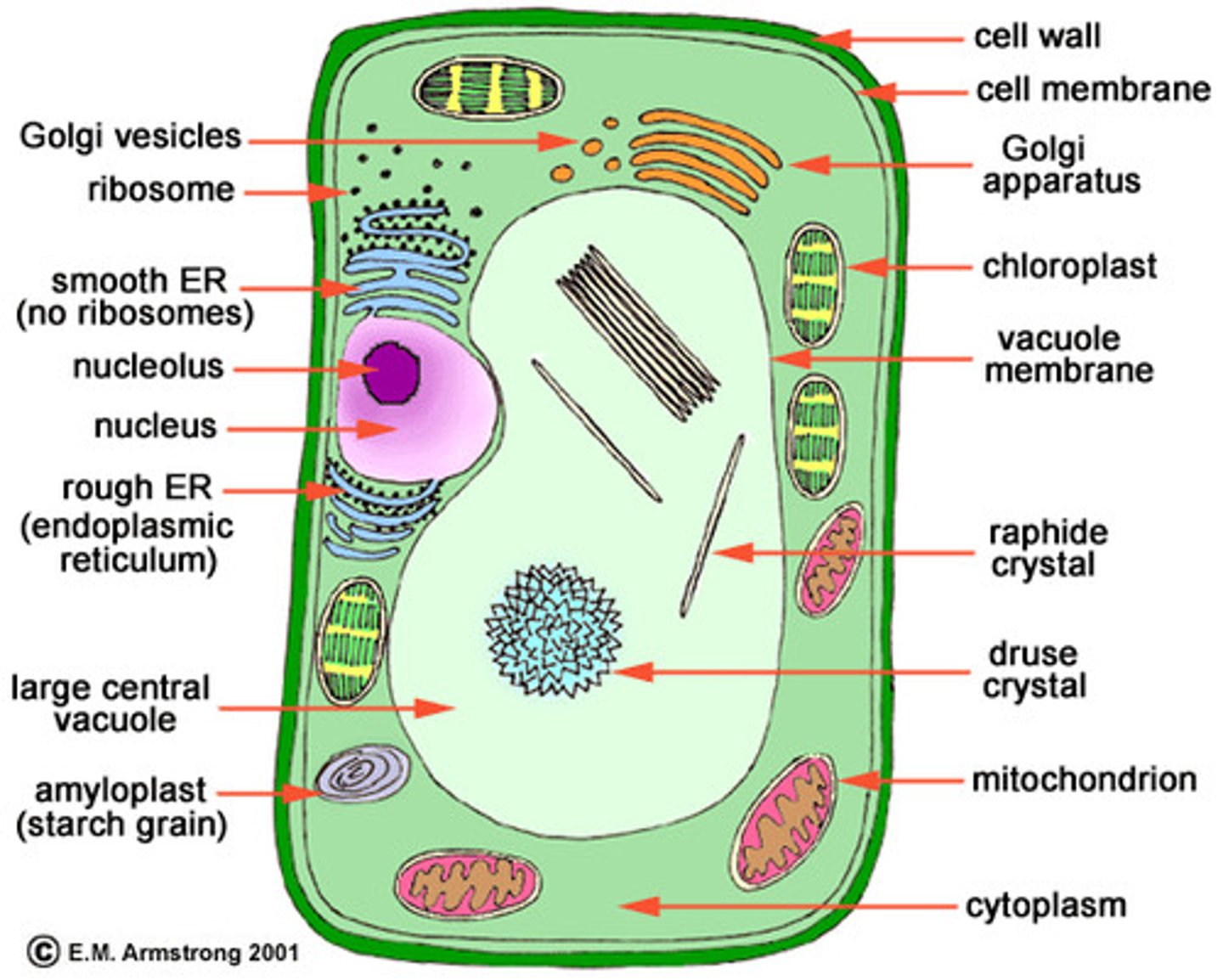
Plant cell
Cell wall with an inner plasma membrane, chloroplasts that photosynthesize, carbohydrate storages of starch, large fluid-filled vacuoles that are surrounded by a membrane (tonoplast), it controls the movement of substances from the cytoplasm, they have a fixed shape that is usually irregular
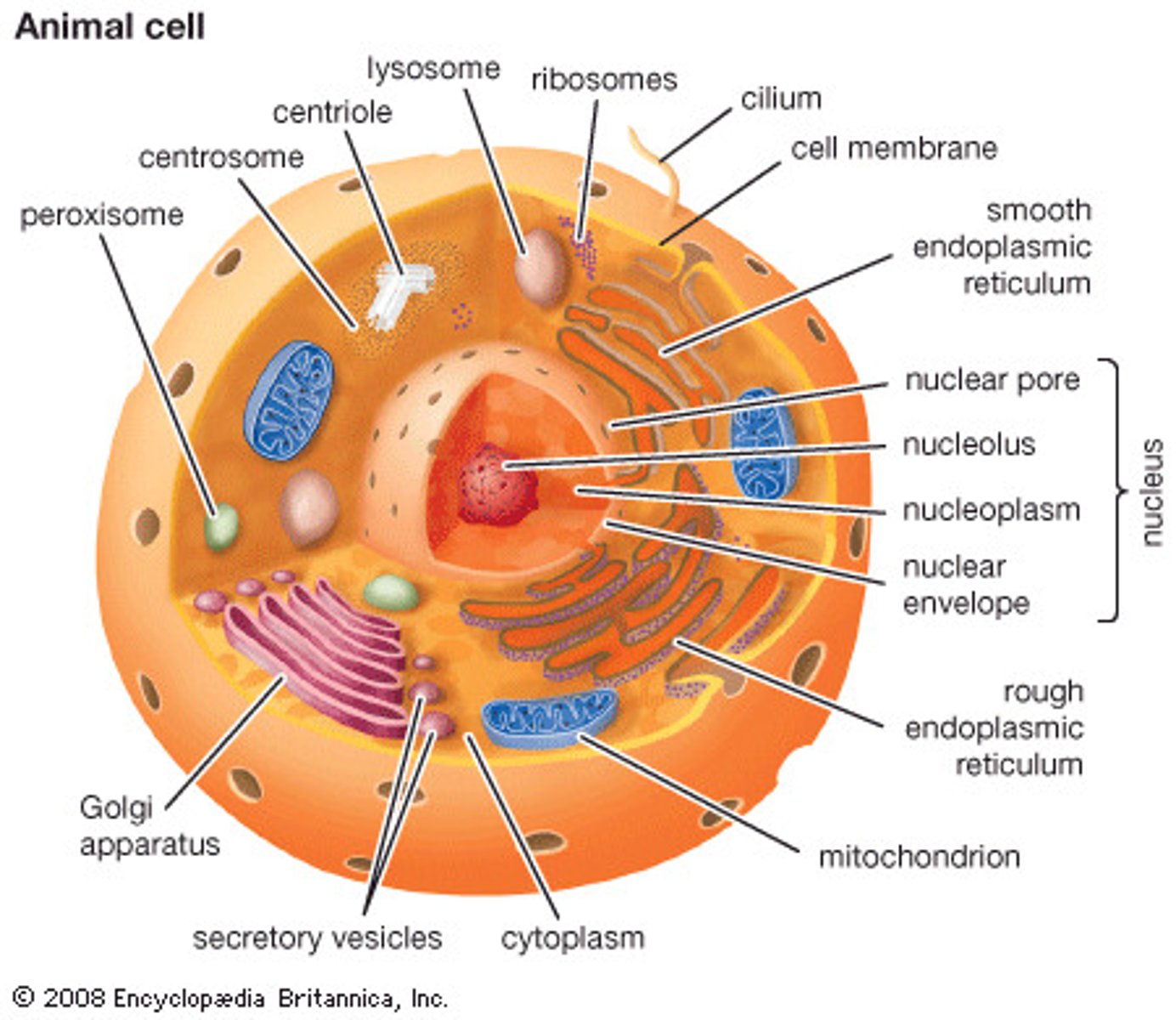
Animal cell
Only have a plasma membrane, no chloroplast present, carbohydrate storages of glycogen, only have small temporary vacuoles, they have a flexible shape but are usually rounded
METABOLISM
Chemical reactions inside the cell, including respiration to release energy
NUTRITION
Obtaining food, to provide energy and the materials needed for growth
GROWTH
An irreversible increase in size
RESPONSE
The ability to react to changes in the environment
EXCRETION
Getting rid of the waste products of metabolism
REPRODUCTION
Producing offspring either sexually or asexually
Cell
Basic unit of life.
Organelle
A discrete structure within a cell that performs a specific function.
Hyphae
Filaments or threads within a fungus.
Stem cells
Cells that are able to differentiate into any other type of cell.
Differentiation
The process of cells specialising in multicellular organisms. Requires cell division and controlled gene expression.
Photosynthesis
A chemical reaction that produces organic compounds from CO2 using light energy.
Chlorophyll
A pigment protein in chloroplasts that traps light energy for use in photosynthesis.
Photolysis
A process that uses light energy to split a water molecule into Oxygen and Hydrogen. Splitting releases an electron that can be used in future reactions.
Limiting Factor
Any factor that slows down the rate of reaction when it is reduced.
Wavelength
The distance between two peaks of a wave.
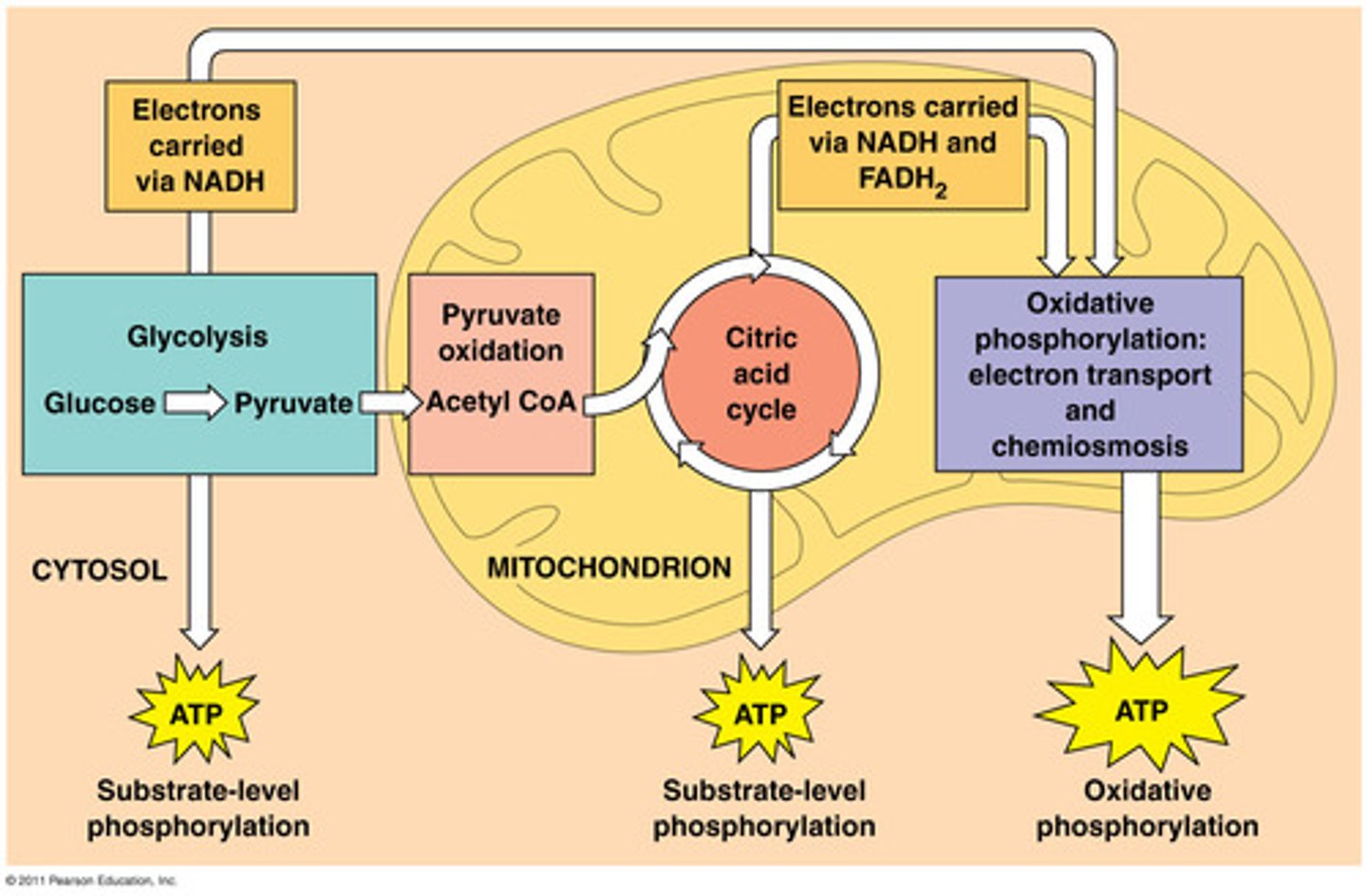
Cell respiration
A chemical reaction that releases energy inside cells to produce ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The energy currency inside cells and is manufactured during respiration.
Adenosine Diphosphate
One of two molecules formed when ATP is used inside cells. The other is inorganic phosphate P04-
Aerobic respiration
Respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Ethanol
A compound that is one of the waste products of anaerobic respiration in yeast.
Carbon dioxide
A compound that is a waste product of anaerobic respiration in yeast and aerobic respiration in animals.
Lactate
A compound that is the waste product of anaerobic respiration in animal cells.
Glycolysis
A chemical reaction in respiration where glucose is broken into two pyruvate molecules. It occurs in the cytoplasm.
Pyruvate
An intermediate compound in respiration that can be broken down in the mitochondria in aerobic respiration or in the cytoplasm in anaerobic respiration.
Species
Organisms that are able to interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Reproductive Isolation
An inability to interbreed.