Chemistry 1.1 The Nature of Substances and Chemical Reactions
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is an element?
An element is a substance made up of a single type of atom. These substances cannot be broken down into any simpler substance.
What is a compound?
A substance made from two or more elements that are chemically joined. They have completely different properties from their constituent elements.
How are elements and simple molecules represented using chemical formulae?
Use chemical symbols to state the number and type of each atom present.
E.g. O₂ represents the element oxygen made up of 2 atoms of oxygen.
E.g. H₂O represents a molecule with 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen.
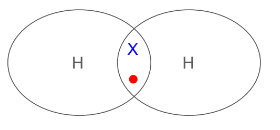
How can you represent simple molecules using a diagram and key?
Create a dot and cross diagram to model the bonding in simple molecules. E.g. A hydrogen molecule forms when a hydrogen atom shares its outer electron with another hydrogen atom.
Key:
● Outer shell of each atom is drawn as a circle.
● Circles overlap where there is a covalent bond.
● Electrons from one atom are drawn as dots, and electrons from another atom as crosses.
How can you determine the formulae of ionic compounds given the number of the ions they contain?
The overall charge of a compound is zero, so the number of positively and negatively charged ions must be balanced so there is no net charge.
E.g. Magnesium forms a 2+ ion and chlorine forms a 1- ion. So for every magnesium ion, there must be two chlorine ions to give the ionic compound an overall charge of zero. This gives the chemical formula MgCl₂.
What is relative atomic mass?
The average mass value, which takes the mass and abundance of isotopes of an element into account, on a scale where the mass of ¹²C is 12.
What is relative formula mass?
The addition of all the relative atomic mass values for all the atoms in the formula. The relative formula mass of a substance is called one mole of that substance.
What is the percentage composition of a compound?
Divide the relative atomic mass of each element by the total relative formula mass of the whole compound, then multiply by 100.
What are the methods by which mixtures can be separated (there are 4)? Do these involve chemical reactions?
Filtration, evaporation, chromatography, distillation. They do not involve chemical reactions as the atoms/molecules in mixtures are not chemically joined.
What is chromatographic data analysis?
An analytical technique separating compounds by their relative speeds in a solvent as it spreads through the paper. The more soluble a substance is, the further up the paper it travels. Compounds in a mixture separate into different spots, but a pure substance will produce a single spot in all solvents.
What are Rf values?
Rf value = distance moved by substance ÷ distance moved by solvent.
What is a chemical reaction?
A process by which atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form products. The number and type of each atom present in the reactants will also be present in the products—this is why chemical equations must be balanced.
What are the observations that show a reaction has taken place?
● Colour changes
● Effervescence - occurs when a gas is released and fizzing is seen
● Temperature changes - exothermic reactions give off heat to the surroundings (causing an increase in temperature), whereas endothermic reactions take in heat from the surroundings (causing a decrease in temperature).
How can you represent chemical reactions using word equations?
Word equations use the chemical names instead of formulas to show the reaction.
E.g. methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
How can you represent chemical reactions using chemical equations?
Chemical equations use the chemical formulas and show the ratio of molecules reacting—total relative mass of reactants and products is equal.
E.g. CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O (shows combustion of methane).
What is the percentage yield of a chemical reaction?
Percentage yield = (mass of product produced ÷ theoretical maximum mass of product possible) × 100.
How can you calculate the empirical formula from reacting mass data?
Calculate the number of moles = mass (in grams) ÷ relative atomic mass. The ratio is calculated by dividing each number of moles by the lowest number of moles present. Multiply the ratio so there are no decimals. This gives the empirical formula.
How can you calculate the masses of reactants or products from a balanced chemical equation?
Calculate the number of moles = mass (in grams) ÷ relative atomic mass.
Multiply the moles by the ratios given by the balanced chemical equation. Now calculate the mass of a reactant or product using the equation:
mass (in grams) = relative atomic mass × moles.
What is the Avogadro constant?
The number of atoms/ions/molecules that make up 1 mole of a substance. This number is called the Avogadro constant and is 6.02 × 10²³.
How can you convert amount of substance (in grams) to moles?
Number of moles = mass of particle (in grams) ÷ relative atomic mass of particle.
How can you convert moles to amount of substance in grams?
Mass of particle (in grams) = number of moles × relative atomic mass of particle.