Caribbean Studies Module 1 ( CARIBBEAN SOCIETY AND CULTURE)
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions of Caribbean, Historical Process, Society and Culture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
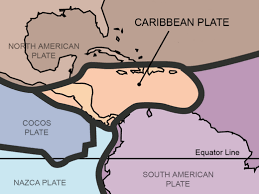
What is the geological definition of the Caribbean?
The geological definition of the Caribbean refers to the area defined by the Caribbean Plate that shares all seismic, tectonic, and volcanic features.

What is the historical definition of the Caribbean?
The historical definition of the Caribbean refers to countries that have shared similar experiences of European colonisation, slavery, indentureship, and history of a plantation system.
What is the political definition of the Caribbean?
The political definition refers to the socio-economic and other groupings found in the region. For example countries that have shared a similar political systems like independent states, associated states, and dependents states.

What are some examples of Independent States?
Jamaica, Haiti, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, St Kitts and Nevis, Dominica , St Lucia, Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Grenada.
What are some associated states or some former british colonies.
Antigua, Grenada, Dominica, St Vincent, St Lucia. They have maintains a semi-independent political status while still being tied to Britain in certain areas such as defense and foreign affairs.
What are some examples of Britsih dependent states / colonial dependencies?
These states enjoys the rights and privileges of Great Britain. They are British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Anguilla, Montserrat and Turks and Caicos.
What are the four sub regions of the Caribbean
The lesser antilles, the greater antilles, the mainland territories, and other territories.
What Caribbean countries are comprised of the lesser antilles?
Barbados, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Grenada, Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Anguilla, and British Virgin Islands.
What Caribbean states are comprised of the Greater antilles ?
Jamaica, Hispaniola, Cuba, and Puerto Rico.

Give me an overview of the Historical Process.
Caribbean society formed out of the meeting and mixing of different groups of people from different societies and cultures in different parts of the world. Some of these groups were removed forcibly from their homelands, while others migrated voluntarily. This blend of Indigenous, African, European, and Asian influences shaped the diverse cultural landscape of the Caribbean. Hence why it is called a ‘melting pot’.
Describe the migratory movements and establishment settlements of different groups from the pre-Columbian time up to 1838.