Ecology Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
ecology def
the scientific study of interactions among orgs and the environment
field is always changing
field is always changing
2
New cards
ecological systems
biological entities that have their own internal processes and interact with their external surroundings
3
New cards
individual
a living being
__**the most fundamental unit of ecology**__
__**unit of natural selection**__
smallest level at which we can study ecology
\
__**the most fundamental unit of ecology**__
__**unit of natural selection**__
smallest level at which we can study ecology
\
4
New cards
individual species
a grp of orgs that interbreed with each other and produce fertile offspring
can be complicated: ex: dogs are same species but can look diff, some birds can look the same but are diff species
can be complicated: ex: dogs are same species but can look diff, some birds can look the same but are diff species
5
New cards
population
individuals of the same species living in a particular area
__**unit of evolution**__
evolution can impact the pop level→ when multiple individuals have adaptations that could influence at the pop level
factors: geographic range, abundance, density, change in size, composition
__**unit of evolution**__
evolution can impact the pop level→ when multiple individuals have adaptations that could influence at the pop level
factors: geographic range, abundance, density, change in size, composition
6
New cards
community
all pops of species living together in a particular area
all interact w each other
hard to pinpoint where one community starts and other begins→ can be very gradual
all interact w each other
hard to pinpoint where one community starts and other begins→ can be very gradual
7
New cards
ecosystem
one or more communities of living orgs interacting w their non living physical or chemical environments
__**Abiotic factors added**__
pH, salinity levels, soil levels, weather
__**Abiotic factors added**__
pH, salinity levels, soil levels, weather
8
New cards
landscape
mult ecosystems that are connected by the mvmt of individuals, pops, matter, and energy
mvmt of individuals key
mvmt of individuals key
9
New cards
biosphere
all the ecosystems on earth
landscapes interacting, climate, large scale migration
landscapes interacting, climate, large scale migration
10
New cards
individual approach to studying ecology
emphasizes the way in which an individuals morphology, physiology, and behavior enable it to survive in its environment
11
New cards
adaptation
a characteristic of an org that makes it well suited to its environment
12
New cards
population approach to studying ecology
emphasizes variation over time and space in the number, density, and composition of individuals
sex ratio, birth/death rates, immigration and emigration, genetic makeup
sex ratio, birth/death rates, immigration and emigration, genetic makeup
13
New cards
community approach to studying ecology
emphasis on diversity and relative abundances of diff kinds of orgs living together in the same place
how many species are there, looking at diversity in comm
how many species are there, looking at diversity in comm
14
New cards
ecosystem approach to studying ecology
emphasis on storage and transfer of energy and matter
15
New cards
landscape approach to studying ecology
concerned with the mvmt of energy, matter and individuals btwn diff ecosystems
16
New cards
biosphere approach to studying ecology
largest scale, mvmts of air and water and the energy and chemical elements they contain
17
New cards
weather
short term patterns of the atmosphere
time and location
variation over period of hours or days
time and location
variation over period of hours or days
18
New cards
climate
long term patterns of weather (30 y or more)
average weather
average weather
19
New cards
greenhouse effect
process of solar radiation striking earth, being converted into infrared radiation and being reabsorbed by atmospheric gases
20
New cards
factors that determine the climate of an area
latitude, land water distribution, atmospheric components, prevailing winds, ocean currents, altitude/topography
21
New cards
latitude influence on climate
the suns light is diffused towards the north and south poles
the suns rays are strongest at the equator and then diffused towards the top and bottom of the earth
\
during diff times of the year, earth is closer or farther away from the sun
the suns rays are strongest at the equator and then diffused towards the top and bottom of the earth
\
during diff times of the year, earth is closer or farther away from the sun
22
New cards
land-water distribution influence on climate
uneven heating drives weather and climate
\
land surface= low SH= quickly heat up
water= high SH= take longer to heat up
\
sc is by the coast- temps do not fluctuate as much
midwest varies a lot in temp
\
land surface= low SH= quickly heat up
water= high SH= take longer to heat up
\
sc is by the coast- temps do not fluctuate as much
midwest varies a lot in temp
23
New cards
specific heat
items with low specific heat will quickly warm up
high SH take longer to warm up
high SH take longer to warm up
24
New cards
atmospheric currents influence on climate
circulations of air
warm air rises= less dense= more active atoms
cold air sinks= more dense= less active atoms
\
at equator → heats up more
* hot air rises
* as it rises, it cools and condenses→ rain
* cool air sinks and begins to warm and flow back towards equator
* ^^process called hadley cells
warm air rises= less dense= more active atoms
cold air sinks= more dense= less active atoms
\
at equator → heats up more
* hot air rises
* as it rises, it cools and condenses→ rain
* cool air sinks and begins to warm and flow back towards equator
* ^^process called hadley cells
25
New cards
hadley cells
* hot air rises
* as it rises, it cools and condenses→ rain
* cool air sinks and begins to warm and flow back towards equator
30˚ N and 30˚ S
high pressure
creates deserts at 30 ˚ N and S
* as it rises, it cools and condenses→ rain
* cool air sinks and begins to warm and flow back towards equator
30˚ N and 30˚ S
high pressure
creates deserts at 30 ˚ N and S
26
New cards
intertropical convergence zone
area where 2 hadley cells converge and cause large amts of precipitation
27
New cards
global currents (air)
hadley cell- 0 and 30
ferrel cell - 30 and 60
polar cell- 60 and 90
\
low pressure = rain
high pressure= dry = air moving back down towards surface
\
ferrel cell - 30 and 60
polar cell- 60 and 90
\
low pressure = rain
high pressure= dry = air moving back down towards surface
\
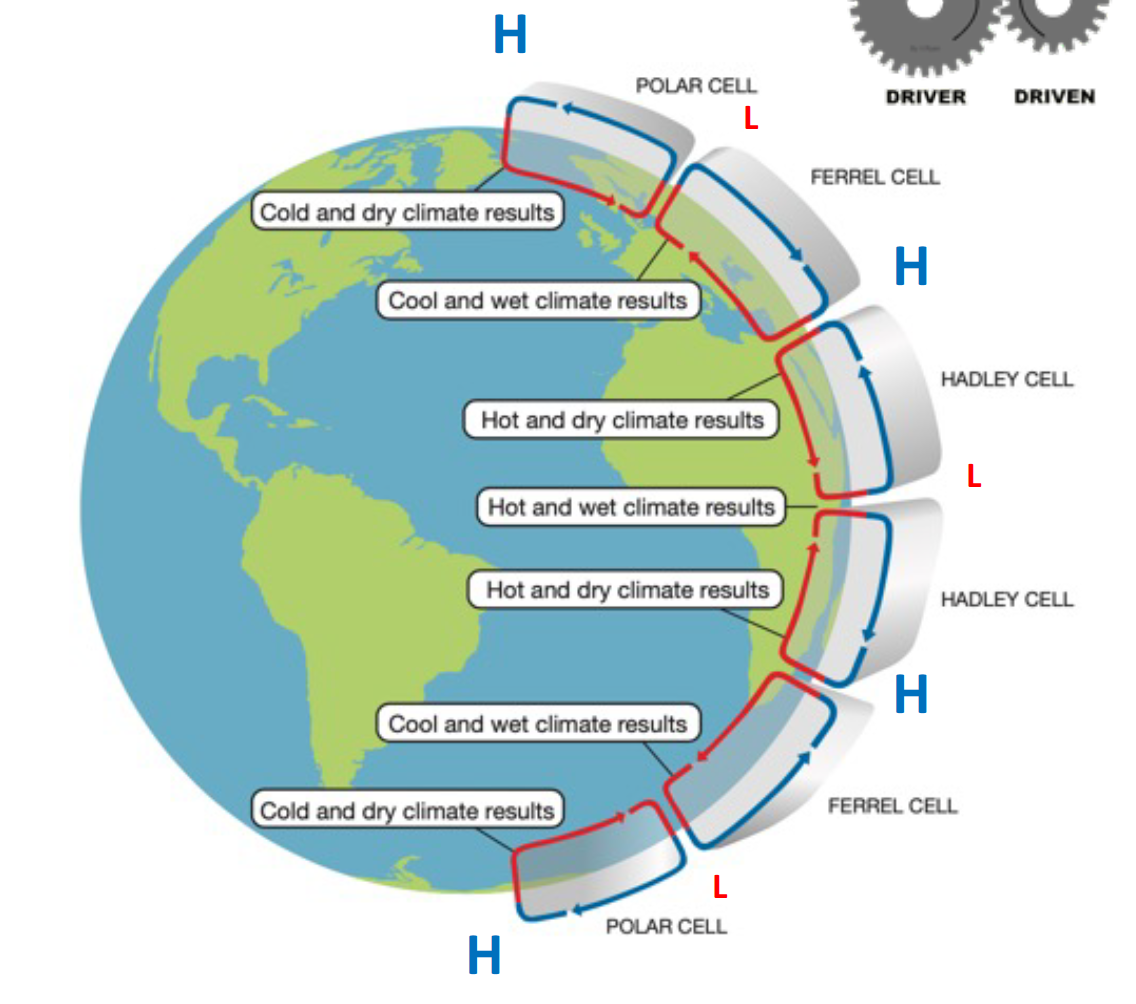
28
New cards
coriolis effect
the deflection of an obj path due to the rotation of the earth
\
north-
high P= clockwise
low P= counterclockwise
\
south-
high P= counterclockwise
low P= clockwise
\
north-
high P= clockwise
low P= counterclockwise
\
south-
high P= counterclockwise
low P= clockwise
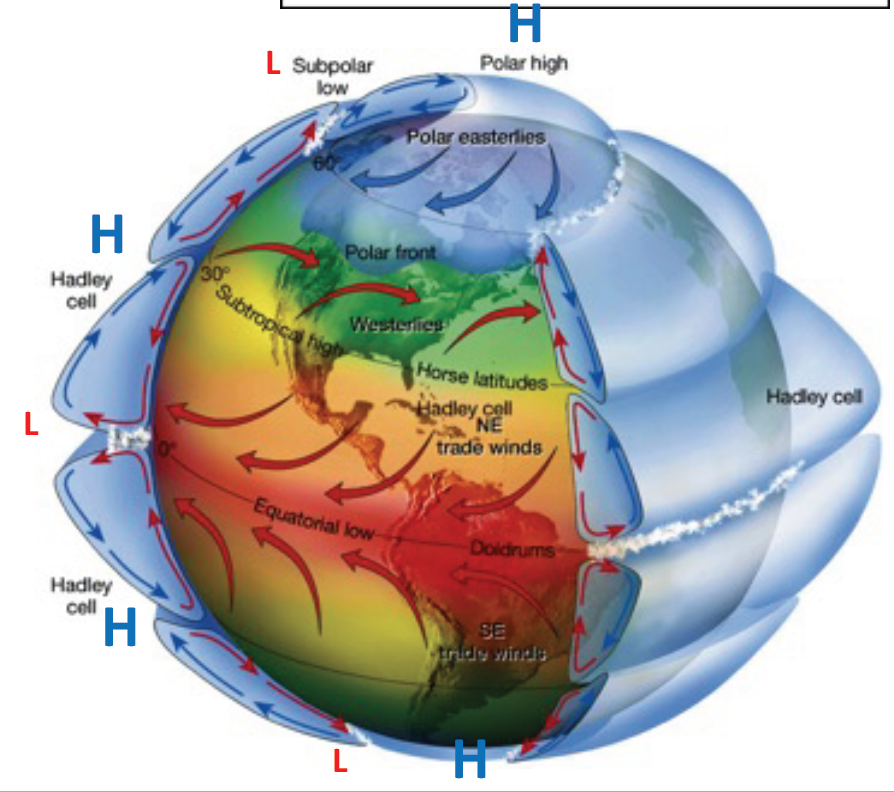
29
New cards
ocean currents
unequal heating, coriolis effect, predominant wind directions, topography of ocean basins, diffs in salinity
\
we have 8cm more of water at equator
high heat moves to low heat
\
thermohaline circulation- global pattern of surface and deep water currents that flow as a result of variations in temp and salinity that change the density of H2O
* if some cities are on same latitude, why do they not have the same temp?→ warm water flows towards europe, cool water towards NA
\
we have 8cm more of water at equator
high heat moves to low heat
\
thermohaline circulation- global pattern of surface and deep water currents that flow as a result of variations in temp and salinity that change the density of H2O
* if some cities are on same latitude, why do they not have the same temp?→ warm water flows towards europe, cool water towards NA
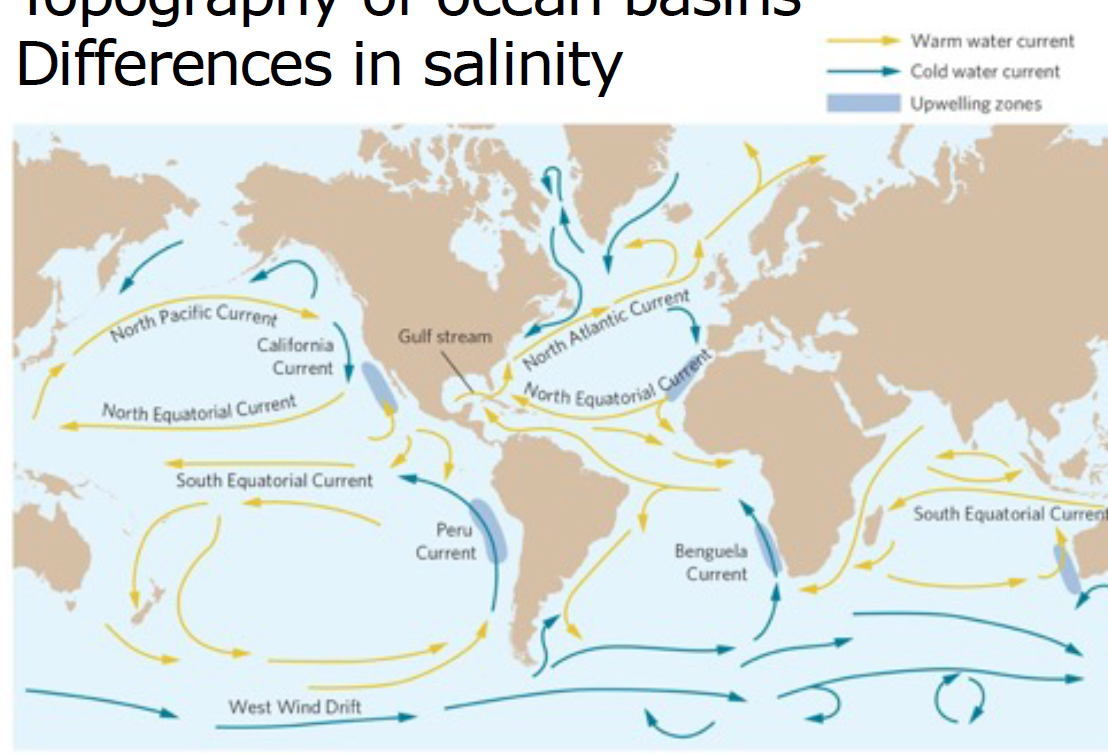
30
New cards
altitude
higher elevation= less SA= less infrared radiation = colder the temp
31
New cards
rain shadow effect
a region w dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean, causing precipitation on the windward side
32
New cards
biome
geographic region that contains communities composed of orgs w similar adaptations
categorized by major plant growth forms
categorized by major plant growth forms
33
New cards
convergent evolution
a phenomenon in which 2 species that are not releated, look similar due to similar selective forces they have evolved under
34
New cards
what are limiting factors of plant growth?
sunlight and moisture
35
New cards
tropical rainforest biome
close to equator (amazon)
warm and humid, large amts of rain
neutral, not nutrient rich soil due to vegetation quickly taking up nutrients
greatest biodiversity
poison frongs, jaguar, sloth
warm and humid, large amts of rain
neutral, not nutrient rich soil due to vegetation quickly taking up nutrients
greatest biodiversity
poison frongs, jaguar, sloth
36
New cards
desert biome
midlatitudes (sahara)
very dry and arid, high rates of evaporation
soil is rich in minerals
cacti, tumbleweeds
tortoise, fennec fox, gila monster
very dry and arid, high rates of evaporation
soil is rich in minerals
cacti, tumbleweeds
tortoise, fennec fox, gila monster
37
New cards
tropical seasonal forest: savanna biome
africa, northern australia
warm all year round, dry and wet season
porous, low fertility soil
eucalyptus trees, grasses, baobob trees
warthogs, sebras, elephants
warm all year round, dry and wet season
porous, low fertility soil
eucalyptus trees, grasses, baobob trees
warthogs, sebras, elephants
38
New cards
woodland- shrubland biome
west coastal regions (southern cal, mexico)
hot and dry summers, cool moist winters , little rain
fertile, mildly acidic soil
shrubs and short trees
deer, goats, amphibians
hot and dry summers, cool moist winters , little rain
fertile, mildly acidic soil
shrubs and short trees
deer, goats, amphibians
39
New cards
temperate grassland biome
midlatitudes (midwest, nebraska)
cold winters, warm summers, some rain
deep and dark fertile soil
buffalo grass, sunflowers
deer, prairie dogs
cold winters, warm summers, some rain
deep and dark fertile soil
buffalo grass, sunflowers
deer, prairie dogs
40
New cards
northern coniferous forest biome
northern continents (pacific northwest of america)
cool and moist all year
fungi
pine, spruce, fir, hemlock
black bear, red fox, grizzly bear, bobcat
cool and moist all year
fungi
pine, spruce, fir, hemlock
black bear, red fox, grizzly bear, bobcat
41
New cards
temperate seasonal forest
eastern NA
mild winters, hot and humid summers
rich soil
broadleaf trees, mosses, mountain laurel
raccoon, moose, mountain lion, squirrel
mild winters, hot and humid summers
rich soil
broadleaf trees, mosses, mountain laurel
raccoon, moose, mountain lion, squirrel
42
New cards
Tundra
poles of earth
subfreezing temps and low precipitation
nutrient poor soil
arctic moss, cotton grass, lichen
arctic hare, arctic wolf, reindeer
subfreezing temps and low precipitation
nutrient poor soil
arctic moss, cotton grass, lichen
arctic hare, arctic wolf, reindeer
43
New cards
temperate rainforest
along coastlines, new zealand, pacific coast in NA
long wet winter, short dry summer
fertile soil
sequoia trees, douglas fir , mosses, evergreen huckleberry
flying squirrels, great horned owls, black bear
long wet winter, short dry summer
fertile soil
sequoia trees, douglas fir , mosses, evergreen huckleberry
flying squirrels, great horned owls, black bear
44
New cards
what properties affect how aquatic orgs live?
density
viscosity
depth
inorganic nutrients
temp
viscosity
depth
inorganic nutrients
temp
45
New cards
density
covalent bonds btwn O and Hs in H2O
hydrogen bond btwn 2 h2O molecules
\
less dense obj= floats
dense obj= sinks
swim bladder in fish
* filled with o2= less dense= floats
* deflated swim bladder= denser= sinks
\
manatees fart to sink in the water
hydrogen bond btwn 2 h2O molecules
\
less dense obj= floats
dense obj= sinks
swim bladder in fish
* filled with o2= less dense= floats
* deflated swim bladder= denser= sinks
\
manatees fart to sink in the water
46
New cards
viscosity
the thickness of a fluid that causes obj to encounter resistance as they move through it
\
streamline moves better
large projections= causes drag
\
streamline moves better
large projections= causes drag
47
New cards
depth
conditions:
no light, cold, high pressure, limited O2
\
anglerfish- produce own light
coral- uses sulfur
deep sea snailfish- has gap in skull, as they get deeper pieces overlap, bones made of cartilage, hypermobile
no light, cold, high pressure, limited O2
\
anglerfish- produce own light
coral- uses sulfur
deep sea snailfish- has gap in skull, as they get deeper pieces overlap, bones made of cartilage, hypermobile
48
New cards
inorganic nutrients
water is powerful solvent - can dissolve many subs
water is polar
salt breaks up water structure
\
osmoregulation- the mechs that orgs use to maintain proper solute balance
* fish in high solute enviornment- excrete most of solute out in urine, take in water through mouth , solutes goes out through gills and urine
* fish in low solute enviornment= retain most of solute taken in via gills and mouth
water is polar
salt breaks up water structure
\
osmoregulation- the mechs that orgs use to maintain proper solute balance
* fish in high solute enviornment- excrete most of solute out in urine, take in water through mouth , solutes goes out through gills and urine
* fish in low solute enviornment= retain most of solute taken in via gills and mouth
49
New cards
osmosis
mvmt of H2O across a semi permeable mem
__**water will move from low solute conc to high solute conc**__
__**water will move from low solute conc to high solute conc**__
50
New cards
mangrove salinity adaptation
water has high salinity, water is going to want to flow out of the mangrove
not good for mangrove
mangrove will expend a lot of energy to inc internal conc in order to move water in
have to expel excess salt from water inside through their leaves
not good for mangrove
mangrove will expend a lot of energy to inc internal conc in order to move water in
have to expel excess salt from water inside through their leaves
51
New cards
pH
high H= acidic
low H= alkaline
\
low number= acidic
high number= alkaline
low H= alkaline
\
low number= acidic
high number= alkaline
52
New cards
CO2 in water
H2CO3 unstable→ add H
H added which makes pH dec (more acidic) → coral bleaching
H added which makes pH dec (more acidic) → coral bleaching
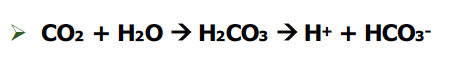
53
New cards
O2 in water
higher temps= less O2
deeper= less O2
\
shallow cold water holds O2 better than shallow warm water
deeper water holds onto O2 better, but far from surface where O2 is
deeper= less O2
\
shallow cold water holds O2 better than shallow warm water
deeper water holds onto O2 better, but far from surface where O2 is
54
New cards
countercurrent circulation
adaptation to O2
mvmt of 2 fluids in opp directions on either side of a barrier thorugh which heat or dissolved subs (O2) are exchanged
mvmt of 2 fluids in opp directions on either side of a barrier thorugh which heat or dissolved subs (O2) are exchanged
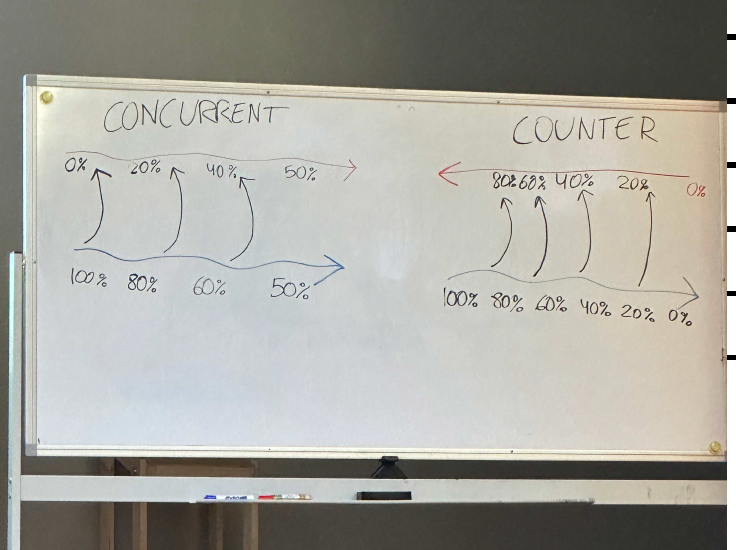
55
New cards
thermoregulation
the ability of an org to control the temp of its body
cold temps:
* fat/blubber
* high metabolism→ generates heat
* countercurrent circulation
\
glycerol prevents hydrogen bonds from coming together to freeze
glycoproteins- lower freezing temp of water→ allow fish to be frozen solid but cells are not perforated so fish lives
→ supercooling- a process in which glycoproteins in the blood impede ice formation by coating any ice crystals that begin to form
thermal optimum- range of temps within orgs perform best
\
\
cold temps:
* fat/blubber
* high metabolism→ generates heat
* countercurrent circulation
\
glycerol prevents hydrogen bonds from coming together to freeze
glycoproteins- lower freezing temp of water→ allow fish to be frozen solid but cells are not perforated so fish lives
→ supercooling- a process in which glycoproteins in the blood impede ice formation by coating any ice crystals that begin to form
thermal optimum- range of temps within orgs perform best
\
\
56
New cards
liebigs law of the minimum
if one of the essential plant nutrients is deficient, plant growth will be poor, even if all the other essential nutrients are abundant
57
New cards
essential nutrients of plants
O2
C
H
N
P
Ca
K
C
H
N
P
Ca
K
58
New cards
water potential
a measure of water’s potential energy which indicates its tendency to move from one area to another
gravity- high grav=more likely to move
pressure- high pressure= more likely to move
osmotic potential- higher OP= more likely to move
matric potential - higher MP= more likely to move
gravity- high grav=more likely to move
pressure- high pressure= more likely to move
osmotic potential- higher OP= more likely to move
matric potential - higher MP= more likely to move
59
New cards
matric potential
the potential energy generated by the attractive forces btwn water molecules and soil particles
electrical charges
electrical charges
60
New cards
field capacity
the max amt of water held by soil particles against the force of gravity
61
New cards
wilting point
the water potential at which most plants can no longer retrieve water from the soil
62
New cards
soil texture and water intake
silt= larger gaps= less SA= water flows through= oxygenated
clay= no gaps= more SA= water retained= deoxygenated
\
less gaps= more SA= more water retained
clay= no gaps= more SA= water retained= deoxygenated
\
less gaps= more SA= more water retained
63
New cards
cohesion tension theory
mechanism of h2o mvmt from roots to leaves due to __**water cohesion and water tension**__
\
gradient differential pulls H2o into roots
tension pulls H2O up in xylem
tension cont to pull h2O up through leaf veins and water diffused out of the stoma
\
gradient differential pulls H2o into roots
tension pulls H2O up in xylem
tension cont to pull h2O up through leaf veins and water diffused out of the stoma
64
New cards
65
New cards
how does water move in dry or saline soil?
lower water potential of roots → build up of nutrients
nutrients will build up internal concentration which will bring in h2o from soil ( water from low sol to high sol)
nutrients will build up internal concentration which will bring in h2o from soil ( water from low sol to high sol)
66
New cards
C3 plants
most common, most efficient in wet, cool climates
photosynthesis occurs normally
photosynthesis occurs normally
67
New cards
C4 plants
plant shielded from O2 buildup
Co2 moved to bundle sheath cells
stoma closed, buildup of CO2
do best in hot sunny climates
\
Co2 moved to bundle sheath cells
stoma closed, buildup of CO2
do best in hot sunny climates
\
68
New cards
CAM plants
changes timing of photosynthesis
assimilation of CO2 happens at night
allows plant to grow in dry environments
assimilation of CO2 happens at night
allows plant to grow in dry environments
69
New cards
terrestrial plant adaptations to temperature
improve water intake and retention
* long roots search for more water vs horizontal shallow roots vs horizontal roots that collect water immediatly when it rains
reduce transpiration
* leaves with spikes/hairs retain moisture better
* thick waxy leaves hold onto water better
reduce buildup of heat in tissue
* long roots search for more water vs horizontal shallow roots vs horizontal roots that collect water immediatly when it rains
reduce transpiration
* leaves with spikes/hairs retain moisture better
* thick waxy leaves hold onto water better
reduce buildup of heat in tissue
70
New cards
kangaroo rat adaptations - water and salt
live in deserts- water is scarce
rats never drink water!
urinate crystals
nose has folds- so much SA that the water vapor in breath condensates in nose and they swallow it
\- get all the water from their food
extremely long loop of henley- where water gets reabsorbed in kidneys-> longer the loop, the more water reabsorbed
rats never drink water!
urinate crystals
nose has folds- so much SA that the water vapor in breath condensates in nose and they swallow it
\- get all the water from their food
extremely long loop of henley- where water gets reabsorbed in kidneys-> longer the loop, the more water reabsorbed
71
New cards
homeotherm
can maintain constant body temp
72
New cards
endotherm
use metabolic heat to raise body temp
73
New cards
poikilotherm
no constant body temp
do not have constant body temp, do not have as narrow of a range as homeotherms
do not have constant body temp, do not have as narrow of a range as homeotherms
74
New cards
ectotherm
body temp determined by environment
75
New cards
heterotherm
-sometimes constant, sometimes rely on environment
ex: bat
76
New cards
radiation
emission of EM energy by a surface
77
New cards
conduction
the transfer of the kinetic energy of heat btwn substances that are __**in contact**__ with one another
78
New cards
convection
transfer of heat by mvmt of __**liquids and gases**__
79
New cards
evaporation
the transformation of water from liquid to a gaseous state w input of heat energy
80
New cards
acclimation
an environmentally induced change in an individuals physiology
\
goldfish exp:
goldfish at 5 deg C, others at 25 deg C
goldfish at 5 deg had cold water isozymes
goldfish at 25 had warm water isozyme
when raced, 5 deg goldfish performed better
in cold water conditions and 25 deg
performed best at warmer temps
\
goldfish exp:
goldfish at 5 deg C, others at 25 deg C
goldfish at 5 deg had cold water isozymes
goldfish at 25 had warm water isozyme
when raced, 5 deg goldfish performed better
in cold water conditions and 25 deg
performed best at warmer temps
81
New cards
SA to vol ratio
SA inc by 2
vol inc by 3
\
colder you are the less surface area you want and more volume
* if you are in the tundra, you do not want a lot of skin showing, but you want a lot of puffy coats
the warmer you are the more SA you want and less volume
* in the desert, you want more skin showing(shorts) and no puffy coats
vol inc by 3
\
colder you are the less surface area you want and more volume
* if you are in the tundra, you do not want a lot of skin showing, but you want a lot of puffy coats
the warmer you are the more SA you want and less volume
* in the desert, you want more skin showing(shorts) and no puffy coats
82
New cards
blood shunting
we can close precap sphincters, cutting off circulation
to extremeties in favor of keeping organs warm
to extremeties in favor of keeping organs warm
83
New cards
microhabitat
a specific location within a habitat that typically differs in environmental conditions from other parts of the habitat
\
\
84
New cards
migration
seasonal mvmt of animals from one area to another
85
New cards
dormancy
a condition in which orgs dramatically reduce their metabolic processes
diapause
hibernation
torpor
aestivation
diapause
hibernation
torpor
aestivation
86
New cards
diapause
insects
dormancy in period of unfavorable environmental conditions
dormancy in period of unfavorable environmental conditions
87
New cards
hibernation
mammals
reduce the energetic costs of being active by lowering their heart rate and dec their body temp
reduce the energetic costs of being active by lowering their heart rate and dec their body temp
88
New cards
torpor
birds and mammals
brief period of dormancy where individuals reduce their activity and body temp
brief period of dormancy where individuals reduce their activity and body temp
89
New cards
aestivation
summer
the shutting down of metabolic processes during the summer in response to hot or dry conditions
the shutting down of metabolic processes during the summer in response to hot or dry conditions
90
New cards
life history
schedule of an orgs growth, development, reproduction, and survival
can look at age and size at maturity, number and size of offspring, and lifespan/reproductive investment
can look at age and size at maturity, number and size of offspring, and lifespan/reproductive investment
91
New cards
fecundity
the number of offspring produced by an org per reproductive episode
\
every time i give birth, how many offspring come of it?
\
every time i give birth, how many offspring come of it?
92
New cards
parity
the number of reproductive episodes that an org experiences
\
how many times do you give birth?
\
how many times do you give birth?
93
New cards
parental investment
the amt of time and energy given to an offspring by its parents
\
do i take care of you?
\
do i take care of you?
94
New cards
longevity
the life span of an org, also known as life expectancy
95
New cards
variation in life history
how orgs allocate energy to growth, survival and reproduction
variation within species in how orgs allocate energy-
genetic reasons- certain amt of offspring at a time
environmental reasons- if enviornmental conditions favorable, then more energy allocated to growth
mix of both
variation within species in how orgs allocate energy-
genetic reasons- certain amt of offspring at a time
environmental reasons- if enviornmental conditions favorable, then more energy allocated to growth
mix of both
96
New cards
what are the life history categories?
r selection and K selection
97
New cards
r selection
high rates of pop growth, reproduce fast
die at young age, energy invested in amt of offspring
early maturation, low parental investment
mice, weedy plants
die at young age, energy invested in amt of offspring
early maturation, low parental investment
mice, weedy plants
98
New cards
k selection
slow rates of pop growth
long lived, develop slowly
late maturation
invest heavily in each offspring
large mammals
long lived, develop slowly
late maturation
invest heavily in each offspring
large mammals
99
New cards
the r selection and k selection are on a ……
continuum.
multiple orgs fall in between these categories
multiple orgs fall in between these categories
100
New cards
stress tolerators plants
grow in non ideal conditions (low pH, high solute, dry soil)
cannot allocate energy towards growing fast, growth is slow
sexual maturity is late, not many seeds
__**HIGH asexual reproduction**__
\
cannot allocate energy towards growing fast, growth is slow
sexual maturity is late, not many seeds
__**HIGH asexual reproduction**__
\