MCB 181: Exam 3 Practice Questions
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Why must gene expression be controlled in single-celled organisms?
A. ensure all genes are expressed at all times for maximum efficiency
B. prevent mutations from occurring in DNA sequence
C. allow them to respond to real-time environmental factors
D. ensure that every cell in a multicellular organism performs the same function
C
ALL cells (prokaryotes/eukaryotes) must be able to adjust which genes to express to respond in real time to environmental factors
Which of the following is an example of positive regulation of transcription?
A. an activating transcription factor binding to the promoter
B. epigenetic modifications that silence gene expression
C. addition of 5’ cap for mRNA stability
D. transcription factor enhancing tRNA activity
A
positive regulation: transcription is stimulated +
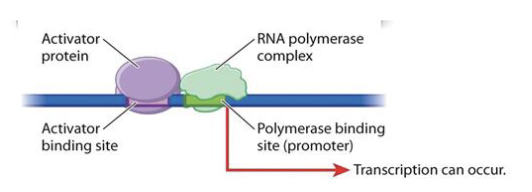
T/F: Prokaryotes regulate gene expression through mRNA splicing to removed introns before translation.
False
mRNA processing is only in eukaryotes
T/F: The promoter is a regulatory protein that attaches to a specific DNA sequences near the start of a gene to activate its expression when the cell needs it.
False
promoter = sequence of DNA
Which of the following gene regulation mechanisms are found only in eukaryotic cells and not in prokaryotic cells?
I. alternative splicing
II. addition of 5’ cap
III. epigenetic regulation
ALL
Skin cells and pancreatic cells have different
A. genes
B. mRNA
C. proteins
B/C
What would be a prokaryotes “activator sequence?”
A. transcription factor
B. enhancer
C. gene
D. 5’ cap
B: enhancer
T/F: Transcription in prokaryotes is rapidly turned on/off in response to environmental changes and involves both positive and negative regulators.
True
T/F: Gene regulation can occur only during transcription and translation.
False
transcriptional level
post-transcriptional level
translation level
post-translational level
T/F: Gene regulation in multicellular organisms leads to differential gene expression and specialized cell functions.
True
The type of gene regulation in which transcription of a gene depends on the presence of a particular combination of enhancers and other regulatory transcription factors is known as:
combinatorial control
T/F: A typical eukaryotic gene may be regulated by multiple enhancers and silencers of different kinds, each with one or more regulatory TFs that can interact with it.
True
The lac operon in E. coli is responsible for breaking down lactose. Which of the following mutations would most likely result in the constant expression of the lac operon, regardless of lactose availability?
A. a mutation in lacP that reduces RNA poly. binding efficiency
B. mutation in lacI that prevents it from binding to lacP
C. mutation in repressor that permanently binds it to the operator sequence
D. mutation in lacO that prevents the repressor from binding
D. mutation in lacO that prevents the repressor from binding
can’t stop
CRP, an activator of the lac operon, binds to the CRP binding site (an activator sequence) to enhance transcription when lactose is present and glucose is low. Suppose a mutation occurs that prevents CRP from binding to its site. What is the most likely effect of this mutation on lac operon transcription?
A. The lac operon will be transcribed at high levels whenever lactose is present since the repressor is unbound
B. The lac operon will have reduced transcription, even when glucose levels are low
C. The lac operon will have reduced transcription because transcription cannot occur in the absence of lactose
D. The mutation will have no effect because CRP does not regulate transcription
B
reduce transcription
T/F: A mutation in an enhancer sequence that prevents the binding of associated activating transcription factors would likely lead to lower transcriptional rates of the gene.
True
reduce transcription
T/F: The binding of silencers to repressor DNA sequences negatively regulates gene expression.
False
lac operon can’t be transcribed
Which of the following are ways that a eukaryotic cell can control whether and/or how it uses a gene in the DNA to make a functional protein? Select all that apply.
A. removing the gene from the nucleus if it’s not needed
B. controlling which transcription factors are available in the cell to bind
to the gene’s regulatory sequences
C. alternatively splicing the mRNA transcript
D. altering the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA
E. controlling the stability of the mRNA transcript
F. blocking initiation factors from binding to the 5’ cap of the mRNA
transcript
G. modifying the protein product after translation to change its activity
B, C, E, F, G
T/F: Eukaryotes, but not prokaryotes, can control which genes in their genome are transcribed at any given moment.
False
What is the function of a gene’s promoter?
A. a gene’s promoter is a protein that binds to the DNA to
promote transcription of the gene
B. a gene’s promoter is the sequence of DNA where RNA
polymerase binds and begins transcription of the gene
C. a gene’s promoter is a sequence of DNA where an
activator protein binds to increase transcription of the
gene
B: where RNA poly. binds to start transcription
T/F: When lactose is not present in the environment, the lac genes aren’t transcribed because the repressor won’t bind to lacO.
False
bc the RNA poly. won’t bind to lacO
Which of the following mutations will allow transcription of the lacZ
and lacY genes to proceed regardless of whether lactose is present?
A. a mutation in lacO that prevents the repressor from binding
B. a mutation in lacI that produces a protein that can’t bind lactose
C. a mutation in lacI that produces a protein that can’t bind to lacO
A/C
How do enhancers contribute to the regulation of gene expression?
an enhancer is a region of eukaryotic DNA associated with a gene that positively regulates that genes transcription when bound to its unique transcription factor
Pancreatic B cells specialize in making and secreting insulin peptides. Layers of epithelial cells can be found in places like the lining of the intestines and in skin. Which of the following would you predict about the chromatin containing the insulin gene in these two different types of cells?
open in pancreatic cells & condensed in epithelial cells
FOXP2, a gene involved in brain development, has 2 enhancers that regulate its transcription. If a neuron (brain cell) has open chromatin in the DNA region where FOXP2 is located, but has condensed chromatin in the DNA region where its associated enhancers are, what do you predict this means for the transcription of FOXP2?
low/ no transcription
How would histone tail acetylation affect the transcription of a gene associated with (wrapped around) those histones?
acetylating histone tails will most likely increases the transcription of the gene associated with it
A researcher is studying how exercise levels affect epigenetic regulation of certain genes. They have found the CpG sites near the gene MT-ND6 have much lower rates of methylation in people who exercise more. Which of the following would the researcher predict based on this finding?
the MT-ND6 gene has higher expression in people who exercise more
T/F: Chemical changes to the histone proteins or DNA bases can lead to chromatin remodeling.
True
acetylation histone tails & methylating CpG sites
Scientists want to study gene expression in newly discovered species. Which of the following epigenetic modifications would most likely open chromatin & promote transcription?
A. DNA methylation
B. histone acetylation
C. histone deacetylation
D. addition of 5’ cap
B. histone acetylation
A liver cell and a neuron both contain the gene for digestive enzyme. However, this enzyme is only needed in the liver. What is the most likely chromatin state of this gene in the neuron?
condensed chromatin bc the neuron doesn’t need to express this gene
Which of the following is false regarding the methylation of CpG sites?
A. Methylation of CpG sites prevents activating transcription factors from binding to the promoter
B. Methylation of CpG sites increases repressor binding
C. methylation of CpG sites recruits histone-modifying enzymes to open chromatin
D. methylation of CpG sites decreases gene expression
C. methylation of CpG sites recruits histone-modifying enzymes to open chromatin
T/F: CpG methylation can change in response to environmental cues, providing a way to turn gene transcription on/ off in real time.
True
DNA replication is semi-conservative. What does this mean?
each newly synthesized DNA molecule is composed of one original strand & one newly synthesized strand
one parent strand + one daughter strand
What is the function of DNA polymerase’s?
A. form phosphodiester bonds btwn adjacent nucleotides to build daughter strands
B. transcribe parent strand into RNA
C. remove RNA primer from newly formed daughter strand
A. form phosphodiester bonds btwn adjacent nucleotides to build daughter strands
T/F: DNA can only be synthesized in 5’ to 3’ direction.
True
Why is lagging strand necessary in DNA replication?
DNA is antiparallel & both strands are used as templates simultaneously, yet DNA synthesis can only occur 5’ to 3’
T/F: Actively dividing cells proceed through the following stages of the cell cyle: G1, interphase, G2, & M phase.
False
interphase & M phase
T/F: Nucleotides are added to the growing strand through the formation of a peptide bond.
False
phosphodiester bonds
T/F: Synthesis of the growing strand occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
True
DNA is made 5’ to 3’
T/F: Complementary base pairing with template DNA facilitates the synthesis of the growing strand.
True
need complementary base pairing
T/F: The DNA template strand is read in the 3’ to 5’ direction during transcription, but in the 5’ to 3’ direction for DNA replication.
False
DNA is ALWAYS read 3’ to 5’
Which protein involved in DNA replication connects discontinuous fragments of DNA together?
DNA ligase
Which protein involved in DNA replication relieves the stress of unwinding from the replication fork?
Topoisomerase
Which protein involved in DNA replication prevents unwound DNA strands from rejoining?
single-stranded binding proteins
Which protein involved in DNA replication unwinds the DNA double helix?
helicase
Which protein involved in DNA replication adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of an RNA primer?
DNA polymerase
Researchers are studying the activity of RNA primase in leading and lagging strands, and they have come to you for expertise. Based on your understanding of RNA primase, what insights would you offer?
RNA primase will be more active in lagging strand synthesis because multiple RNA primers are needed to initiate each discontinuous fragment of the DNA.
Order the phases of the cell cycle from first to last.
M phase, S phase, G2, G0, G1
GO, G1, S phase, G2, M phase
Replication of DNA in eukaryote occurs during which phase of cell cyle?
A. s phase
B. g2
C. m phase
D. g1 phase
S phase
Before a cell can enter of the M phase, what must occur?
A. cell must replicate chromosomes
B. cell must be fertilized
C. nucleus must divide
D. nuclear envelope mist disintegrate
E. sister chromatids must be separates
A. cell must replicate chromosomes
What is the first thing to occur in DNA replication?
strands of DNA double helix are separated by helicase
Which of the strands uses a template for DNA replication?
A. lagging strand
B. leading strand
C. both
c. both
On which strand are new nucleotides being added in the same direction as the replication fork is opening?
leading strand
RNA primase lays down an RNA primer to start DNA replication. If a mutation occurs that blocks the function of RNA primase, which synthesis of which strand is affected? why?
both bc DNA polyerase can only add new nucleotides to a 3'‘ -OH present at the end of the RNA primer
The lagging strand has its ___ end pointed toward the replication fork and is synthesized ____
5’ & segments
The leading strand will have ___ RNA primer(s) and lagging strand will have ___ RNA primer(s).
one & many
Which enzymes relieves the tension on the double helix during DNA replication?
topoisomerase
Order the enzymes based on what order they work in during DNA replication
DNA poly., primase, ligase, helicase
helicase, primase, DNA poly., ligase
Loss of function of which of these enzymes would prevent the addition of DNA nucleotides in DNA replication?
DNA ligase, RNA primase, DNA polymerase. helicase
RNA primase, DNA polymerase. helicase
What does DNA ligase do?
joins DNA fragments together
What is one similarity and one difference between transcription and DNA replication?
Similarity: both processes involve DNA and RNA
Difference: one is involved in the central dogma and the other is involved in cell cycle
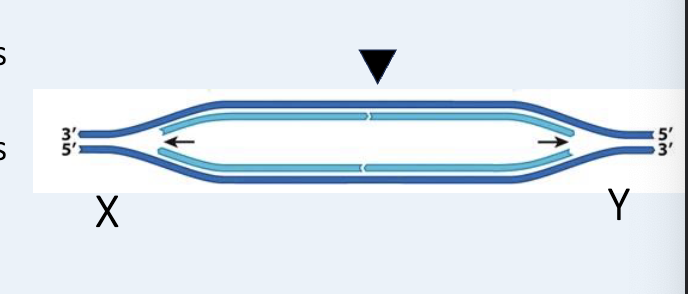
For the figure, indicate whether the bottom strand is leading or lagging at X and Y replication forks.
@ X bottom strand is leading and @ Y its lagging
T/F: To the right of the origin (dotted line), the lagging strand is synthesized on the bottom strand.
False
What is chromatin?
dense fiber formed by DNA wrapped around histones
How are sister chromatids related to one another?
one is an exact replica of the other, made during S phase
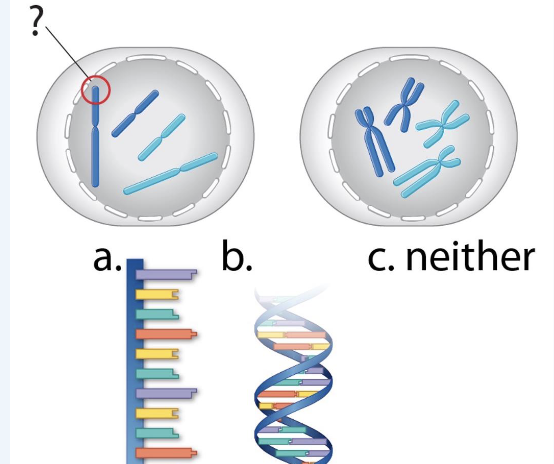
If you were to zoom in one the circled part of chromosomes, what would it look like?
B - double helix
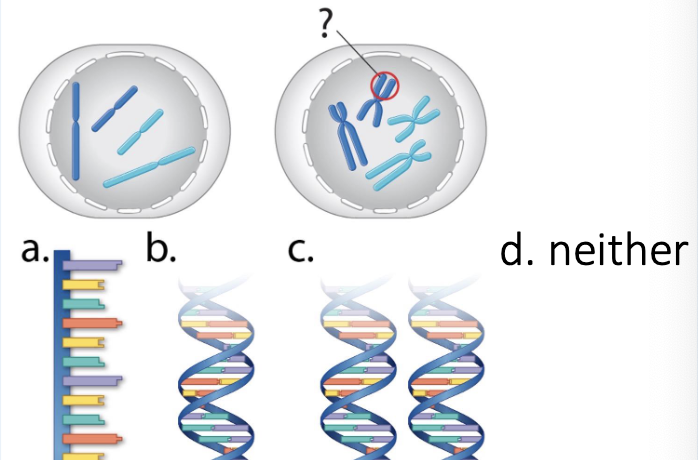
If you were to zoom in one the circled part of chromosomes, what would it look like?
C. two chromosomes so 2 double helixes
Which cytoskeletal element forms the contractile ring?
actin microfilaments
Which of the statements are true of mitotic cell division?
A. it is a form of sexual reproduction and produces gamete
B. process that ends once organism’s development is complete & no longer occurs in adult organisms
C. results in 2 daughter cells that are not genetically identical
D. requires e/a of 46 chromosomes are duplicated during S phase
D. 46 chromosomes have to be duplicated
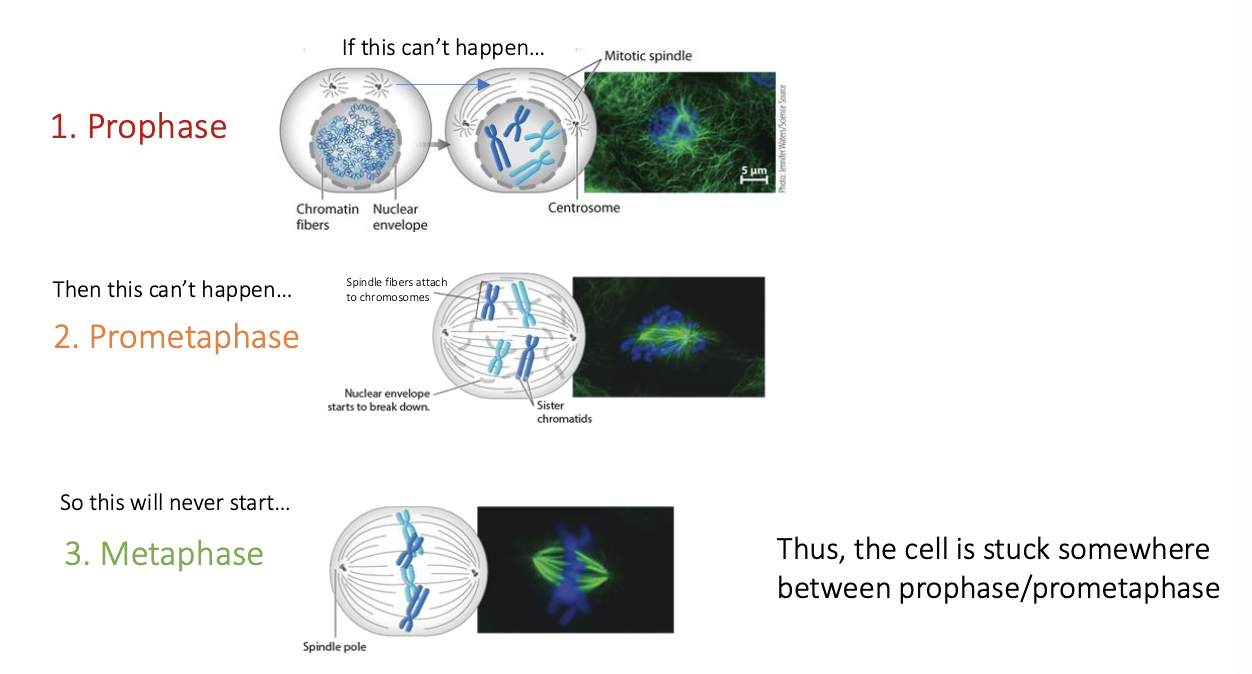
Colchicine is a drug that blocks the assembly of microtubules. If dividing cells are treated with colchicine, at which stage of mitosis would you predict the arrest would occur?
Prophase
Which of the scenarios below would most likely contribute to uncontrolled cell proliferation (cancer)?
A. mutant cyclin that cannot bind to its normal CDK binding partner
B. mutant enzyme needed for microtubule synthesis/polymerization
C. mutant CDK that was active in the absence of its cyclin binding partner
D. mutant DNA synthesis mechanism causing blocked chromosome replication
E. mutant centromere that causes reduced microtubule attachment
C. mutant CDK
T/F: CDK levels remain fairly constant throughout the cell cycle.
True. CDK is dependent
Which of the following would be most likely to lead to cancer?
A. activation of a tumor suppressor gene
B. activation of a proto-oncogene
C. activation of an oncogene and the inactivation of a tumor suppressor gene
D. activation of an oncogene and a tumor suppressor gene
C - activation of an oncogene and the inactivation of a tumor suppressor gene
Fill in the blanks.
When a growing Okazaki fragment comes into contact with the ____ of the previous fragment, this sequence is removed and ____ replaces it with _____.
RNA primer, DNA polymerase, DNA nucleotides
T/F: The leading strand is the daughter strand with its 3’ end pointed towards the replication fork and can be synthesized continuously.
True - 3’ end toward fork
Which statement is FALSE about DNA replication?
A. DNA can only be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction
B. The lagging strand requires DNA ligase activity
C. DNA polymerase replicates DNA one strand at a time
D. Okazaki fragments refer to the pieces of the lagging strand
C. both strands
Which of the following functions does DNA polymerase perform?
A. forming phosphodiester bonds between DNA nucleotides
B. proofreading errors during daughter strand synthesis
C. initiating DNA synthesis
D. removing RNA primer
A, B, D
Which of the statements is true regarding telomeres?
A. telomeres are enzymes that repair telomerases, which cap the end of linear chromosomes
B. telomeres shorten with every cell division in somatic cells because telomerase is less active
C. telomeres are typically only a few base pairs in size and contain unique sequences
D. telomere repeats are added to the same extent in germ cells and somatic cells
B!
Zebrafish undergo mitotic cell division for growth and tissue repair. Before mitosis, a zebrafish cell contains 50 chromosomes, organized into 25 pairs. After mitosis, how many chromosomes will be present in each of the daughter cells?
50
During which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope break down?
prometaphase
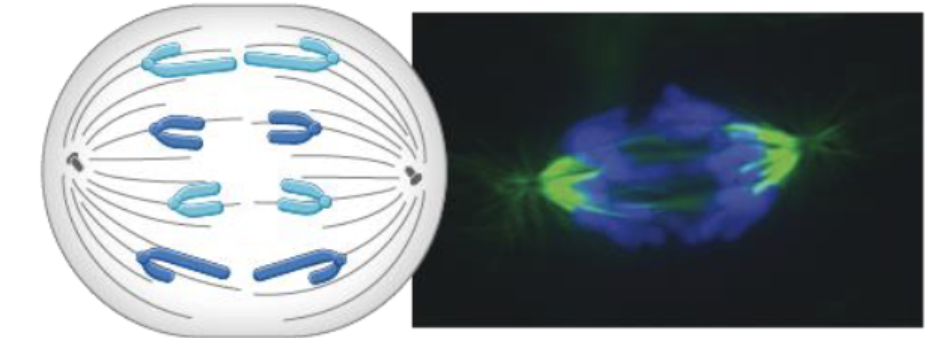
In the figure below, what events are taking place during this phase of mitosis?
separation of sister chromatids = anaphase
T/F: At the end of mitosis, each daughter cell is genetically identical, each receiving two sister chromatids per chromosome.
False
Fill in the blanks.
The amount of ___ varies throughout the cell cycle, but the amount of ___ is fairly constant.
cyclin & CDK