2.01 Disorders of the eyelids
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
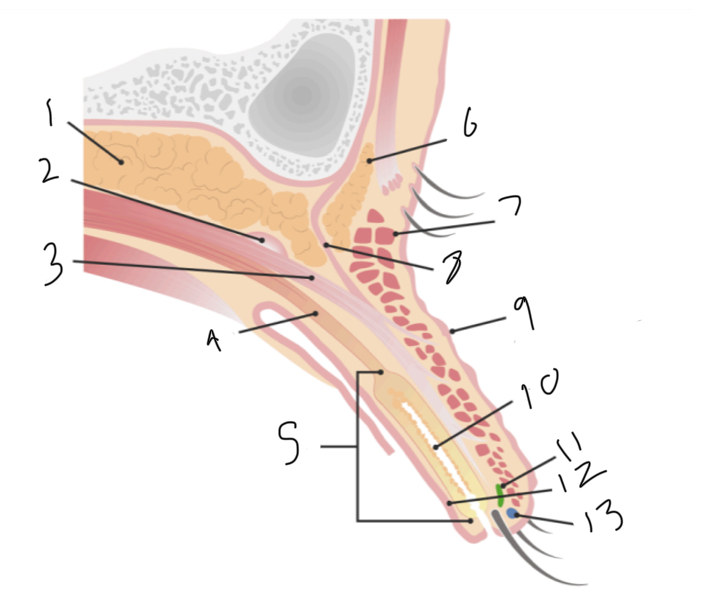
Label
Preaponeurotic fat pad
Superior transverse ligament (whitnalls)
Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Müller muscle
Tarsus
Brow fat pad
orbicularis oculi muscle
Orbital septum
Upper lid crease at levator insertiom
Meibomian gland
Gland of zeis
Conjunctiva
Gland of moll
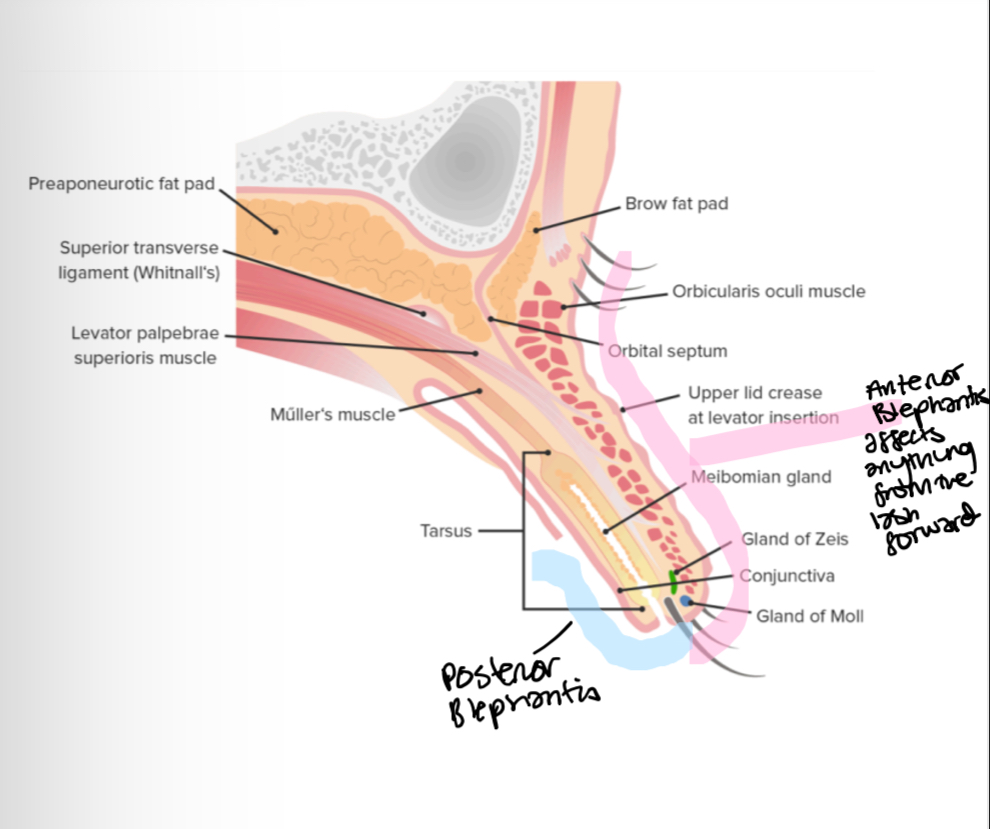
What is anterior blepharitis
Chronic inflammation of eyelash and follicle and its associated gland
Anterior blepharitis - causes
Infection
Infestation
Inflammation
Such as staphylococcal bacteria (infestive), demodex mites, or seborrheic (greasy oily skin)
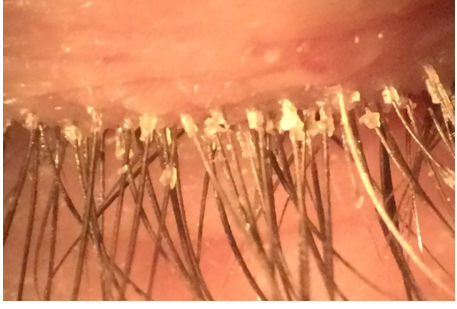
What is this
Anterior Blepharitis
How to distinguish between anterior blepharitis and dry eye
In AB symptoms are worse in the morning
In dry eye symptoms get worse as the day goes on
What does chronic mean
No full cure, condition can come back
Anterior/posterior blepharitis - risk factors

Anterior/posterior blepharitis - symptoms
Same except worse on awakening is only for anterior blepharitis

Anterior Blepharitis - signs for
bacterial
Seborrheic
Demodex

What is seborrheic
Bacterial toxins irritate/inflame your eye but youre not infected
Lifecycle of demodex mites
3 weeks
Anterior Blepharitis- treatments

What is posterior blepharitis/meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD)
Chronic posterior lid inflammation typically due to meibomian glands
Posterior blepharitis/MGD - causes
Glands dont produce good quality meibum/oil (too thick)
Meibomian glands stop producing oil (extreme)
Posterior blepharitis/MGD - Signs
also dry eye symptoms -
increased tear film evaporation
Irritation
Redness
Reflex tearing
Corneal conjunctival exposure (extreme)

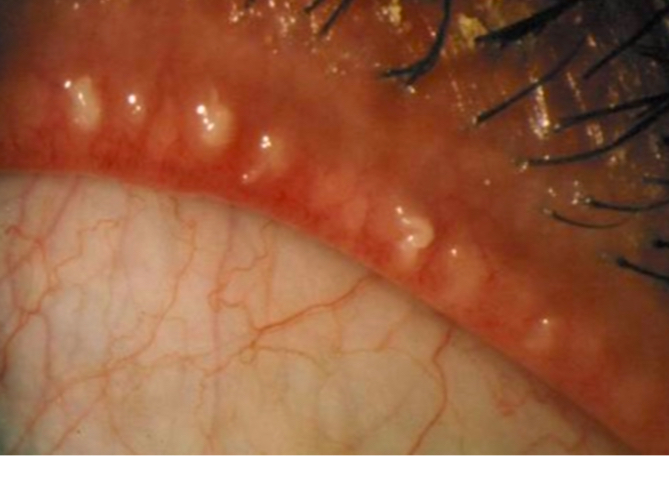
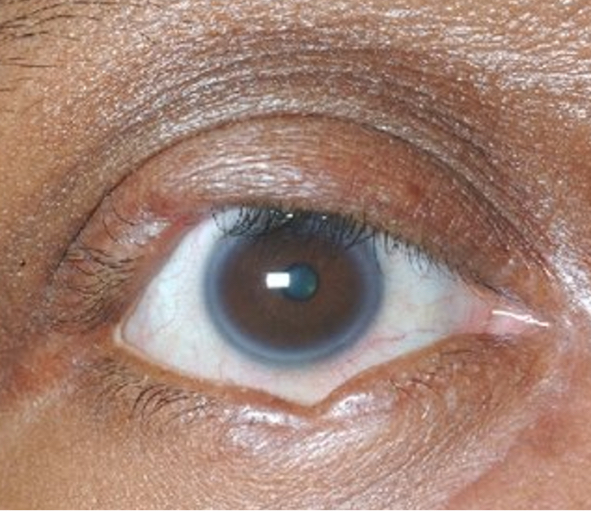
What is this
Posterior blepharitis/MGD
Capped meibomian glands
Posterior blepharitis/MGD - Treatments

What is this
Posterior blepharitis/MGD
Notching due to meibomian gland death
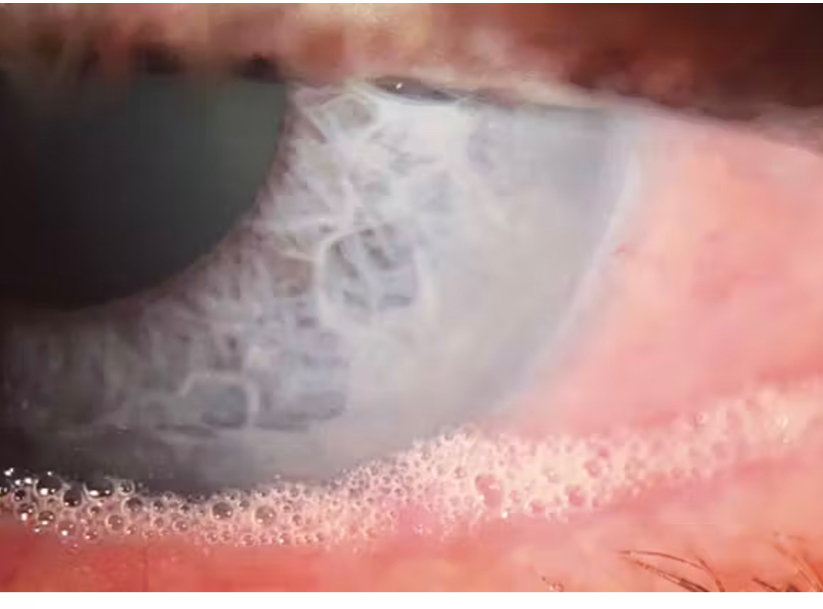
What is this
Posterior blepharitis/MGD
Foamy tear film
What is an ectropion
When the eyelid turns outwards
Ectropian - causes
Usually no cause it happens on its own
Associates with aging due to horizontal eyelid laxity - lose muscle tension so lid droops out
cicratrial ectropion (due to scarring or prior surgery causing lid contraction )
paralytic ectropion (due to a facial palsy - lose laxity due to nerve fibre loss - eyelid cant blink and starts to droop )
Ectropian - symptoms
Eyelash loss

What is epiphoria
Excess tearing
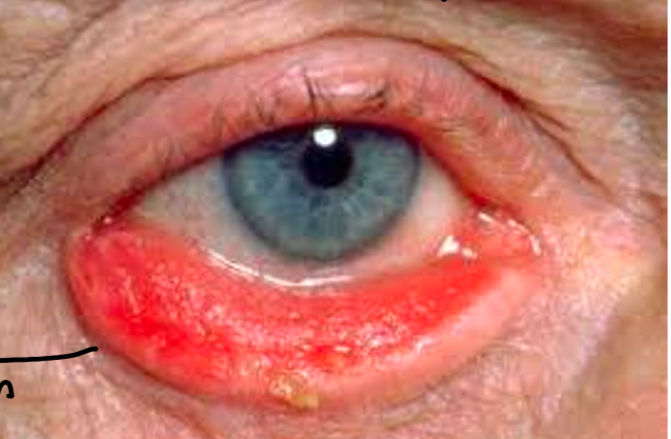
What is this
Ectropion
Ectropion - management and treatment
Management:
Topical lubricants (helps dry eye symptoms)
Lid hygiene (stop blepharitis)
Treatment:
surgery where lid can be excised and pulled together to tighten routine refferel is indicated
What is an entropion
When the eyelid turns inwards
Entropion - causes
Irregularities of lid skin and muscle tension
Skin/conjunctiva contracts and tightens causing lid to fold inwards
Scarring of conjunctical tissue
Prolapse of orbital fat into lower lid
Entropion - symptoms
Similar to ectropion but more severe
Stinging
Itchy
Severe pain
Photophobia
Entropioin - signs
Trichiasis
Deep and perfuse corneal staining
Red eye
Epiphoria
Inflamed lids
Chemosis
What is trichiasis
Misdirected eyelashes
Can grow inwards and scratch cornea
Entropion - management and treatment
Management:
Bandage contact lenses - protect the cornea from scratching
Chemodenervation. - drugs to reduce nerve impulses
Topical lubricants - smooth the surface and keep eye moist
Treatment:
Refer within 2 weeks
Surgery
What is ditichiasis
Additional row of eyelashes
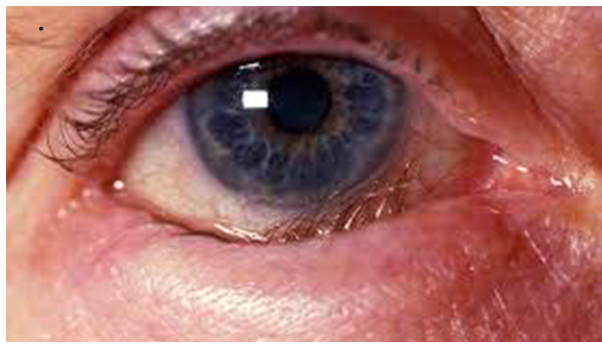
What is this
Entropion
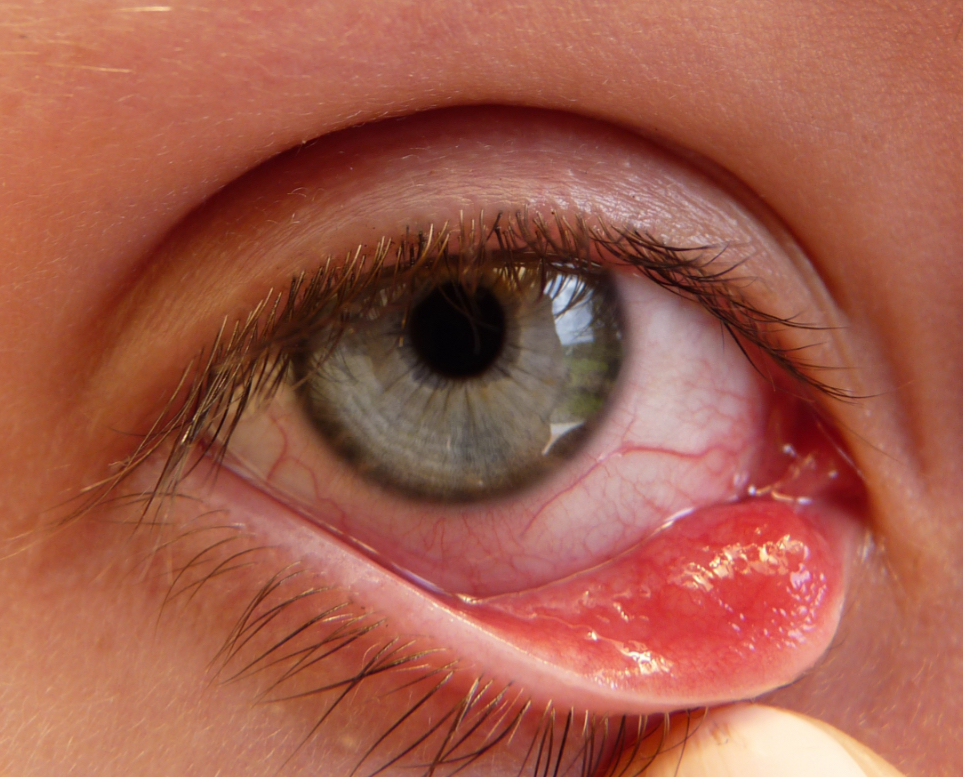
What is a chalazion
A small granuloma (area of inflammation)
Chalazion - risk factors
Prior blepharitis
Meibonian gland dysfunction
Seborrheic dermatitis
Rosacea
Chalazion - causes
Thickening and blockage of meibum which leaks into surrounding tissue outside of acinor cell/ducts and causes inflammation (more common on top lid bc more meibomian glands)
Sterile (no infeciton)
Chalazion - symptoms
Symptomless (sterile - no infection)
Typically unilateral unless underlying systemic condition
Chalazion - signs
Defined Promenant red bump
When inverting the lid the tarsal surface will not be smooth - will have an irregular nodule or cobblestone like appearance
Chalazion - management/treatment
Can resolve spontaneously but can take a few months
Eyebag/hot compress (melts meibum and enourages its content release to reduce swelling)
Lid massage
Can be referred - HES will either use steriod injection to reduce inflammation or perform surgical excision (but referrel not always accepted)
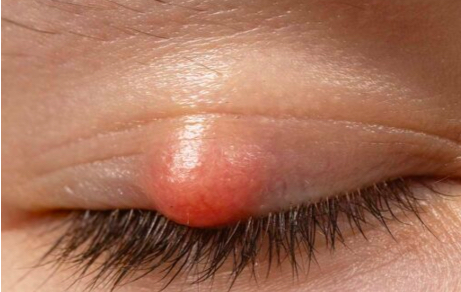
What is this
Chalazion
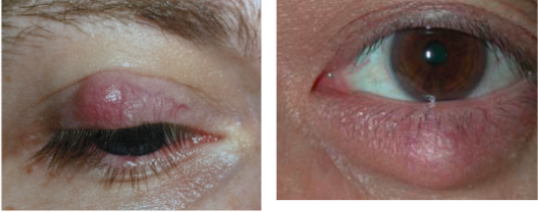
What is this
Chalazion
What is this
Chalazion
What is a hordeolum
Stye
Infected lesion, typically from an eyelash follicle which then spreads to one of the lid glands
Can be internal or external
Hordeolum - causes (internal and external)
Interal - meibomian glands
External - blockage of glands of zeis
How to tell the difference between hordeolum and chalazion
Hordeolum is more painful becuase theyre infected
Hordeolum - symptoms
Pain (internal hordeolum is more painful than external)
Tenderness
Swelling
Burning sensation
Hordeolum - risk factors
Prior infection eg respiritory infection/cold
Similar to blepharitis and chalazions
Onset is sudden and without warning
Hordeolum - signs
Trichiasis (bump causes eyeslashes to be misdirected)
Filled with mucopurulent pus
Anterior and posterior form a nodular mass and a larger redder amount of inflammation than a chalazion
Hordeolum - management/treatment
Similar to chalazion
Warm compress to soften the coagulated material and allow it to drain but it can be painful
Usually spontaneosly resolve in a fortnight
Best to monitor and refer if it doesnt resolve in 3 weeks
If it doesnt resolve, antibiotics may be prescribed as it may increase the risk of cellulitis or other secondary infections
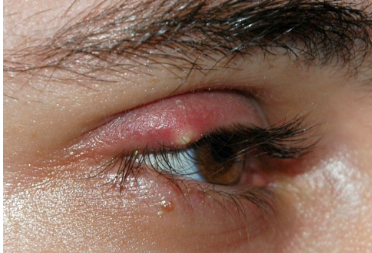
What is this
Hordeolum
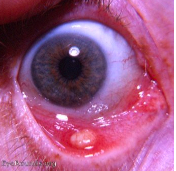
What is this
Hordeolum
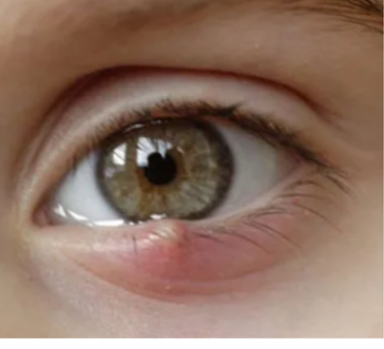
What is this
Hordeolum
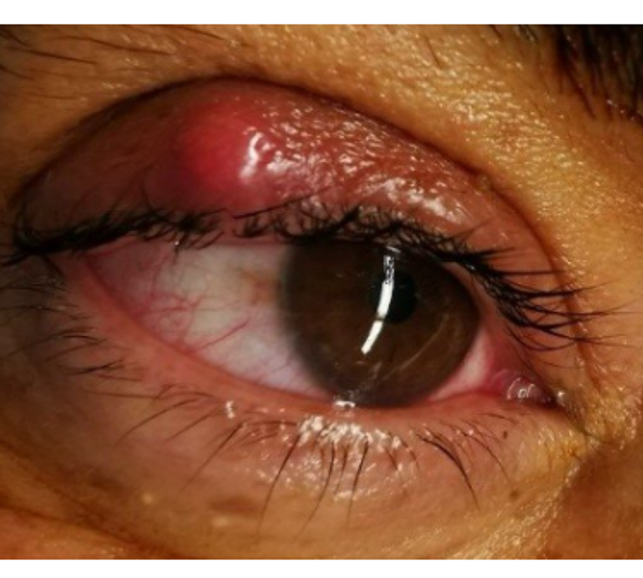
What is this
Hordeolum
What is Xanthalasma
Raised plaques that may look nodular and have a yellow like tinge
Accumulation of lipid/fat deposits under the skin (usually medial and bilateral but asymmetric)
Xanthalasma - symptoms
Asymptomatic
Although patients can find it cosmetically unappealing
Xanthalasma - causes
Idiopathic (unknown)
Correlations with arcus, high blood lipids/cholesterol
What is arcus
White tinge around cornea
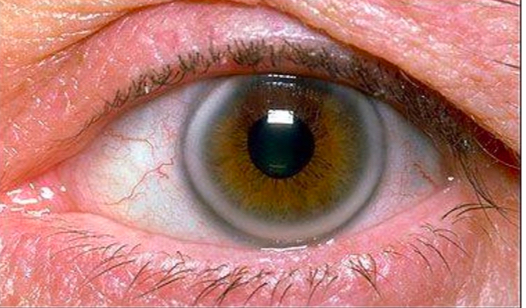
Xanthalasma - risk factors
Arcus
High blood lipids/cholestrol
More frequent in older peoplle
Rare in younger people but then can be due to other systemic conditions
Xanthalasma - management/treatment
Reassure patient and refer to GP non urgently for lipid evaluation blood test if not done recently
Treatment is surgical and only cosmetic (private) as it has a high rate of recurrence
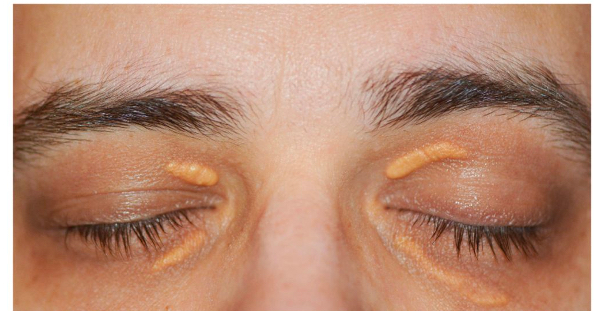
What is this
Xanthalasma
What is mollescum contagiosm
A type of virus that can infect skin, giving pink/flesh coloured bumps that can have a central crater
Usually in clusters but can be in isolation. Can be found around the body
Mollescum Contagiosm - symptoms
Usually asymptomatic But if any infection enters the eye it can case viral conjunctivitis like symptoms with follicles on the tarsal conjunctiva
Flesh coloured bumps
Discharge is watery if popped
Tends to get worse before it gets better
Mollescum Contagiosm - treatment
Can resolve spontaneously over a few months
Refer if it doesnt resolve in over 2 months
No treatment usually necessary just advise on hygiene/reduction of transmission (as its a virus)
Treatment can include removal and cauterization/cryotherapy
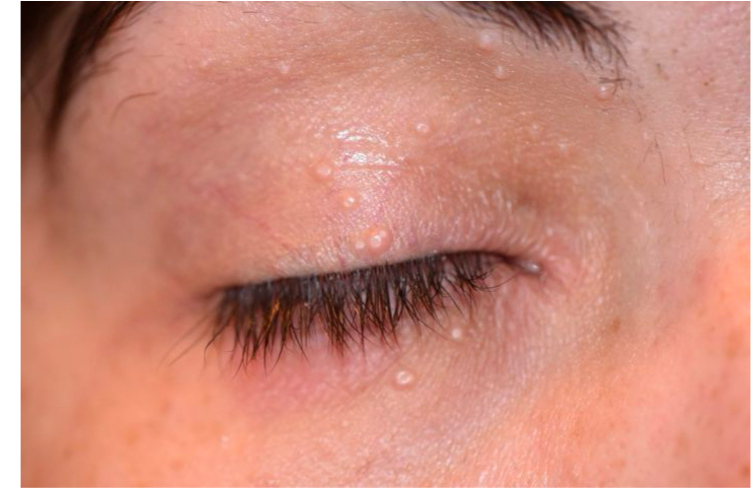
What is this
Mollescum Contagiosm
What is Sqamous papilloma
Skin tag that can occur around the body
Sqamous papilloma - risk factors
Obesity
More common in older poeple
Sqamous papilloma - signs
Brownish or flesh coloured
Had a larger viewable size
Can appear nodular and/or finger like projections
Sqamous papilloma - treatment
Minimal risk so treatment is only cosmetic - surgical excision
Sqamous papilloma - symptoms
No symptoms
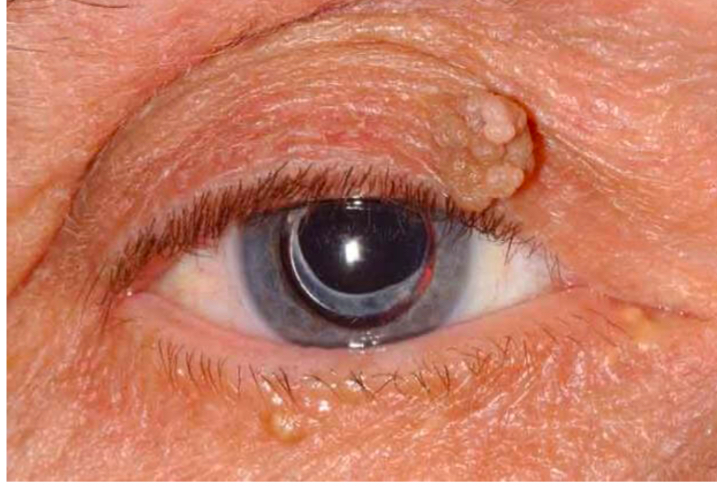
What is this
Sqamous papilloma
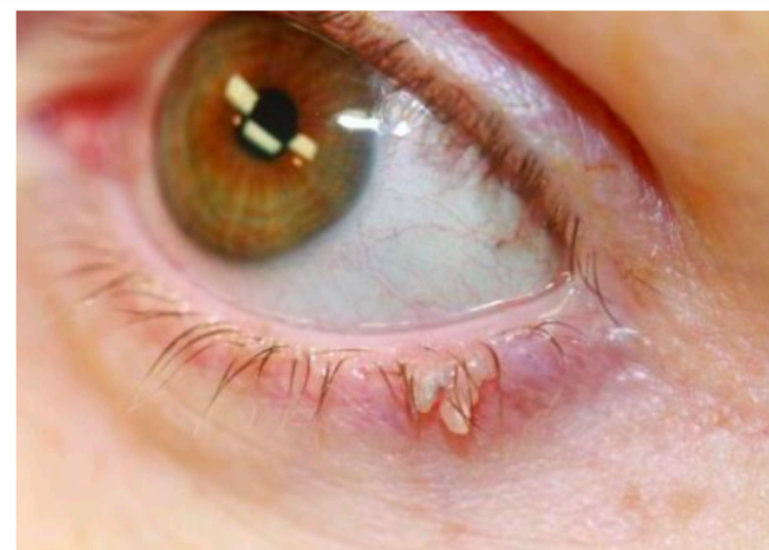
What is this
Sqamous papilloma
What is Cysts of Moll (apocrine hidrocystomas)
Benign, fluid filled cysts that develop from the blocked glands of moll
Cysts of Moll - symptoms
Painless unless infected
Cysts of Moll - signs
Small, round, fluid filled cysts on the eyelid margin
Translucent or bluish appearance
Slowly growing
Soft and fluctuant on palpation
Cysts of Moll - risk factors
Older people
Hot climates
Blockage of appocrine sweat gland (glands of moll)
Cysts of Moll - causes
Blockage of glands of moll
Accumuation of sweat and glandular secretions
Cysts of Moll - management/treatment
Warm compress to help it drain
Surgical excision
Antibiotics if infected
Needle aspiration (drains the fluid) - providees temporary relief but recurrance is common
What is Cysts of Zeiss
Benign, oil filled cysts that develop from the blocked glands of zeiss
Cysts of Zeiss - symptoms/signs
Small, round, yellowish cysts on the yelid margin
Painless
Slow. Growing
Firm to touch
Contains oily or sebaceous material
Cysts of Zeiss - risk factors
Older people
Poor lid hygeine
Cysts of Zeiss - causes
Blockage of glands of zeiss
Accumulation of sebaceous secretions
Cysts of Zeiss - management/treatment
Needle aspiration
Surgical excision
Warm compress
Antibiotics (if secondary infection occurs)
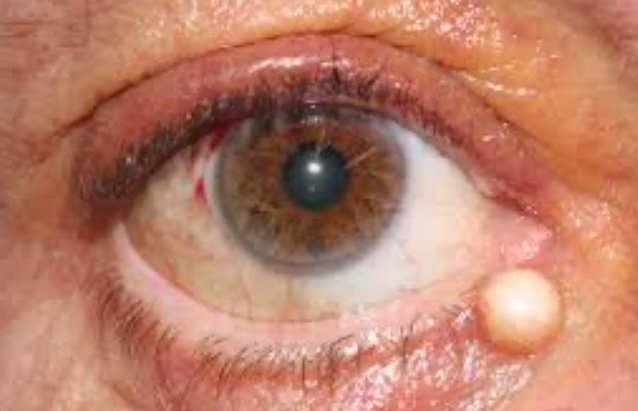
What is this
Cysts of Zeiss
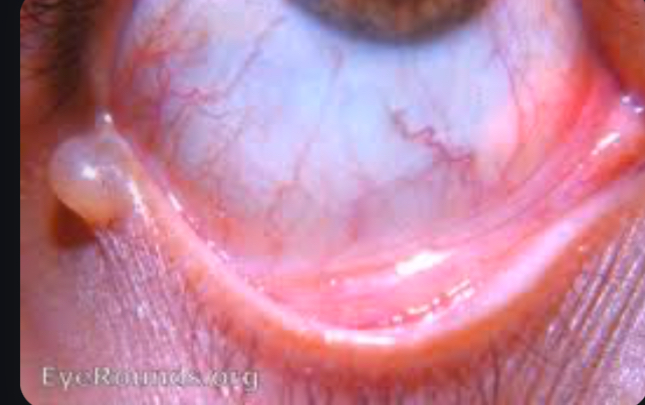
What is this
Cysts of moll
What is a benign tumor
Abormal but noncancerous collection of cells that may or may not be progessive in its size
What is a malignant tumor
Abormal cancerous growth of cells that progresses and is expected to get worse, and is capable of invading adjacent tissues
What is metastasise
Spread to other parts of the body
Do benign or malignant lesions ulcerate?
Malignant
What is ulceration of a lesion
When theres a breakage or cratering of the skin
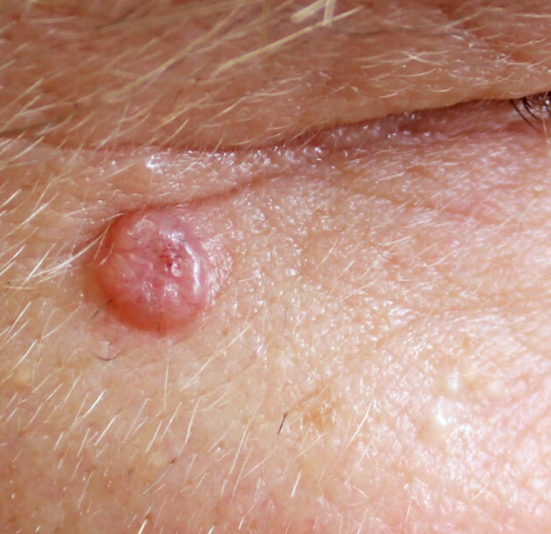
Are benign or malignant lesions painful
Benign are usually more painful but not always
If something is growing quickly and is painful it could be a cyst or infection rather than a tumor
Are benign or malignant lesions firm?
Malignant
What shape is a malignant lesion?
They have a very diffuse, irregular, asymmetric shape and are raised
The more weird the shape the more suspicious it is
Malignant lesions coloud
Usually darker if they have lots of material/pigment in them
But so can benign lesions
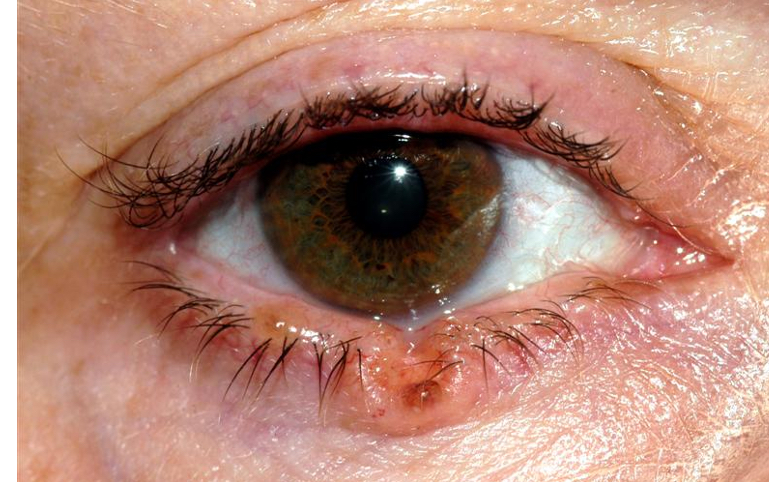
Do benign or malignant lesions cause telangiectasia?
Malignant
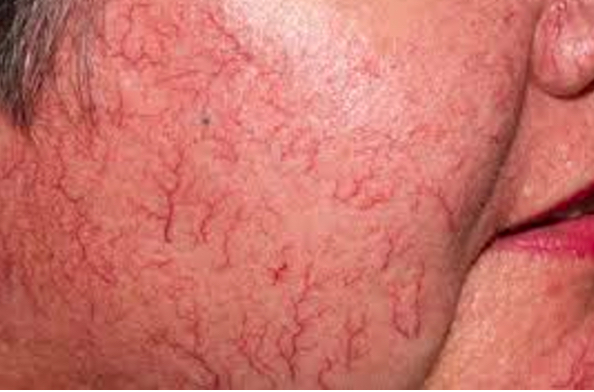
What is telangiectasia
When blood vessels appear more obviously
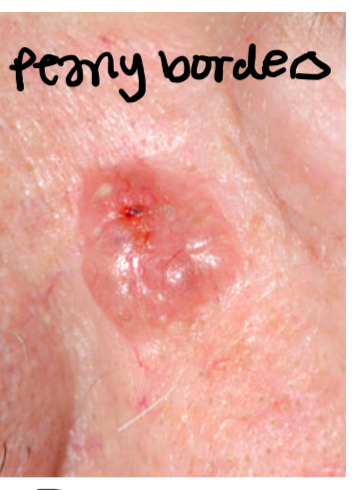
What is pearly border and they they appear in benign or malignant lesions
Malignant lesions
It is a rolled transculcent margins that are shiny and whitish
Do benign or malignant lesions have feeder vessels
Malignant
What are feeder vessels and what do they do
Cause the blood supply to look aggravated
Cancer cells need more blood becuase they grow at a faster rate so they encourage blood vessels to grow into them
What is basal cell carcinoma
A malignant skin cancer
Most common cancer in europe
Basal/squamous cell carcinoma - risk factors
Sun exposure (more common in people who live in sunny climates)
Old age