Robotics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Why robots
reduced production cost, increased productivity, improved product quality
Manual labour/Hard/Soft Automation - cost effectivenes
Hard automation - automated to do one thing no intelligence, soft automation robot flexible can be reprogrammed.
Up to a point, manual labour cheapest, then soft automation, then hard automation. (As production volume increases)
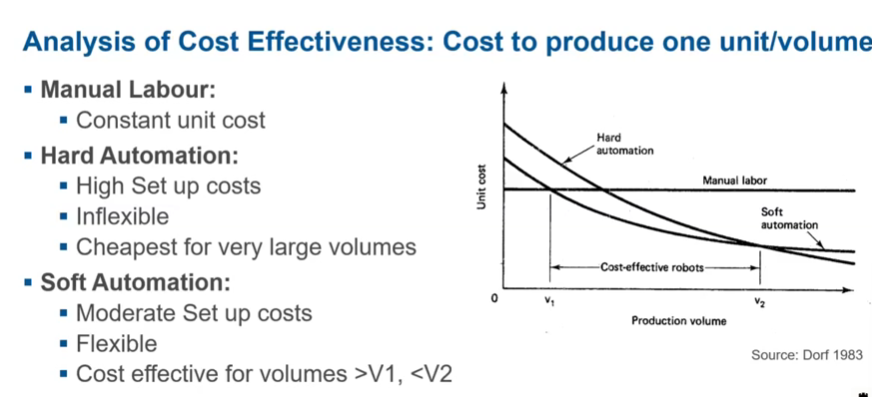
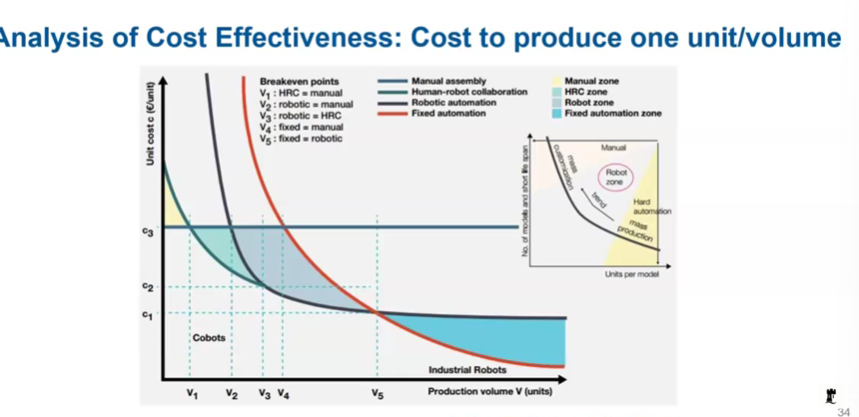
Manual labour + soft automation = collaborative robots

Main components and structure of industrial robot - links, actuators, joints, arm/manipulators, wrist, end effector
Arm/manipulator is everything from base to wrist.
Each joint has actuator.
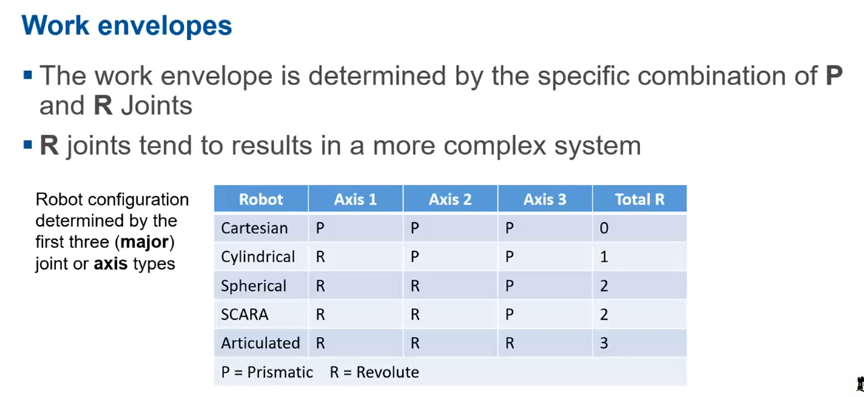
Work envelope - everywhere the robot can reach.
Configuration

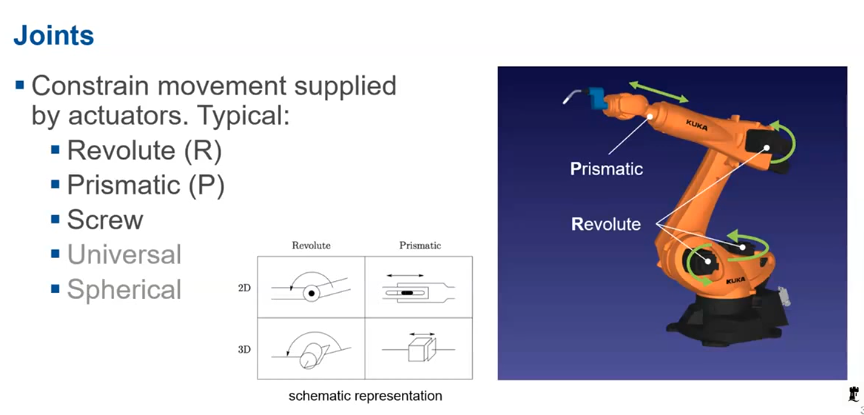
Types of joints - revolute and prismatic
revolute, prismatic, screw, universal, spherical

Actuators/ pros and cons of energy sources for actuators

End effectors
tool connected to the final link, connected by wrist joint

Sensor systems

Motion control method
point to point
continuous path

Work envelope is determined by configuration
robot specification
capacity and speed - how much you want to lift, how quickly you want to move it
reach and stroke - how far robot has to reach
tool orientation - does the wrist need to be fully flexible or can it fixed in some way
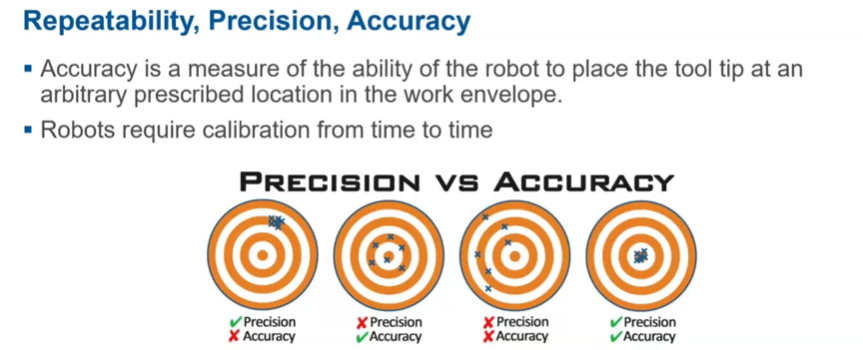
repeatability, precision, accuracy

Number of axis-major/minor
major axis position the wrist, the next 3 orient the tool. Additional joints are introduced to move around obstacles
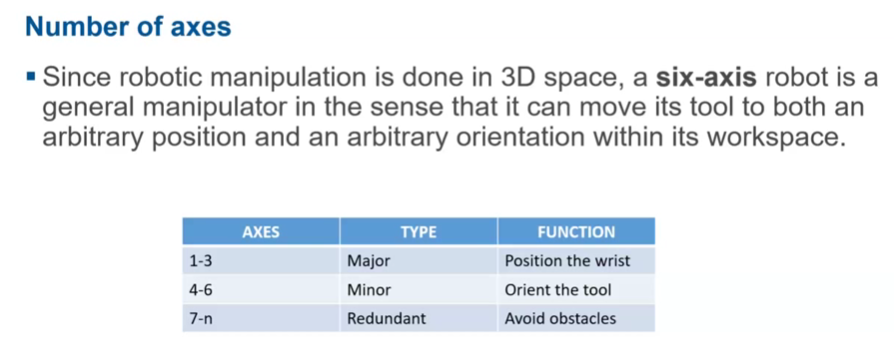
Redundant joint example
Used to move around obstacle
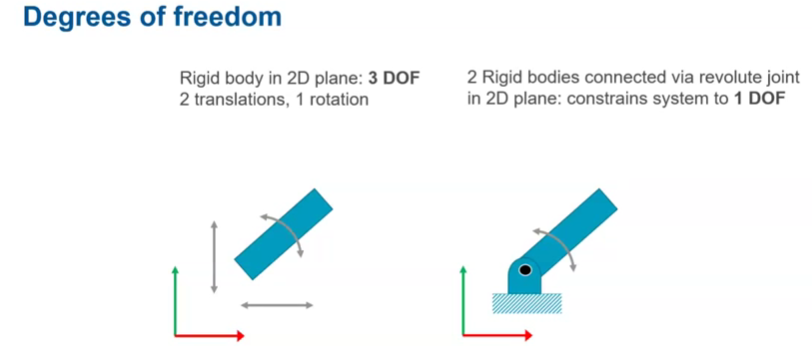
degrees of freedom
3 translation to position the end effector:
up/down, back/forward, left/right
3 rotational to
yaw - vertical axis
pitch - back and forward
roll - horizontal
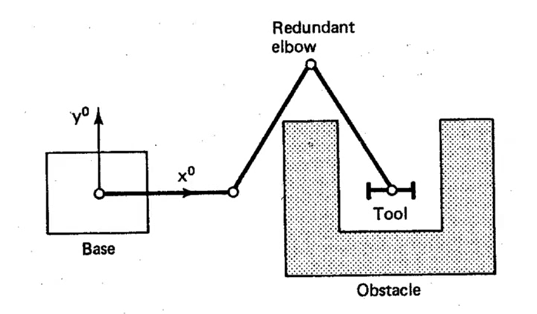
Degrees of freedom example: 2D space
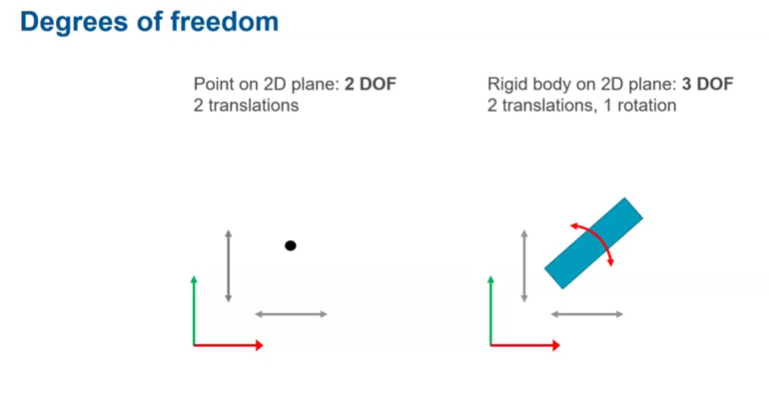
Degrees of freedom example: 3D space
DOF - robots
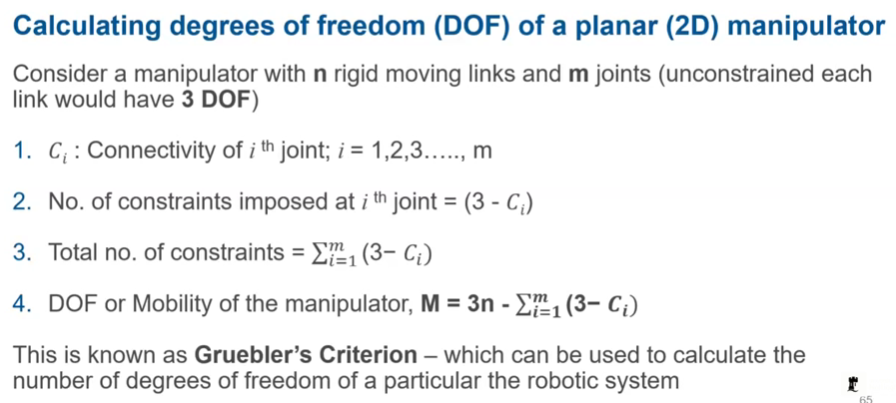
Calculating DOF -2D
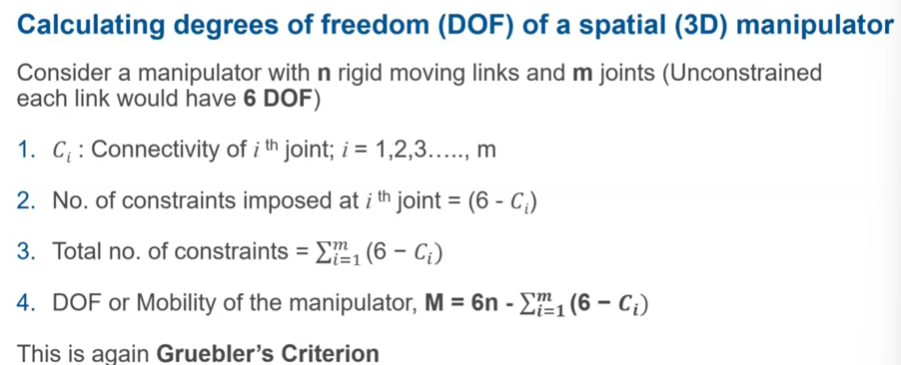
Calculating DOF -3D
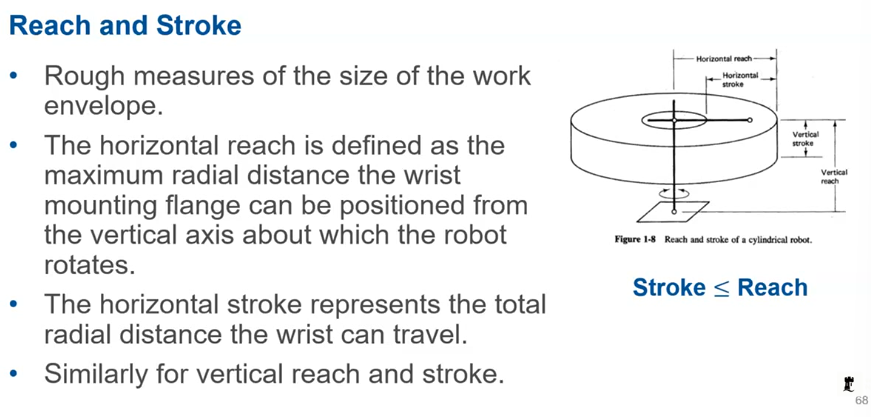
Reach and stroke
horizontal/vertical
reach - maximum distance the end effector can be positioned from the vertical axis it rotates about
stroke - the total radial distance it can travel
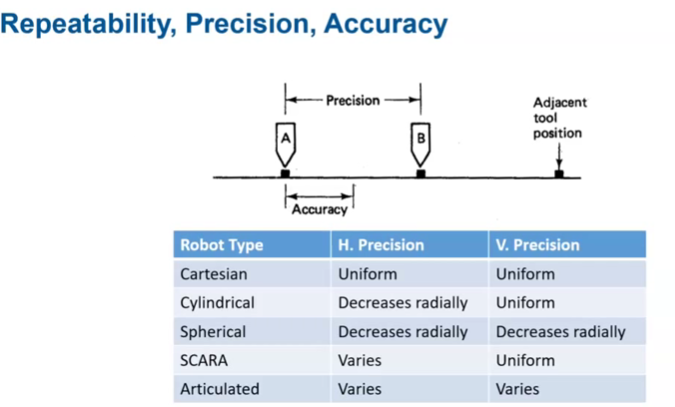
Reapeatability, precision, accuracy
horizonal precision decreases when the radius is bigger (for rotary joint)

More on the precision/accuracy
robots need calibration from time to time
Capacity and speed

Motivation for coordination transformations
Find the formula that relates tool coordinates to the base coordinates

2D geometry

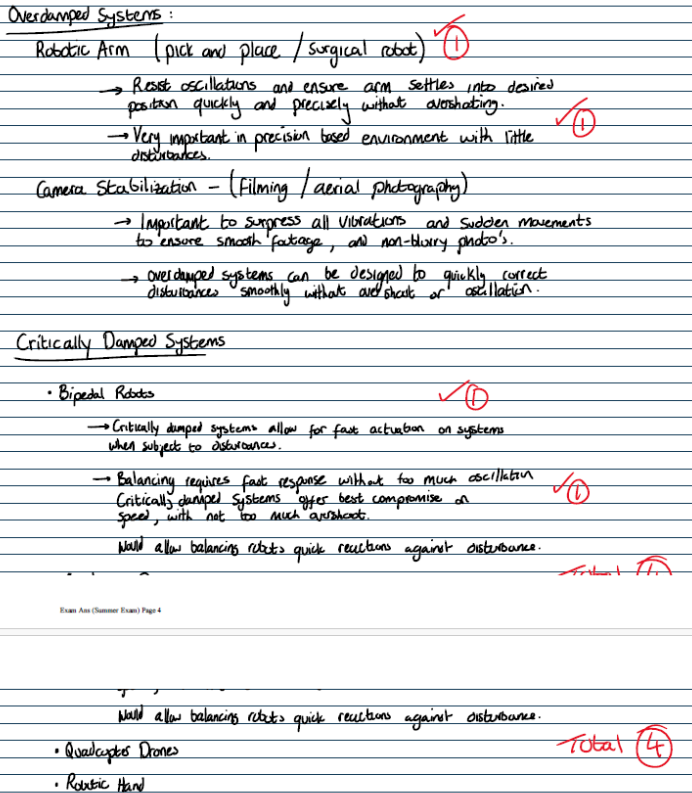
over damped and critically damped systems
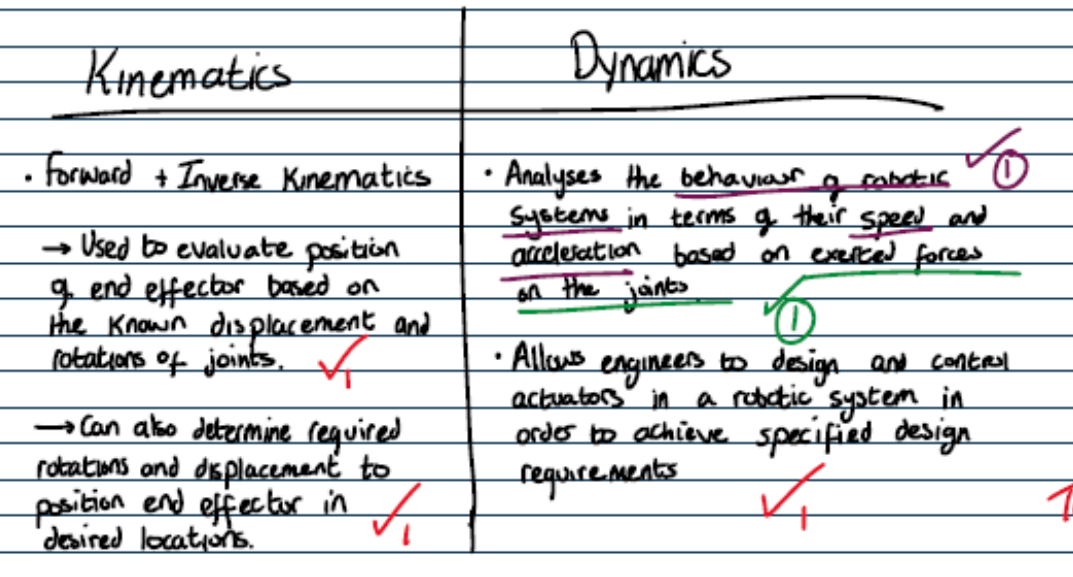
kinematics vs dynamics
robot dynamic equation

scara robot
