Bio-Transcription/Translation/ Replication
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
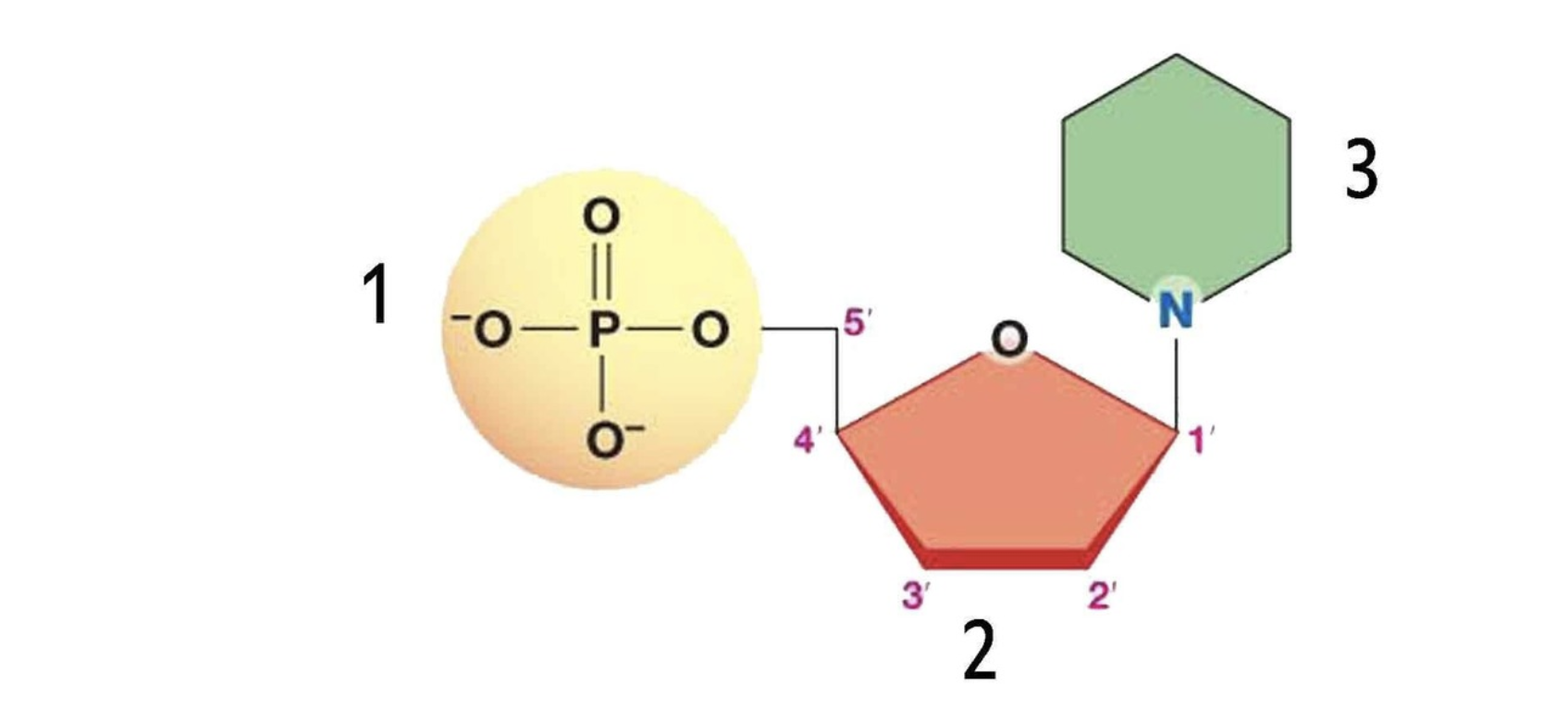
What type of biomolecule is this
Nucleic Acid
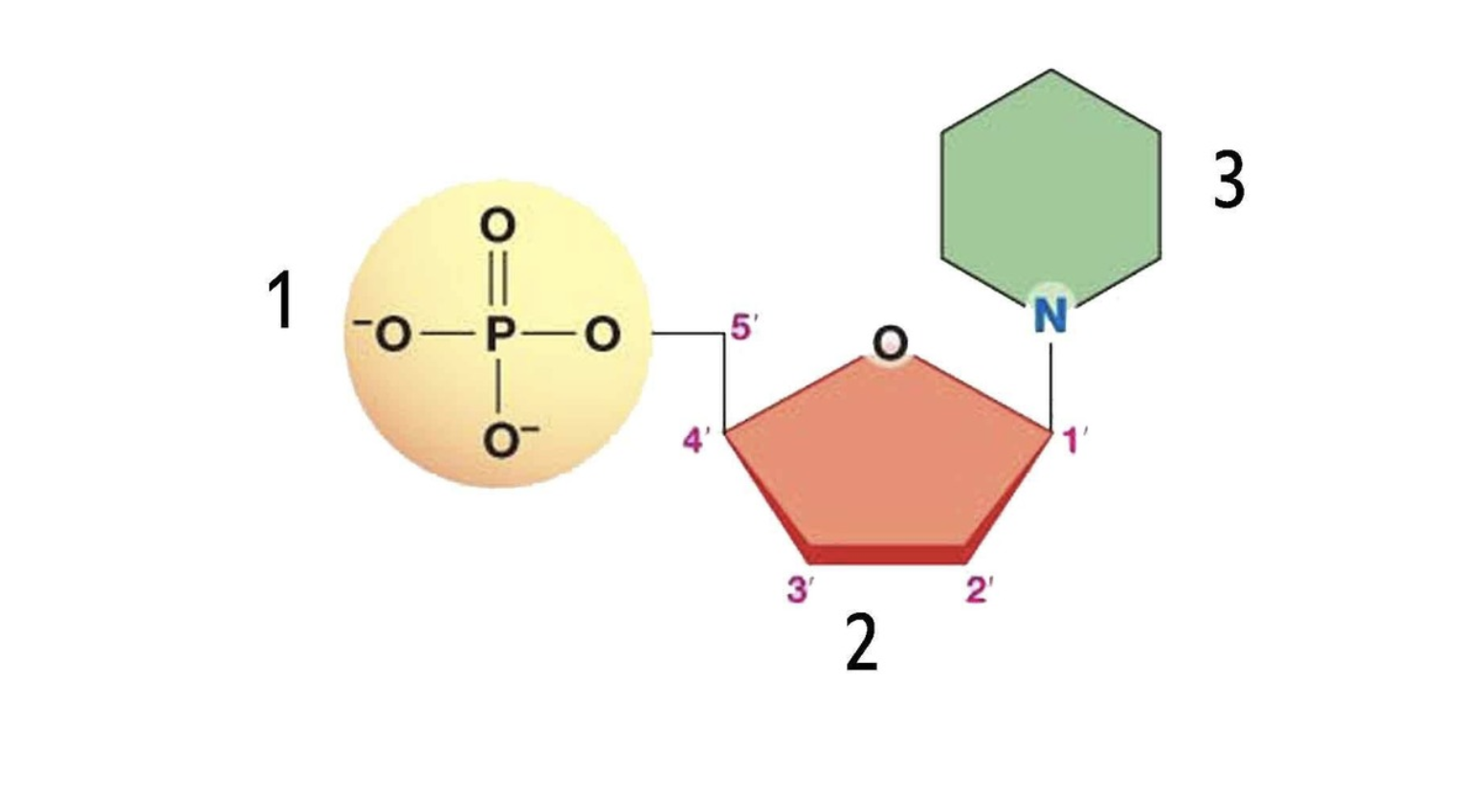
What is the name of this monomer
Nucleotide
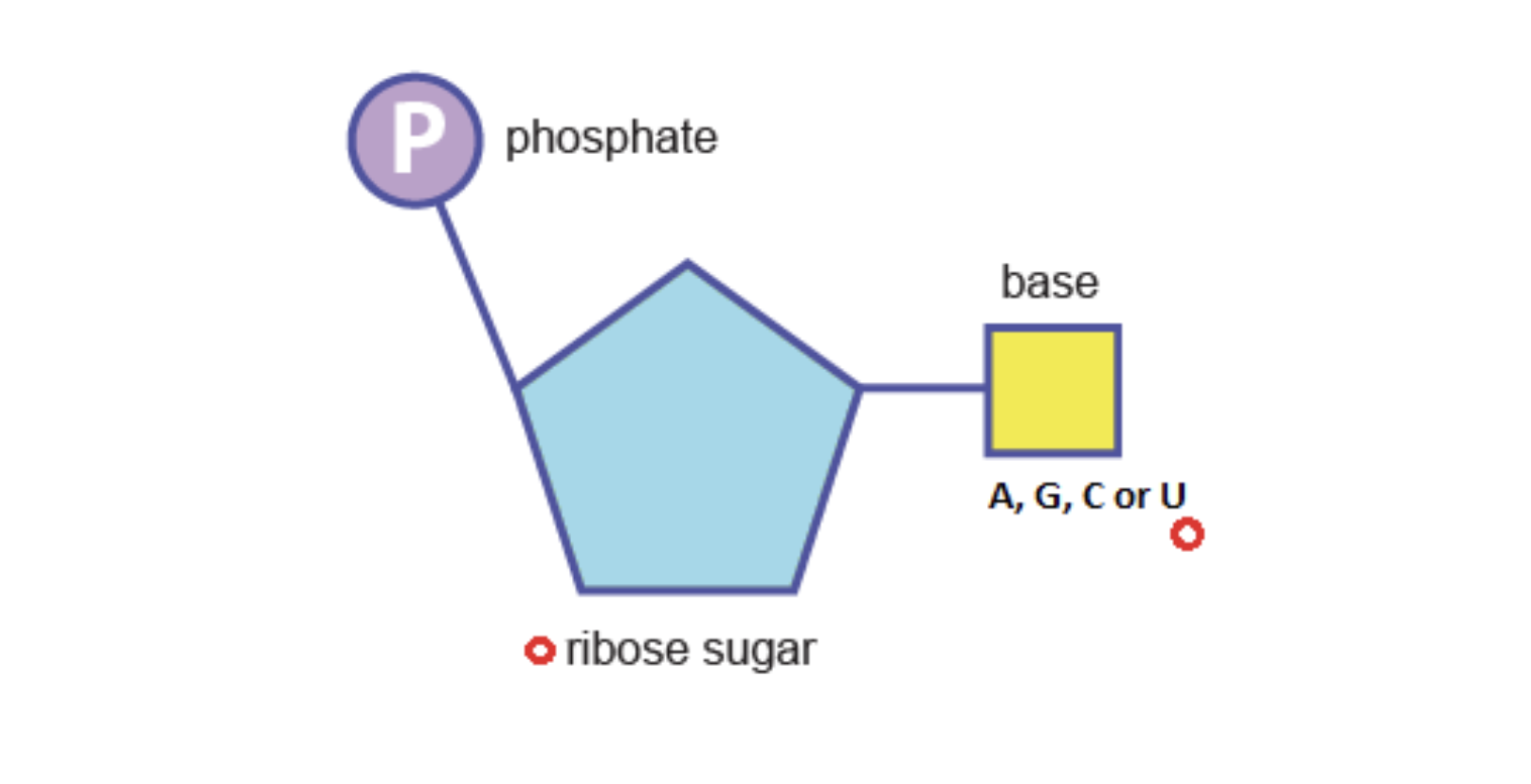
Are you looking at DNA or RNA?
RNA, ribose sugar and U instead of T
What pairs with T in RNA?
NOTHING, Rna has no T
What bases are purines (double ring)
A and G
Which bases are pyrimidines? (single ring)
T, C, U
True or False - Purines pair with purines
False
What type of bond holds two base pairs together?
Hydrogen bonds
When does DNA replication happen?
During Synthesis
Where does DNA replication occur?
Nucleus
Helicase
In DNA replication, this enzyme unzips the DNA molecule
Primase
In DNA replication, this enzyme tells the builder enzyme where to begin
DNA Polymerase
In DNA replication, the enzyme builds the new strands of DNA
Ligase
In DNA replication, this enzyme is responsible for gluing together pieces of the lagging strand
What do 3’ and 5’ represent on the sugar phosphate backbone?
The direction of the sugar molecule in the backbone/position of the carbons in the sugar
In DNA replication, what direction is the new molecule built?
5’ TO 3’
What is the term we use to describe the fact that new molecules of DNA contain one strand of the old molecule and one strand that is newly synthesized?
Semi-conservative
Where does Transcription take place
In the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic cell/ In the cytoplasm in a Prokaryotic cell
Where does Translation take place
On Ribosomes in the cells cytoplasm
mRNA
Carries instructions for polypeptide synthesis
Ribosomal RNA
Forms an important part of both subunits of the ribosome
tRNA
Carries amino acids to the ribosomes and matches them to the coded mRNA message.
What is the first stage of RNA synthesis
Transcription
Promoters
tell the enzyme where to start transcribing DNA.
What happens to the newly made mRNA before it leaves the nucleus
RNA editing
5’ Cap
helps mRNA leave the nucleus and attach to ribosome
Poly-A tail
provides protection from degradation by exonucleases
Codons
Is a group of three nucleotide bases in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid.
There are BLANK possible three-base codons in the genetic code.
64
Translation starts when
a ribosome attaches to an mRNA molecule. Then, tRNA molecules, carrying amino acids with them, bind to mRNA codons.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology
that information is transferred from DNA to RNA to protein.
Gene Expression
When a gene of DNA code is used to build a protein
Mutations
are changes in genetic information.
Somatic mutations
acquired during life to a body cell/ cannot be passed down
Germ Line mutations
occur in a parent’s egg or sperm cell, resulting in a fertilized egg cell that has the mutation/ can be passed down
point mutation
a change in a single nucleotide
In a substitution
one base is changed to a different base.
Insertion mutation
when a single extra base is added into the code
Deletion mutation
when a single base is removed from the code
Inversion
reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome.
Translocation
occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another.
Repressor
Binds to the operator to prevent trasncription
Operator
The point where transcription can be blocked or allowed
Lactose
Is a molecule that organisms can digest
Prokaryotic Genes-operons
Only transcribes genes when they need to and happens when you consume lactose
RNA Polymerase
copies a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence
Point nonsense
Prematurely stops protein synthesis, by adding a stopped codon
Point Silence
One or more nucleotides are changed which results in same amino acid, or similar amino acid
MicroRNA
binds with mRNA to silence/inhibit expression, stopping translation
Heterochromatin
tightly wound chromatin
Euchromatin
loosely wound chromatin
Histone acetylation
loosens the chromatin, allows transcription
Methylation
Tightens chromatin, inhibits transcription
Transcription Factors
bind to the enhancer in DNA and regulate the expression of genes