Lecture 4 - Human Nervous System
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
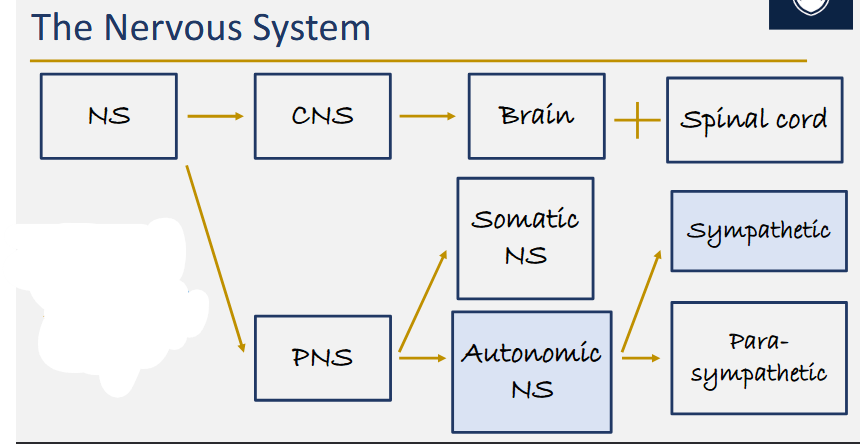
what is the central nervous system
the brain and the spinal cord
what is the peripheral nervous system
all parts of the nervous system found outside of the skull and spinal column
describe the structure of the nervous system
what is the somatic nervous system
the part of the nervous system that controls voluntary movements and sensory inputs (sensory and motor)
what are efferent neurons
carry motor signals to the periperhy
what are afferent neurons
carry sensory information to the CNS
what are cranial nerves?
12 pairs of nerves that emerge directly from the brain (primarily the brainstem), rather than the spinal cord. They control a wide range of sensory and motor functions, mostly in the head and neck.
what are spinal nerves
31 pairs of mixed nerves that emerge from the spinal cord
each spinal nerve connects to the spinal cord trhough
dorsal root (sensory input)
ventral root (motor output)
what is the autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions
what is the sympathetic nervous system
the part of the autonomic nervous system that mobilizes energy resources in threatening situations
what is the main neurotransmitter for the sympathetic nervous system?
epinephrine (aka adrenaline)
what is the para-sympathetic nervous system
the part of the autonomic nervous system that promotes calming and energy conservation activities in the body
what is the main neurotransmitter in the para-sympathetic nervous system
acetylcholine

organize the following ANS actions into sympathetic and parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Increase heartbeat
• Dilate pupils (open)
• Stimulate secretion by sweat glands
• Inhibit saliva production
parasympathetic
Decrease heartbeat
• Constrict pupils (close)
• Contract bladder
• Dilate blood vessels in the digestive system
what is autonomic ganglia?
groups of neurons located outside the CNS
what are preganglionic neurons
they run from the CNS to the autonomic ganglia
what are postganglionic neurons
they run from the autonomic ganglia to targets in the body
what is the third major division of the autonomic nervous system
enteric nervous system
what is the enteric nervous system
a third major division of the autonomic nervous system that is a local network of neurons that governs function of the gut and maintains fluid and nutrient balance in the gut
describe Rene Descartes contributions to our understanding of the brain
proposed dualism — humans have a non-material soul as well as a matreial body
what is phrenology
assigned separate functions to different bumps on the skull
describe Broca’s contributions to our understanding of the brain
language ability is restricted to a small area of the brain called Broca’s area
what is cerebral cortex
the outermost layer of the brain—a thin, wrinkled sheet of gray matter that covers the cerebrum
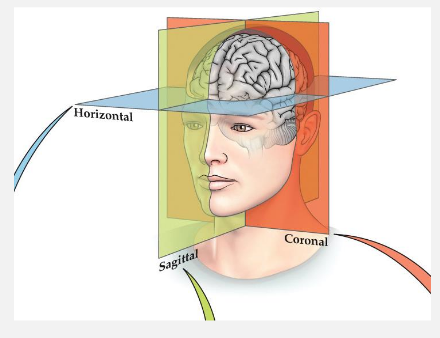
describe all of the anatomic conventions
horizontal: divides the brain into an upper and lower part
sagittal: divides the body into left and right halves
coronal: divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) regions
what is white matter
axons
what is grey matter
cell bodies
what is the difference between white matter and grey matter
axons are myelinated
how does white matter and grey matter function together
white matter allow grey matter to communicate with each other and connects the two hemispheres of the brain
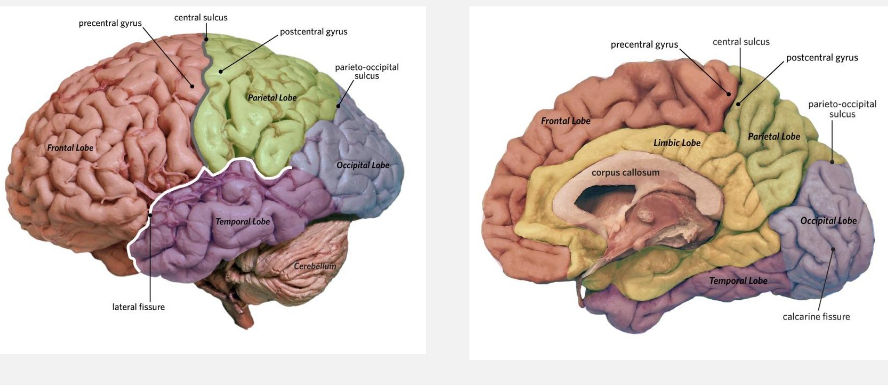
the cortex has 4 lobes…
frontal
parietal
occipital
temporal
what are the primary functions of the 4 lobes in the cortex
frontal: movement and high-level cogntiion
parietal: spatial cognition, sensory processing
occipital: visual processing
temporal: auditory processing, sense of smell, aspects of learning
what is the postcentral gyrus?
is a strip of cortex behind the central cortex that is important for touch
what is the sensory homunculus
the human body maps onto the seomatosensory cortex (part of the parietal lobe)
what is the precentral gyrus
in the frontal lobe, important for motor control
what is the motor homunculus
motor control is somatotopically mapped along the precentral gyrus
describe the basic brain anatomy
Describe the basic developmental stages of the human brain.
25 days — neural tube and divided into three primary vesicles
forebrain
midbrain
hindbrain
50 days — 3 regions further subdivided
forebrain
telencophalon
diencephalon
midbrain
mesencephalon
hindbrain
metencephalon
myelencephalon
how to remember the sub regions of the hindbrain
myel — marrow, spinal cord
myelencephalon
met — beside/after
metencephalon
what is the primary structure that results from the myelencephalon
medulla
what is the purpose of the medulla
regulates breathing and HR
what are the primary structures that result from the metencephalon
pons (brainstem)
cerebellum
what is the pons
a “bridge” that connects medulla to midbrain
what is the cerebellum
responsible for balance and coordination
how to remember the sub regions of the midbrain
mes — middle
mesencephalon
what is the function of the midbrain
sensroy and motor function
reticular formation, sleep,arousal, temperature control, motor control
how to remember the sub regions of the forebrain
tel — far off distanct
telencephalon
di — two
diencephalon
what are the primary structures that result from the diencephalon
thalamus
hypothalamus
what is the thalamus
replay station for all incoming sensory information
what is the hypothalamus
below the thalamus, contains nuclei with many vital functions (hunger, thirst, temperature regulation, sex, and more)
what is the primary structure that result from the telencephalon
cerebral cortex
what is the cerebral cortex responsible for
higher cortical functioning