AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2
1/268
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
269 Terms
What theory can we use to explain how various factors affect the rate of a reaction?
Collision theory
What is collision theory?
Chemical reactions can occur only when reacting particles collide with each other and with sufficient energy
What is the activation energy of a reaction?
The minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react
How do you increase the surface area of a solid reactant?
Grind it into a powder that has smaller particle size
What effect does increasing the temperature of a reaction by 10°C have on the rate of a reaction?
It doubles it
What is a catalyst?
A chemical that changes the rate of a chemical reaction but is not used up in the reaction
How do catalysts increase the rate of a reaction?
By providing a different pathway for the reaction that has a lower activation energy
How do you know in a reaction that a chemical is used in a reaction is a catalyst?
It is not included in the chemical equation for the reaction
What is a reversible reaction?
Where the products of a chemical reaction can react to produce the original reactants
What is the symbol used in reversible reaction equations that shows that the reaction is reversible?
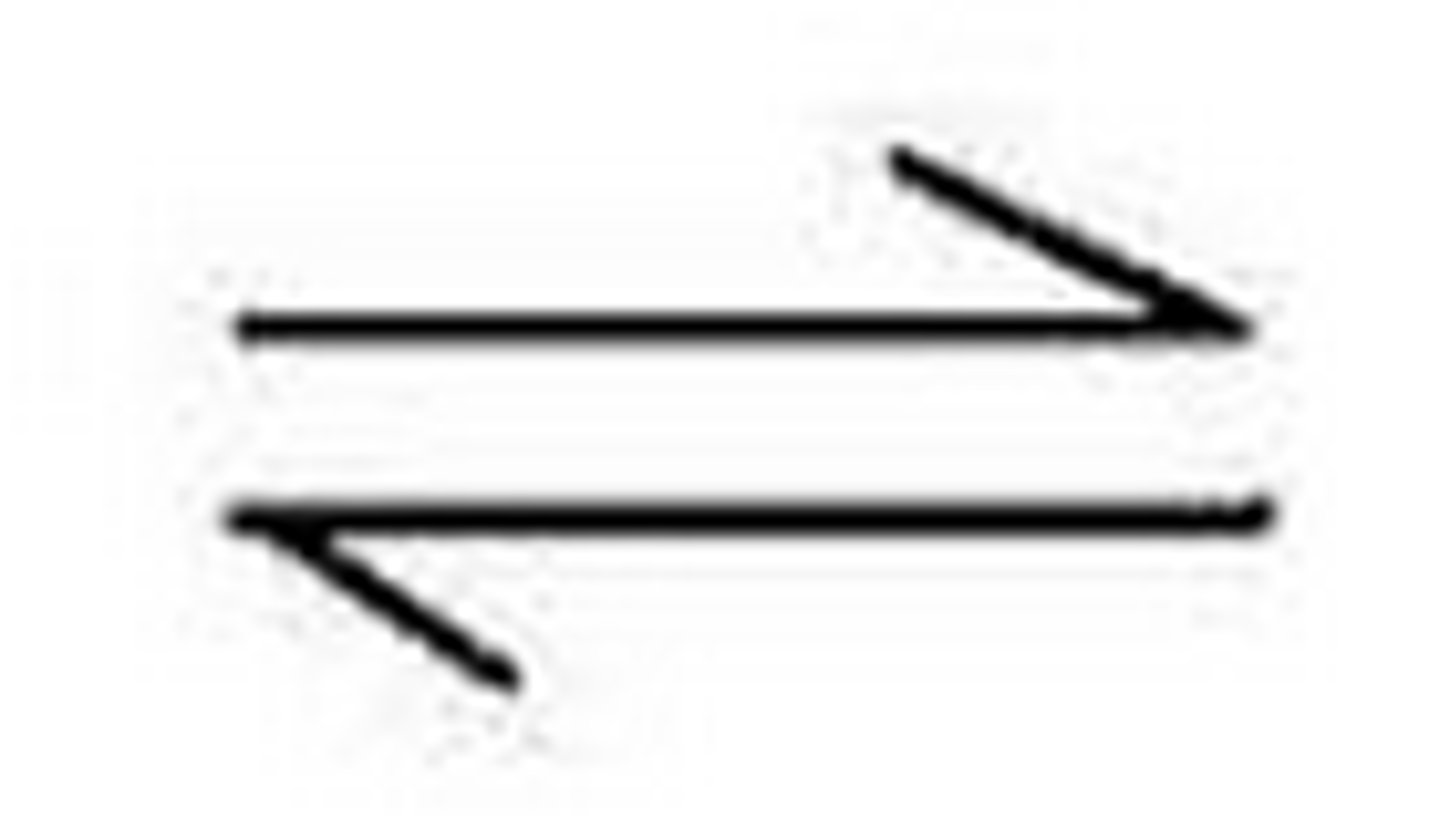
How can you change the direction of a reversible reaction?
By changing the conditions; for example heating or cooling the reaction
Describe the energy changes in a reversible reaction
One direction will be exothermic and the other direction endothermic
When is equilibrium in a reversible reaction achieved in apparatus which prevents the escape of reactants and products?
When the rate of the forward and reverse reactions occur at exactly the same rate
What affects the relative amount of all the reactants and products at equilibrium in a reversible reaction?
The conditions
What happens to an equilibrium if any of the conditions change?
The system responds to counteract the change
What does Le Chatelier's principle predict?
The effects of changing conditions on a system at equilibrium
What affect will changing the concentration of one of the reactants in a reversible reaction have on the equilibrium?
The system will no longer be in equilibrium and the concentration of all the substances will change until equilibrium is reached again
What happens when the concentration of a reactant is increased in a reversible reaction?
More products will be formed until equilibrium is reached again
What happens when the concentration of a product is decreased in a reversible reaction?
More reactant will react until equilibrium is reached again
What happens when the temperature of a system in equilibrium is increased?
The relative amount of products at equilibrium increases for an endothermic reaction OR The relative amount of products at equilibrium decreases for an exothermic reaction
What happens when the temperature of a system in equilibrium is decreased?
The relative amount of products at equilibrium decreases for an endothermic reaction OR The relative amount of products at equilibrium increases for an exothermic reaction
What happens in gaseous reactions when the pressure of a system in equilibrium is increased?
The equilibrium position shifts towards the side with the smaller number of molecules as shown by the symbol equation for the reaction
What happens in gaseous reactions when the pressure of a system in equilibrium is decreased?
The equilibrium position shifts towards the side with the larger number of molecules as shown by the symbol equation for the reaction
Where is crude oil found?
In rocks
What is crude oil formed from?
The remains of an ancient biomass consisting mainly of plankton that was buried in mud
What chemically is crude oil?
A mixture of a large number of compounds; mainly hydrocarbons
What is a hydrocarbon?
A molecule made up of carbon and hydrogen only
What type of hydrocarbons are most of those found in crude oil?
Alkanes
What is the general formula of alkanes?
CnH2n + 2
What are the first four members of the homologous series of alkanes called?
Methane, ethane, propane and butane
What is a homologous series?
A family of organic compounds that have the same functional group, similar chemical properties and the same general formula
How can you separate crude oil into fractions?
By fractional distillation
What does each fraction of crude oil contain?
Molecules with a similar number of carbon atoms
What can we use each fraction of crude oil for?
As fuels or feedstocks for the petrochemical industry
Name five fuels produced from crude oil
Petrol, diesel, kerosene, heavy fuel oil and liquified petroleum gases
Name four useful materials produced by the petrochemical industry from crude oil fractions
Solvents, lubricants, polymers and detergents
Why are there such a vast range of natural and synthetic carbon compounds?
Because of carbon atoms' ability to form families of compounds
Describe the four steps involved in fractional distillation
Crude oil is heated to evaporate it and turn it into a vapour, the vapour rises through the column and cools, the vapours condense when they are cool enough, and liquids are removed from the column at different heights
What three properties of hydrocarbon change as the size of the molecule increase?
Boiling point, viscosity and flammability
How does the boiling point of a hydrocarbon change as its size increases?
It increases
How does the viscosity of a hydrocarbon change as its size increases?
It increases
How does the flammability of a hydrocarbon change as its size increases?
It decreases
Why are hydrocarbons good fuels?
Because during their combustion they release energy
What happens to the carbon and hydrogen in a hydrocarbon during combustion?
They are oxidised
What are the products of complete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
Carbon dioxide and water
What is the name of the process where hydrocarbons are broken down to produce smaller more useful molecules?
Cracking
Name the two types of cracking
Catalytic cracking and steam cracking
What are the conditions for catalytic cracking?
550°C using a zeolite catalyst containing aluminium oxide and silicon oxide
What are the conditions for steam cracking?
550°C and steam
What is always produced when an alkane undergoes cracking?
Smaller alkane molecule(s) and an alkene
Which is more reactive, an alkene or an alkane?
An alkene
How can you test for an alkene?
React it with bromine water
What do you observe when bromine water is mixed with an alkane?
There is no colour change; the bromine water remains orange/brown
What do you observe when bromine water is mixed with an alkene?
There is a colour change; the bromine water turns colourless
Why are alkanes cracked?
Because there is a high demand for fuels and some of the products of cracking are useful as fuels
What are alkenes used for?
To produce polymers and as starting materials to produce other chemicals
What are alkenes?
Hydrocarbons with a double carbon-carbon bond
What is the general formula of an alkene?
CnH2n
What do saturated hydrocarbons only contain?
Single bonds
Why are alkenes unsaturated hydrocarbons?
Because they contain two fewer hydrogen atoms that the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms
What are the names of the first four members of the homologous series of alkenes?
Ethene, propene, butene, pentene
What is the functional group in alkenes?
C=C
What determines the reactions of organic compounds?
The reactions of the functional group
How do alkenes react with oxygen?
They undergo incomplete combustion, burning in air typically with a smoky flame
How do alkenes react with hydrogen, water and the halogens?
By the addition of atoms across the carbon-carbon double bond so that the double bond becomes a single carbon-carbon bond
What conditions are required for alkenes to react with hydrogen?
Hydrogenation requires a catalyst
What conditions are required for alkenes to react with water?
Hydration requires the use of steam at 300°C and a catalyst
What conditions are required for alkenes to react with halogens?
None; the reaction is spontaneous
What is the functional group in alcohols?
-OH
What are the names of the first four members of the homologous series of alcohols?
Methanol, ethanol, propanol and butanol
What happens when ethanol reacts with sodium?
Bubbles of hydrogen gas are seen and sodium ethoxide is produced
C2H5OH + Na → H2 + C2H5ONa
What happens when alcohols burn in air?
They undergo complete combustion to form carbon dioxide and water
What happens when alcohols are added to water?
They dissolve; though solubility decreases as the molecules increases in size, so butanol is less soluble
What happens when alcohols react with an oxidising agent?
They are oxidised to carboxylic acids
How are aqueous solutions of ethanol produced?
By fermentation of sugar solutions using yeast
What is the word equation for the fermentation of sugar solution using yeast?
Glucose à Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
What are the conditions for fermentation of sugar solution to produce ethanol?
Anaerobic conditions (absence of oxygen), 25-35°C
What is the functional group in carboxylic acids?
-COOH
What are the names of the first four members of the homologous series of carboxylic acids?
Methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, propanoic acid, butanoic acid
What happens when carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates?
React to form a salt, carbon dioxide and water
What happens when carboxylic acids are added to water?
They dissolve to form acidic solutions
What happens when carboxylic acids react with alcohols?
They form esters
Why are carboxylic acids weak rather than strong acids?
Carboxylic acids only partially ionise so do not contain as many hydrogen ions as strong acids (which fully ionise) so the pH is higher
What is the name of ester formed from ethanoic acid and ethanol?
Ethyl ethanoate
What are esters used for?
Solvents or because they have fruity smells
What is the word equation for the formation of esters?
Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water
What is the name of the reaction that turns alkene into polymers?
Addition polymerisation
What happens in an addition polymerisation reaction?
Many small molecules (monomers) join together to form large molecules (polymers)
What is a repeating unit?
A part of a polymer that would make a complete polymer molecule if many of them were joined end to end
What is the name of the polymer made from propene?
Poly(propene)
What is condensation polymerisation?
Where monomers with two functional groups join together, usually losing small molecules such as water (which is why they are called condensation reactions)
What are amino acids?
Organic molecules that have two different functional groups (-COOH and -NH2) in the molecule
What are formed when amino acids react by condensation polymerisation?
Polypeptides
What is formed when different amino acids are formed into polypeptides?
Proteins
What is DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a large molecule essential for life
What is the function of DNA?
It encodes genetic instructions for the development and functioning of living organisms and viruses
Describe the structure of DNA
Two polymer chains made form four different monomers called nucleotides, in the form of a double helix
Name three naturally occurring polymers important for life
Proteins, starch and cellulose
What is the monomer that the naturally occurring polymers starch and cellulose are made from?
Glucose