Topic 5b Motivation
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is motivation according to Chamorro-Premuzic
an internal, dynamic state that drives action, energises and directs behaviour, and aims to satisfy needs
Why is motivation considered an individual difference
people differ in trait and state levels of motivation, influencing life outcomes
How does motivation differ from personality?
Personality is relatively stable; motivation is dynamic and goal-directed.
Who distinguished from primary needs and secondary/psychogenic needs (think love as a need, and marriage)
Murray
What are secondary/psychogenic needs
needs derived from biology and/or psychology
What two factors fuel motive -> behaviour
press and need
What do more recent models of motivation include to distinguish it from mood
goals
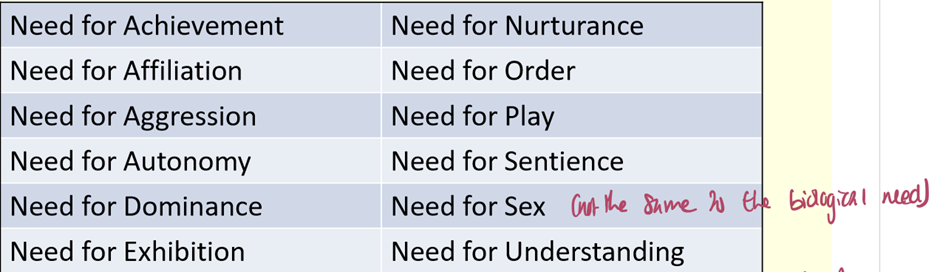
Explain the model of motivation that Murray proposed
identified 20 psychogenic needs based on interviews and observations
What 3 secondary needs does most research now focus on
need for achievement, affiliation and power
What theory of individual differences of motivation was proposed following on from Murray’s 3 secondary needs
McClelland’s Acquired Needs Theory
How did McClelland measure 3 needs in his theory
using TAT
What is TAT
thematic apperception test
What does TAT offer access to?
implicit motives
What bias does TAT reduce
social desirability bias
What data does TAT produce
richer, more nuanced data
Other than questionable reliability and inconsistent validity, what are 2 other limitations of TAT
interpretation is subjective and differences in sensitivity to situation/stimulus
What potential sub components of need for achievement and power did Schultheiss find
hope and fear components
What 4 subtypes into the need for affiliation did Hill find
need for emotional support, positive simulation, attention from others and social comparison
What is the distinction between state and trait motives?
Trait motives are enduring dispositions; state motives are temporary activations.
Those who have a need for achievement, what level of task difficulty do they prefer and why
moderate difficulty which can indicate ability
What preference for work settings do individuals with a need for achievement have
frequent feedback on current vs previous performance
What 2 individual-level outcomes are linked to high need for achievement (think economics and leadership)
entrepreneurial success and innovation, and poor leadership and managerial skills
What 2 societal-level outcomes are linked to high need for achievement (consider individual-level outcomes)
economic growth and innovation, and civil war and ineffective leadership
Why do those with a high need for achievement have ineffective leadership
difficulty in compromising, wanting to achieve goals
Who used a content analysis of popular literation to estimate need for achievement and economic growth (two Bs)
Bradburn and Berlew
What was Bradburn & Berlew’s main finding of higher achievement imagery?
correlated with industrial growth (coal imports)
Other than dominance and control, what else can need for power demonstrate
desire to influence and have impact
What generative correlation exists between high need for power and profession preference
more attracted by jobs involving teaching
What generative correlation exists between high need for power and family (in females)
larger families and greater involvement in parenting
What 3 individual-level correlates are linked to high Need for Power?
Higher testosterone, sexual activity and aggression, leadership and career success.
What 2 societal-level correlates are linked to Need for Power?
Increased war and arms and effective leadership.
What real-life example did Spangler and House study to investigate need for power and effective leadership
US Presidents’ inaugural speeches
What did Spangler and House look at in US Presidents’ inaugural speeches
Presidential Performance
What needs predicated Presidential Performance
high need for power, lower needs for achievement and affiliation
What individual-level correlates are linked to high Need for Affiliation?
Preference for similar others; dislike of dissimilar others.
What 2 societal-level correlates are linked to Need for Affiliation?
Peace and disarmament; political scandal.
What did Langer and Winter highlight as important to avoid/resolve conflicts
concessions
What need was positively related to concession vs negatively related to concessions, according to Langer and Winter
high need for affiliation vs high need for power
What physiological marker is linked to high need for power, according to Schultheiss
high testosterone
What physiological response does high need for power trigger, according to Schultheiss
sympathetic nervous system stress response
3 ways in which high need for power cause health issues through the activation of the sympathetic nervous system stress response
issues with blood pressure, immunity function and susceptibility to illness
What 4 measures did McClelland, Alexander and Marks collect in male prison inmates to investigate the negative health effects of need for power
TAT, number of stressors, number and severity of illnesses and salivary immunoglobulin-A (S-IgA)
What is an indicator of better immune functioning
high S-IgA
Was S-IgA high or low in those with a high need for power
low
What was McClelland et al.’s key finding about motives and stress for health outcomes?
High Need for Power + high stress = poorer health outcomes.
What important distinction did McClelland and Schultheiss make about the health effects of need for power, is it just need for power?
‘stressed power motive’ associated with poorer health, high need for power is not a general vulnerability
What branch of the autonomic nervous system is need for affiliation linked with and what is the effect of this, according to Schultheiss
parasympathetic, increased immune functioning (positive effects on health)
What two things did McClelland and Kirshnit aim to study in their test for need for affiliation and health outcomes
priming need for affiliation via films and levels of S-IgA
Did manipulation of need for affiliation work following films
yes
How did priming need for affiliation effect levels of S-IgA, what does this suggest about affiliation and health
increased, evidence protective effects of need for affiliation
Did priming need for power impact levels of S-IgA, suggesting higher stress and poorer health, what was found?
no, inhibited power motive syndrome
What is inhibited power motive syndrome
high need for power + low need for affiliation + high inhibition
What is inhibited power motive linked to
stress and poor health