4.3 classification and evolution
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
define classification
the process of naming and arranging organisms into groups based on their characteristics
name the groups in the classification system
domain
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
what are the two components to a binomial name?
generic name = the genus that the organism belongs to, two closely related species will share the same genus
specific name = the species that the organism belongs to
what is the advantage of the binomial naming system?
it is universal; an organism’s binomial name is the same everywhere in the world
name the five kingdoms and the three domains
kingdoms: prokaryotae, protoctista, fungi, plantae, animalia
domains: bacteria, archaea, eukaryota
how was the domain system of classification developed?
by analysing molecular differences between organisms to determine their evolutionary relationships (phylogeny)
what is the difference between classification and phylogeny?
classification is simply sorting organisms into groups
phylogeny investigates the evolutionary relationships between organisms
explain how natural selection results in evolution?
random mutations result in new alleles
some alleles provide an advantage against selection pressures, making an individual more likely to survive and reproduce
their offspring receive the new allele, and are said to have ‘evolved’ a new characteristic
how did Darwin and Wallace contribute to the theory of evolution?
they observed that bird have many different beak shapes
they concluded that birds with beak shapes most suited to the food they eat are more likely to survive and therefore pass this beak shape onto their offspring
give other evidence for the theory of evolution
fossils - allow us to compare extinct organisms to today’s organisms
genomic DNA - sequencing of genomes have shown how closely related we are to primates
molecular - proteins are composed of the same 20 amino acids in all organisms
what causes variation?
genetic = mutations, random fertilisation
environmental = climate, diet, culture
what is intraspecific variation?
variation within the same species
what is interspecific variation?
variation between different species
what is continuous variation?
when the individuals in a population vary within a range - no distinct categories e.g. humans can be any height within a range, not just tall or short
give some examples of continuous variation:
milk yield in cows
human mass
number of leaves
width of E. coli
length of a flagellum
what is discontinuous variation?
when there are 2 or more distinct categories - each individual falls into only one category
give some examples of discontinuous variation:
human blood group
colour of courgettes
antibiotic resistance
how can variation be caused by genes?
differences in genotype result in variation in phenotype
examples of variation caused by only genetic factors include blood group and antibiotic resistance in bacteria
you inherit your genes from parents so variation caused by genetic factors is inherited
how can variation be caused by environmental factors?
variation can be caused by differences in environment like climate, food and lifestyle
characteristics controlled by environmental factors can change over an organism’s life
e.g. accents, if you have pierced ears or not
how can variation be influences by genetic and environmental factors?
genetic factors determine the characteristics and organism is born with, but environmental factors can influence how some characteristics develop
e.g. height - genes determine how tall an organism can grow but diet or nutrient availability affect how tall they actually grow
what does the mean tell you about two samples?
how much variation there is between the two samples
what does the standard deviation tell you about a sample?
how much the values in a single sample vary about the mean
for mean what graph do we use?
normal distribution
bell-shaped
symmetrical about the mean
what can standard deviation sometimes be written as?
9+- 3
mean = 9
standard deviation = 3
most of the values are spread between 6 and 12
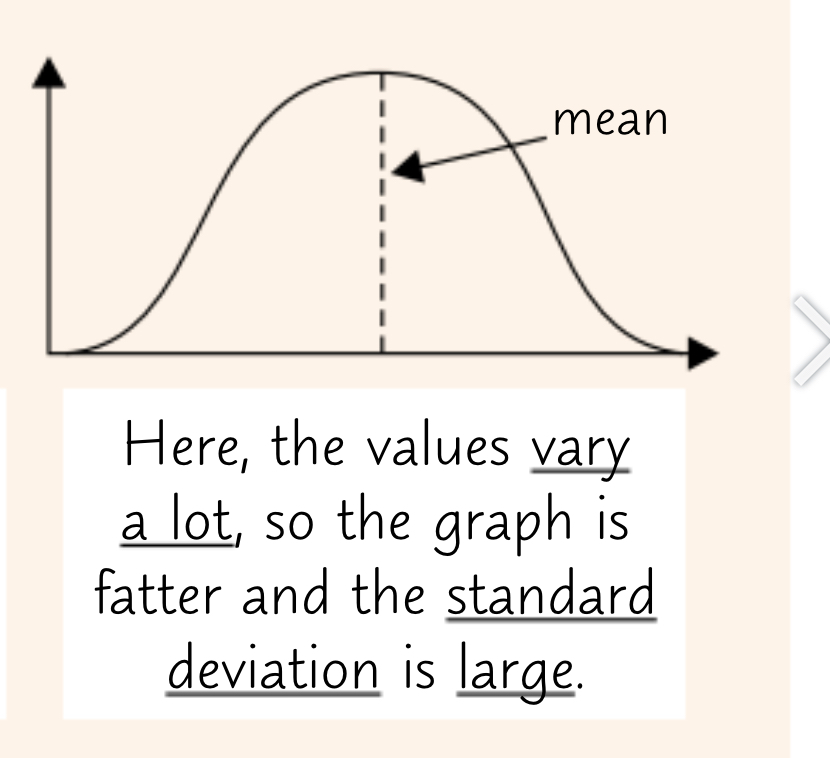
what does a large sd tell you about a sample?
the values in the sample vary a lot - graph is wider
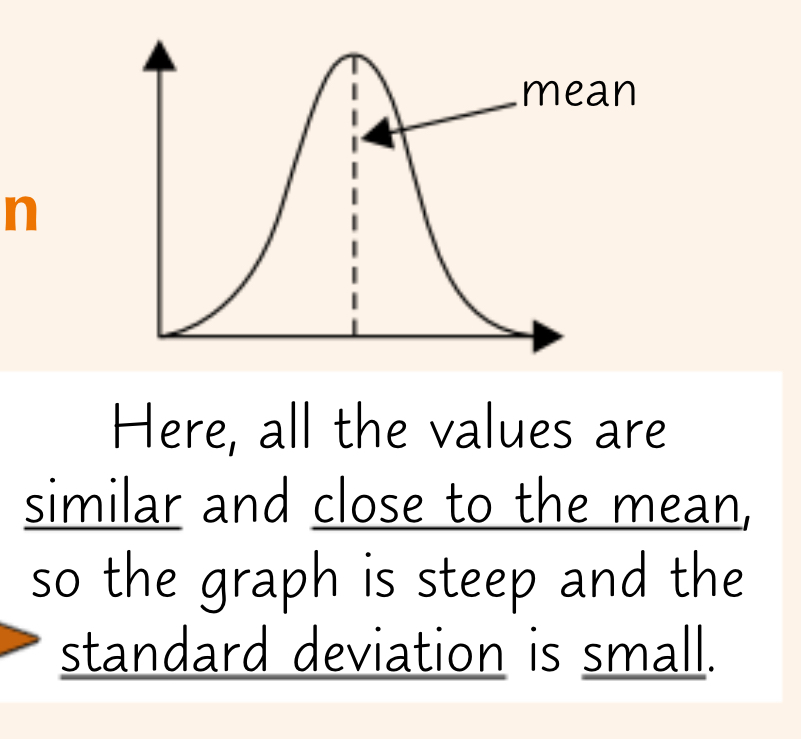
what does a small sd tell you about a sample?
most of the data is around the mean - little variation
what is the formula for calculating standard deviation?
x = value in the data set
x bar = mean
sigma = sum of
n = total no. of values
s = sd
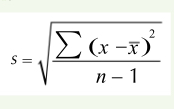
how do adaptations develop?
because of evolution by natural selection
give some examples of behavioural adaptations?
they are ways an organisms acts that increase its chance of survival
possums ‘play dead’ to escape attacks from predators
scorpions dance before mating = this makes sure they attract a mate of the same species, increasing the likelihood of successful mating
give some examples of physiological adaptations?
processes inside an organisms body that increase its chance of survival