Post Op Care and Surgical Complications PT1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Post- Op Care Goals
-examine for early complications
-remove surgical drains and tubes ASAP
-ambulation
-pain management
-monitor fluid and electrolyte balance
Post-Op Care Phases
1. PACU: Immediate
2. Hospitalization: Intermediate
3. Home or Long-term care: Convalescent (transition to full recovery)
________ and ________ phases are directed at maintaining homeostasis, treatment of pain, prevention and early detection of complications
immediate and intermediate
PACU (post anesthesia care unit) is also known as the ___ post op period
immediate
**BP, HR, and RR: heavily monitored vitals
**ins and outs: monitored
PACU
-trained personnel and equipment
-recovery area after surgery
-discharged when CV, pulm, and neuro functions at baseline
typical time a patient is in the PACU
1-3 hours
The intermediate post-op period occurs after ___ ____ until hospital discharge
anesthesia recovery
Intermediate Post- Op Period
-wound care
-drain management
-pulmonary care
-fluid and electrolyte care
-GI tract care
-pain management
Wound Care
-healing starts within hours after operation
-deeper structures sealed off from environment within 48 hours
wounds should be healed with ______________
aseptic technique
dressings can be removed post-op day ______
3 or 4 (**removed sooner if wet/ contaminated or symptoms of infection)
sutures/ staples removed post-op day ______ and replaced with tape
5
a full shower can be done on post-op day ______ if incision healing well
7
Surgical Drains
-prevent or treat unwanted accumulation of fluid
-evacuate air from pleural cavity
-placed in separate incision
-handle in aseptic technique and remove ASAP
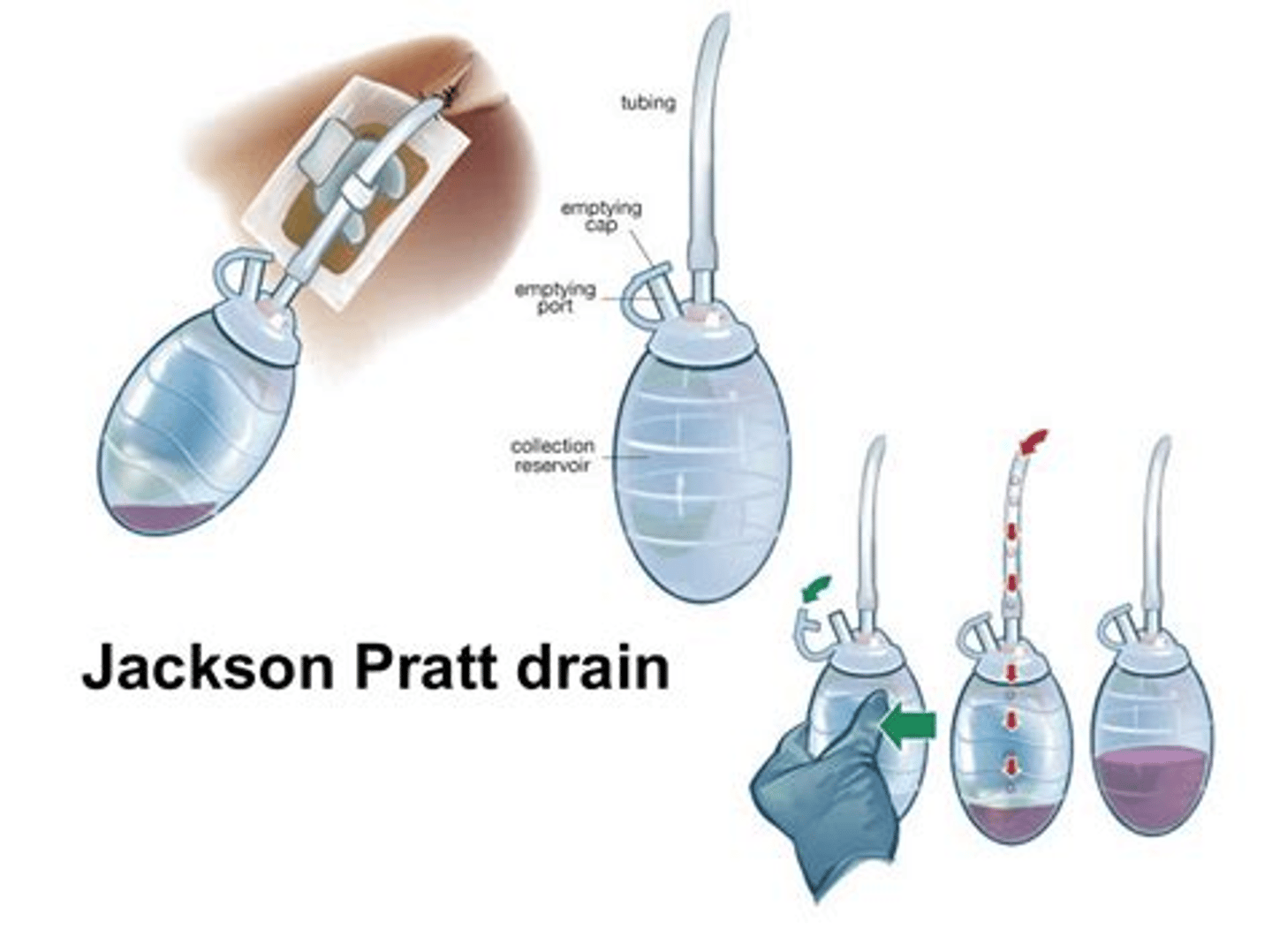
Closed Surgical Drains
-preferred type
-connected to a suction device
-Jackson-Pratt and Blake drains
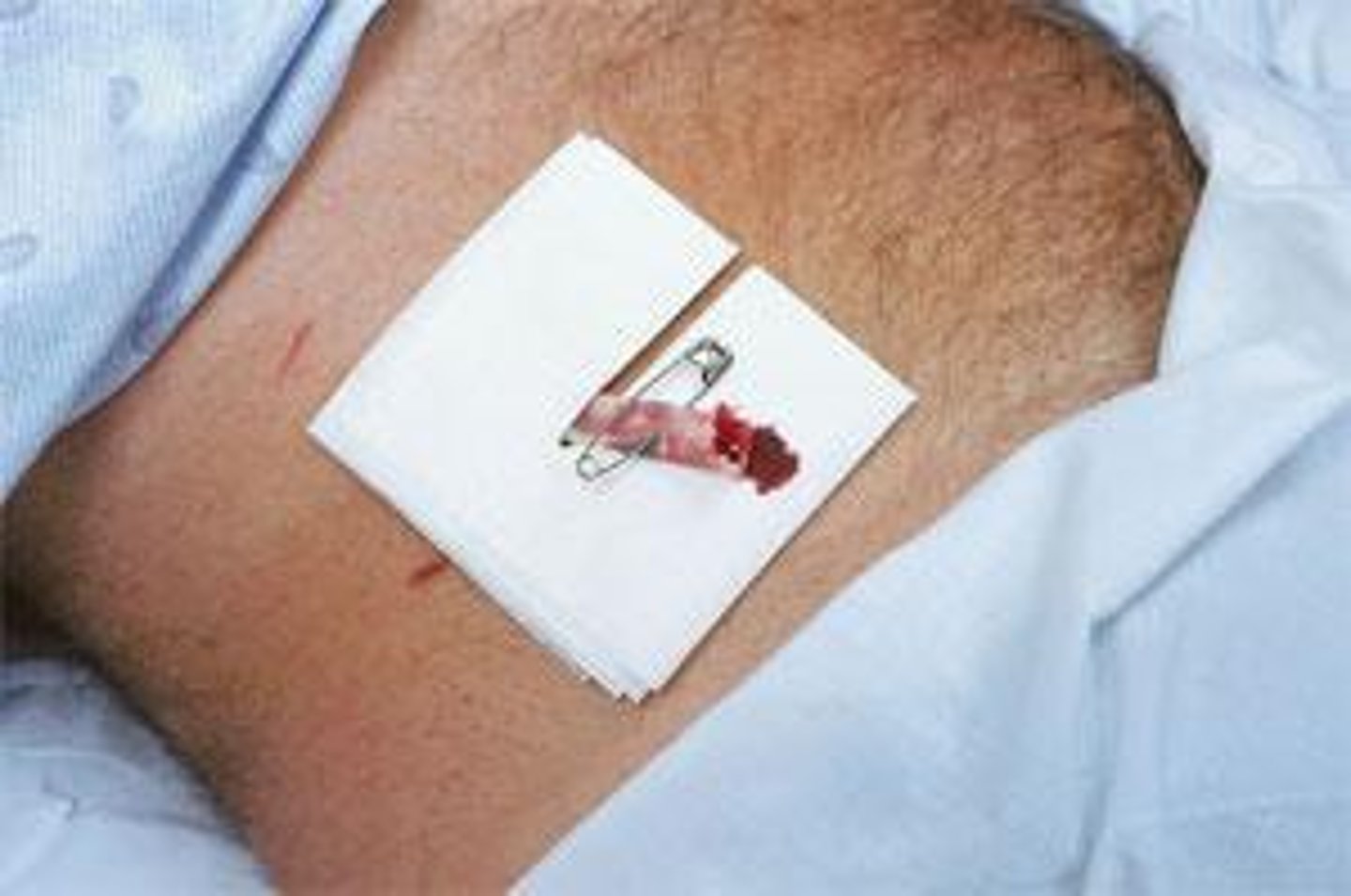
Open Surgical Drains
-more prone to contamination
-Penrose drain
Decreased Vital Capacity
-common after abdominal surgery
-Immediate: 40% of pre-op values
-POD 7: 60-70% of pre-op values
Decreased Funcitonal Residual Capacity
POD 1: 70% of pre-op levels and gradually returns to normal over 10 days
Change in Pulmonary Function
-due to pain, neural reflexes, abdominal distention, shallow breathing
-decreased vital capacity and decreased functional residual capacity
Decreased Pulmonary Function RFs
-obesity
-smoking
-pre-existing lung disease
-elderly
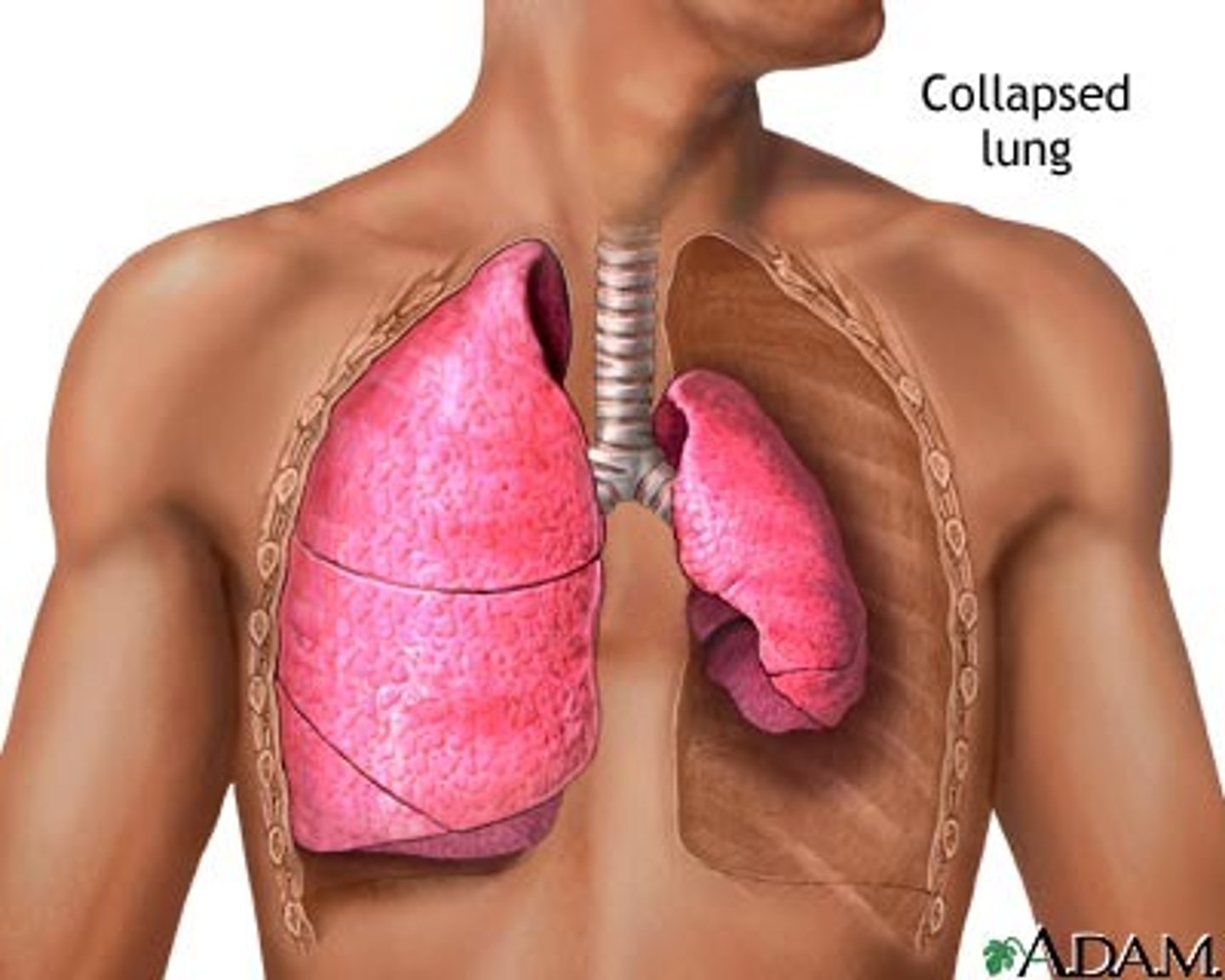
Pulmonary Concerns
-atelectasis (biggest concern; MC complication)
-pulmonary edema
-pneumonia
Pulmonary Preventative Measures
-deep breathing and coughing
-incentive spirometers
-early mobilization
-manage comorbidities appropriately
Deep Breathing Exercise Example
slow deep breath, hold for 2-5 seconds, slowly exhale
Fluid Maintenance Requirement
-weight (kg) x 30
-normal: 1500-2500 mL/day
Conditions requiring need for extra fluids
-fever
-hyperventilation
-loss during surgery
-condition increasing catabolic rate
-loss from drains
-from tissue edema and ileus (third space loss)
Conditions requiring need to measure electrolytes
-extra fluid losses than expected
-sepsis
-pre-existing electrolyte abnormality
-renal insufficiency (kidney disease)
Weight should be taken before surgery and can be used after surgery to evaluate ___ ____
fluid status
with a laparotomy GI peristalsis temporarily _________
decreases
peristalsis in the small intestine usually returns within _________
24 hours
peristalsis in the right colon usually returns within _________
48 hours
peristalsis in the left colon usually returns within ____________
72 hours
used if patient develops gastric distention, vomiting or ileus
NG
Advancing the diet
-fully conscious, NG tube out, GI function returned
-start with liquids and advance to soft foods
Antiemetics
-Ondansetron
-Prochlorperazine
Post-Op Pain Control
-Morphine
-Hydrocodone/ APAP
-Ketorolac
-PCA
PCA
-patient controlled analgesia
-med administration under patients control but within safe limits
Post- Op Bowel Protocols
-usually implemented before a patient has a problem
-Docusate
-Bisacodyl
-Milk of Magnesia
Post-Op Fever are usually ___ if in the immediate phase
benign
5 Ws of post op fever
-wind (pulm)
-water (UTI)
-wound (infection)
-walking (DVT/PE)
-wonder drug (meds)
Wind
-fever occurring on POD 0-2
-atelectasis
-pneumonia (secondary to atelectasis, ventilator, aspiration)
UTI
-fever occurring on POD 3-5
-MC due to indwelling catheter
Wound
infection or abscess causing a fever on POD 5
DVT/PE
fever on POD 7
Post-Op Pulm Complications
-most common single cause of morbidity
-2nd MC cause of death in patients >60 yo
med interactions and adverse reactions can cause a post-op fever ___________
anytime
Atelectasis S/S
-fever
-tachypnea
-tachycardia
-low O2
-scattered rales
-decreased breath sounds
prevention of atelectasis
deep breathing and incentive spirometry
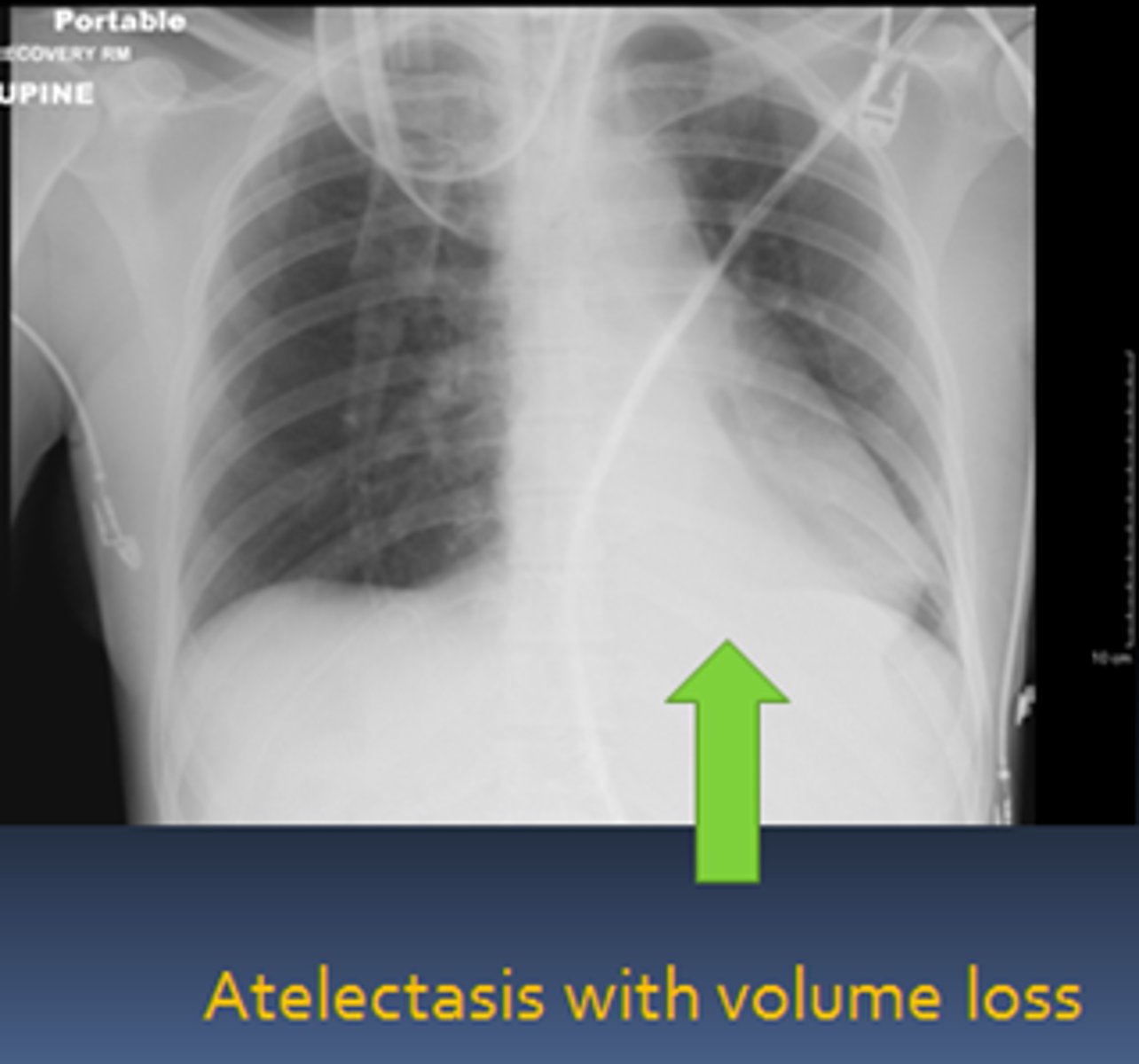
Atelectasis diagnostics
CXR
Atelectasis Treatment
-chest percussion
-coughing
-deep suctioning
Pneumonia
-secondary to atelectasis and or stagnant fluid
-can be ventilator associated or aspiration related
Pneumonia Diagnosis
-CXR
-CBC
-+/- sputum culture
treatment for pneumonia
abxs
Pneumothorax
-accidentally by procedure
-spontaneously in patients with underlyng lung disease
pneumothorax diagnostics
CXR
treatment for pneumothorax
thoracostomy
Pulmonary Embolus
-blood, air, fat
-thromboembolism from DVT MC (fat emboli MC if long bone fx or joint replacement)
PE diagnostics
-if stable: CTA
-if contrast allergy or dec kidney function: V/Q scan
PE treatment
-if stable: anticoagulation
-if unstable: tx shock, thrombolysis or suction embolectomy
UTI can be caused by pre-existing ___, ____, or ____
contamination, urinary retention, or instrumentation
UTI S/S
-fever
-dysuria
-urinary frequency or urgency
-flank pain
UTI diagnostics
urinalysis and urine culture
UTI treatment
abxs
Urinary Retention
due to interference with neural pathways responsible for normal emptying of bladder or over distention of bladder
urinary retention diagnostics
bladder US
urinary retention treatment
catheter