1.1 - lenses
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
what is a lens?
a transparent material causing light to refract
what are some uses for lenses?
eyes
telescopes
cameras
what is refraction?
change of speed of light
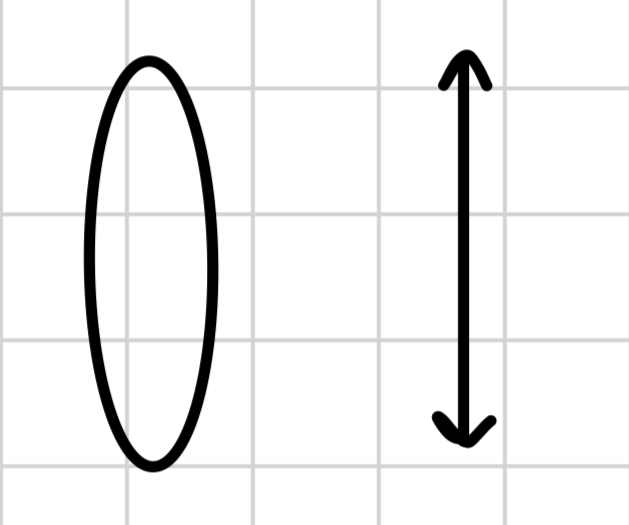
what are the 2 types of lenses?
convex - converging, oval shaped
concave - diverging, curves inwards
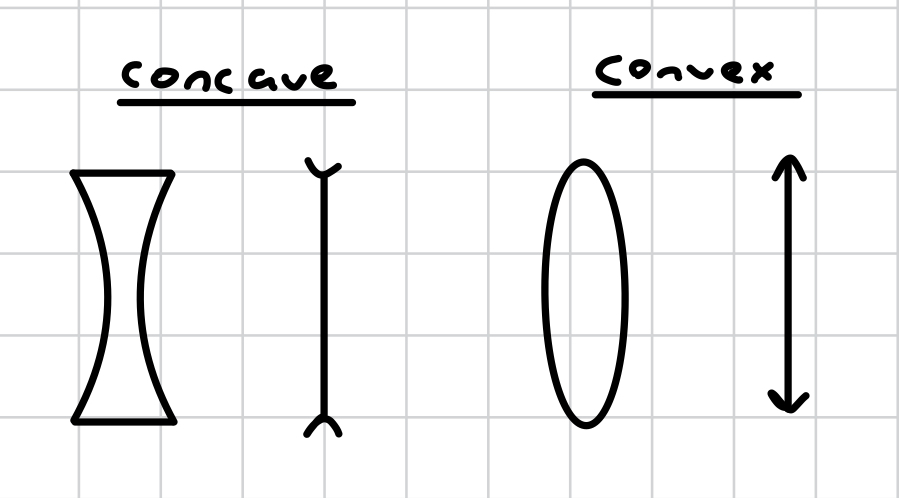
for lens questions, what feature do we consider the incident rays to have?
parallel
is convex converging or diverging?
converging
is concave converging or diverging?
diverging
which lens is an oval shape?
convex
which lens curves inwards?
concave
what is a converging lens?
convex
what is a diverging lens?
concave
what does converging mean?
rays tend to a point, i.e., refract towards each other until they cross
how do we investigate a converging lens?
by using a lamp box with a crosswire as an object
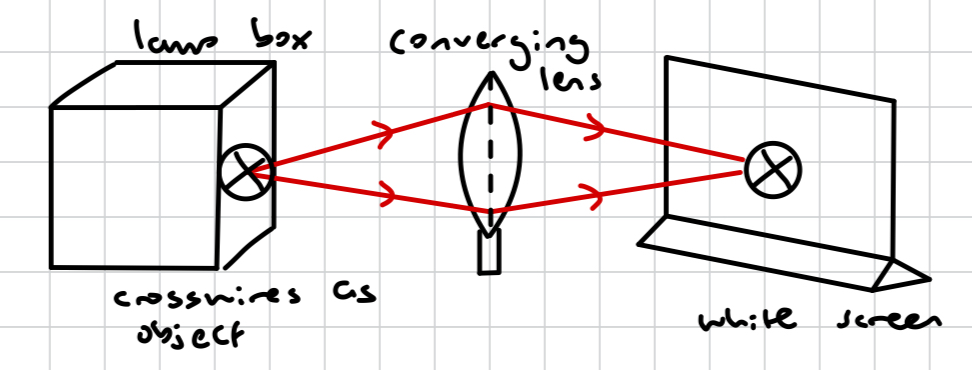
how do we use a lamp box with a crosswire as an object to investigate a converging lens?
light rays from the illuminated crosswire (the object) are refracted by the lens, forming an image of the crosswire on the white screen
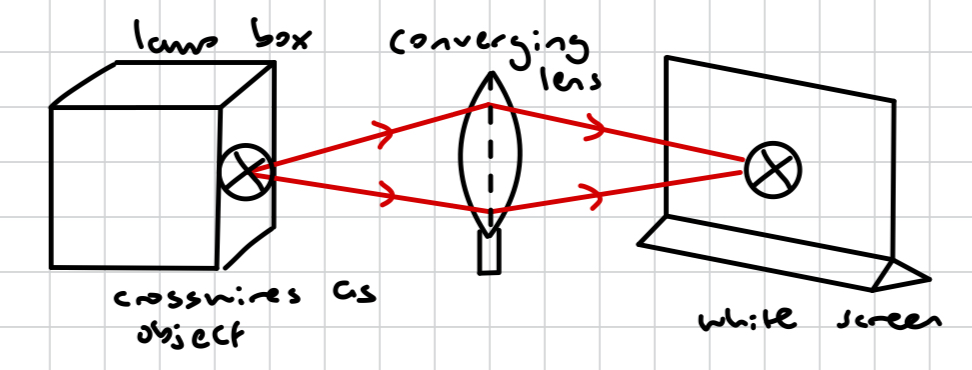
for a lamp box, how do we form a larger image?
by moving the object nearer to the lens
for a lamp box, is the image produced real or virtual? why?
real, because it’s formed on the screen where the rays converge
for a lamp box, where must the object be relative to the lens for an image to form?
beyond the principal focus (F). if the object is moved nearer the F, then the screen must be moved further from the lens
for a lamp box, what must be done to get a clear image if the object is moved nearer to the principal focus?
the screen must be moved further from the lens
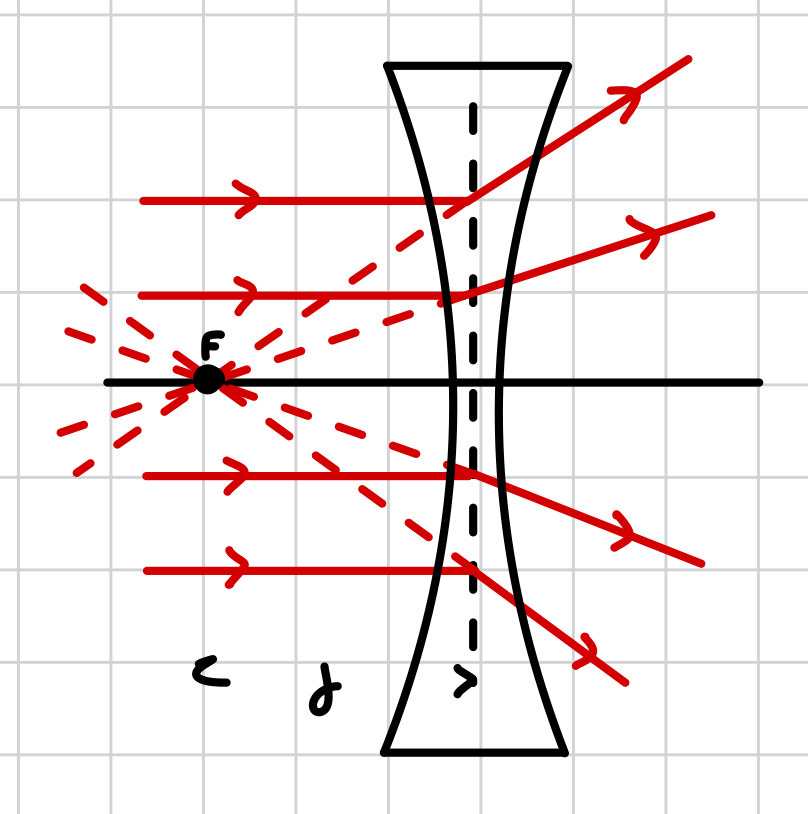
what does diverging mean?
rays refract away from each other
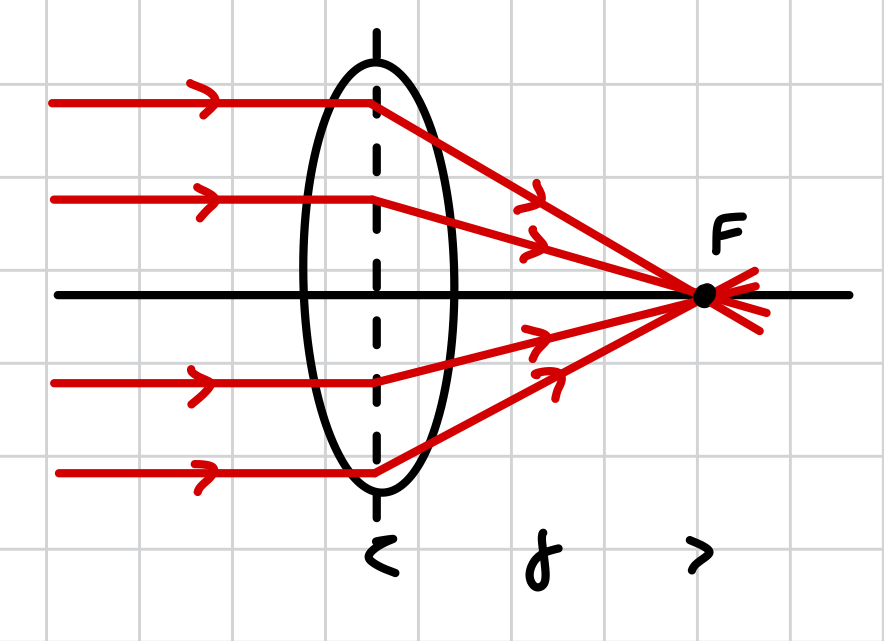
what happens to light rays when passing through a convex lens?
they refract (bend) towards each other until meeting (converging) at the principle focus
what happens to light rays when passing through a concave lens?
they refract (bend) away from each other (diverge)
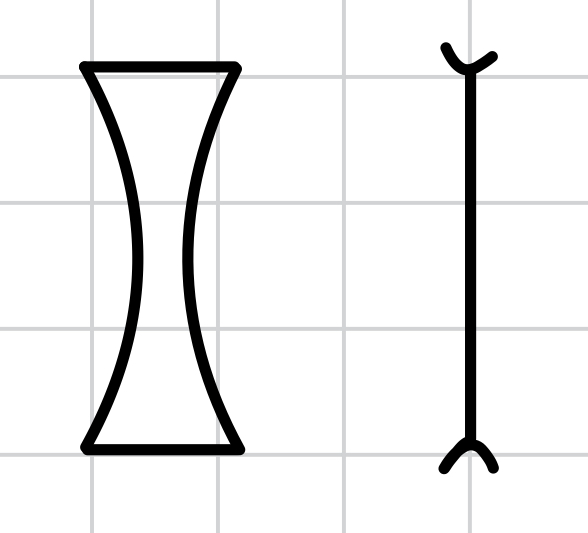
how do we represent a convex lens?
how do we represent a concave lens?
what is the principal axis?
imaginary line perpendicular to the middle of lens where an incident ray of light would not refract
what is the focal plane?
the planes on each side of the lens, perpendicular to the principal axis DIAGRAM
what is the principal focus (F)?
where rays of light, parallel to the lens, converge
what is the point of convergence?
where rays of light converge. when rays are parallel to the lens, this is at the principal focus on the principal axis
where do rays of light converge when the incident light rays are parallel?
at the principal focus, on the principal axis
in which case are the incident rays parallel?
when the object is distance
in which case are the incident rays not parallel?
when the object is not distant, i.e., when it can be placed on a ray diagram
where do rays of light converge when the incident rays aren’t parallel?
at the point of convergence. this is commonly not on the principal axis
what is the focal length (f)?
the length between the principal focus (F) and the centre of a lens
what is the object distance (u)?
the distance from the object to the centre of the lens
what is the height (h)?
the height of the object
F - ?
f - ?
u - ?
h - ?
F - principal focus
f - focal length
u - object distance
h - height of object
which lens is for short-sightedness?
concave lens
which lens is for long-sightedness?
convex lens
what does it mean to be short-sighted?
can see short distances, can’t see long distances
what does it mean to be long-sighted?
can see long distances, can’t see short distances
how does a concave lens help short-sightedness?
DO LATER
how does a convex lens help long-sightedness?
DO LATER
how do we represent objects and images in diagrams?
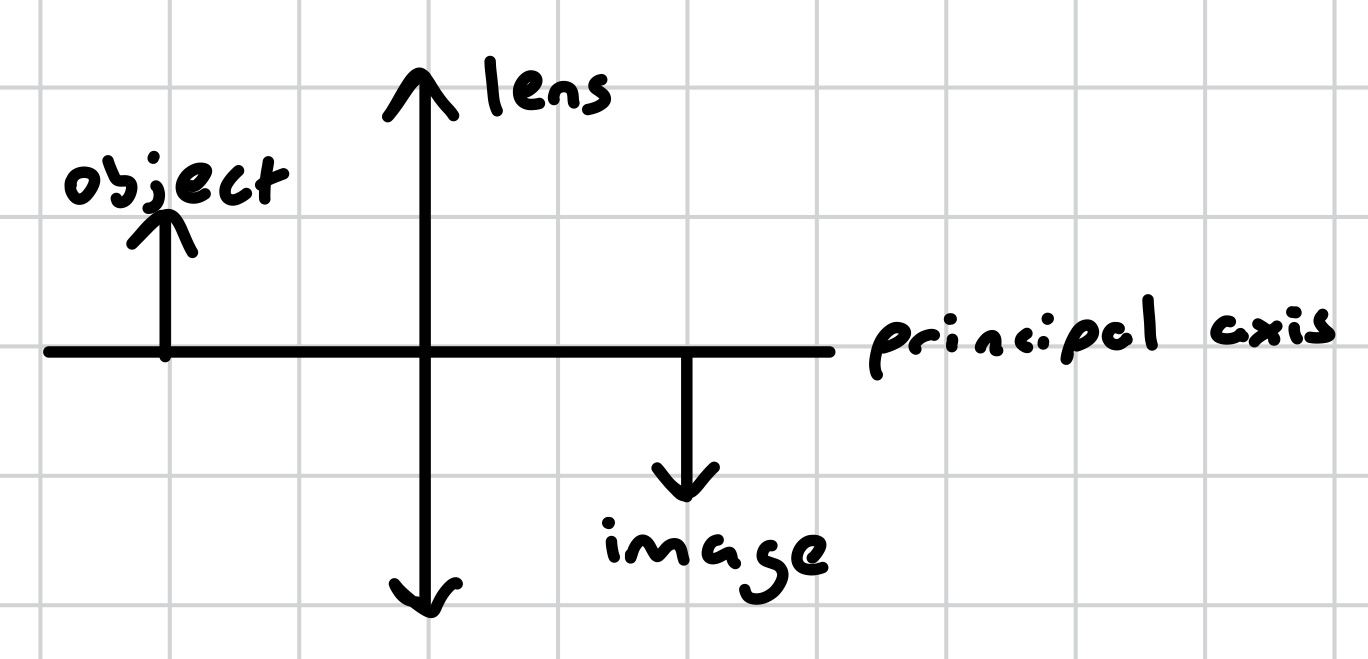
what is the focal length between?
the principal focus and the centre of the lens
does the focal length depend on the object or the lens?
lens
does the object distance depend on the object or the lens?
object
what assumptions we can make about the lens?
the lens is thin
there are only a few incident rays
why do we assume the lens is thin?
otherwise we can’t use a single line to represent it
if the lens is thin, then light refracts from the centre. this doesn’t happen in reality because light refracts as soon as it hits the lens
why do we assume there are only a few incident rays?
to make modelling easier
what does the position and nature of the image formed by a lens depend on?
the focal length (f) of the lens and the object distance (u)to the lens
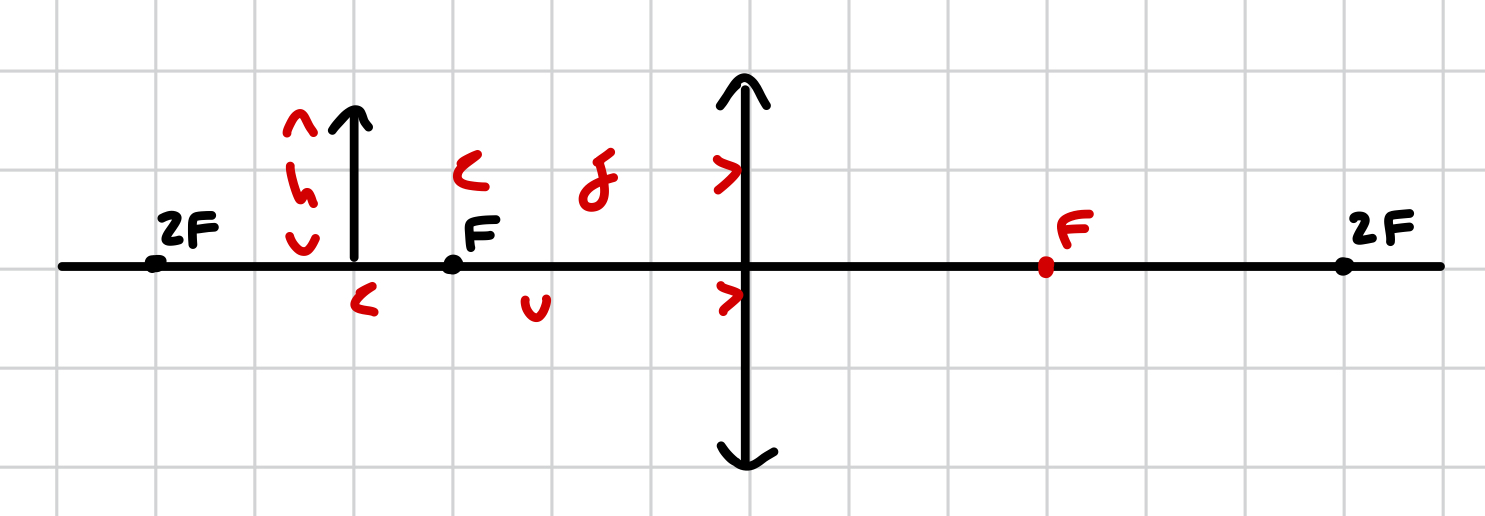
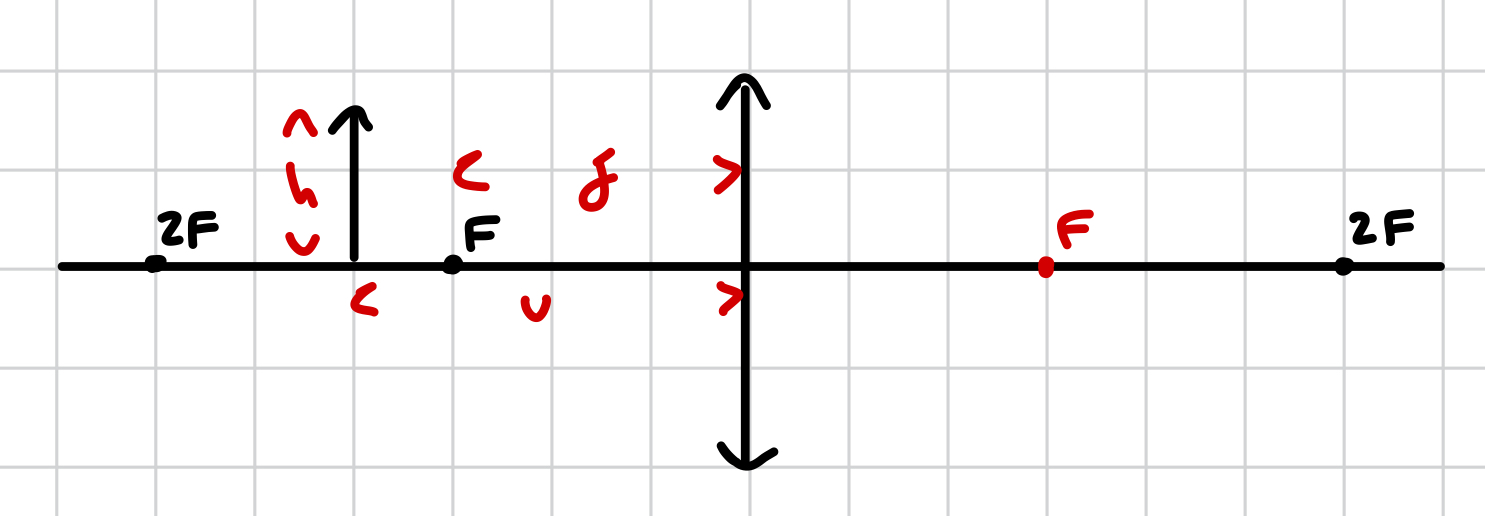
basic lens diagram (excluding rays)
F length is the same difference
only go up to 2F
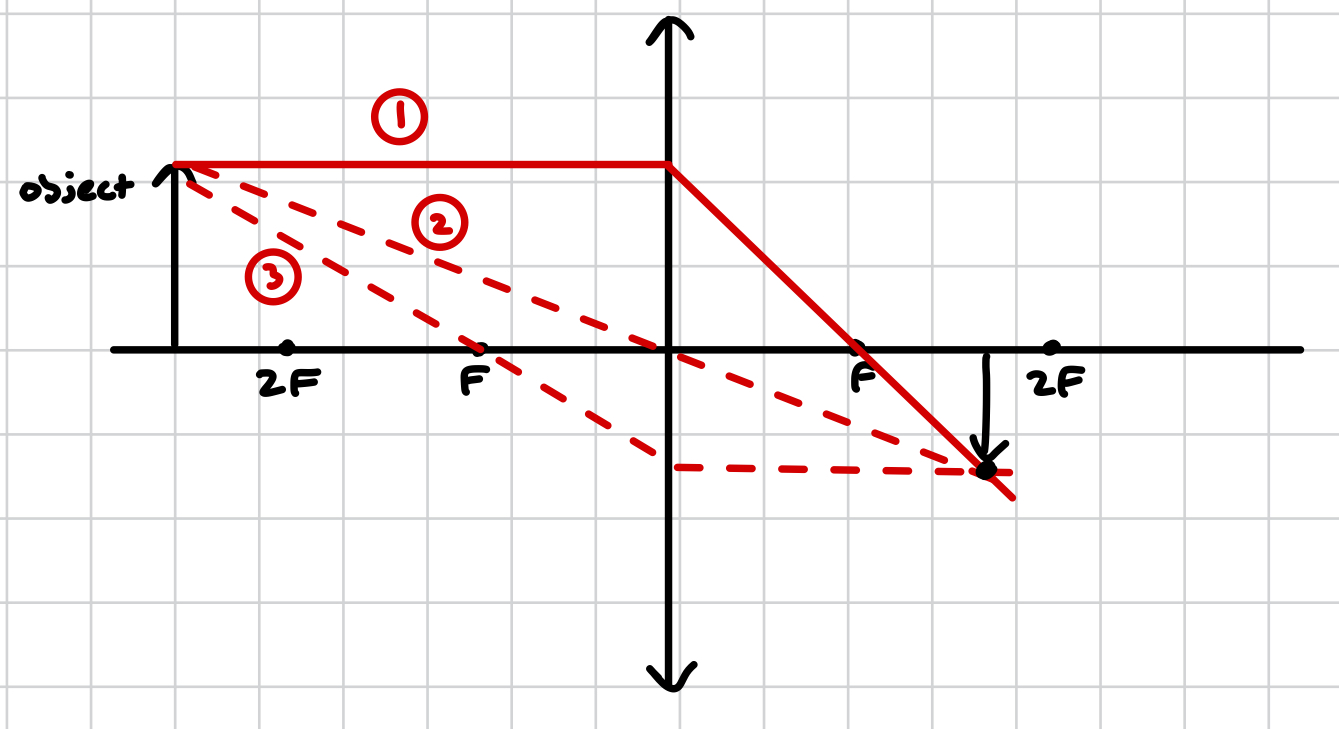
how do different light rays from an object pass through a converging lens?
ray is parallel to the axis and refracted through F (opposite side of the lens)
ray passes through the centre of the lens
passes through F (on the same side as the lens) and refracted parallel to the axis
for a lens diagram, why do we typically only go up to 2F?
because after 2F there aren’t many changes since most changes happen between F and 2F
is the focal distance (f) the same before and after the lens?
yessir
real image vs virtual image
real image - produced on the opposite side (of the lens) to the object
virtual image - produced on the same side as the object
where is a real image produced?
on the opposite side (of the lens) to the object
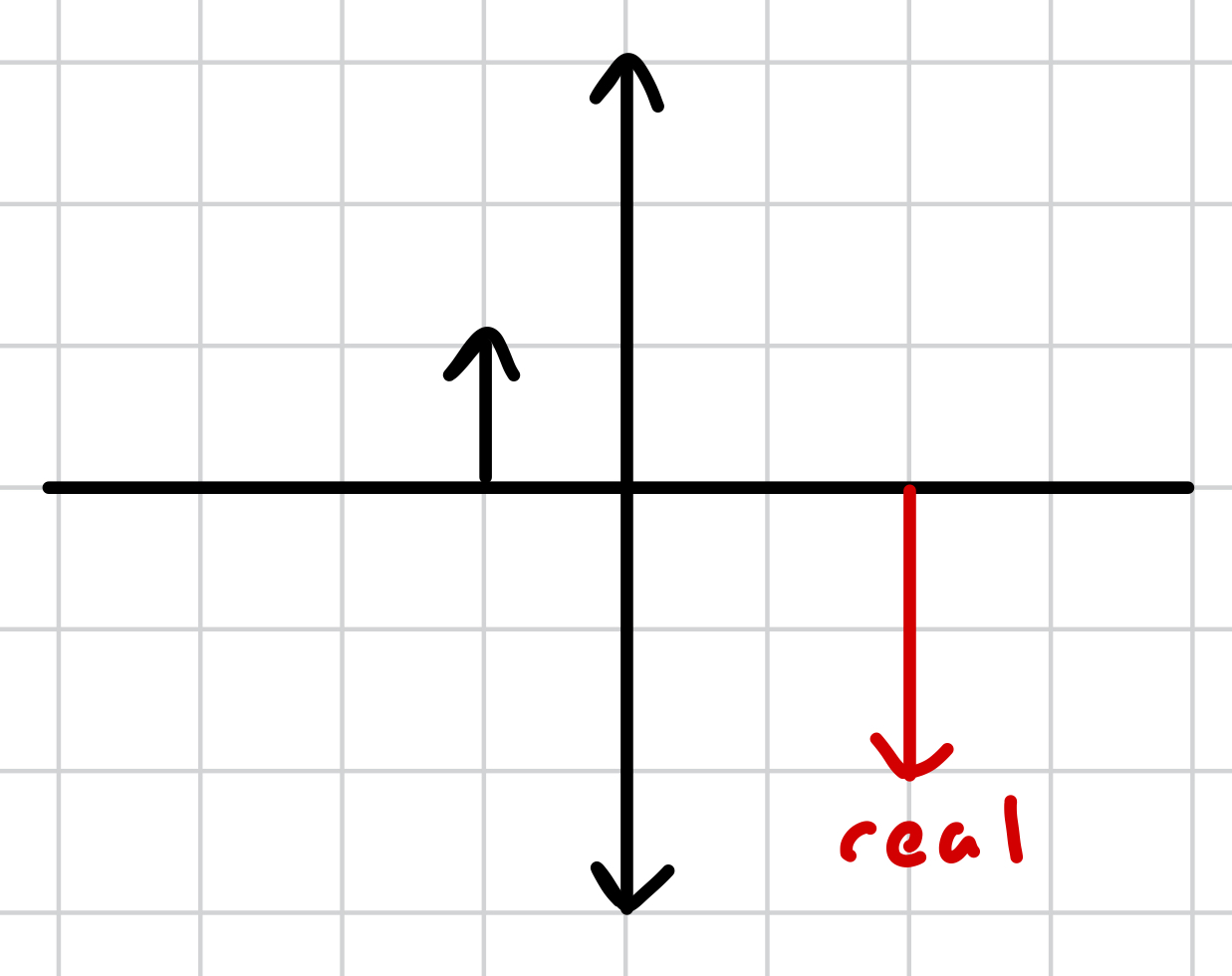
where is a virtual image produced?
on the same side (of the lens) as the object
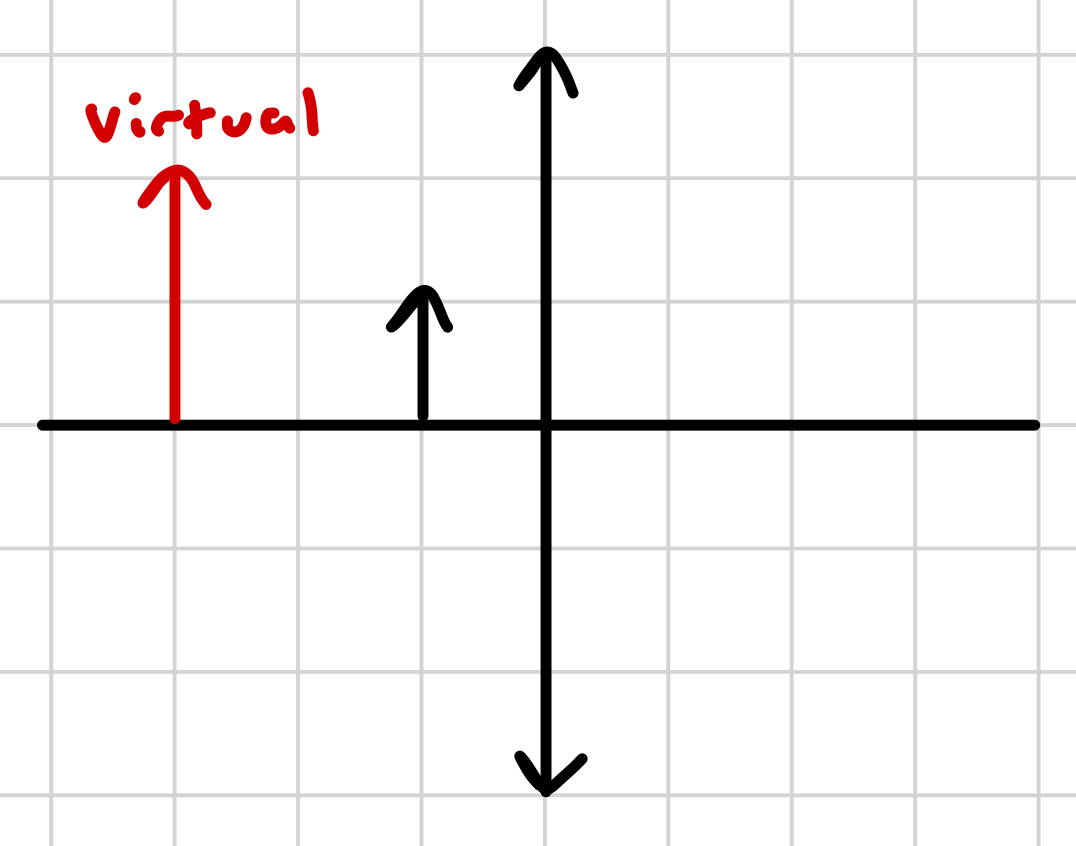
how do we form a real image with a converging lens?
the object must be beyond the principal focus of the lens
how do we form a virtual image with a converging lens?
the object must be before the principal focus of the lens
for a converging lens, where must the object be placed to form;
a real image
a virtual image
no image
real image - beyond the principal focus
virtual image - before the principal focus
no image - on the principal focus
how does a magnifying glass work?
the object is placed before the principal focus of the lens, forming a upright, magnified, virtual image that can only be seen by looking through the lens
are magnifying glasses converging or diverging lenses?
converging lenses, that produce a virtual image
do magnifying glasses produce a real or virtual image?
virtual image
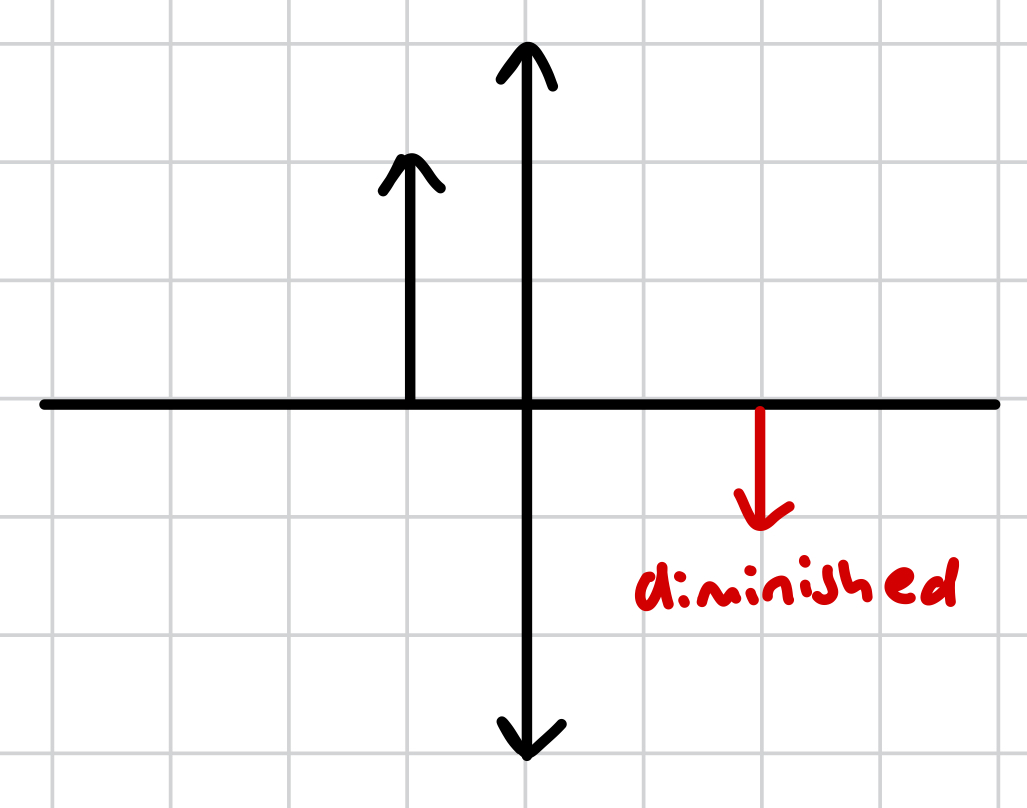
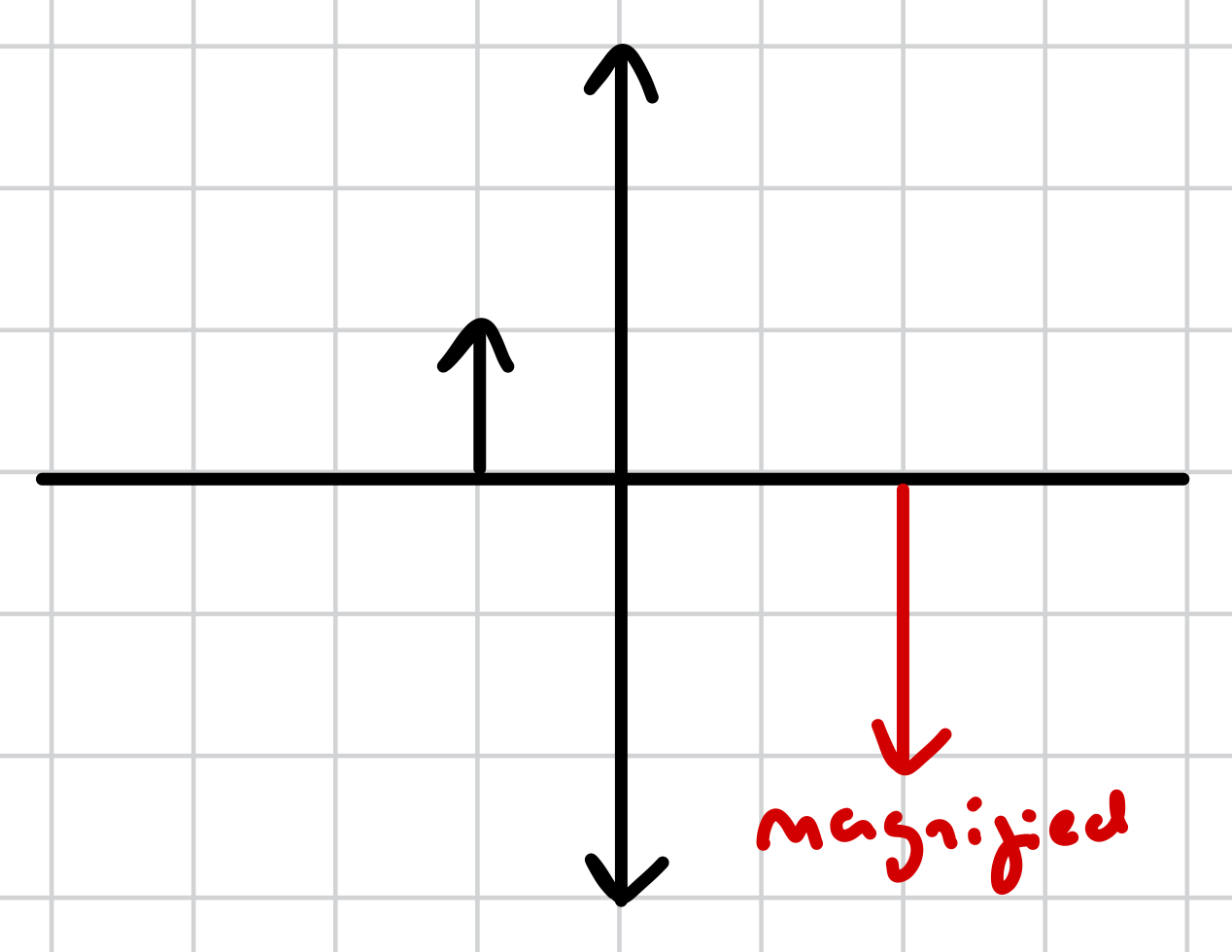
diminished vs magnified vs same size
diminished - image produced is smaller than the object
magnified - image produced is bigger than the object
same size - image produced is the same size as the object
what does diminished mean?
the image produced is smaller than the object
what does magnified mean?
the image produced is larger than the object
inverted vs upright
inverted - image produced is flipped vertically
upright - vertical orientation of image is maintained
what does inverted mean?
image produced is flipped vertically
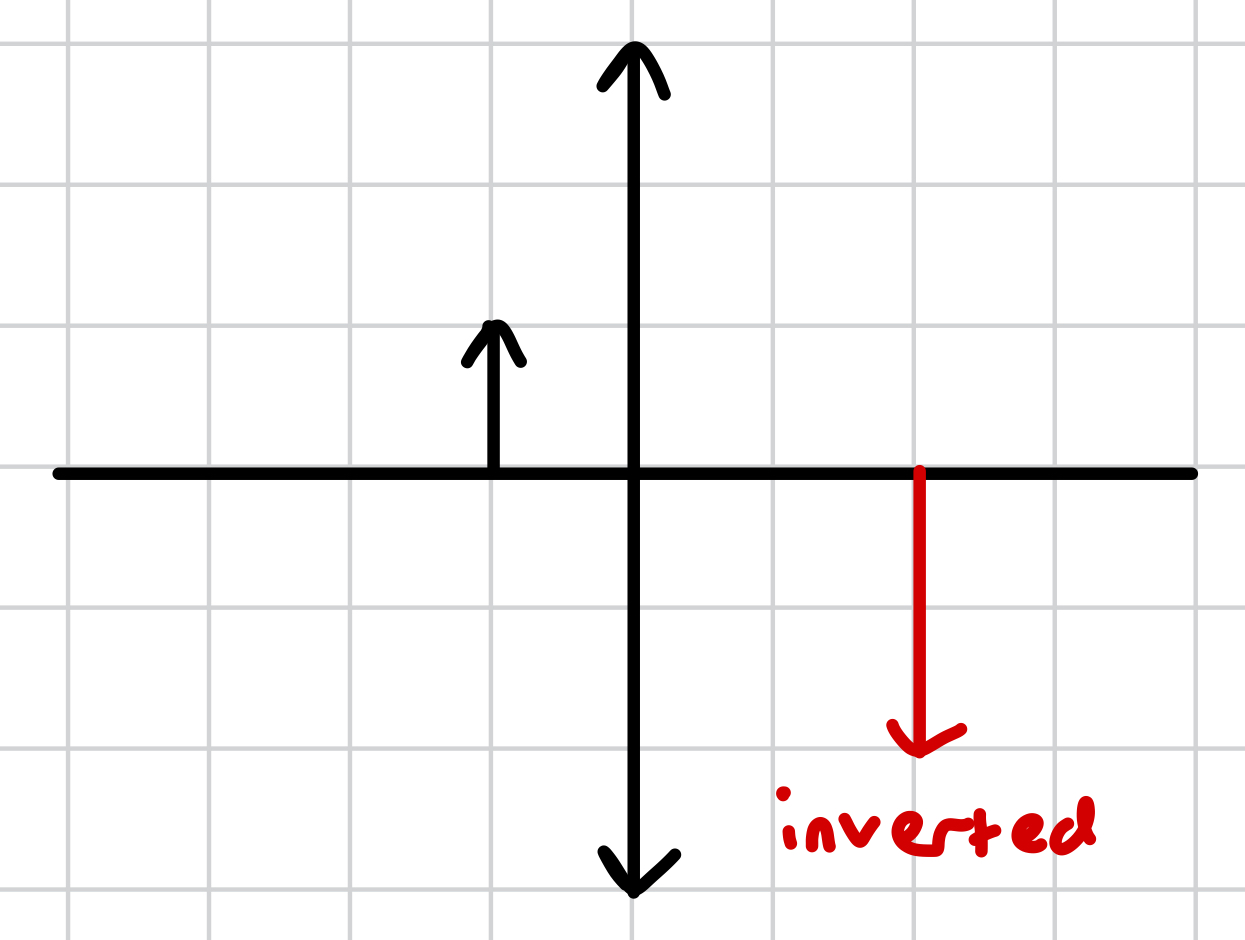
what does upright mean?
vertical orientation of image is maintained
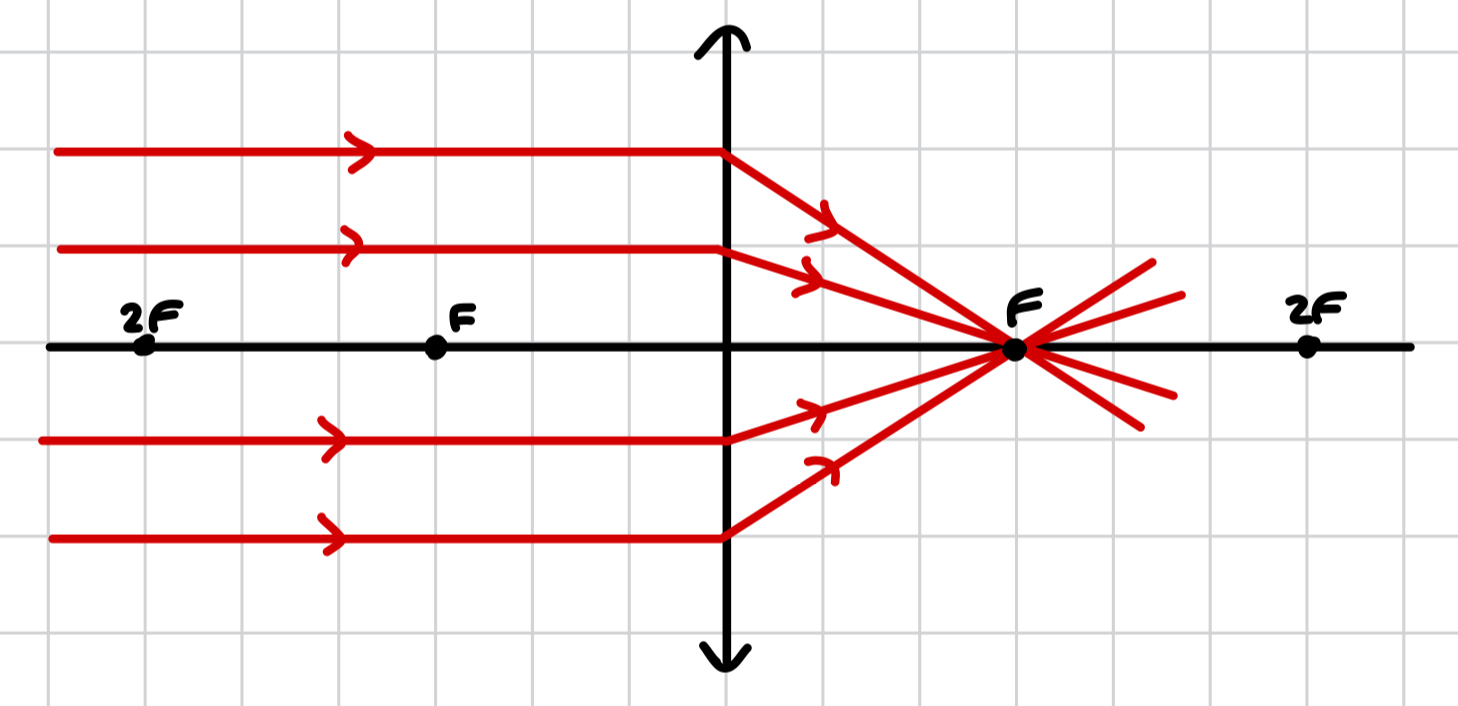
what image is produced by a convex lens when the object is distant?
at F
real image
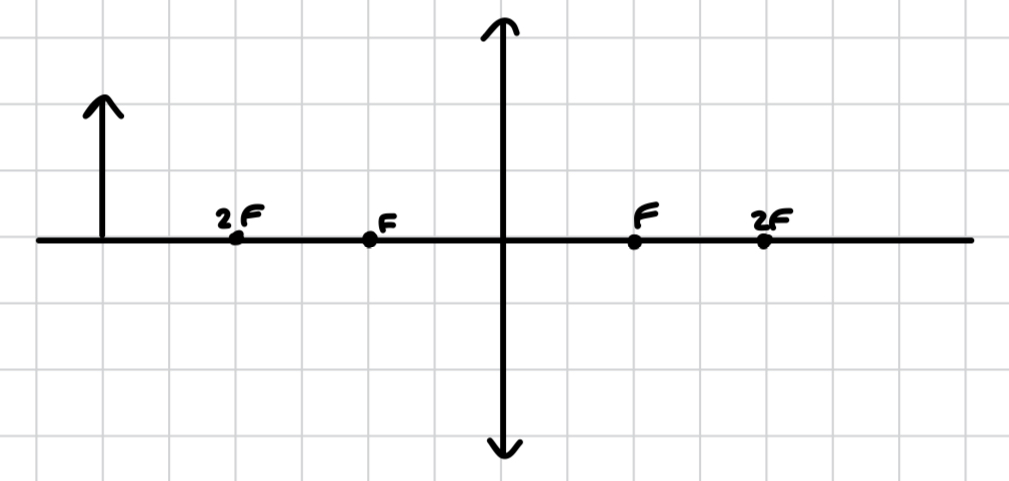
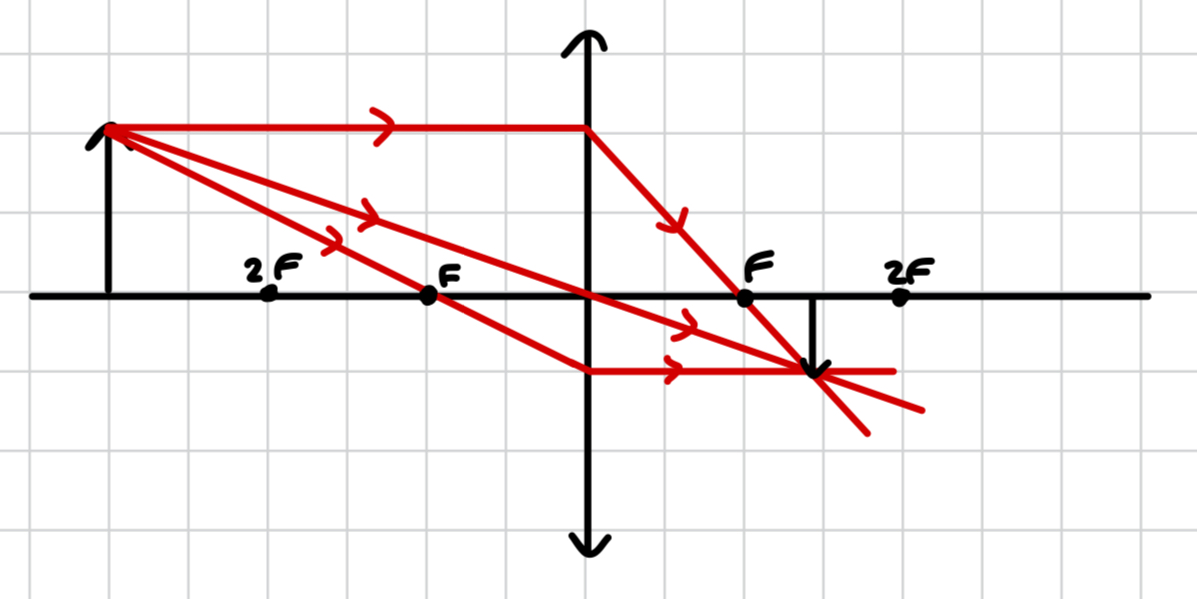
what image is produced by a convex lens when the object is after 2F?
F < image < 2F
real, inverted, diminished
what image is produced by a convex lens when the object is at 2F?
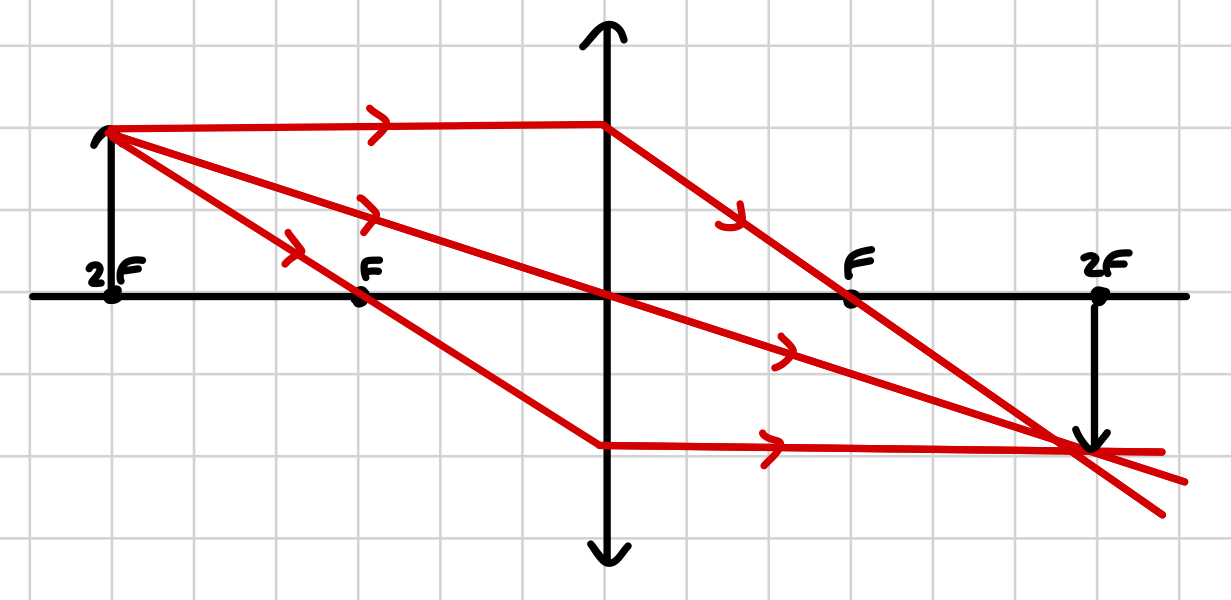
at 2F
real, inverted, same size
what image is produced by a convex lens when the object is between 2F and F?
after 2F
real, inverted, magnified
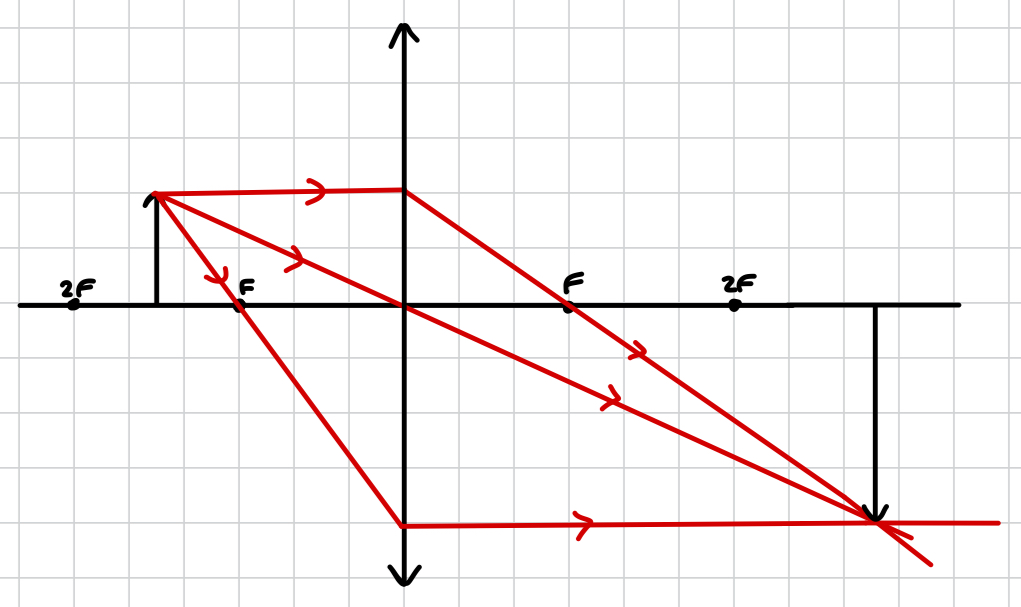
what image is produced by a convex lens when the object is at F?
no image is produced as rays are parallel and therefore will never converge or diverge
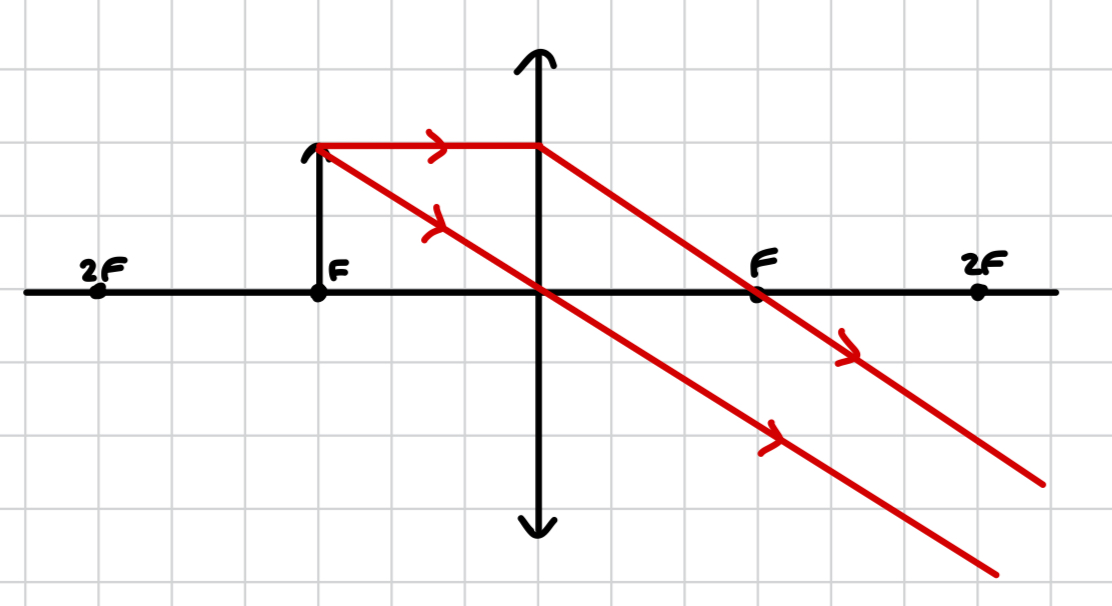
what image is produced by a convex lens when the object is after F?
at F
virtual, upright, magnified
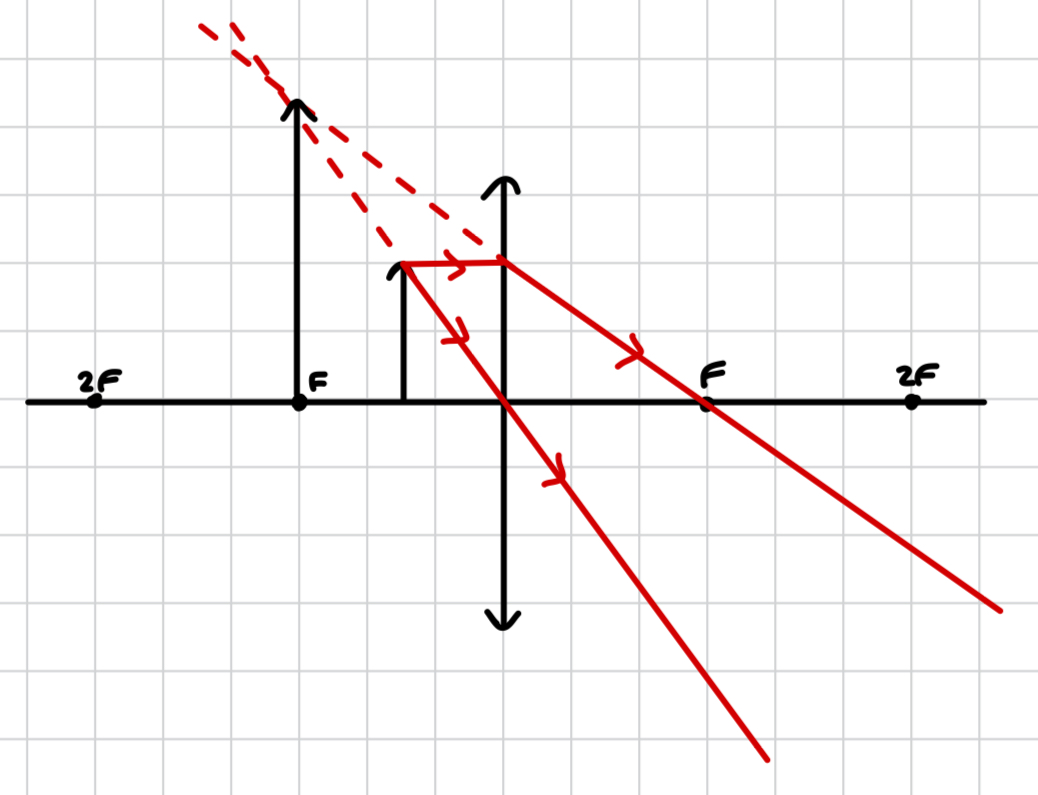
which object placement produces an image between F and 2F through a convex lens?
object after 2F
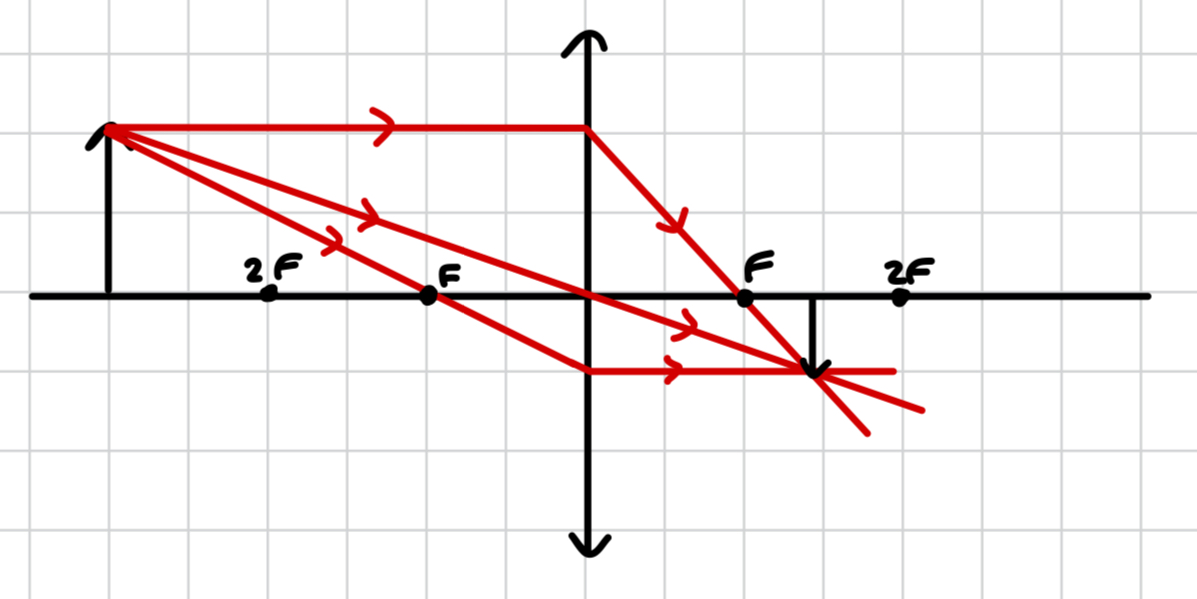
which object placement produces an image at 2F through a convex lens?
object at 2F
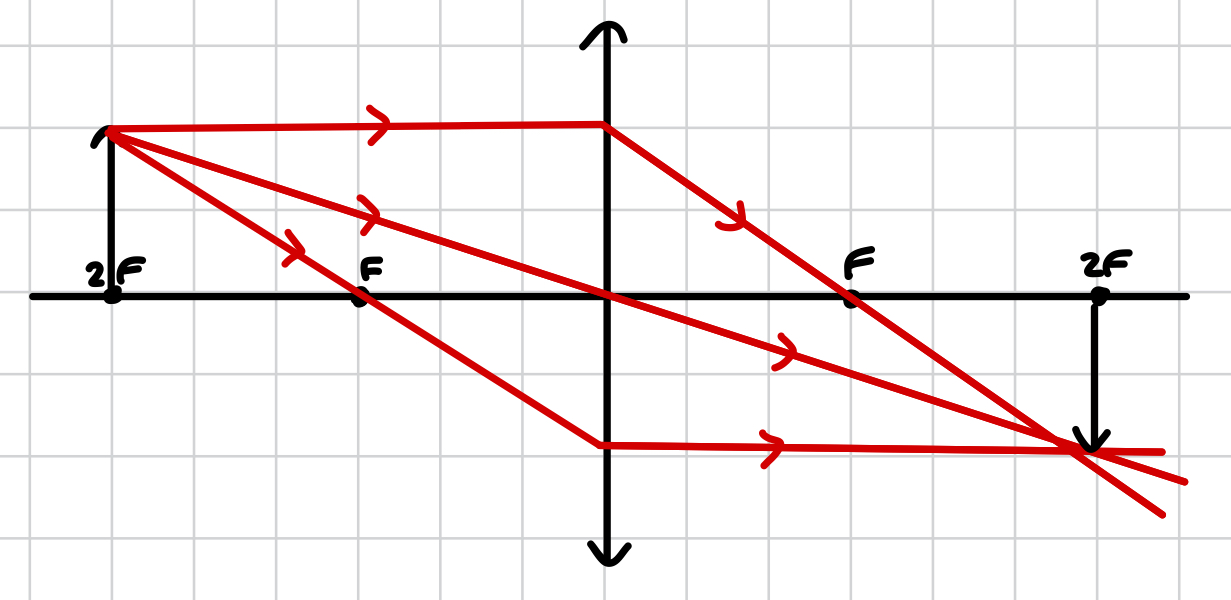
which object placement produces an image after 2F through a convex lens?
object between 2F and F
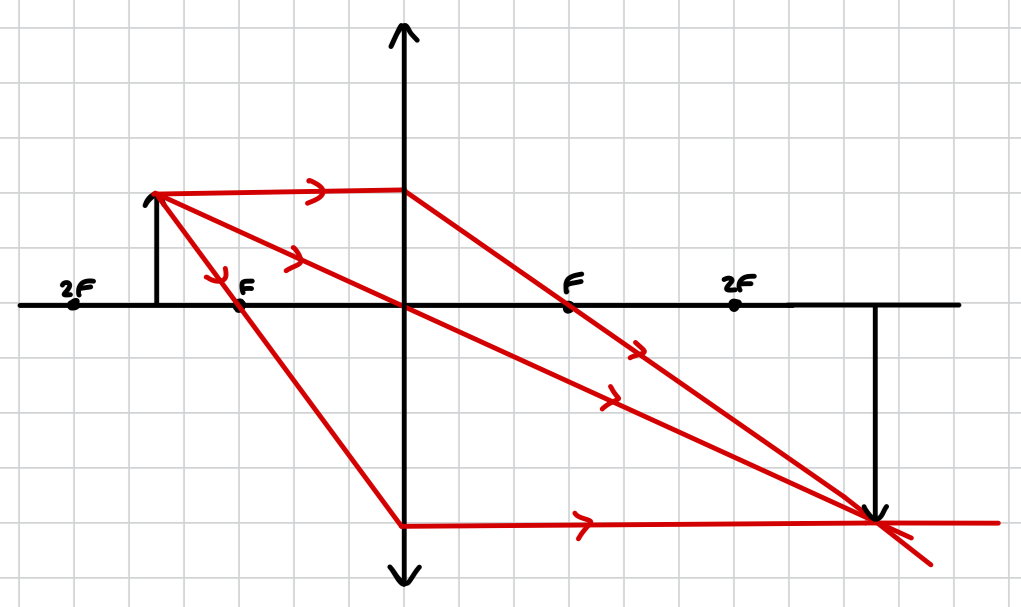
which object placement doesn’t produce an image through a convex lens?
object at F
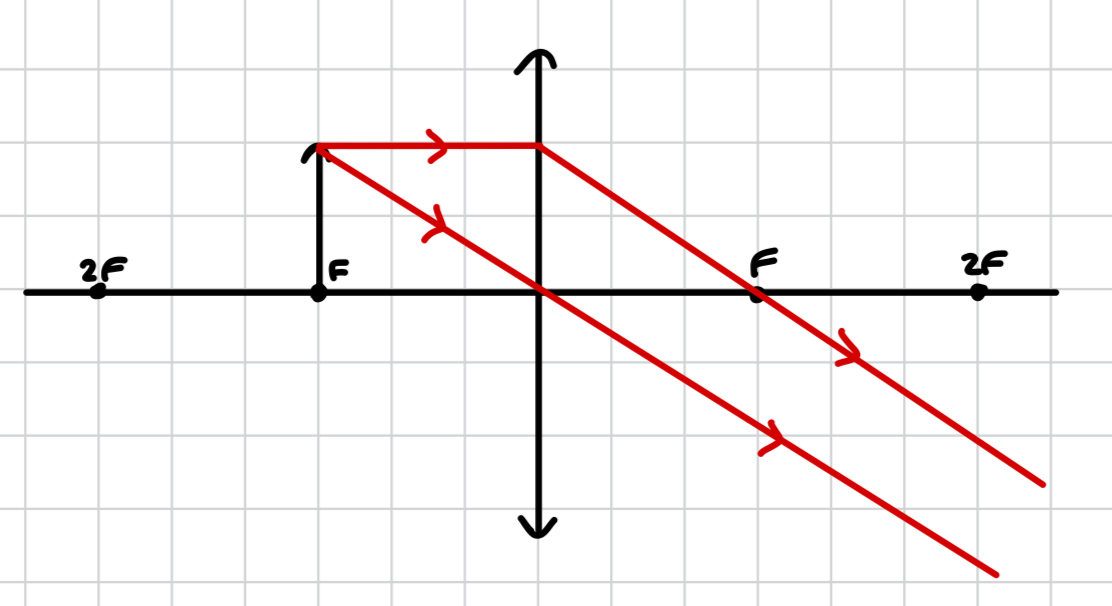
why does an object at F not produce an image through a convex lens?
there is no ray going through F as the object is at F, and the rays are parallel, so no converging or diverging occurs. no converging means no real image is produced, and no diverging means no virtual image is produced. therefore no image is produced
which object placement produces a virtual image?
object after F
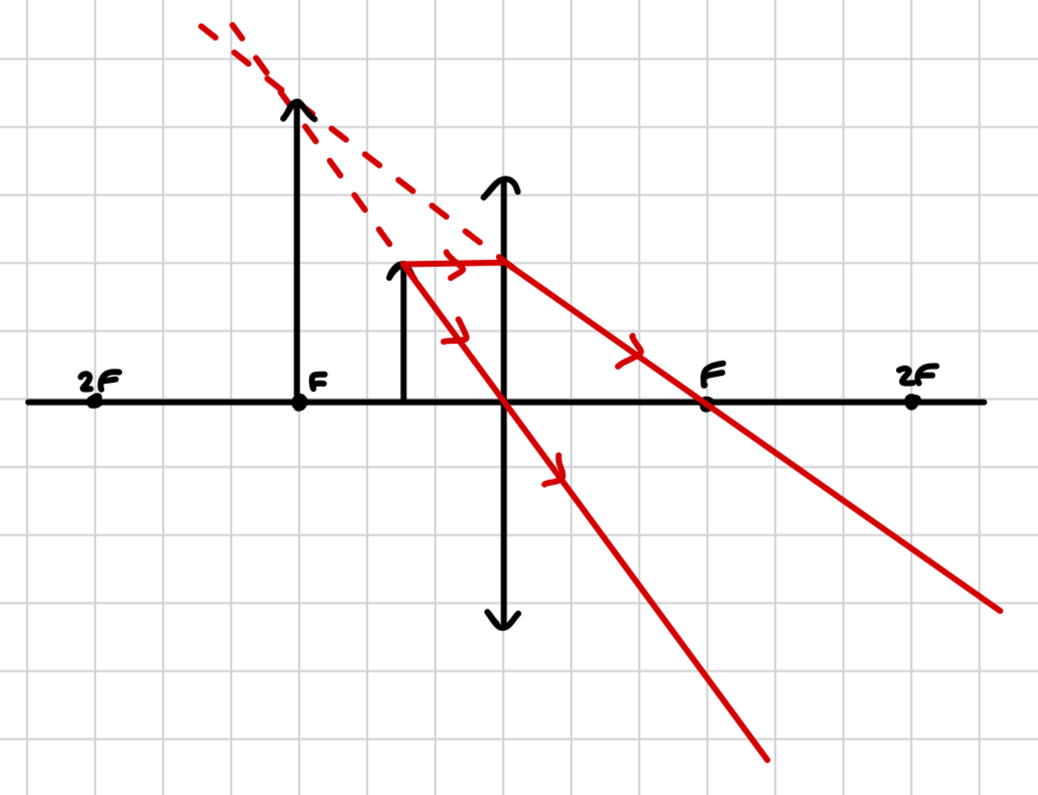
which refractive pattern produces a real image?
converging
why does a converging refracting pattern produce a real image?
after passing through the centre of the lens, the rays bend towards each other (converge). they meet at a point on the opposite side of the lens to the object, meaning a real image is produced
which refractive pattern produces a virtual image?
diverging
why does a diverging refractive pattern produce a virtual image?
after passing through the centre of the lens, the rays refract away from each other (diverge). this means on the opposite side of the lens, where a real image would be produced, the rays never meet. instead, the rays converge in the opposite direction, producing a virtual image as they converge at the same side as the object
what happens when an object is placed in the focal plane?
light rays from any point on the object are refracted by the lens to form a parallel beam, forming a virtual image at infinity when looking through the lens (not an infinity mirror tho)
what image is formed when an object is placed in the focal plane?
a virtual image at infinity
how do you see a virtual image?
by looking through the lens