Constitution and Federalist Era
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Milboer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
demographics of America 1790
The South had a large enslaved population, which was central to the agricultural economy, particularly in tobacco, rice, and indigo production.
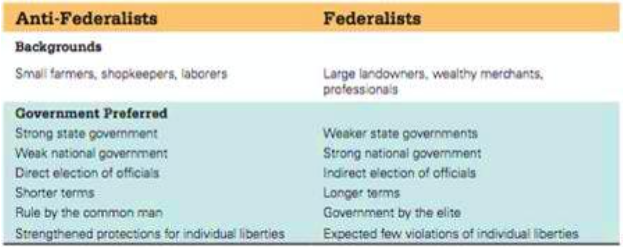
Federalists were in big cities like NYC
Anti Federalists were in rural areas like small farmers/ hillbillies
National Power
strong federal government (washington & adams)
Washington's cabinet
Secretary of Treasury - Alexander Hamilton
Secretary of War - Henry Knox
Secretary of State - Thomas Jefferson
Attorney General - Edmund Randolph
Hamilton's plan for debt
Bank of the U.S.- not an enumerated power
Excise taxes- taxing is an enumerated power
Funding at par (paying back the debt of the revolution at its full value)
Assumption of state debts
Tariffs
BE FAT
Judiciary Act
Set up the court system for U.S
Supreme court, 3 circuit courts, thirteen district courts
John Jay named first chief justice of supreme court
Us attorney and US marshall created to serve as prosecutor and police
Deferral judges had final say over constitution
foreign policy
the nation's foreign policy was shaped by its weak central government and limited authority.
guarantees in the Bill of Rights
Protect individual rights; freedom of speech, freedom of the press, etc.
Alexander Hamilton
Federalist
Secretary of Treasury
assumption program
US national govt. should pay all debt, state and national
Wanted assumption of state debts to tighten link between state and National govt.
Some states had already paid debt and opposed assumption
Virginia agrees as long as capitol put on potomac river (between maryland and va)
Hamilton only concerned with building national credit
Payed a portion of war bond price back to the buyer
Bank of the United States
Hamilton wanted a national bank to be jointly owned with private stock holders (Hamilton acting like Britain)
Jefferson and Madison opposed bank
Taxes occurred (including excise tax on whiskey)
Hamilton wanted tariffs to raise revenue and to allow growth of american industry
Farmers opposed because tariff makes prices higher, Tariff never passed
Whiskey Rebellion
National government put a tax on whiskey, farmers in SW Pennsylvania revolted against tax
Protested using similar techniques as sons of liberty in 1765 and shaysites in 1786
“Liberty, Equality, Fraternity”
Rebellion was stopped with a militia, proved national government was strong
political parties
There were the Federalists that believed in a strong central government. Led by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and in the beginning there was James Madison
There were anti federalists that changed to the Democratic Republicans and believed more power to the individual and states because they feared a monarchy forming. Led by Thomas Jefferson, Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry,
neutrality proclamation
Said that the US will not be involved in any European conflicts because the young nation does not have the military power or the funds
Jay's Treaty
Chief justice john jay sent to london in 1794 to make treaty to talk Britain out of its practice of searching and seizing American ships
Solved no problems; bad treaty
Came back with nothing
Mississippi River
Control of the Mississippi River was vital for American trade, particularly for farmers in the west. Washington’s foreign policy aimed to secure American access to the river, which was addressed in Pinckney’s Treaty with Spain in 1795.
Federalists and democratic-republicans
John Adams presidency
Second president, lead to the rise of the different political parties (Federalists & Democratic-Rupublicans)
He dealt with the XYZ Affair and the Quasi-War with France. He also signed the Alien and Sedition Acts, which were highly controversial and seen as an attack on political dissent.
election of 1796
John Adams elected as president, Jefferson elected as VP because he came 2nd
49-51 percent
Adams assumes it is his turn to be president but he is wrong; his best friend ran against him
Adams was federalist candidate, Jefferson was Democratic-Republican
Alien Acts
Increased residency requirements from 5-14 yrs
President given power to deport foreigners in peace or wartime
Immigrants come and practice subsistence farming
No voting for 14 years- 3 votings
Done because the Federalists thought that the immigrants would vote for the Democratic republicans and this was threatening as the vote was very close
Sedition Acts
Made it illegal to criticize the government
Went against 1st amendment rights
compact theory of government
U.S. Constitution was a compact between the states and the federal government. If the federal government violated the compact, the states had the right to nullify federal laws or even secede.
treaty with France
After the Quasi-War, Adams negotiated a peace treaty with France (the Convention of 1800), which ended the hostilities and allowed the U.S. to focus on domestic issues.
9th Amendment
This amendment is meant to ensure that the listing of specific rights in the Constitution (like those in the Bill of Rights) does not mean that other unlisted rights are not also protected
10th Amendment
stating that any power that is not specifically granted to the federal government, or prohibited to the states, is reserved for the states or the people. It’s a way of reinforcing the idea that the federal government has limited, enumerated powers and that the states and the people retain all other powers.
Constitution (SAQ)
A list of enumerated powers, powers that the government has
First 10 things are the bill of rights that the Anti federalists wanted, it is a list of things that the government can’t limit, “list of no”
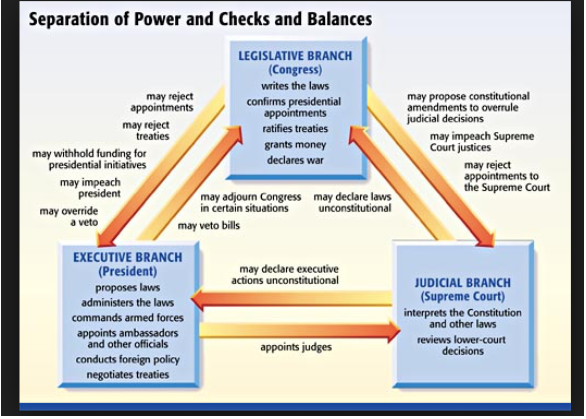
separation of powers (SAQ)
Federalism (SAQ)
Supported a strong national government, weaker state governments, government led by the elite, indirect election of officials, longer terms, few violation of individual liberties