Exam 3 memorizations
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Standard state in regards to gas, liquids, solids, and solutions
Gas: 1 atm
Liquids and Solids: 1 atm (and usually 25 C)
Solutions: 1 M
The activity of a chemical: solids, liquids, gases, solutions, at standard state
solids and liquids: activity = 1
Gases: activity = partial pressure/1 atm
Solutions: activity = concentration/ 1 M
at standard state: activity = 1
K
equilibrium constant
Q
Reaction quotient.
formula for gibbs free energy
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
ΔG = formation products - formation reactants
formula for Reaction Quotient (Q)

formula for equilibrium constant (K)
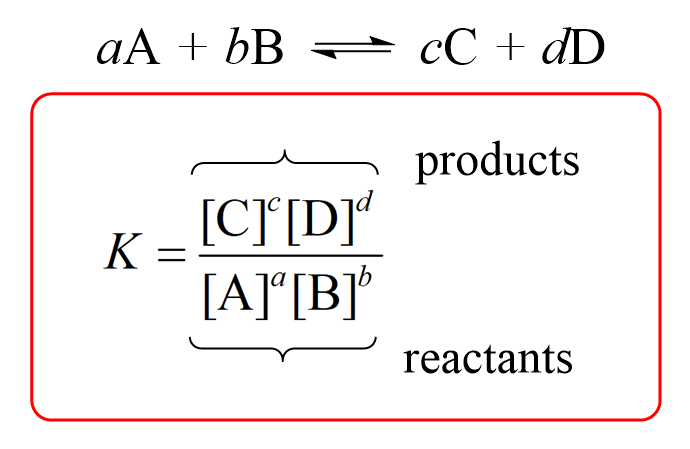
formula for equilibrium constant (K) when all reactants and products are in the same phase
Original formula but omit solids and liquids
Example:
Formula:
2HgO(s) + H2O(l) + 2Cl2(g) ⇌ 2HOCl(aq) + HgO⋅HgCl2(s)
Write out formula omitting (s) and (l)
K = [HOCl]2 / [Cl2]2
![<p><strong>Original formula but omit solids and liquids</strong></p><p></p><p><strong>Example:</strong></p><p><u>Formula:</u></p><p>2HgO(s) + H2O(l) + 2Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) ⇌ 2HOCl(aq) + HgO⋅HgCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</p><p></p><p><u>Write out formula omitting (s) and (l)</u></p><p>K = [HOCl]<sup>2 </sup>/ [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/49b82a33-3465-46cb-84af-92d75054a79f.png)
When K > 1
reaction favors products, equilibrium lies to the right
when K < 1
reaction favors reactants, equilibrium lies to the left
when K = apprx 1
Reaction favors neither products nor reactants, equilibrium lies in the middle
when 10-3 < K < 103
K contains an significant amount of reactions and products at equilibrium
Kp vs Kc
Kp
used for gaseous reactants and based on partial pressures
Kc
reactions in solutions regarding Molar concentrations
Kp = (RT)Δn
R=0.0821
R constant for Latm/molK
0.0821
R constant for J/molK
8.314