Session 10: Personalised Medicine II (Gene Therapy and Immunotherapy)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
The aims of human gene therapy
- Modify or manipulate gene expression
- Alter biological properties of living cells for therapeutic use
- Technique used to modify person's gene to cure/treat disease
Three mechanisms of human gene therapy
1) Replace disease-causing gene with healthy copy
2) Inactivate disease-causing gene
3) Introduce new or modified gene into body to treat disease
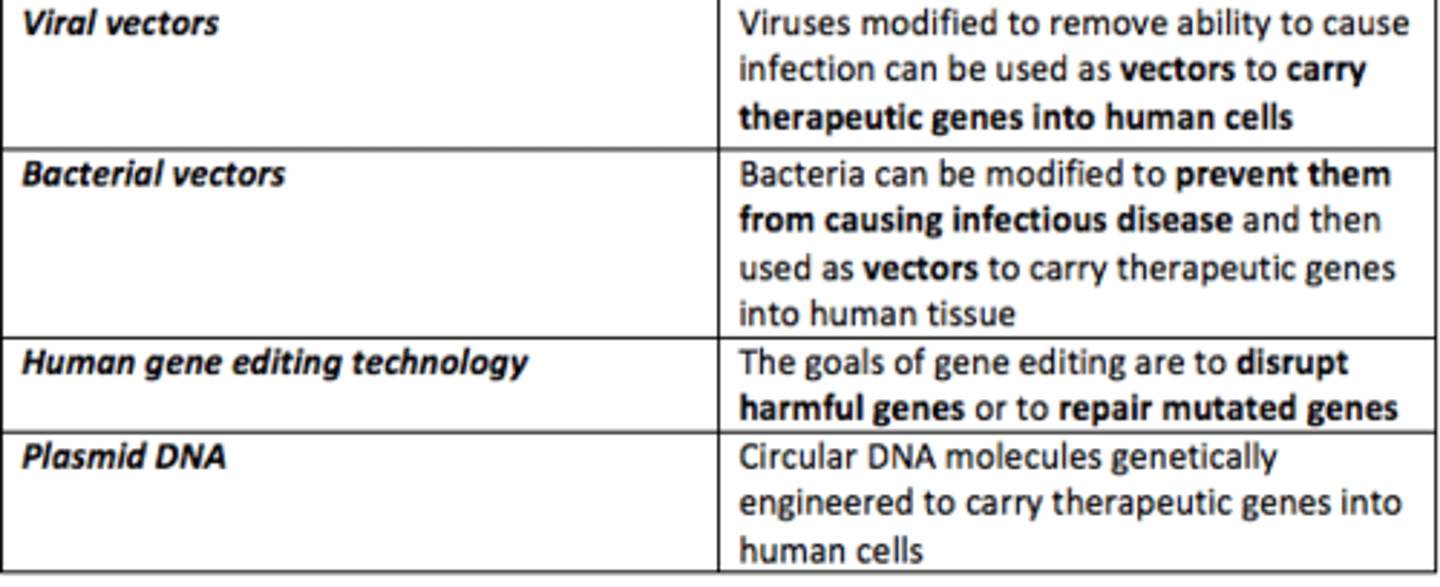
Give some examples of gene therapy vectors
- Viral vectors
- Bacterial vectors
- Plasmid DNA vectors
- Human gene editing technology (CRISPR/CAS9)
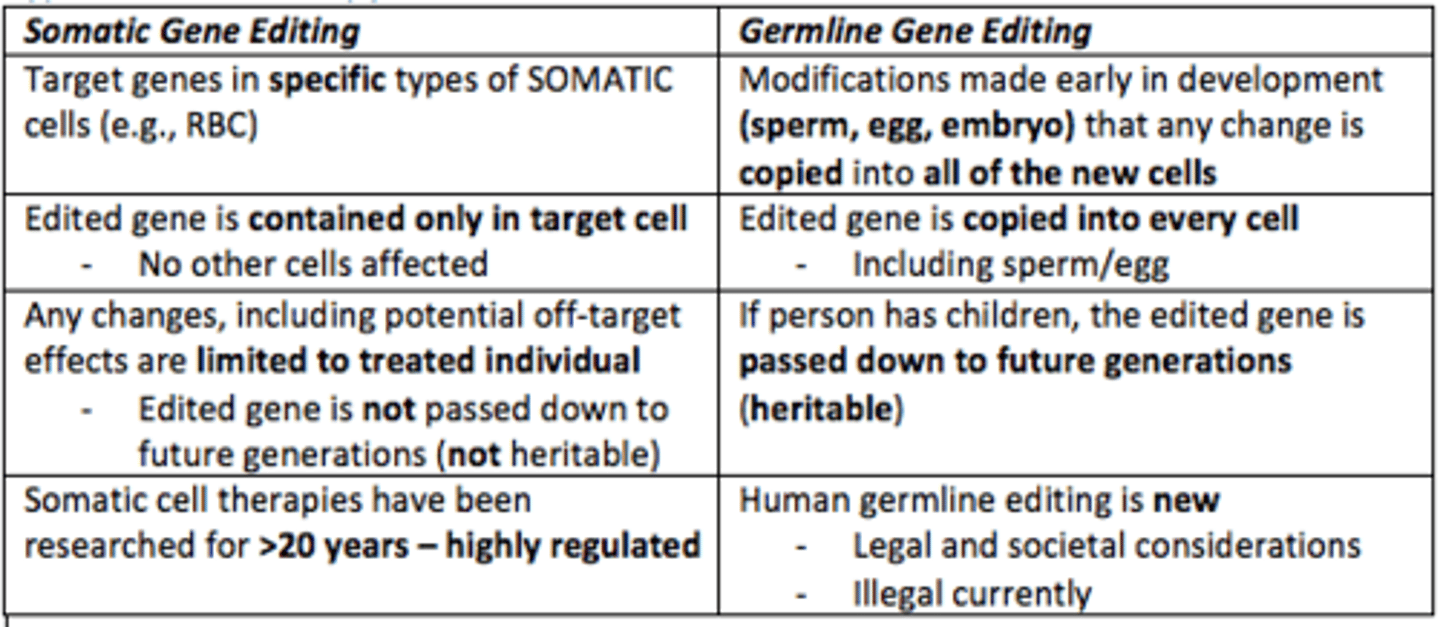
Somatic gene editing
Altering cells that are not heritable
- Edited gene is not passed down to future generations
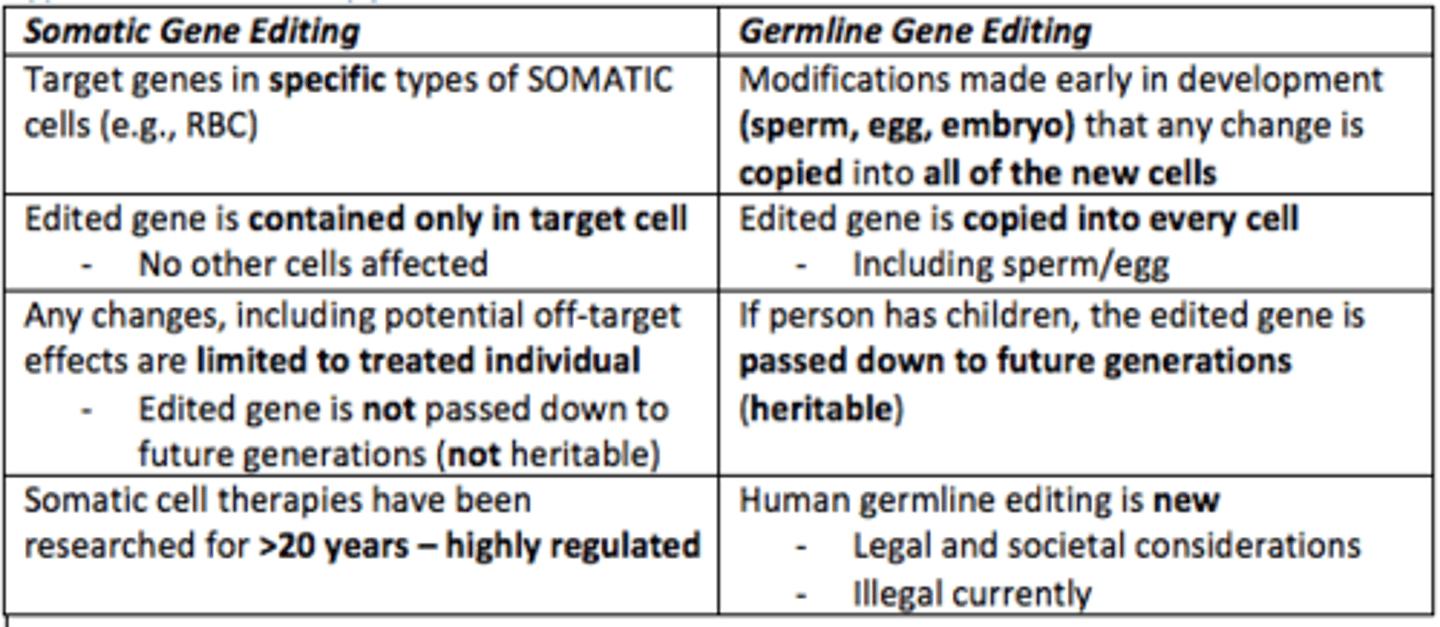
Germline gene editing
Egg/sperm (germ cells)
- Modifies DNA of an embryo
- Passed down to future generations
Most efficient gene therapy vector for delivering therapeutic genetic materials to target cells
Viruses
Benefits of non-viral gene delivery vectors/methods (e.g., electroporation, sonoporation, photoporation, magnetofection)
- Do not cause immunogenicity
- Do not cause carcinogenicity
- Deliver a large size of therapeutic DNA
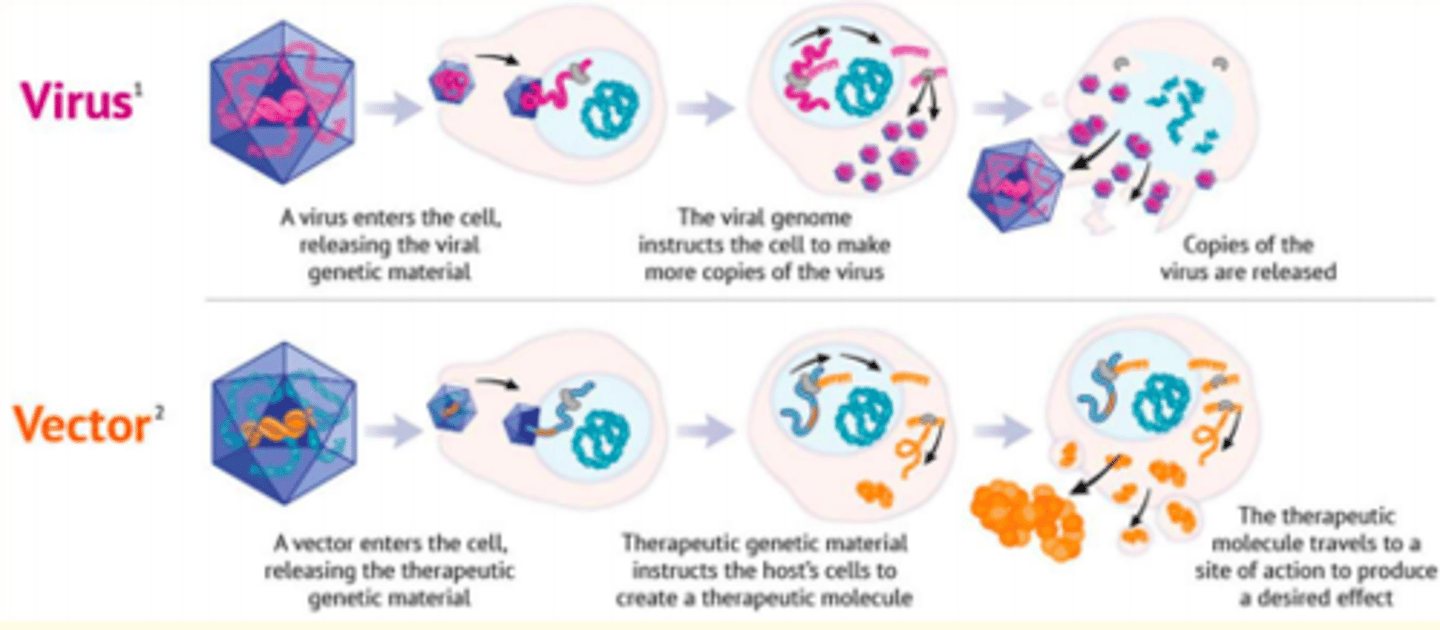
How do viral vectors for gene therapy work?
1) Vector enters cell - releasing therapeutic genetic material
2) Therapeutic genetic material instructs host cell to create therapeutic molecules
3) Therapeutic molecule travels to site of action to produce desired effect
What are the two main types of gene therapy
1) Ex-vivo gene therapy
2) In-vivo gene therapy
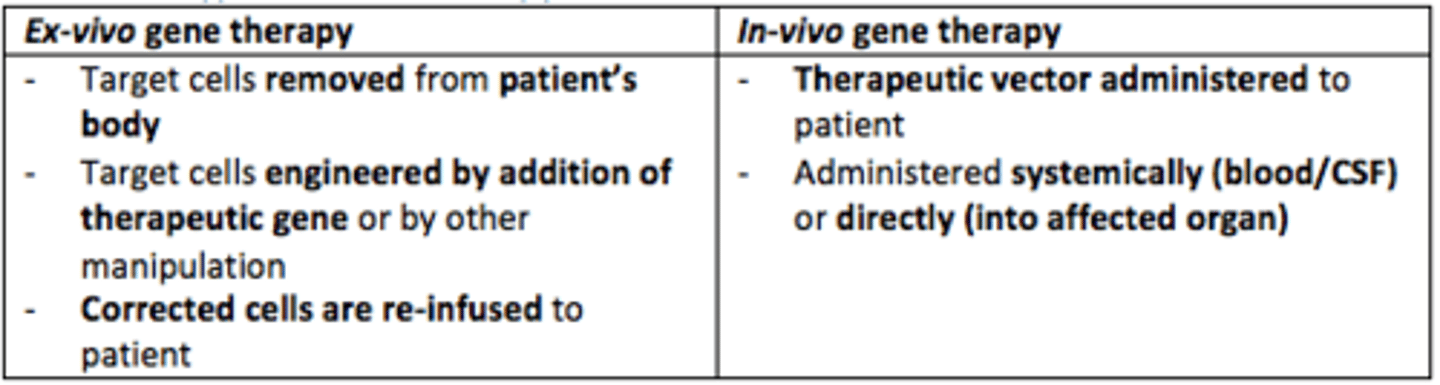
Ex-vivo gene therapy
Target cells removed from patient's body, engineered (addition of therapeutic gene) and then corrected cells are re-infused
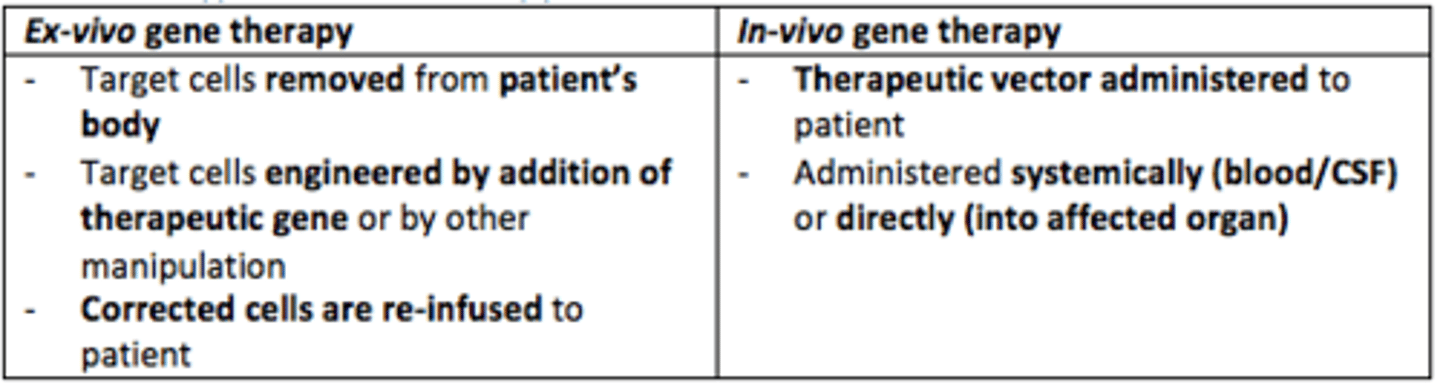
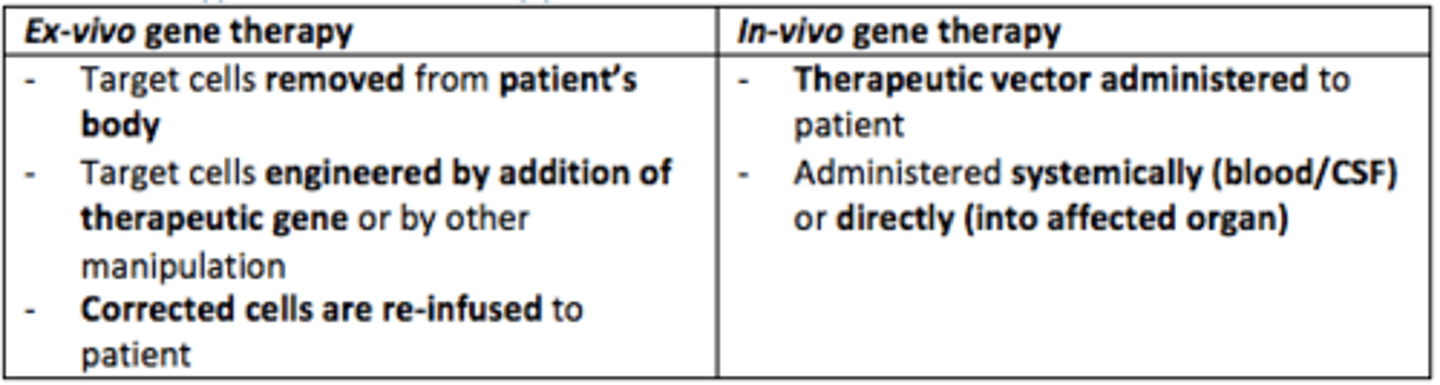
In-vivo gene therapy
Therapeutic vector is administered to patient directly (systemically - blood/CSF or directly into affected organ)
An example of ex-vivo gene therapy and a form of immunotherapy to treat cancer
CAR T-cell Therapy (KYMRIAH)
- Patient's own T cells are genetically engineered to express Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)
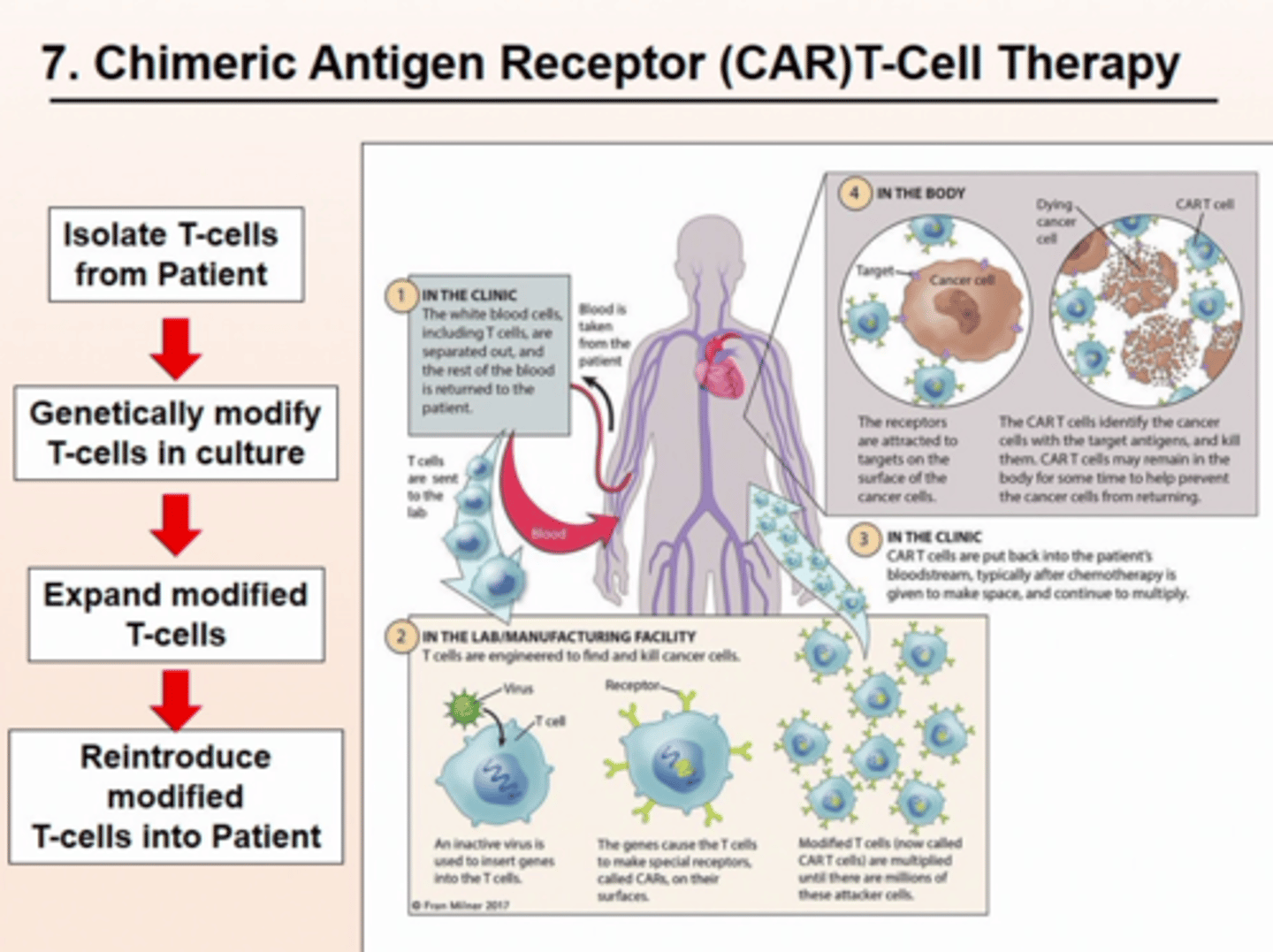
CAR T-cell therapy has been used to treat what form of cancer?
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL)
Benefit of CAR T-cell therapy
No immunogenicity
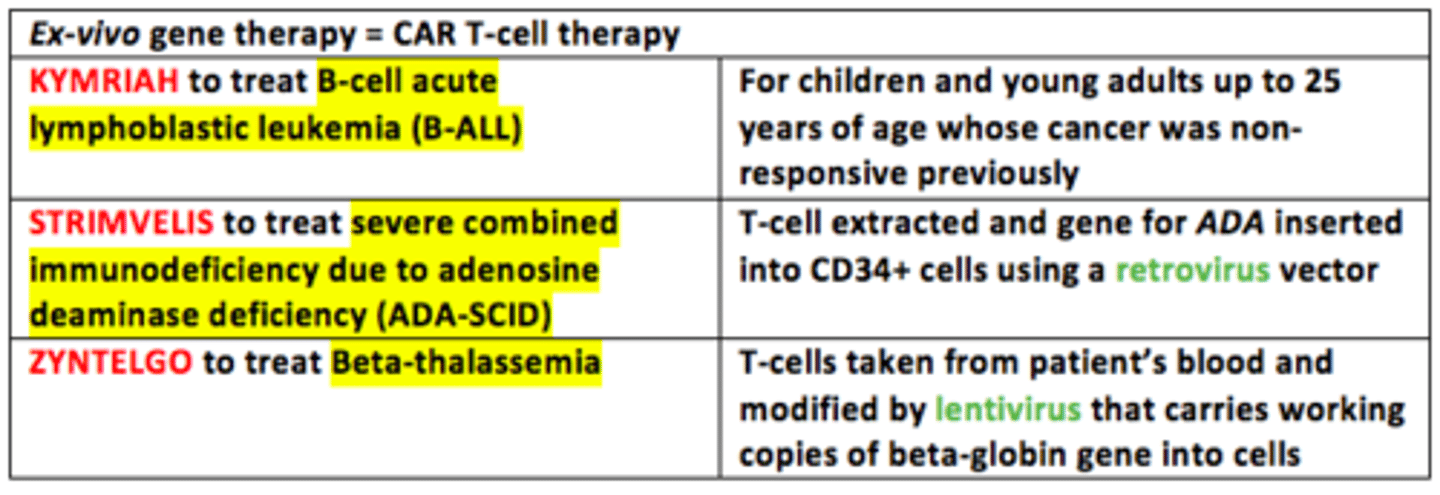
Three examples of applications of ex-vivo CAR T-cell gene therapy
1) KYMRIAH = B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL)
2) STRIMVELIS = severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID)
3) ZYNTELGO = beta-thalassemia
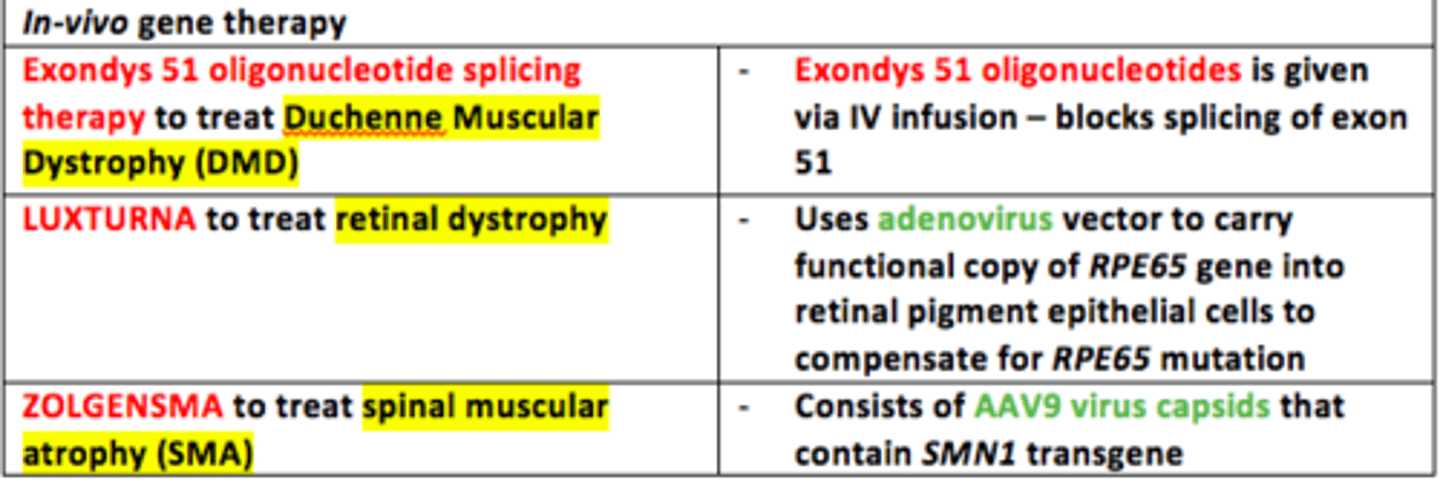
Three examples of applications of in-vivo gene therapy in humans
1) Exondys 51 oligonucleotides splicing therapy = treat Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
2) LUXTURNA = treat retinal dystrophy
3) ZOLGENSMA = treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
Name three types of cancer immunotherapy
1) Antibodies (monoclonal antibodies) that inhibit function of proteins produced by cancer cells
2) CAR T-cell infusion
3) Vaccines

Monoclonal antibody
Any of a preparation of immortalized antibodies that have been produced by a single clone of cultured cells and thus are all SPECIFIC for the same ANTIGEN.
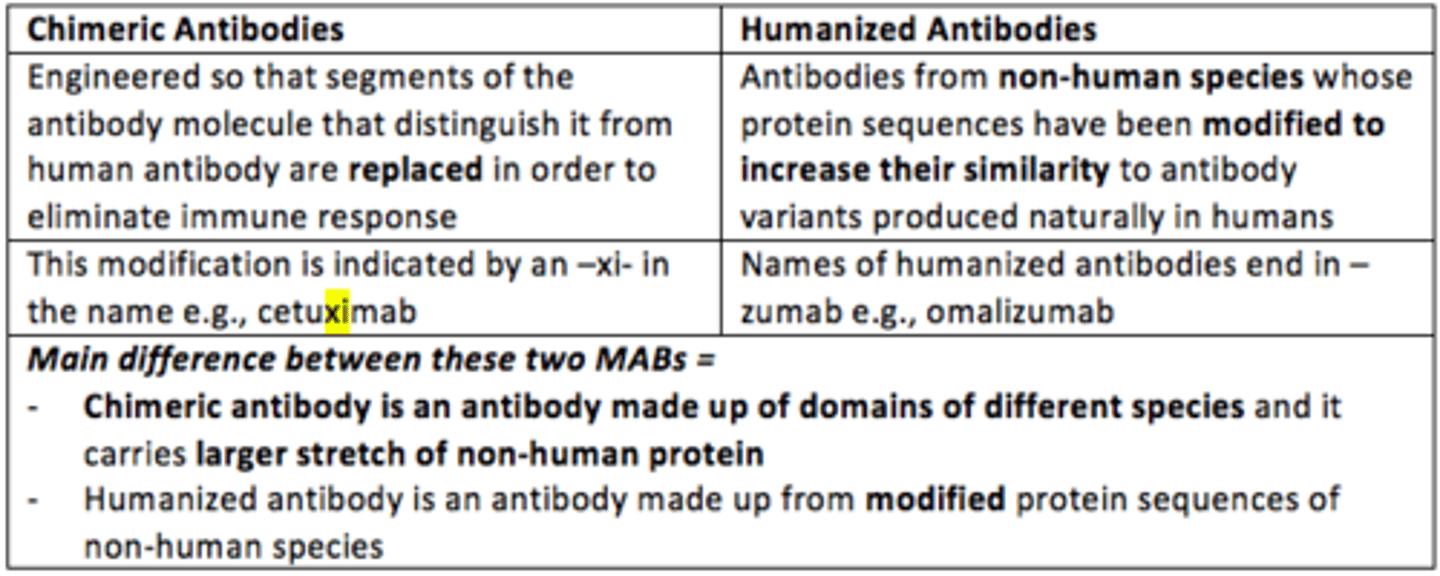
Two main types of monoclonal antibody
- Chimeric monoclonal antibody
- Humanized monoclonal antibody
Main difference between chimeric and humanized monoclonal antibodies
- Chimeric antibody is an antibody made up of domains of different species and it carries larger stretches of non-human protein
- Humanized antibody is an antibody made up from modified protein sequences of non-human species
First approved monoclonal antibody to treat low grade B cell lymphoma
Rituximab
What are the four main mechanisms of monoclonal antibodies (MABs) for cancer therapy?
1) Blocking proliferative signalling
2) Delivering drugs or radiation DIRECTLY to cancer cells
3) Blocking angiogenic signalling
4) Helping immune cells detect and kill cancer
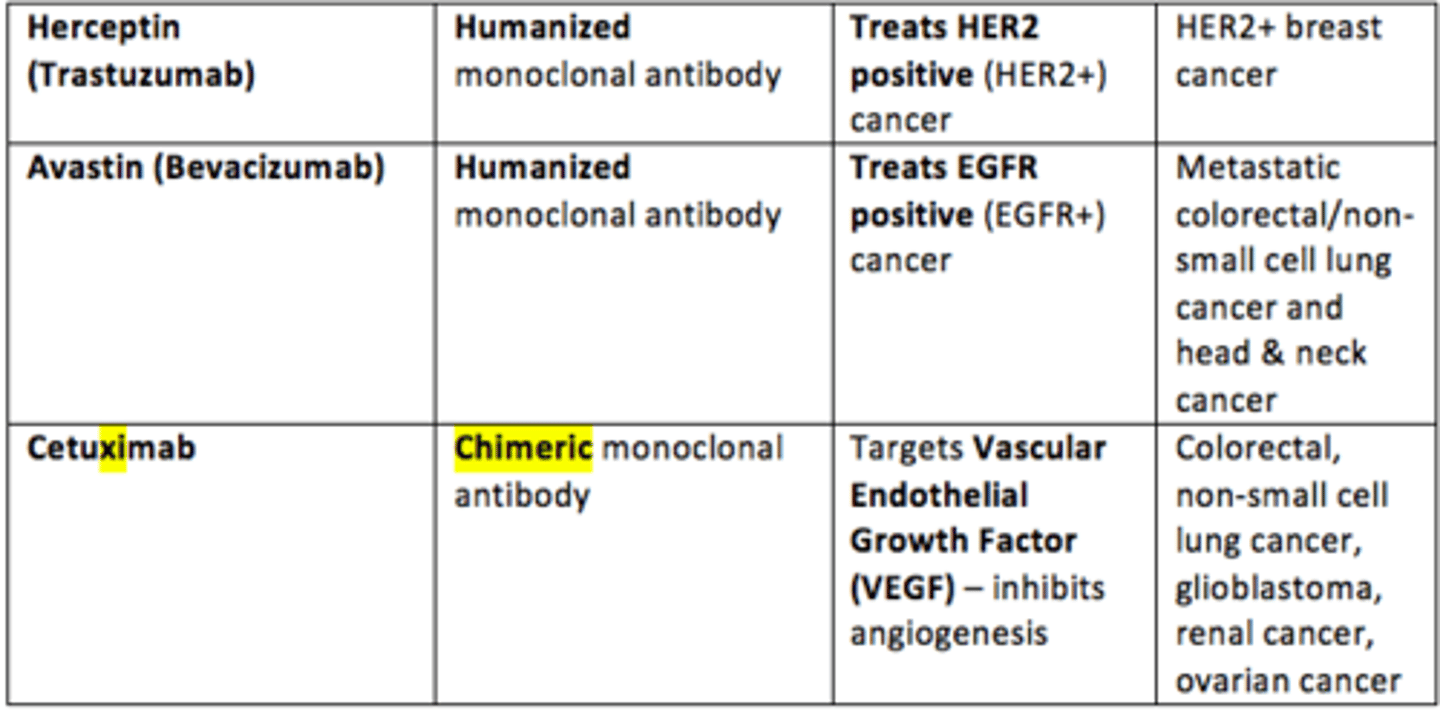
Example of a humanised monoclonal antibody that is used to treat HER2 positive (HER2+) breast cancer
Herceptin (Trastuzumab)
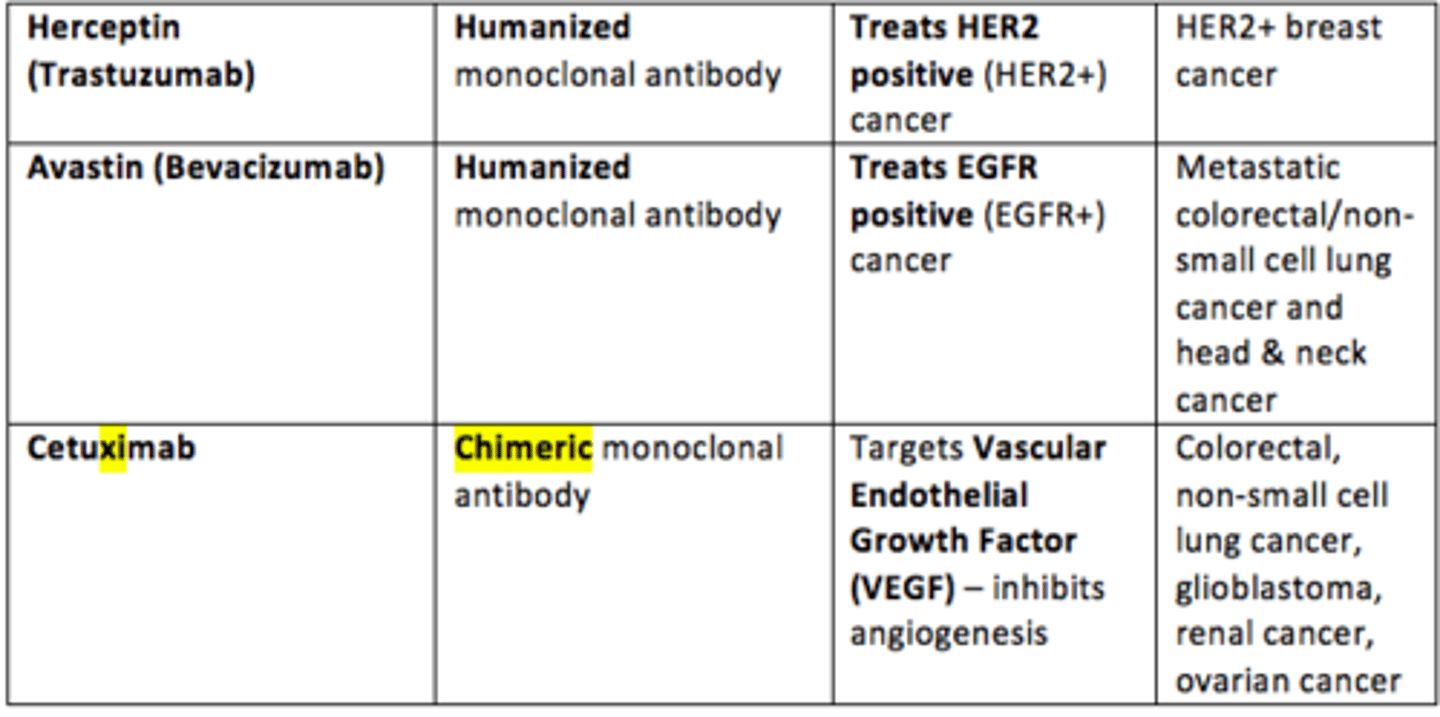
Example of a chimeric monoclonal antibody that is used to treat EGFR positive (EGFR+) metastatic colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, head & neck cancer
Cetuximab
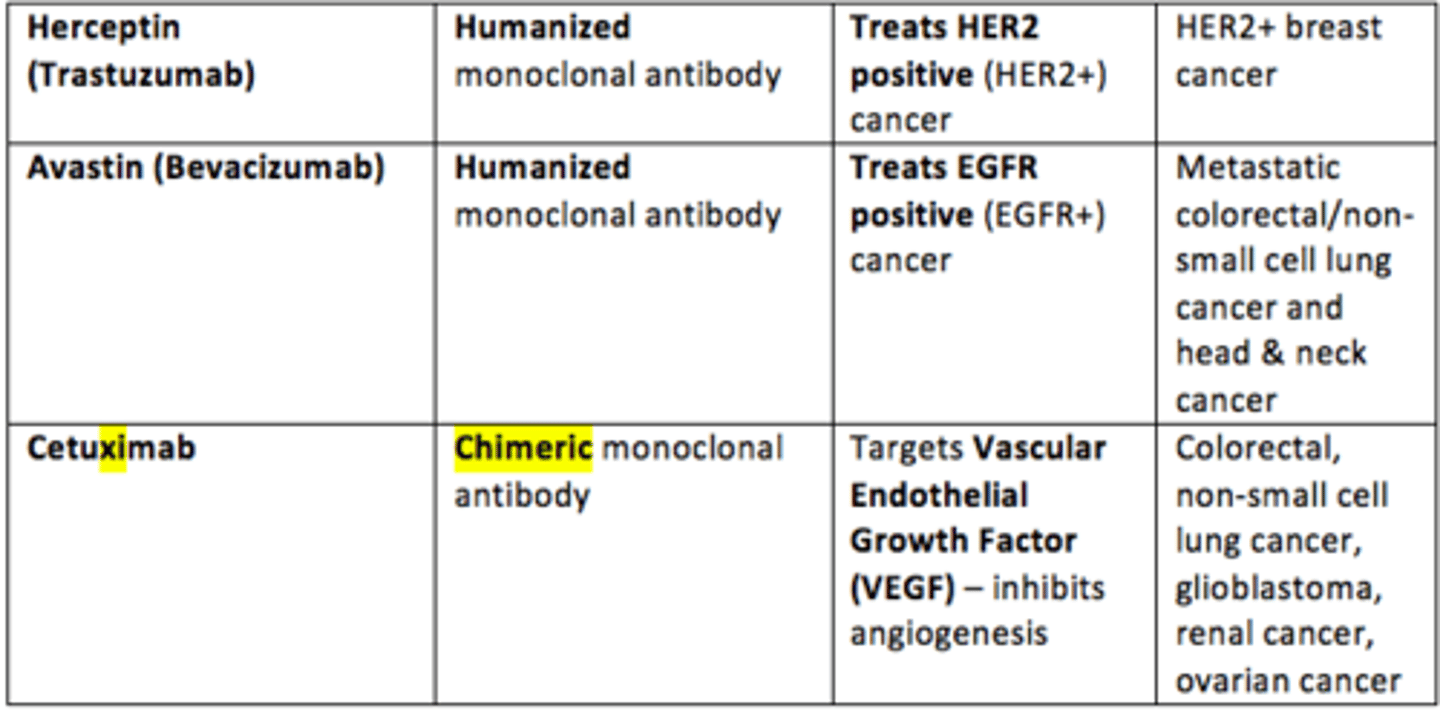
Example of a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) which inhibits angiogenesis in range of cancers
Avastin (Bevacizumab)
Monoclonal antibodies can also funtion as T-cell targeted immunomodulators of what three immune checkpoints?
- CTLA-4
- PD1
- PDL1

What are the three main forms of therapeutic cancer vaccines?
1) DNA vaccines
2) RNA vaccines
3) Peptide vaccines
Example of therapeutic DNA cancer vaccine
HPV vaccine - ovarian cancer
Example of a preventative cancer vaccine
HPV vaccine
How does the HPV vaccine work?
it contains virus-like particles (VLPs) that consist of HPV-L1 protein
Stimulates production of specific neutralising antibodies that blocks HPV