1.1 Cell Structure
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards are for Topic 1 - Cell Biology in AQA GCSE Biology (Triple Higher). They cover specification points 4.1.1.1 - 4.1.1.6.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
What are the two main types of cells?
Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
Cells of animals, plants and fungi are called __________ cells.
eukaryotic
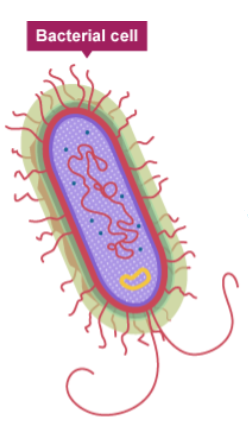
Bacterial cells are a type of ___________ cell.
prokaryotic
What is a key structural difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells regarding genetic material?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that encloses the genetic material, whereas prokaryotic cells do not.
What is the typical size range for a prokaryotic cell?
Most are between 0.2 μm and 2.0 μm.
What is the typical size range for a eukaryotic cell?
Most are between 5 μm and 100 μm.
In a prokaryotic cell, where is the single molecule of DNA found?
It is found free in the cytoplasm.
What are the small, additional rings of DNA found in some prokaryotic cells called?
Plasmids
Which subcellular structures are present in prokaryotic cells but absent from most eukaryotic cells?
A single circular strand of DNA and plasmids; they also lack a true nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
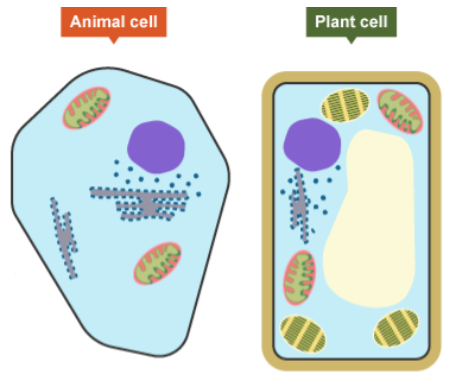
Name the five subcellular structures common to both animal and plant cells.
Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
What is the function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
It contains the genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities.
The jelly-like material where many chemical reactions happen inside a cell is called the _________.
cytoplasm
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Which organelle is the site of aerobic respiration, where most energy is released?
Mitochondria
Protein synthesis occurs in tiny structures called _________.
ribosomes
Name three subcellular structures found in plant cells but not in animal cells.
Chloroplasts, a permanent vacuole, and a cell wall.
What is the function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
Made from cellulose fibres, it strengthens the cell and supports the plant.
What is the function of chloroplasts?
They are the site of photosynthesis, containing chlorophyll to absorb light energy.
What is the purpose of the permanent vacuole in a plant cell?
It is filled with cell sap and helps to keep the cell turgid.
The process by which an unspecialised cell becomes a more specialised cell type is known as cell _______________.
differentiation
Cells that are adapted to perform a specific function are called ___________ cells.
specialised
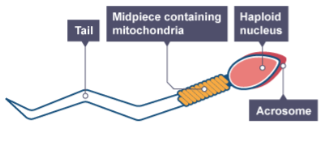
How is a sperm cell adapted for swimming to the egg?
It has a long tail (flagellum) for movement and a streamlined shape.
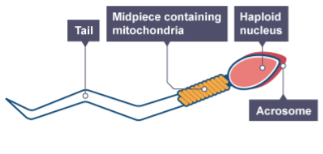
Why does a sperm cell have many mitochondria in its middle piece?
To provide the energy needed for swimming.
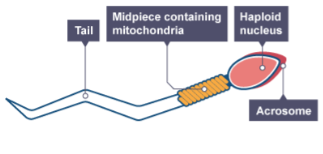
What is contained in the acrosome at the head of a sperm cell and what is its purpose?
It contains digestive enzymes to break through the outer layer of the egg cell.
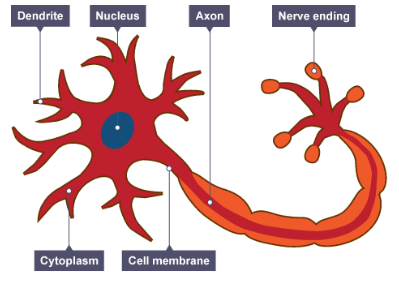
How is a nerve cell adapted for transmitting electrical impulses over long distances?
It is extended, having a long axon.
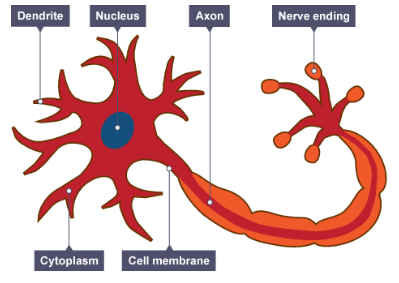
What is the function of the fatty sheath (myelin) that covers a nerve cell?
It insulates the nerve cell and speeds up the nerve impulse.
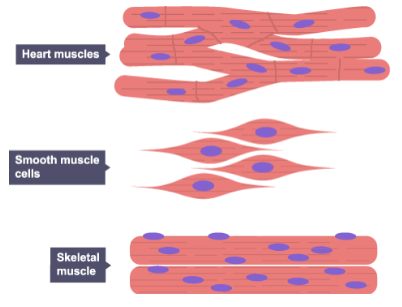
How are muscle cells adapted for contraction?
They contain filaments of protein that slide over each other.
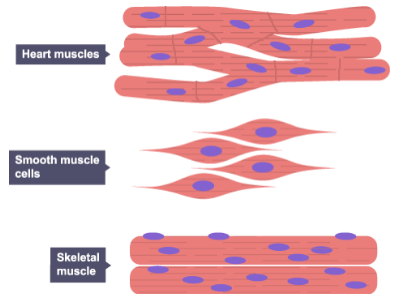
Why are muscle cells packed full of mitochondria?
To provide the energy from respiration required for muscle contraction.

How is a root hair cell adapted for absorbing water and mineral ions?
It has a large surface area and thin walls.

Why do root hair cells not contain chloroplasts?
They are underground and cannot carry out photosynthesis as they receive no light.
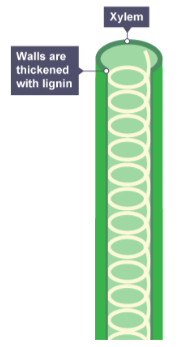
How are xylem cells adapted to form a continuous tube for water transport?
There are no top and bottom walls between the cells, and they become hollow as they die.
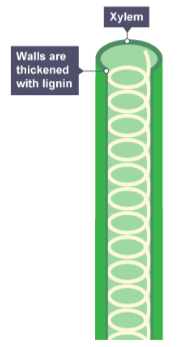
What chemical strengthens the walls of xylem cells, providing support to the plant?
Lignin
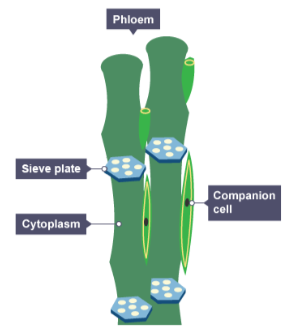
Phloem cells are specialised to transport dissolved sugars. What structures allow substances to move from cell to cell?
Sieve plates, which are pores in the end walls of the cells.
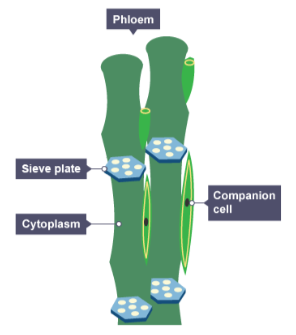
What is the function of companion cells in phloem tissue?
They provide the energy required for transporting substances in the sieve tubes.
The process by which a cell changes to become specialised, involving changes in shape, structure, and organelles, is called _______________.
differentiation
In animals, most cells differentiate at an _____ stage and then lose this ability.
early
In mature animals, cell division is mostly for the purpose of _______ or __________ of damaged cells.
repair, replacement
In plants, many cells retain the ability to ___________ throughout life.
differentiate
What is magnification?
How many times larger an image is than the real object.
What is resolution in microscopy?
The ability to distinguish between two points as separate entities; a measure of the detail in an image.
What is the formula to calculate the total magnification of a compound light microscope?
Magnification of eyepiece lens × magnification of objective lens
What is the formula that links magnification, image size, and the real size of an object?
magnification = size of image / real size of object
A micrograph of a cell measures 100 mm. The real size of the cell is 0.05 mm. What is the magnification?
The magnification is x2000.
What is the primary advantage of an electron microscope over a light microscope?
It has a much greater magnification and resolution.
What is the approximate maximum magnification of a light microscope?
Around x1500 to x2000.
Why is the resolution of an electron microscope so much better than a light microscope?
It uses a beam of electrons, which have a much shorter wavelength than light.
What is the resolution of a light microscope limited to?
Around 0.2 micrometres (μm), or 200 nanometres (nm).
Which type of microscope would be required to see subcellular structures like ribosomes in detail?
An electron microscope
Express 7 μm (the diameter of a red blood cell) in metres using standard form.
7 × 10⁻⁶ m
A __________ is 1/1000 of a metre.
millimetre
A micrometre (μm) is one _________ of a metre.
millionth
A nanometre (nm) is one _________ of a metre.
billionth
The difference calculated in factors of 10 is known as an _____ __ _________.
order of magnitude
If an oak tree is 20m tall and a person is 2m tall, what is the difference in their height by order of magnitude?
One order of magnitude (a factor of 10).
The first step in using a light microscope is to select the ______ power objective lens.
lowest
When focusing a light microscope, which knob should be used first to bring the stage close to the objective lens?
The coarse focus adjustment knob.
When viewing the image, the coarse focus knob should be turned to move the stage ____ from the lens until the image comes into focus.
away
Which adjustment knob is used to get a clear, sharp image when using the high-power objective lens?
The fine focus adjustment knob.
Why are stains, like iodine solution, used when preparing a microscope slide of onion cells?
Most cells are colourless, so stains are used to add contrast and make structures more visible.
Why must a coverslip be lowered carefully onto a specimen on a microscope slide?
To ensure that no air bubbles are trapped underneath.
What is the purpose of culturing microorganisms in a laboratory?
To grow large numbers of them so they can be studied.
What are the two main ways to culture microorganisms in the lab?
In a nutrient broth solution or on an agar gel plate.
What term describes the techniques used to prevent contamination of microbial cultures?
Aseptic techniques
Before use, Petri dishes and culture media must be __________ to kill any unwanted microorganisms.
sterilised
Why are inoculating loops passed through a flame before and after use?
To sterilise them and kill any unwanted microorganisms.
Why should the lid of a Petri dish be secured with tape but not sealed completely?
To prevent airborne microorganisms from contaminating the culture while allowing oxygen to enter, preventing the growth of harmful anaerobic bacteria.
Why are agar plates stored upside down during incubation?
To prevent drops of condensation from falling onto the agar surface and disrupting bacterial growth.
What is the maximum temperature at which cultures should be incubated in a school laboratory and why?
At 25°C, to reduce the chances of growing pathogens that are harmful to humans.
In an investigation into the effect of antibiotics, the clear area around a disc where bacteria have not grown is called the zone of _________.
inhibition
How can the effectiveness of an antibiotic be determined from an agar plate experiment?
By measuring the area or diameter of the zone of inhibition; a larger zone indicates greater effectiveness.
What is the mathematical formula used to calculate the area of a circular zone of inhibition?
Area = πr²
What is the process by which bacteria reproduce?
Binary fission
If a bacterium has a mean division time of 20 minutes, how many rounds of division will it undergo in 3 hours?
9
The formula to calculate the number of bacteria in a population after n rounds of division is: Number at start × _.
2ⁿ
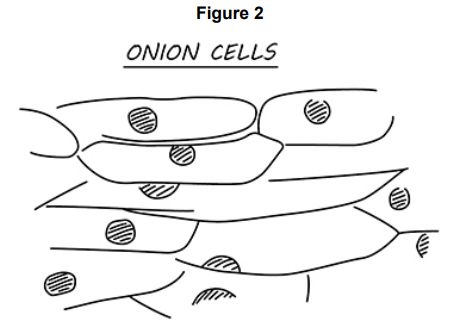
Figure 2 shows a student’s drawing of onion cells.
Give two ways the student could improve the drawing in Figure 2.
Use continuous lines
Label cell parts

Onion cells can be seen using an electron microscope.
Give two ways onion cells would look different when seen using an electron microscope.
Would look more magnified
Sub-cellular structures can be seen in detail

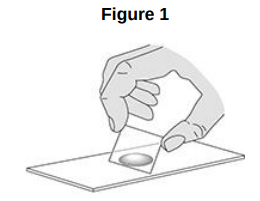
A student prepared some animal cells to view using a microscope. Figure 1 shows the student preparing the cells.
Name two pieces of laboratory equipment the student could have used to prepare cells to view using a microscope.
Slide
Cover slip

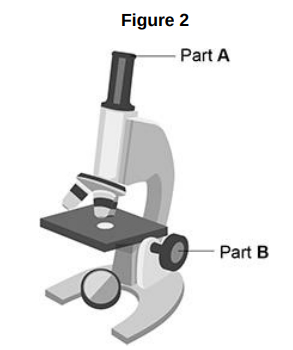
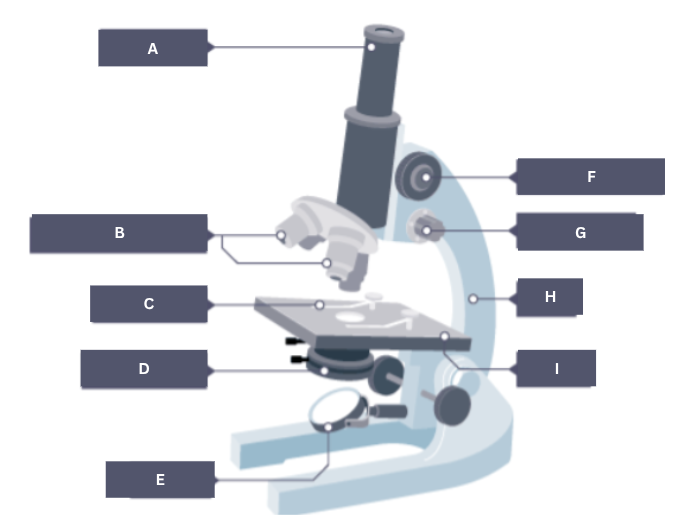
Figure 2 shows a student’s light microscope.
Name part A.
Eyepiece

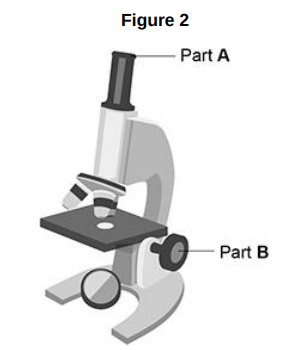
Figure 2 shows a student’s light microscope.
What is the function of part B?
To focus the image

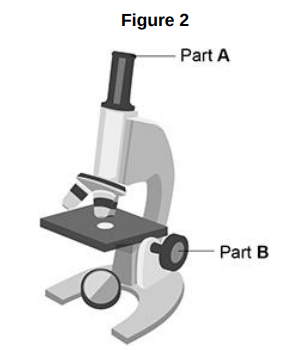
Figure 2 shows a student’s light microscope.
The student tried to look at the cells using the microscope.
Suggest one reason why the student could not see any cells when looking through part A.
The objective lens could be dirty.

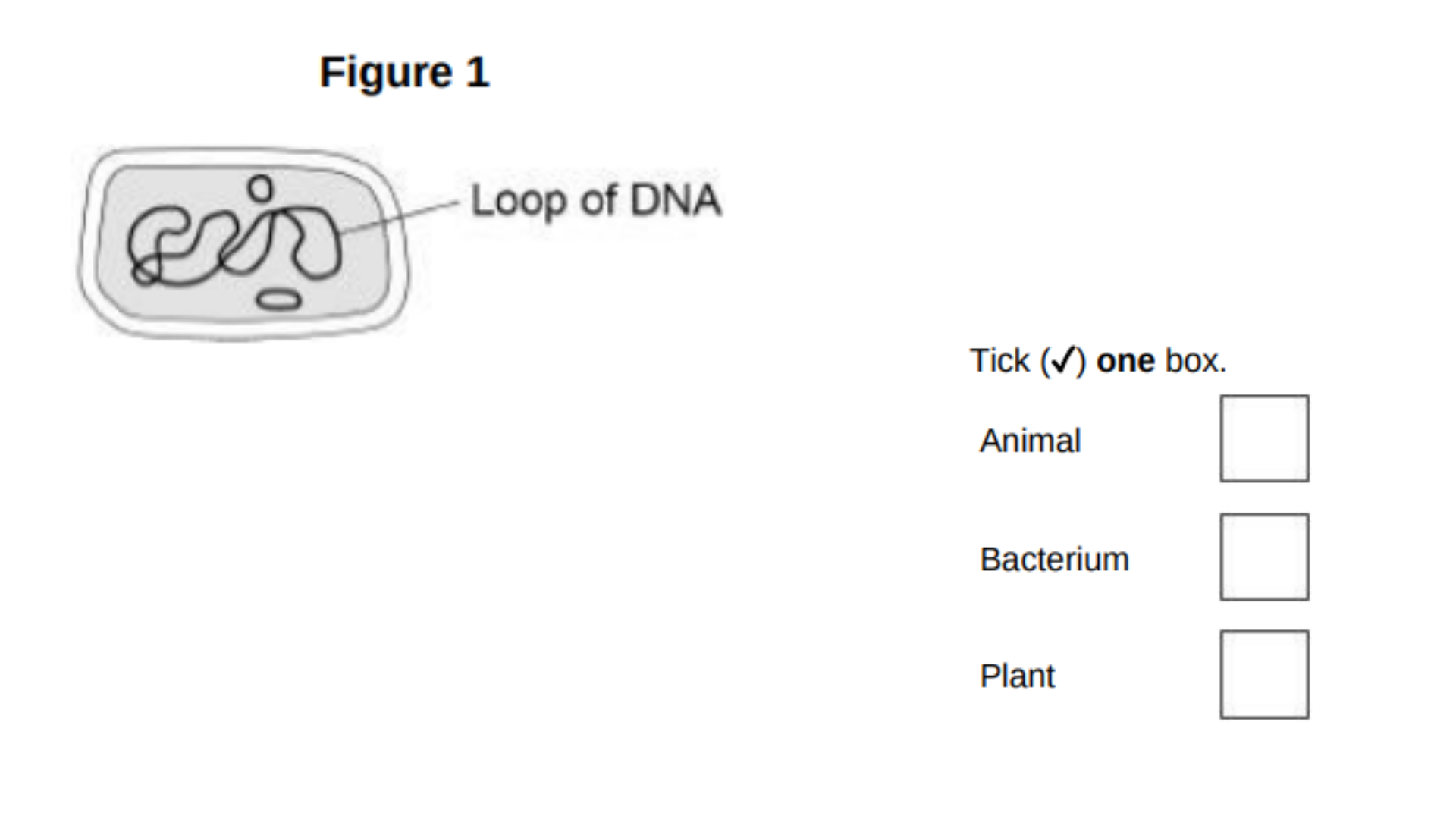
This question is about cells.
Figure 1 shows a cell.
What type of cell is shown in Figure 1?
Bacterium
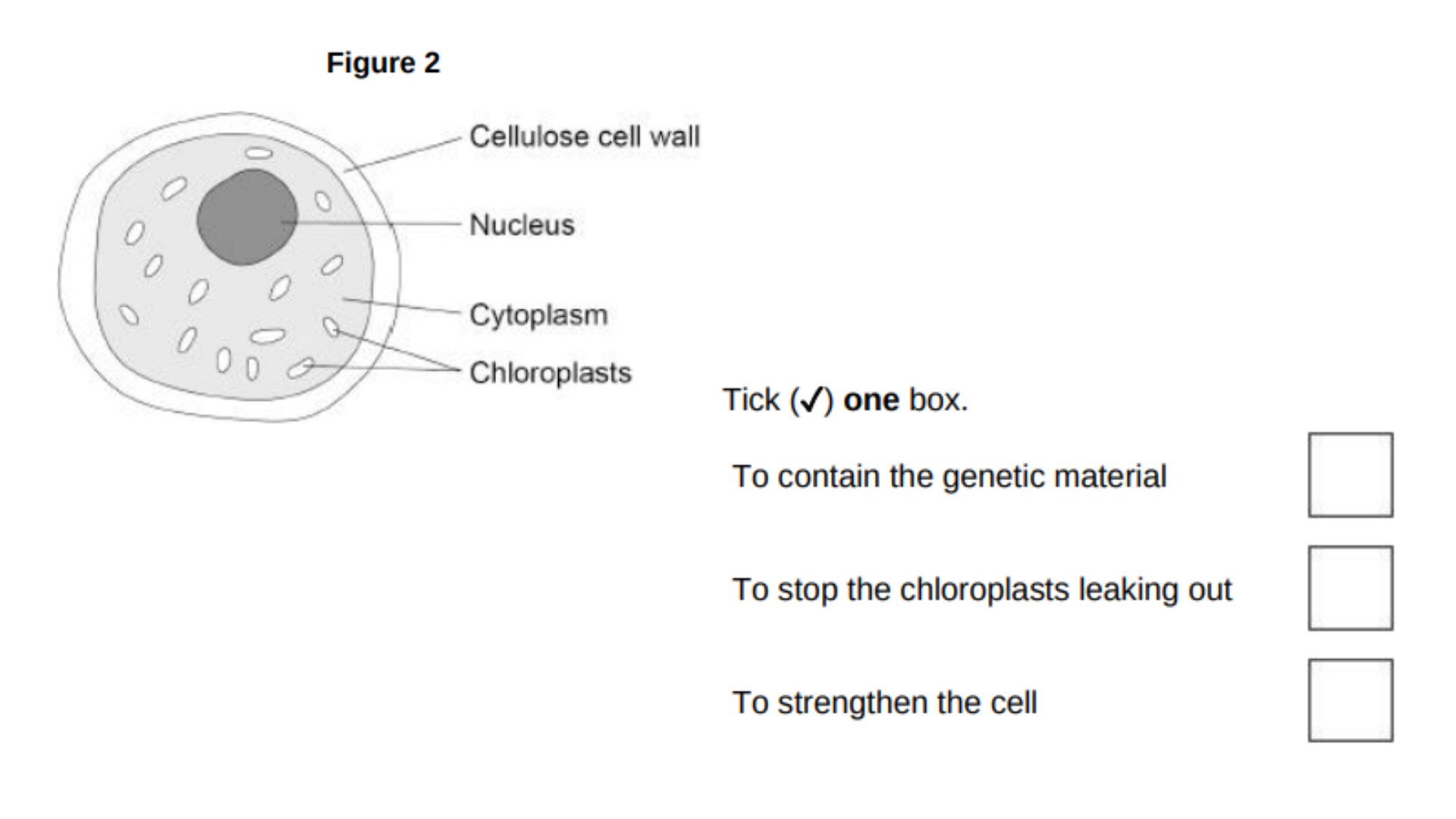
Figure 2 shows an algal cell.
What is the function of the cell wall?
To strengthen the cell
An algal cell is green.
Which part of an algal cell makes it green in colour?
Chloroplast
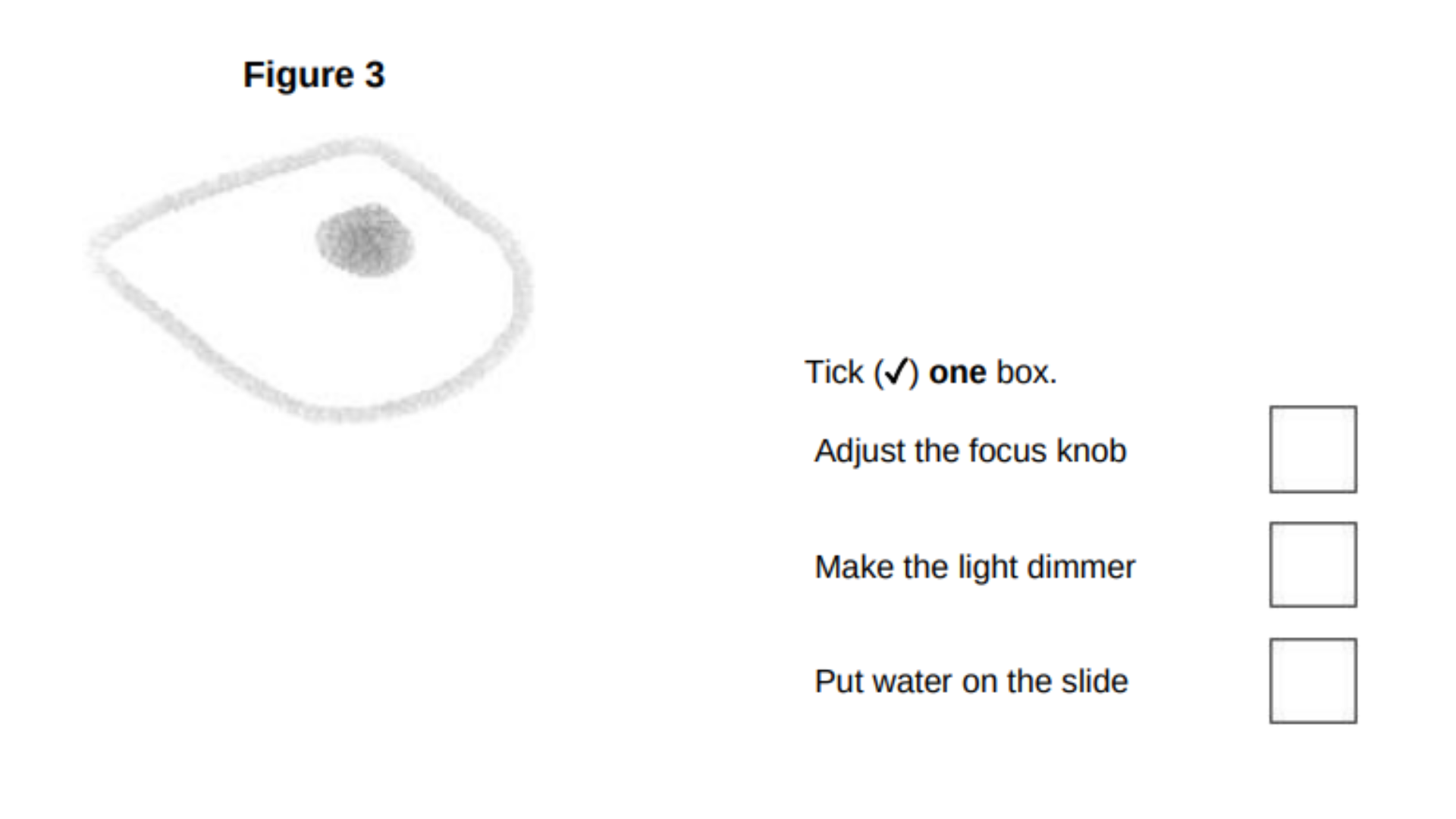
A student prepared a microscope slide of cheek cells.
The student looked at one cell using a microscope.
Figure 3 shows the image the student saw.
What should the student do to get a clear image?
Adjust the focus knob
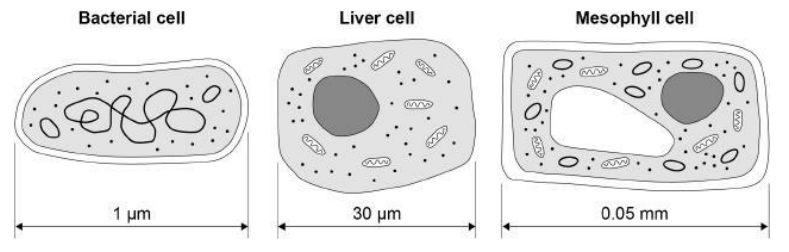
The diagram below shows three types of cell.
Give two similarities between the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cells in the diagram above.
They all have a cytoplasm
They all have ribosomes

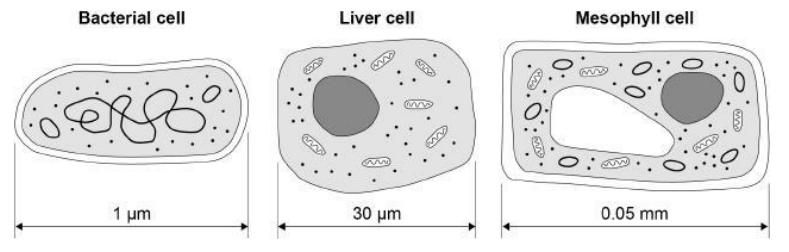
The diagram below shows three types of cell.
Give three differences between the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cells in the diagram above.
The prokaryotic cell doesn’t have its genetic material in a nucleus
The prokaryotic cell has plasmids
The prokaryotic cell is smaller

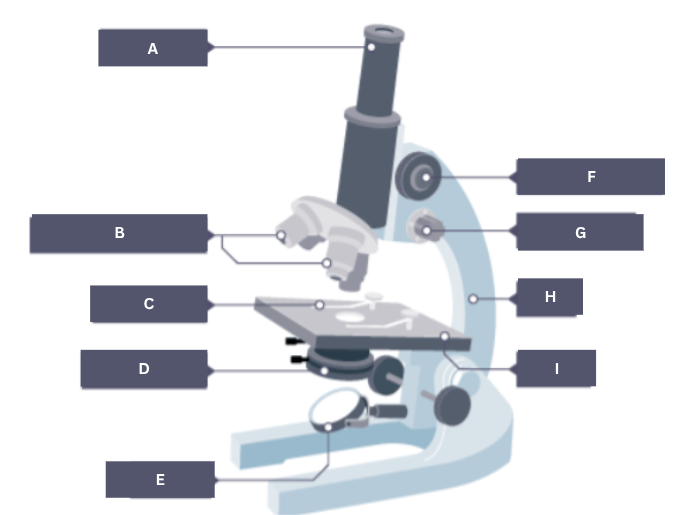
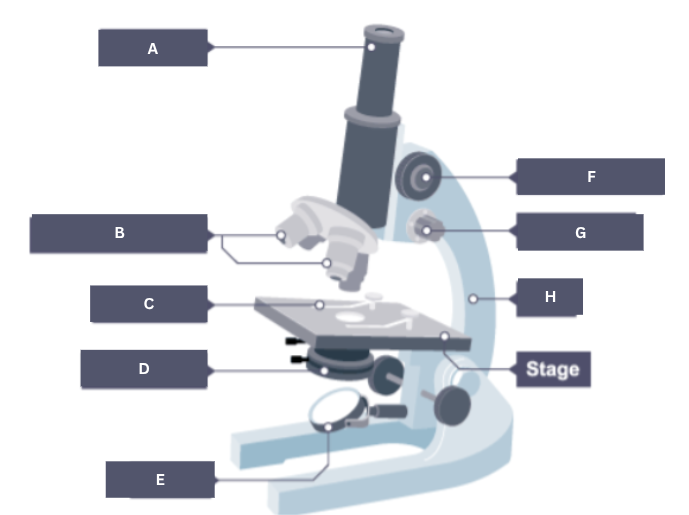
Name the part of the microscope labelled A.
Eyepiece
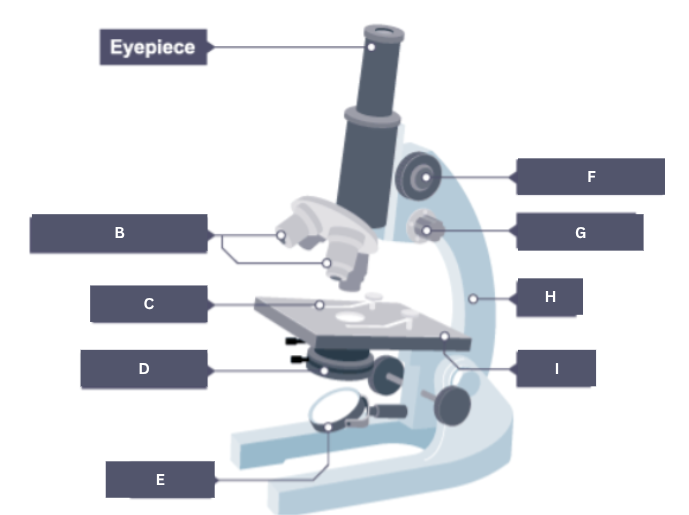
Name the part of the microscope labelled B.
Objective lenses
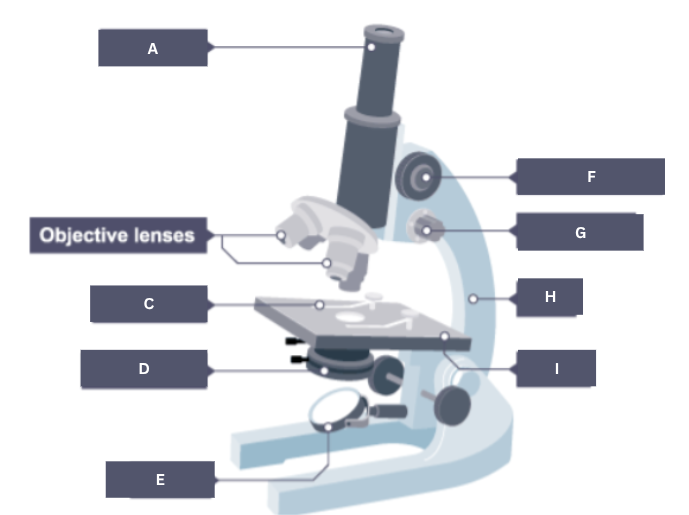
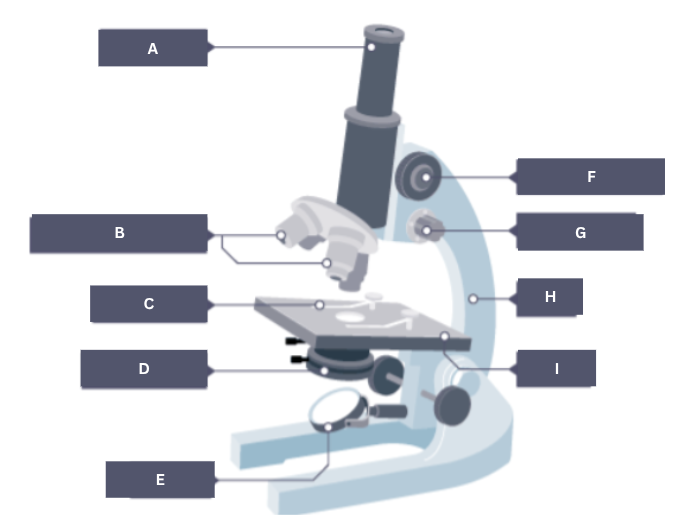
Name the part of the microscope labelled C.
Stage clip
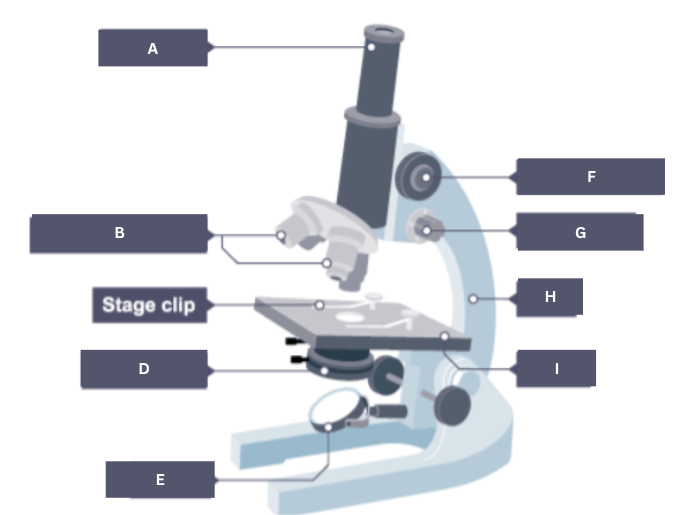
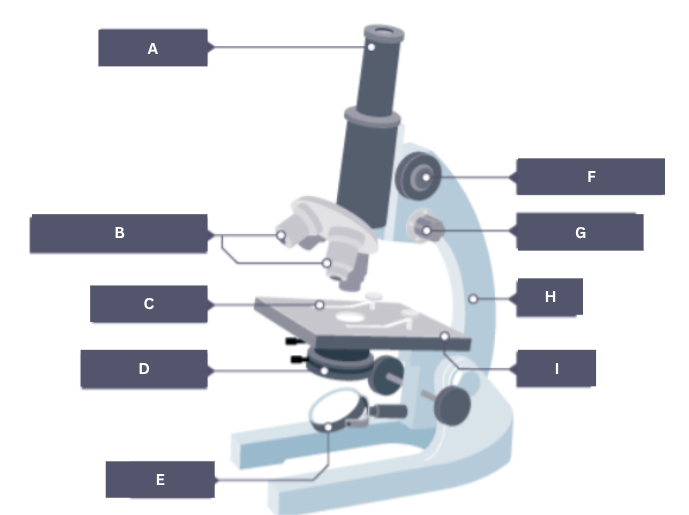
Name the part of the microscope labelled D.
Condenser
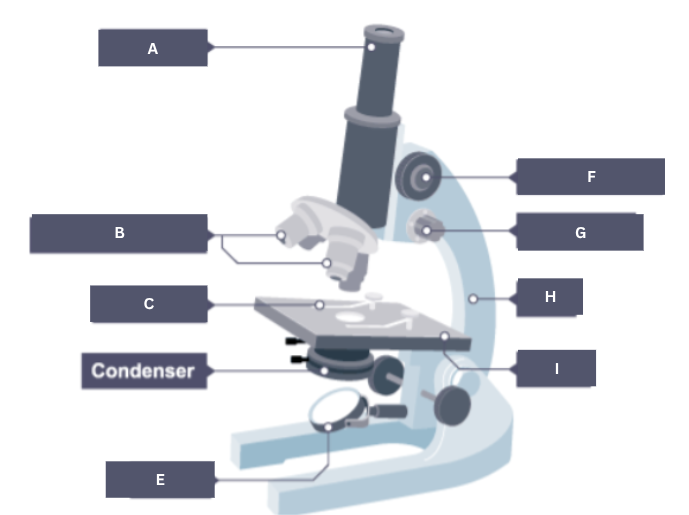
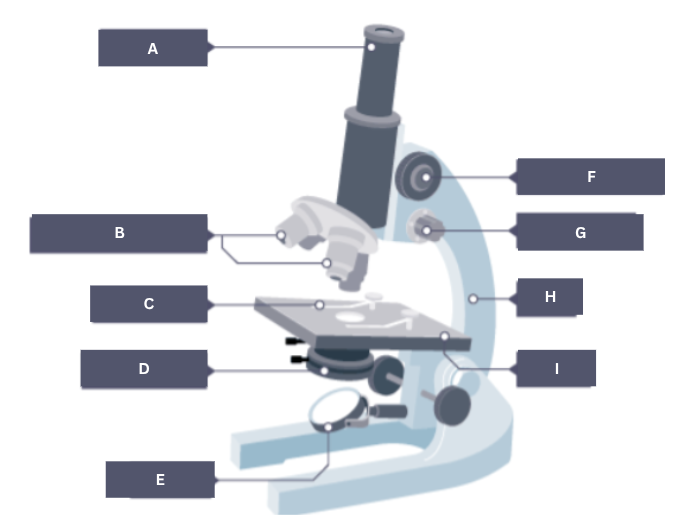
Name the part of the microscope labelled E.
Mirror
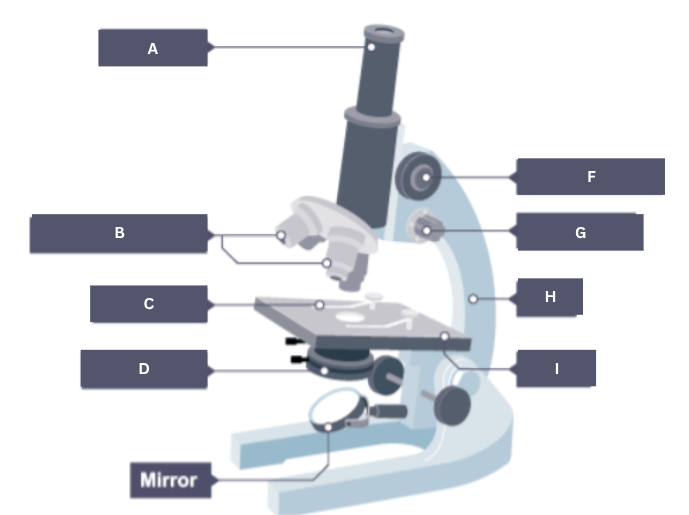
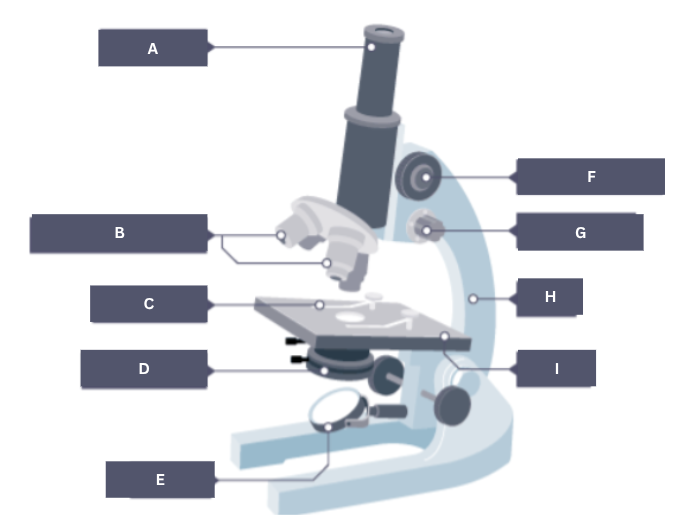
Name the part of the microscope labelled F.
Coarse focus
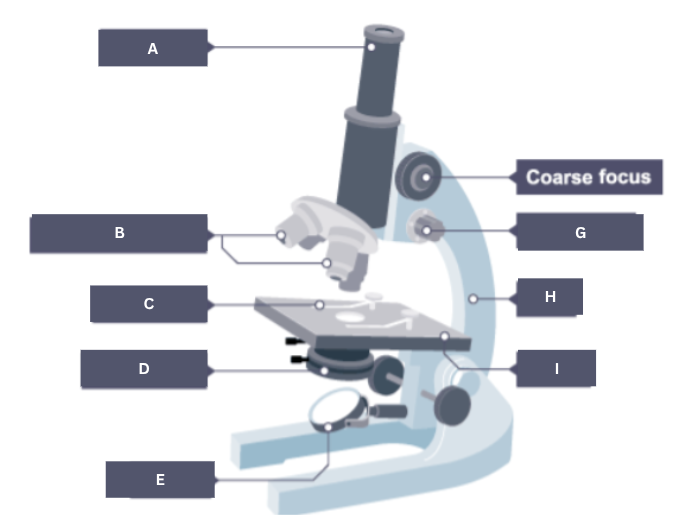
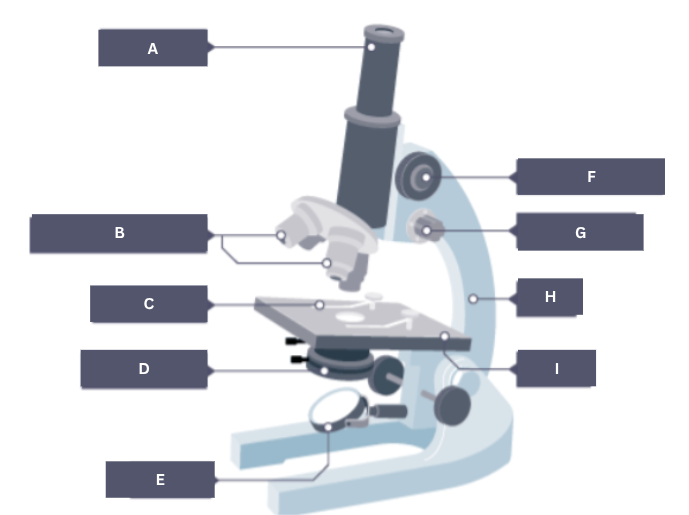
Name the part of the microscope labelled G.
Fine focus
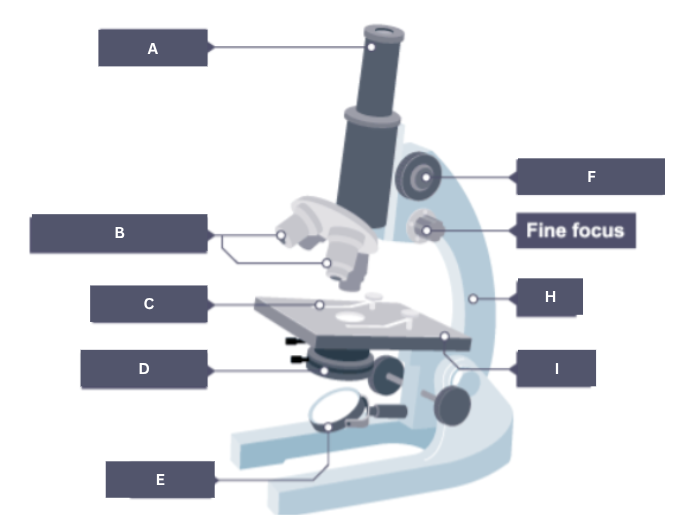
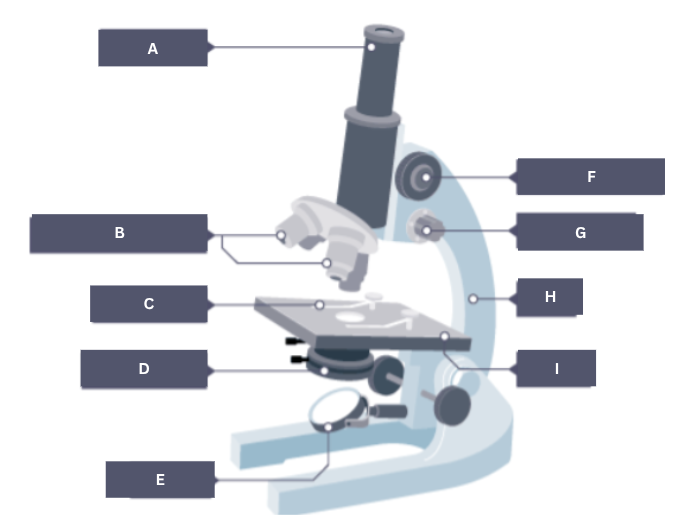
Name the part of the microscope labelled H.
Arm
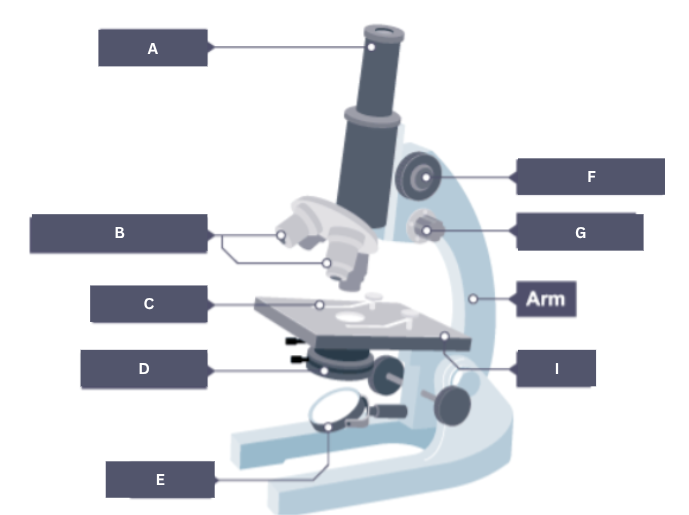
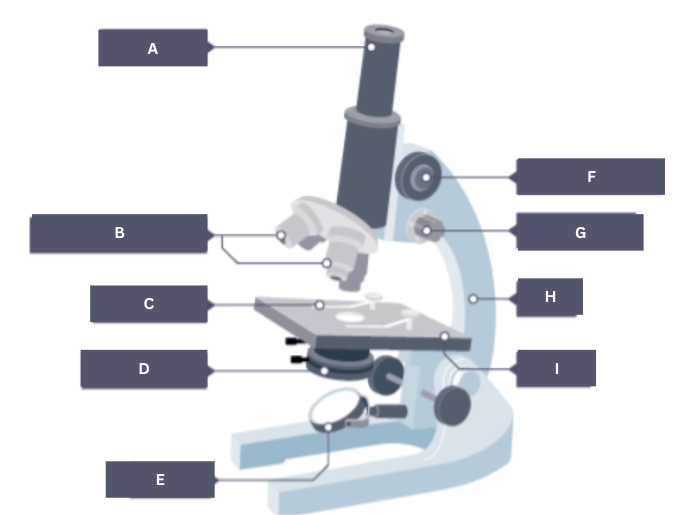
Name the part of the microscope labelled I.
Stage
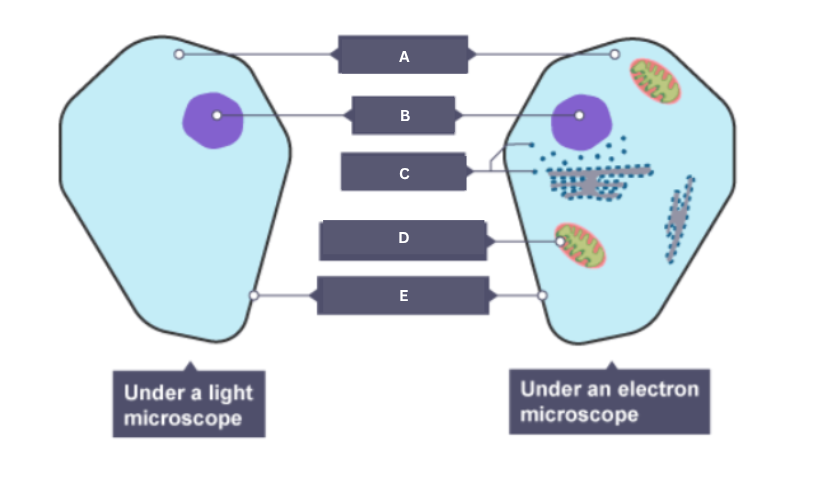
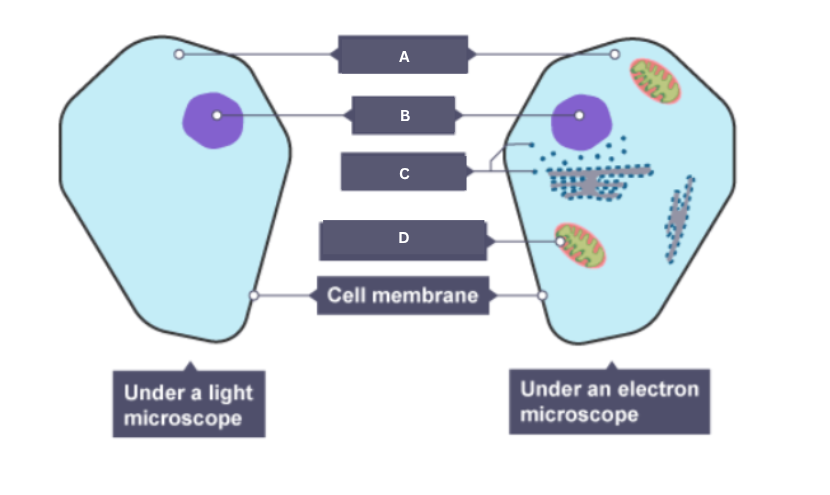
Name the part of the animal cell labelled A.
Cytoplasm
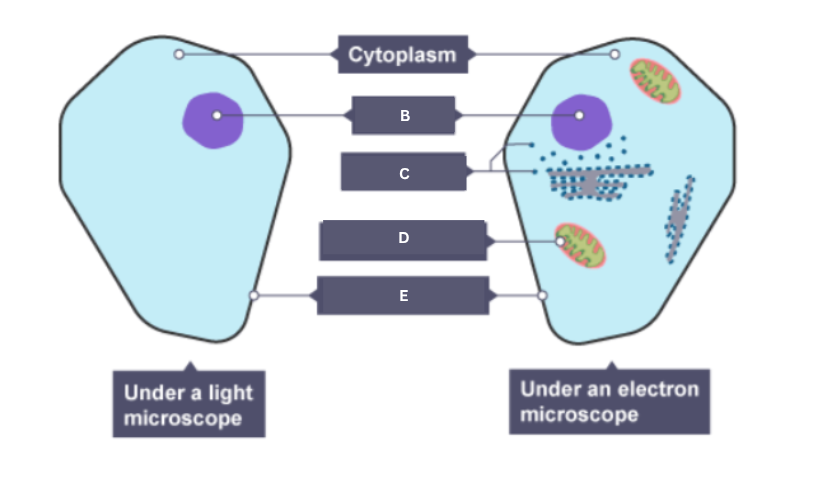
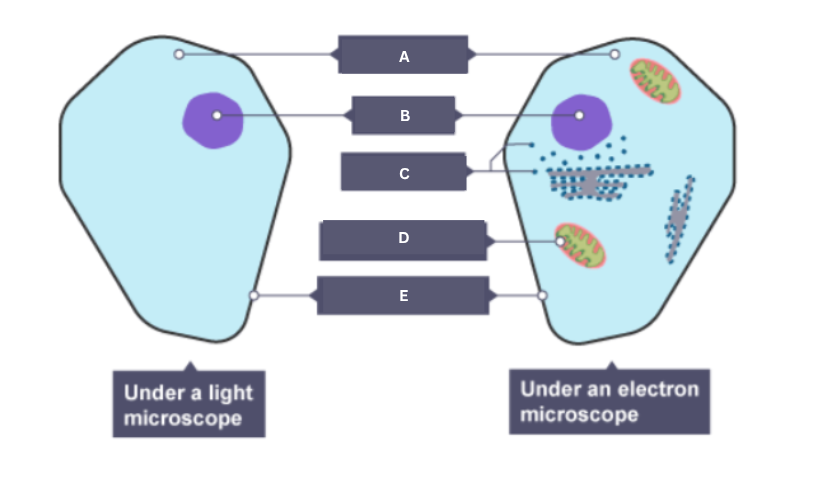
Name the part of the animal cell labelled B.
Nucleus
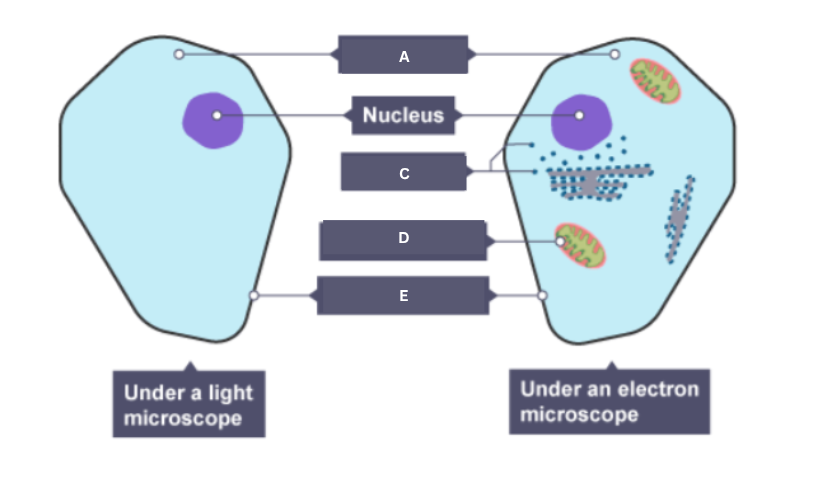
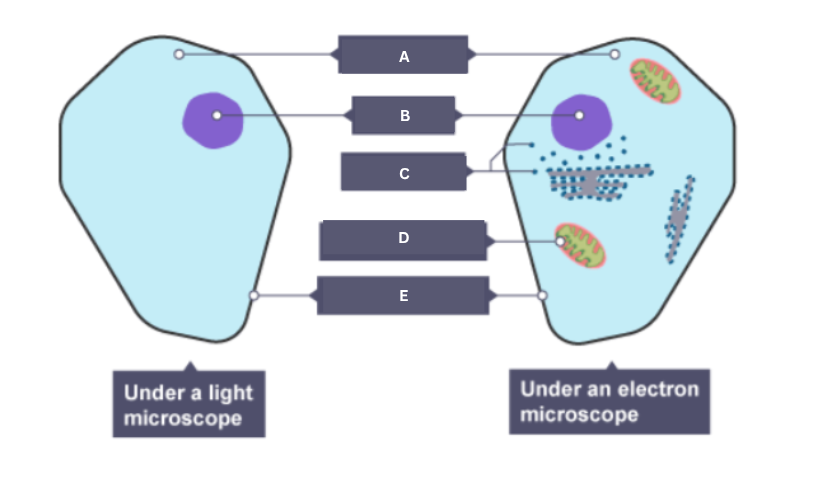
Name the part of the animal cell labelled C.
Ribosome
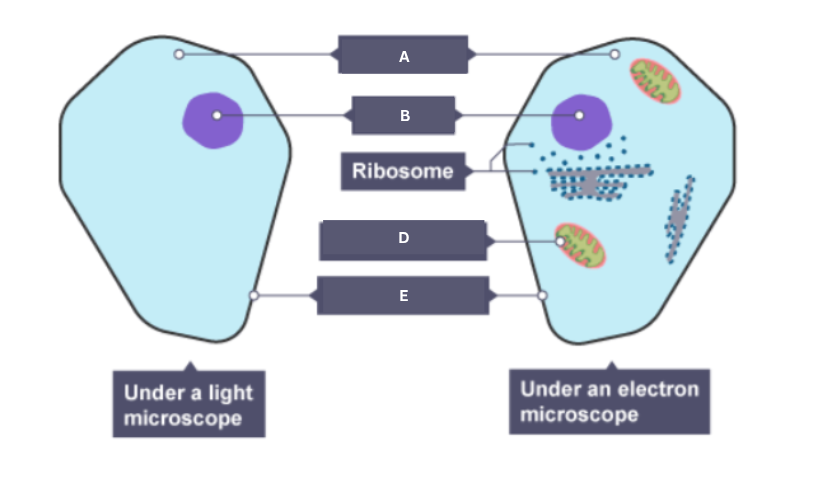
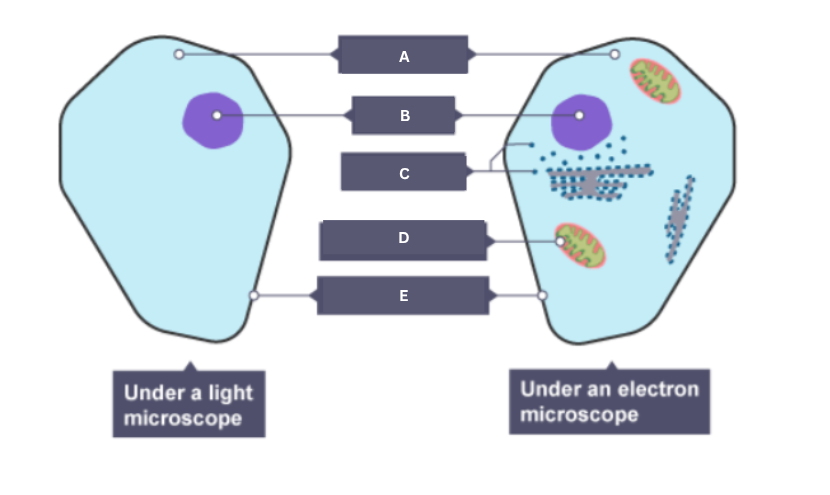
Name the part of the animal cell labelled D.
Mitochondrion
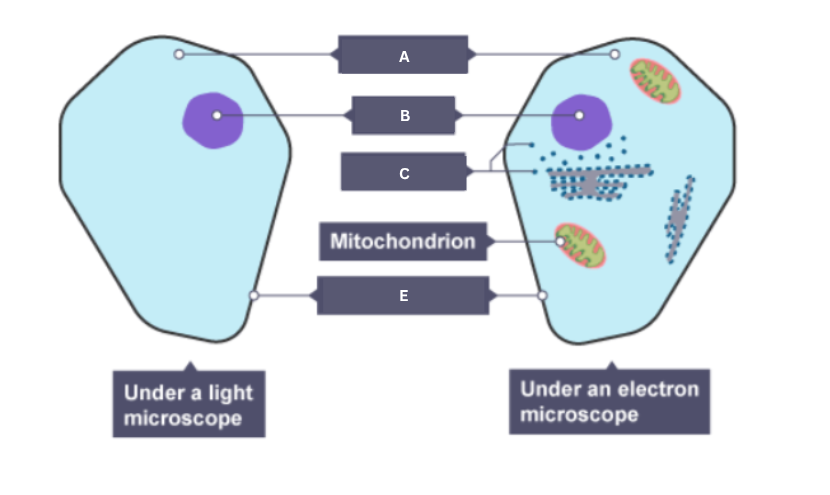
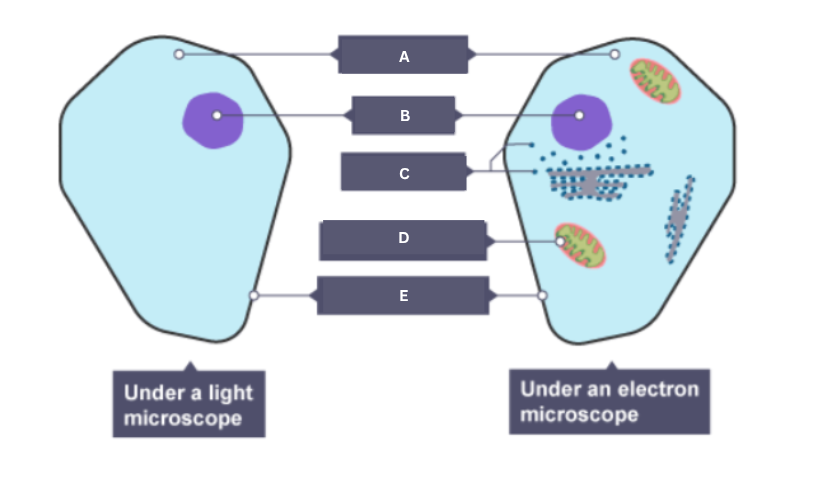
Name the part of the animal cell labelled E.
Cell membrane