Marketing Exam 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Define consumer buyer behavior and consumer market. What are the 3 words?
a. Consumer Buyer Behavior: Buying behavior of final consumers
b. Consumer Market: All the individuals and households that buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption
c. The 3 words are Acquire, Use, and Dispose
What is BBB (what are the two parts)?
BBB stands for Buyer’s Black Box. The parts of BBB are the Buyer’s characteristics and the Buyer’s decision process
What are the 4 characteristics that influence consumer purchases?
a. Cultural: Culture, Subculture, Social Class
b. Social: Groups and social networks, Family, Roles and status
c. Personal: Age and life-cycle stage, Occupation, Economic situation, Environmental situation, Lifestyle, Personality and self-concept
d. Psychological: Motivation, Perception, Learning, Beliefs and attitudes
Define Social Class.
Social Class: relatively permanent and ordered divisions in a society whose members share similar values, interests, and behaviors
Define opinion leader and influencer marketing. Is the family unit important?
a. Opinion Leaders: A person within a reference group who, because of special skills, knowledge, personality, or other characteristics, exerts social influence on others
b. Influencer Marketing: Enlisting established influencers or creating new influencers to spread the word about a company’s brands
c. Yes, the family unit is the most important membership unit reference group
What does AIO stand for?
a. Strong influence on buying decisions
b. Activities (work, hobbies, shopping, sports, social events)
c. Interests (food, fashion, family, recreation)
d. Opinions (about themselves, social issues, business, products)
What is VALS?
VALS is a proprietary psychometric method that measures these and other predictive attitudes—in conjunction with behaviors and demographics—for developing countrywide typologies such as US VALS
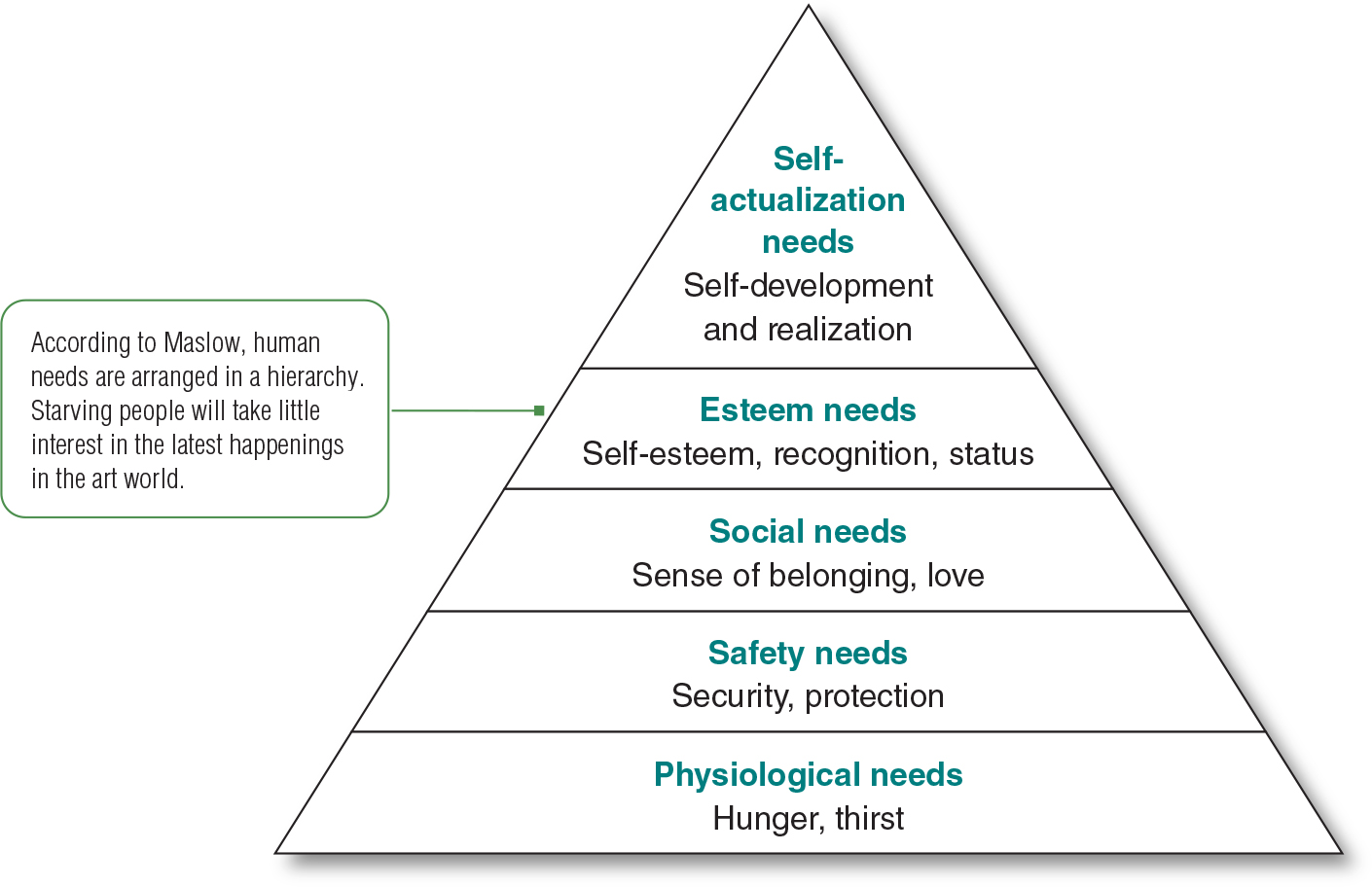
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Figure 5.3
Chart
Define perception.
Perception: Selecting, organizing, and interpreting information to product meaning
What is the JND?
JND stands for Just Noticeable Difference
Is stimulus generalization part of learning?
Yes, it creates a strong drive that helps to motivate towards specific stimuli.
Define belief and attitude. What are the parts of attitude?
a. Attitude: An individual’s enduring evaluation of feelings about and behavioral tendencies toward an object or idea.
b. The parts of attitude: Cognition (beliefs, knowledge, information), Affect (feelings, emotions), Behavior (intentions).
c. Belief: A descriptive thought that a person holds about something.
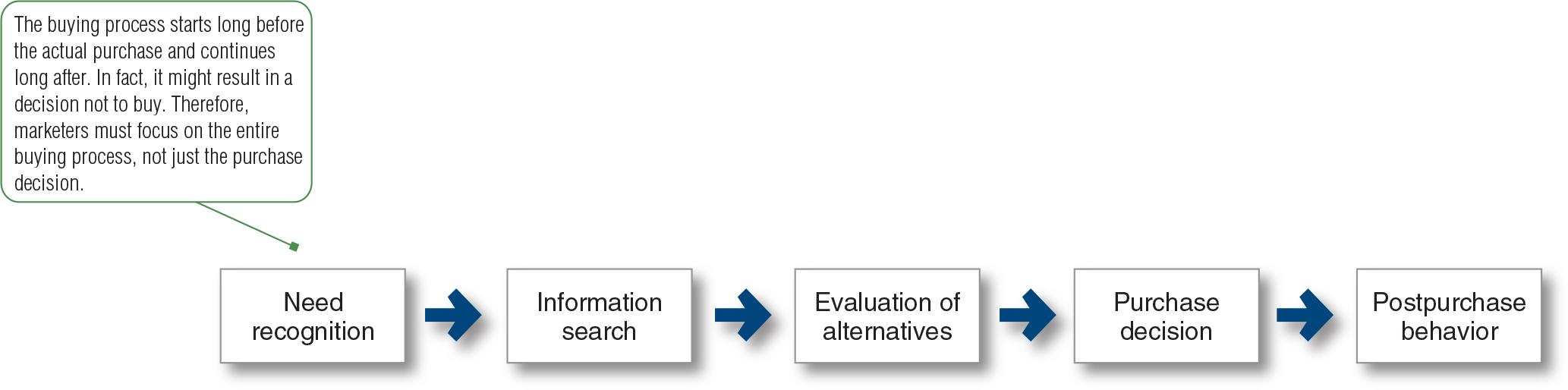
Figure 5.4 Buyer Decision Process
a. The buying process starts long before the actual purchase and continues long after. In fact, it might result in a decision not to buy. Therefore, marketers must focus on the entire buying process, not just the purchase decision.
b. Need Recognition -> Information Search -> Evaluation of Alternatives -> Purchase Decision -> Post-purchase Behavior.
A need occurs when there is enough tension and distance between what and what?
A desired state and an actual condition
What types of information search are there? Which is the least biased?
a. Internal search and external search
b. External search is the least biased
What is universal, retrieval, evoked/consideration set?
A group of brands within a particular product category that the buyer views as alternatives for possible purchase.
In post-purchase, why is cognitive dissonance a concern? Define it.
Cognitive dissonance: A buyer’s doubts shortly after a purchase about whether the decision was the right one; often occurs after expensive, high-involvement purchases.
List the steps in the adoption process. Define adoption process.
a. Adoption Process: The mental process through which an individual passes from first hearing about an innovation to final adoption.
b. The Steps of the Adoption Process: Awareness (the consumer becomes aware of the new product but lacks information about it) Interest (the consumer considers whether trying the new product makes sense) Evaluation (the consumer considers whether trying the new product makes sense) Trial (the consumer tries the new product on a small scale to improve his or her estimate of its value) Adoption (the consumer decides to make full and regular use of the new product).
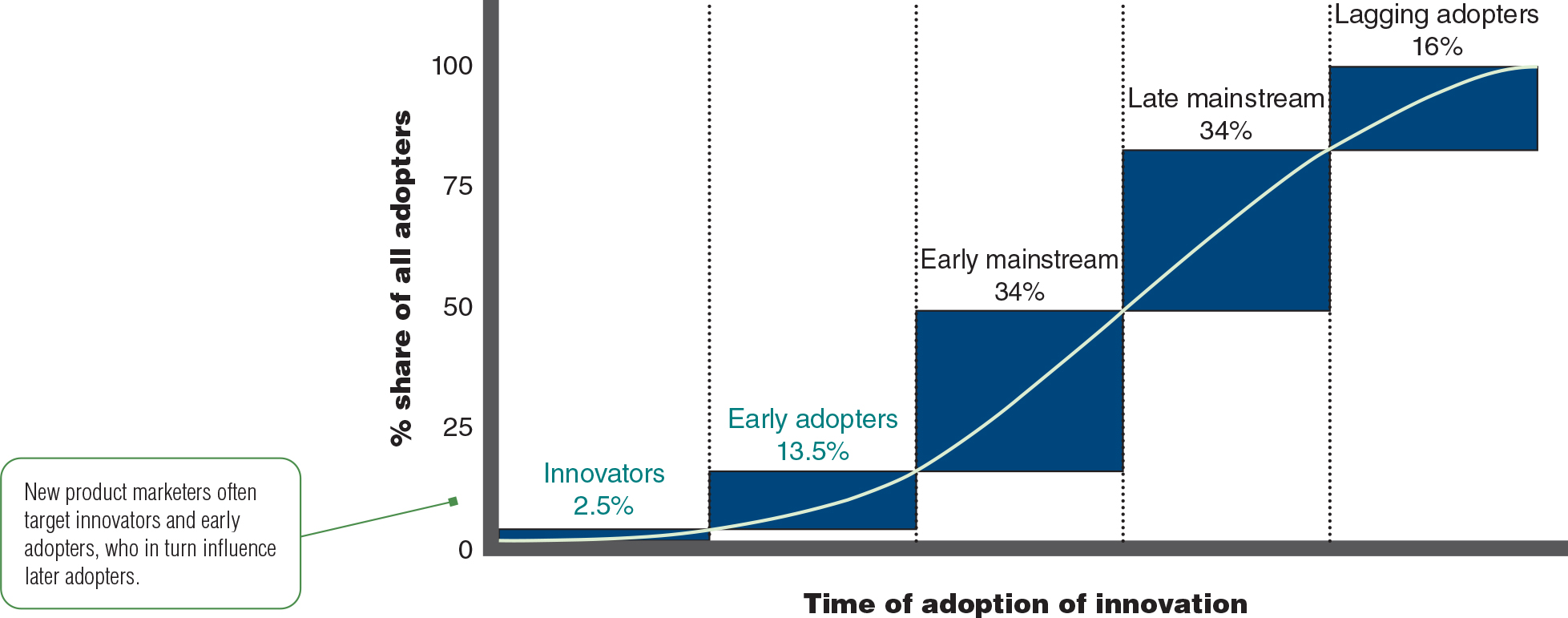
Figure 5.5 Adopter Categories Based on Relative Time of Adoption of Innovations
a. 2.5% Innovators Venturesome Risk
b. 13.5% Early adopters Respect Opinion Leaders
c. 34% Early mainstream Deliberate Rarely leaders
d. 34% Late mainstream Skeptical
e. 16% Lagging adopters Tradition bound Suspicious
What are the 5 characteristics that impact the rate of adoption? List, define.
a. Relative advantage: The degree to which the innovation appears superior to existing products.
b. Compatibility: The degree to which the innovation fits the values and experiences of potential consumers.
c. Complexity: The degree to which the innovation is difficult to understand or use.
d. Divisibility: The degree to which the innovation may be tried on a limited basis.
e. Communicability: The degree to which the results of using the innovation can be observed or described to others.
What are the 3 main differences between consumer and business markets?
a. Market structure and demand
b. Nature of the buying unit
c. Types of decisions and the decision process
What is the difference between a straight rebuy, modified rebuy, new task?
a. Straight rebuy: buyers routinely reorders something without any modifications.
b. Modified rebuy: buyer wants to modify product specifications, prices, terms, or suppliers.
c. New task: buyer purchases a product or service for the first time.
How many stages are there in the business buyer decision process? Is it more or less than the consumer buying process?
a. There are 8 stages in the business buyer decision process; Problem recognition, General need description, Product specification, Supplier search, Proposal solicitation, Supplier selection, Order-routine specification, Performance review
b. The business buyer decision process has more steps than the consumer buying process.
Define market segmentation, targeting, differentiation, and positioning. Figure 6.1.
a. Select customers to serve: Segmentation (divide the total market into smaller segments) and Targeting (select the segment or segments to enter).
b. Decide on a value proposition: Differentiation (differentiate the market offering to create superior customer value) and Positioning (position the market offering in the minds of target customers).
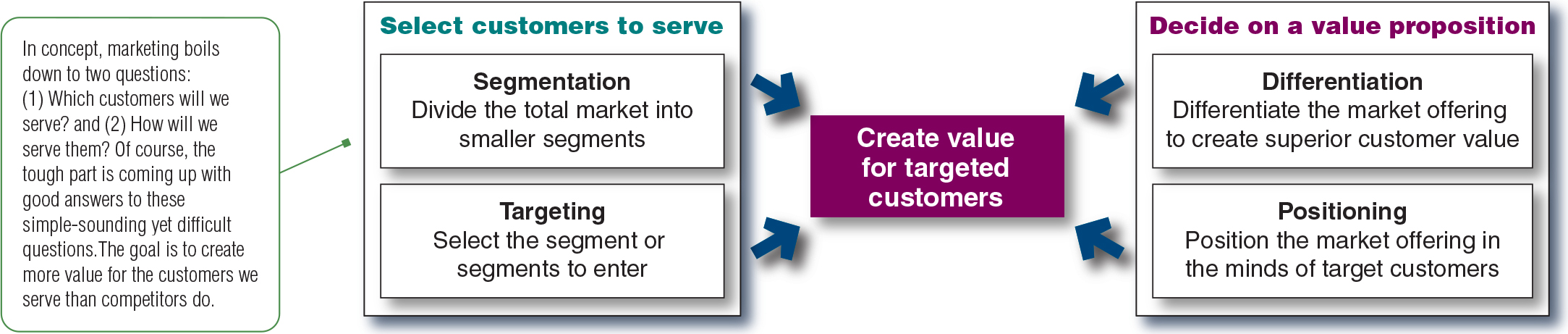
Table 6.1 What are the 4 major segmentation variables and examples?
a. Geographic: nations, regions, states, counties, cities, neighborhoods, population density (urban, suburban, rural), climate.
b. Demographic: age, life-cycle stage, fender, income, occupation, education, religion, ethnicity, generation.
c. Psychographic: social class, lifestyle, personality
d. Behavioral: occasions, benefits, user status, usage rate, loyalty status
Why use multiple segmentation bases?
Marketers rarely limit their segmentation analysis to only one or a few variables. Rather, they often use multiple segmentation bases in an effort to identify smaller, better-defined target groups.
What are the key requirements for effective segmentation?
a. Measurable: size, purchasing power
b. Accessible: reached and served
c. Substantial: profitable enough
d. Differentiable: distinguishable
e. Actionable: effective programs designed to attract
What are the 4 different targeting approaches? Define and provide examples.
a. Undifferentiated Marketing: a market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer.
b. Differentiated Marketing: a market-coverage strategy in which a firm targets several market segments and designs separate offers for each.
c. Concentrated Marketing: a market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large share of one or a few segments or niches.
d. Micromarketing: tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and wants of specific individuals and local customer segments; it includes local marketing and individual marketing.
What is a perceptual map?
Perceptual Map: created by questioning a sample of consumers about their perception of products, brands, and organizations with respect to two or more dimensions.
The full positioning of a brand is called the brand’s __________ _________.
Value Proposition
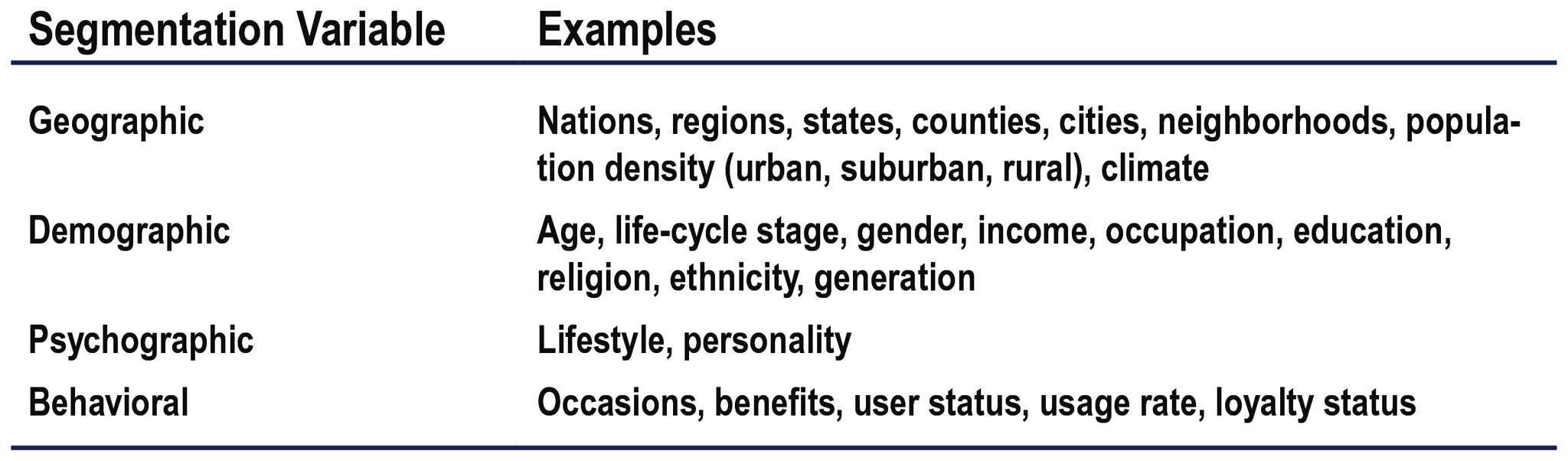
What are the “winning” value propositions? What is ALDI’s? Figure 6.4
a. More for more: provides the most upscale product or service
b. More for the same: high quality at lower prices
c. More for less: best-winning proposition
d. The same for less: gives a good deal
e. Less for much less: meeting consumers’ lower performance or quality requirements at a lower price
f. ALDI uses the value proposition of less for much less.
Define product. Is it the same as a service?
a. Product: is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need.
b. No, a product is not the same as a service.
List the 4 types of consumer products. Define and give examples.
a. Convenience products: are consumer products and services that customers usually buy frequently, immediately, and with minimal comparison and buying effort. Examples: laundry detergent, soft drinks, and fast food.
b. Shopping Products: are less frequently purchased consumer products and services that customers compare carefully on suitability, quality, price, and style. Examples: furniture, clothing, major appliances, and hotel services.
c. Specialty Products: are consumer products and services with unique characteristics or brand identifications for which a significant group of buyers is willing to make a special purchase effort. Examples: specific brands of cars, high-priced photography equipment, designer clothes, gourmet foods, and the services of medical or legal specialists.
d. Unsought products: are consumer products that a consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally consider buying. Examples: life insurance, preplanned funeral services, and blood donations to the Red Cross.
What are the 3 product/service decisions?
a. Individual Product Decisions
b. Product Line Decisions
c. Product Mix Decisions
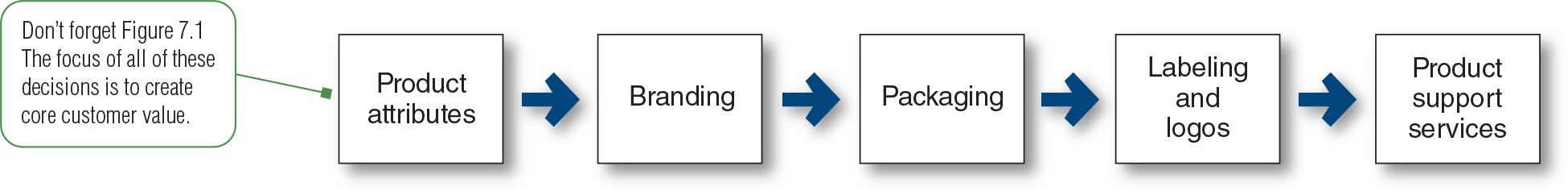
List the 5 individual product decisions. Figure 7.2
a. Product attributes (Quality features design)
b. Branding (Name mark)
c. Packaging (Protect promote)
d. Labeling (Identifies describe promote)
e. Product support services (Customer service)
What is a product line? What is stretching? Filling?
a. Product Line: closely related products that have similar functions and customer groups; are sold through similar outlets or fall within given price ranges.
b. Product Line Stretching: occurs when a company lengthens its product line beyond its current range.
c. Product Line Filling: involves adding more items within the present range of the line.
What are the 3 key product mix decisions? Define them.
a. Width: number of different product lines the company carries.
b. Length: total number of items a company carries.
c. Depth: number of versions offered for each product in the line.
d. Product Mix: consists of all the product lines and items that a particular seller offers for sale.
Figure 7.4
a. Internal Marketing: service firms must sell customer-contact employees on the importance of delighting customers.
b. Company
c. External Marketing
d. Customers
e. Interactive Marketing: Then service firms must help employees master the art of interacting with customers.
f. Employees
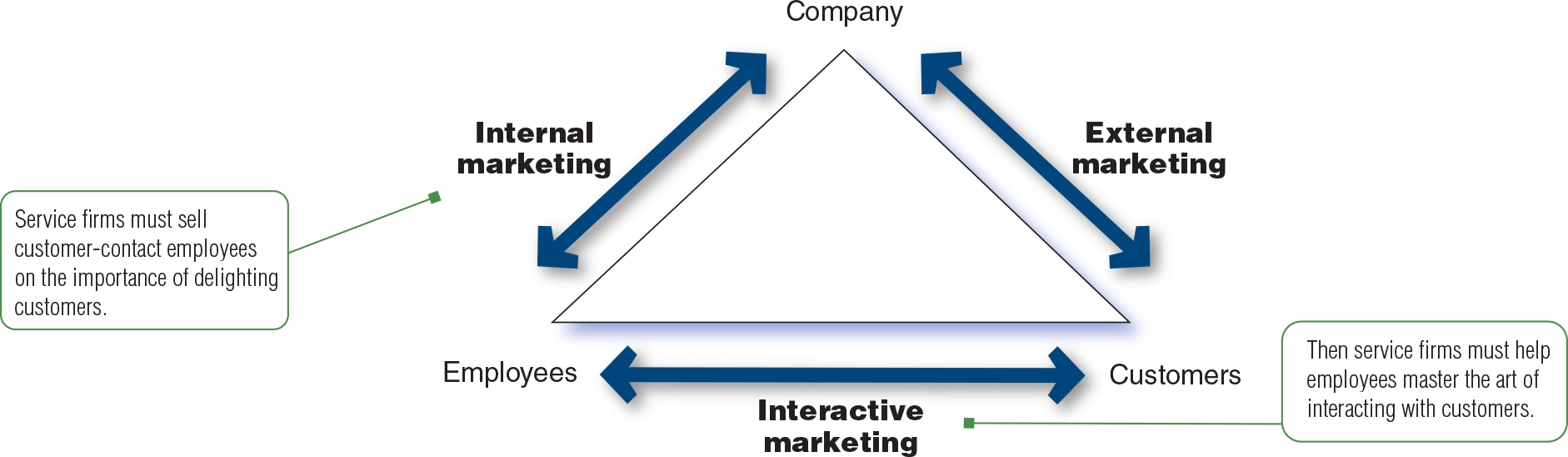
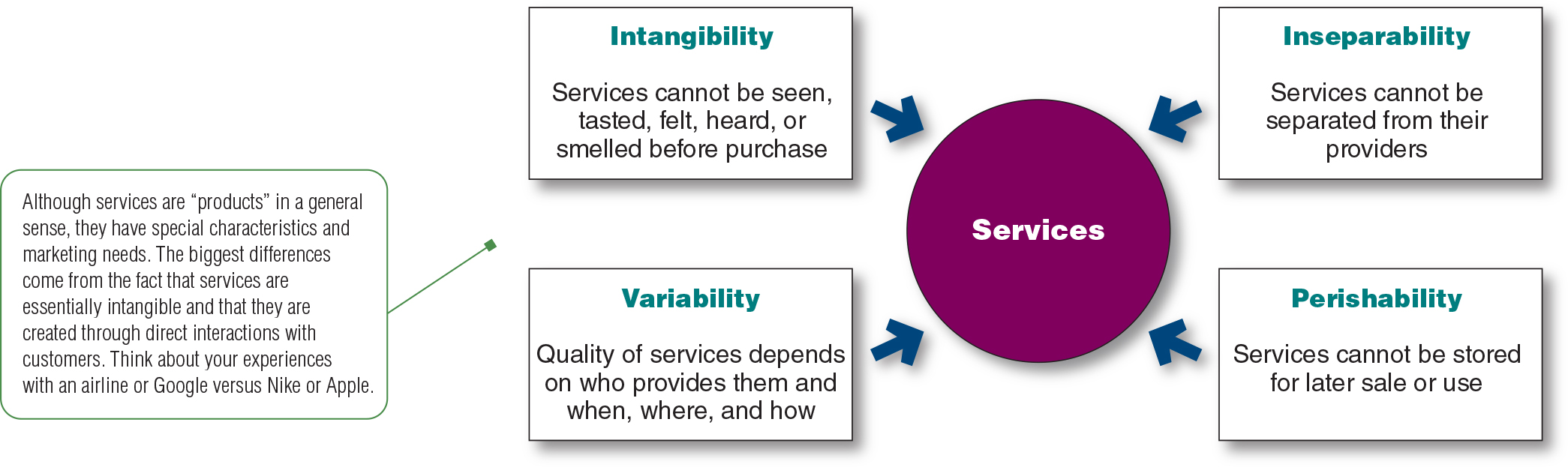
What are the 4 service characteristics (figure 7.3)? Define and provide examples.
a. Intangibility: Services that cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before purchase. Example: people undergoing cosmetic surgery.
b. Inseparability: Services that cannot be separated from their providers. Examples: if a service employee provides the service, then the employee becomes a part of the service.
c. Variability: Quality of services depends on who provides them and when, where, and how. Examples: Marriot has a reputation for providing better services than other hotels.
d. Perishability: Services that cannot be stored for later sale or use. Example: when demand mushrooms during the end-of-year holiday season, amazon must ramp up its delivery capacity, as must parcel delivery firms such as UPS, FedEx, and the USPS.
Review search, experience, and credence qualities.
Pure Tangible Good | Tangible Good with Accompanying Services | Hybrid offer | Service with accompanying minor goods | Pure service |
Soap | Auto with accompanying repair services | Restaurant | Airline trip with accompanying snacks | Doctor’s Exam |
Search Qualities | Vs | Experience Qualities | Vs | Credence Qualities |
What are the 5 links in the service profit chain?
a. Internal Service Quality (superior employee selection/training, quality work environment, strong support for those dealing with customers results in…)
b. Satisfied and productive service employees (which results in…)
c. Greater service value (more effective and efficient customer value creation, engagement, and service delivery, which results in…)
d. Satisfied and loyal customers (will remain loyal, repeat purchase, refer others, which results in…)
e. Healthy service profits and growth (superior service firm performance)
What is brand equity? List and define the 4 dimensions.
a. Brand Equity: the differential effect that knowing the brand name has on customer response to the product or its marketing.
b. Differentiation (what makes the brand standout)
c. Relevance (how consumers feel it meets their needs)
d. Knowledge (how much consumers know about the brand)
e. Esteem (how highly consumers regard and respect the brand)
What is brand positioning?
a. Brand Positioning: marketers should establish a mission and vision for the brand when positioning it.
b. Positions based on: attributes, benefits, beliefs and values (strongest!!!!)
Figure 7.6
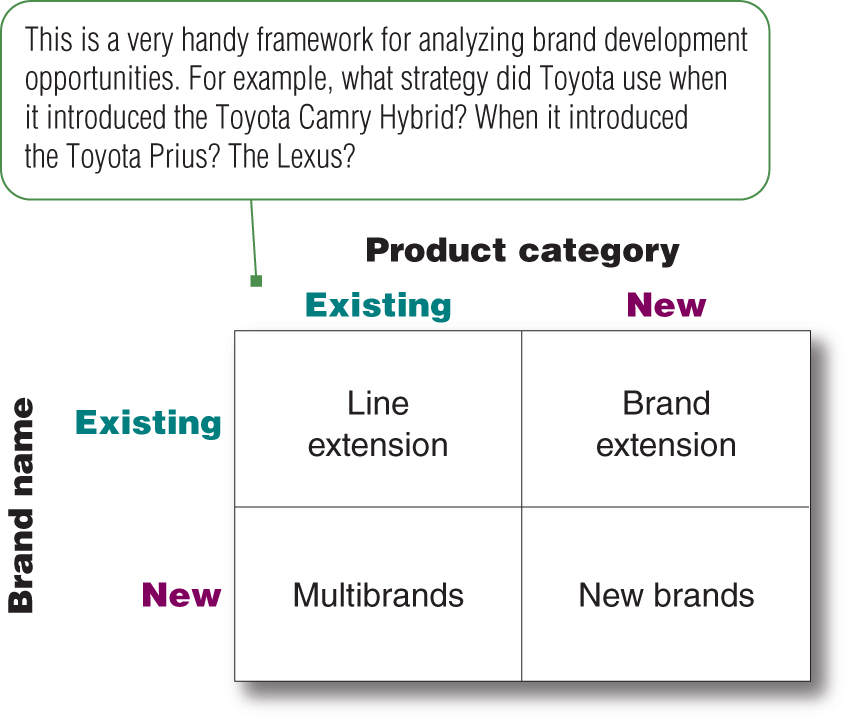
What is new product development?
New Product Development: the development of original products, product improvements, product modifications, and new brands through the firm’s own product development efforts.
Is product and innovation equal/interchangeable?
a. Yes, the word product is also often referred to as innovation.
b. Product=Innovation
Figure 8.1
Idea generation -> Idea screening -> Concept development and testing -> Marketing strategy development -> Business analysis -> Product development -> Test marketing -> Commercialization
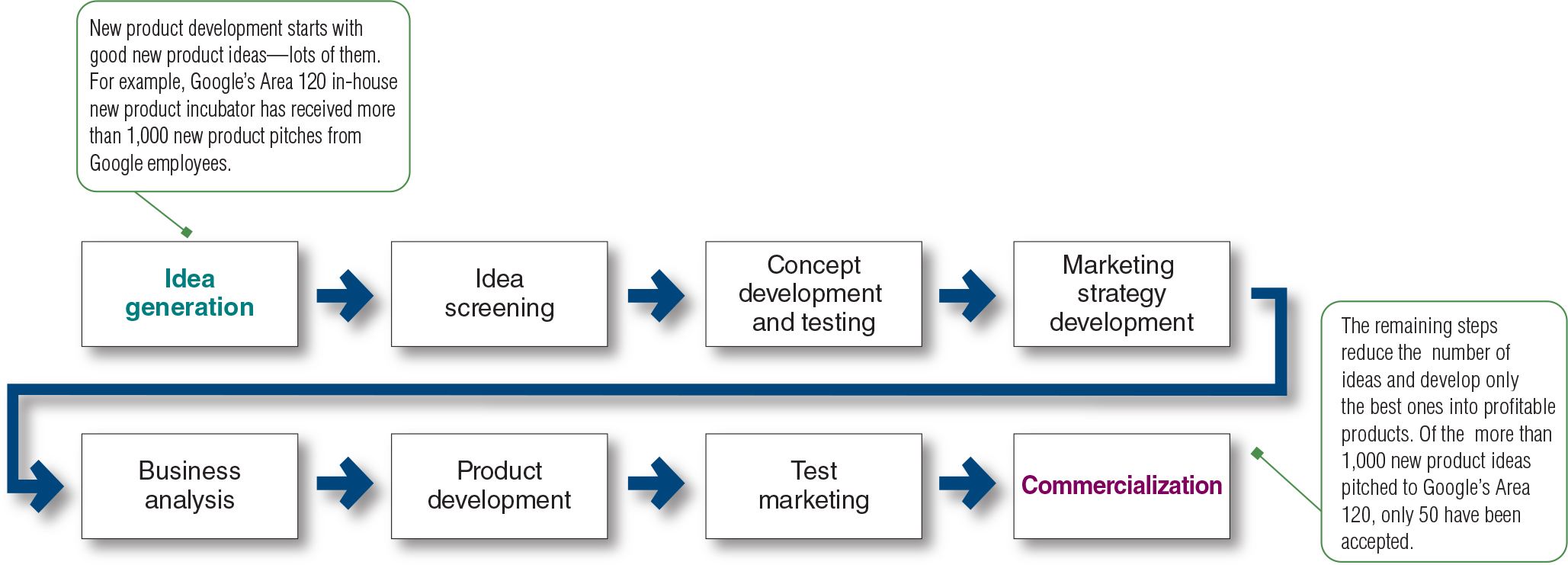
How do you screen ideas? What is meant by R-W-W?
a. A write-up of a new product is presented and evaluated against a set of general criteria.
b. R-W-W is a framework used to screen ideas. It stands for Real, Win, Worth doing
What is meant by product concept? How do you develop one? Is it the same as product idea?
a. Product concept: is a detailed version of the new product idea stated in meaningful consumer terms.
b. A product concept is developed from a product idea.
c. A product concept is not the same as a product idea but is made with the help of the product idea.
Figure 8.2