BIPS Y8
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
T1 SCIENCE REVISION
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
1
New cards
Name the Scientific Methods in order:
- Purpose
- Research
- Hypothesis
- Experiment
- Analysis
- Conclusion
- Research
- Hypothesis
- Experiment
- Analysis
- Conclusion

2
New cards
What is a Scientific Method?
A way in which scientists gather information and answer questions.
3
New cards
What is the goal of science?
To investigate and understand the natural world, explain events and use those explanations to make useful predictions.
4
New cards
What is diffusion?
The random movements of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration.
5
New cards
Where does diffusion happen the fastest? Why?
In gases, because the particles are farthest apart from each other and can travel long distances without hitting other particles.
6
New cards
Examples of some substances that move by diffusion:
Oxygen, perfume, etc.
7
New cards
Diffusion of ____ into the bloodstream.
Oxygen
8
New cards
Diffusion of ____ out of the bloodstream.
Carbon Dioxide
9
New cards
Formula for Aerobic respiration:
Glucose + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
10
New cards
Formula for Anaerobic respiration:
Glucose -> Lactic Acid + Energy
11
New cards
What is Aerobic respiration?
A chemical reaction for respiration WITH oxygen.
12
New cards
What is Anaerobic respiration?
A chemical reaction for respiration WITHOUT oxygen.
13
New cards
What is Mitochondria?
An organelle that performs the process of aerobic respiration.
14
New cards
Mitochondria's structures:
- 2 membranes:
~ Smooth outer membrane
~ Highly folded inner membrane
- Cristae
- Fluid-filled space between the 2 membranes
~ Smooth outer membrane
~ Highly folded inner membrane
- Cristae
- Fluid-filled space between the 2 membranes
15
New cards
Mitochondria's functions:
- Makes ATP energy from cellular respirations
~ Sugar + Oxygen -> ATP
~ Fuels the work of life
~ Sugar + Oxygen -> ATP
~ Fuels the work of life
16
New cards
Note:
Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell and is in BOTH plant cells and animal cells.
17
New cards
The Respiratory System:
A group of specialized organs dedicated to the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
18
New cards
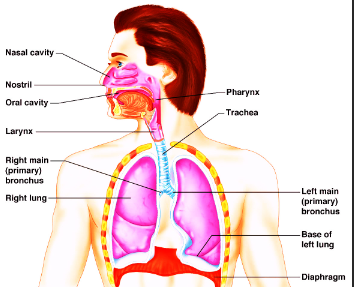
Organs of the Respiratory System in order:
- Nasal Cavity
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Alveoli
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Alveoli
19
New cards
The Nasal Cavity's uses:
Air enters the nose through two nostrils and reaches the nasal cavity. Here, the air is warmed and filtered. The hair present in the nostrils stop the dust or germs from entering the human respiratory system.
20
New cards
Pharynx's uses:
Muscular region connecting the nasal and oral cavities with the help of the Larynx and Esophagus.
21
New cards
Larynx's uses:
The Larynx is the part of the respiratory tract which contains the vocal cords. It has functions in;
~ Respiration (breathing)
~ Phonation (voice production)
~ Deglutition (swallowing)
~ Respiration (breathing)
~ Phonation (voice production)
~ Deglutition (swallowing)
22
New cards
Trachea (windpipe)'s uses:
- The tube that leads to the lungs from the pharynx.
- Contains rings of cartilage.
- Lined with ciliated mucous membrane.
- Contains rings of cartilage.
- Lined with ciliated mucous membrane.
23
New cards
Bronchi's uses:
The two large that connects the trachea to the lungs.
24
New cards
Lungs' uses:
- The lungs are two large sponge-like organs that are located in the chest.
- The lungs are divided into sections called lobes:
~ The left lung has 2 lobes.
~ The right lung has 3 lobes.
- The left lung is smaller than the right lung due to the position of the heart.
- The lungs are divided into sections called lobes:
~ The left lung has 2 lobes.
~ The right lung has 3 lobes.
- The left lung is smaller than the right lung due to the position of the heart.
25
New cards
Alveoli's uses:
- Site of gas exchange.
- The bronchioles end in a cluster of minute air sacs called the alveoli.
- The bronchioles end in a cluster of minute air sacs called the alveoli.
26
New cards
Diaphragm's uses:
The muscle below the lungs that controls breathing.
- Contracts during Inhalation
- Relaxes during Exhalation
- Major muscle of breathing
- Contracts during Inhalation
- Relaxes during Exhalation
- Major muscle of breathing
27
New cards
Intercostal muscle's uses:
Intercostal muscles are found between each of your ribs and provide support to your upper body and assist in breathing.
28
New cards
Respiratory tract function:
Inhale air into the lungs.
29
New cards
Respiratory organs function:
Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in the blood.
30
New cards
What 4 stages can gas exchange in humans be divided into?
- Breathing
- External Respiration
- Internal Respiration
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide transport
- External Respiration
- Internal Respiration
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide transport

31
New cards
Gas Exchange in humans:
- Occurs in the alveoli
- Oxygen diffuses into the blood
- Carbon Dioxide diffuses into the lungs
- Oxygen diffuses into the blood
- Carbon Dioxide diffuses into the lungs
32
New cards
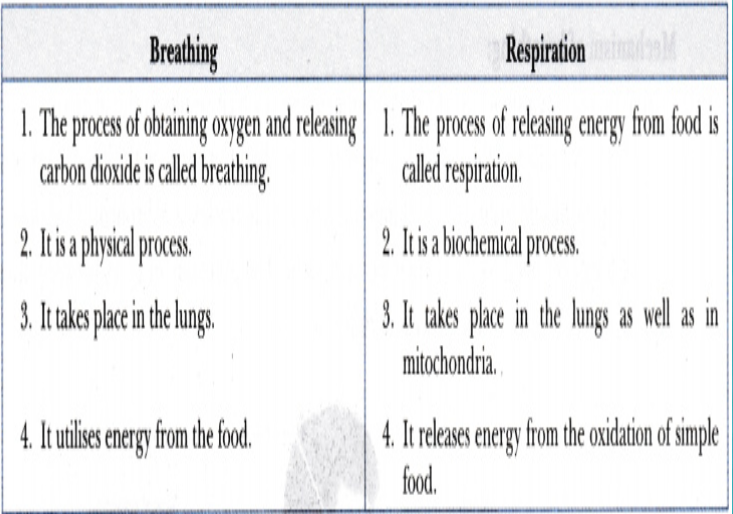
Differences between breathing and respiration:
33
New cards
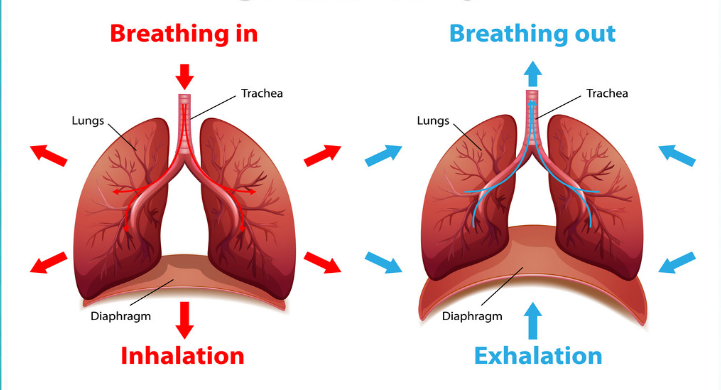
Diagram of breathing in and breathing out:
34
New cards
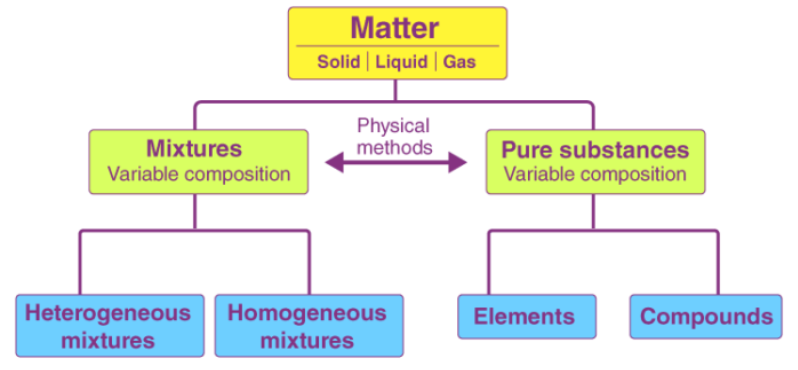
What is a mixture?
A mixture is made up of 2 or more types of atoms that are NOT chemically combined together.
35
New cards
What are the 2 major types of mixtures?
- Heterogeneous; meaning different
- Homogeneous; meaning same
- Homogeneous; meaning same
36
New cards
What are the characteristics of mixtures?
- Variable composition
- Components retain their characteristic properties.
- May be separated into pure substances by physical methods.
- Mixtures of different compositions may have widely different properties.
- Components retain their characteristic properties.
- May be separated into pure substances by physical methods.
- Mixtures of different compositions may have widely different properties.
37
New cards
Note:
38
New cards
What are Pure Substances?
Elements or compounds that consists of only one type of particle, e.g., Oxygen, honey, etc.
39
New cards
What are the characteristics of Pure Substances?
- Pure Substances cannot be separated by physical means.
~ Elements: Cannot be chemically separated, listed in the periodic table.
~ Compounds: Can be chemically separated, made up of elements.
~ Elements: Cannot be chemically separated, listed in the periodic table.
~ Compounds: Can be chemically separated, made up of elements.
40
New cards
Pure Substances' uses:
In the pharmaceutical industry, medicine must be tested for purity before they are sold. Impurities in drugs and food may produce undesirable side effects.
41
New cards
How to determine the purity of a substance?
- Checking the melting point of a substance
- Checking the boiling point of a substance
- Performing Chromatography
- Checking the boiling point of a substance
- Performing Chromatography
42
New cards
What are the factors affecting diffusion?
- Temperature
- Surface Area
- Concentration
- Size of particles
- Diffusion medium
- Surface Area
- Concentration
- Size of particles
- Diffusion medium
43
New cards
What is Pressure?
Pressure is the force per unit area that one object exerts on another.
44
New cards
Pressure depends on __(a)__ over which __(b)__ is distributed
(a) area
(b) force
(b) force
45
New cards
What are the characteristics of pressure in a liquid?
- Acts equally in all directions.
- The bottom of a boat is pushed upward by water pressure.
- Pressure acts upward when pushing a beach ball under water.
- The bottom of a boat is pushed upward by water pressure.
- Pressure acts upward when pushing a beach ball under water.
46
New cards
How does pressure vary?
- When we're on land, the pressure inside our bodies is the same as the pressure of the air around us.
- However, when people go diving, there is extra pressure from the water above. The greater the depth, the higher the pressure.
- When you're deep in the water, the pressure results from the weight of water pressing down on you from above.
- However, when people go diving, there is extra pressure from the water above. The greater the depth, the higher the pressure.
- When you're deep in the water, the pressure results from the weight of water pressing down on you from above.
47
New cards
What are the properties of Gases?
- Gases have mass.
- Gases take shape and volume of all containers.
- Gases are compressible.
- Gases easily move through each other. (e.g., perfume)
- Gases exert pressure.
- Gases take shape and volume of all containers.
- Gases are compressible.
- Gases easily move through each other. (e.g., perfume)
- Gases exert pressure.
48
New cards
What are the characteristics of Pressure in Gases?
- Gases exert pressure on their surroundings.
~ E.g., A balloon filled with air. Air pushes against the elastic sides if the balloon and keeps it firm.
- Gas pressure is the name given to the force exerted by gas particles colliding with the wall of their container.
~ A car tyre contains gas under pressure.
~ E.g., A balloon filled with air. Air pushes against the elastic sides if the balloon and keeps it firm.
- Gas pressure is the name given to the force exerted by gas particles colliding with the wall of their container.
~ A car tyre contains gas under pressure.
49
New cards
Show a diagram showing gaseous particles in a container to represent pressure in gases: (Arrows can be added to show the force exerted by the particles on the walls of the container.)
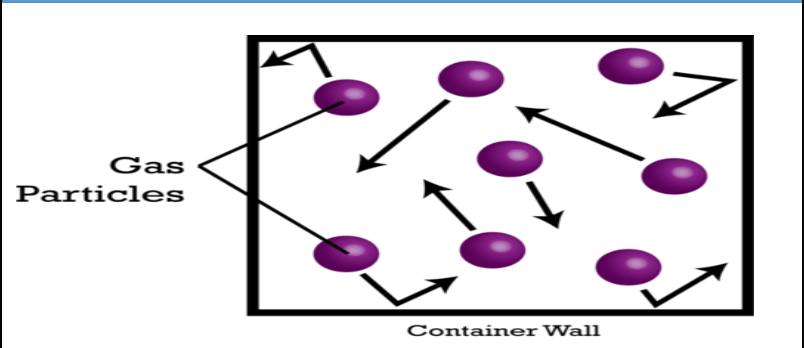
50
New cards
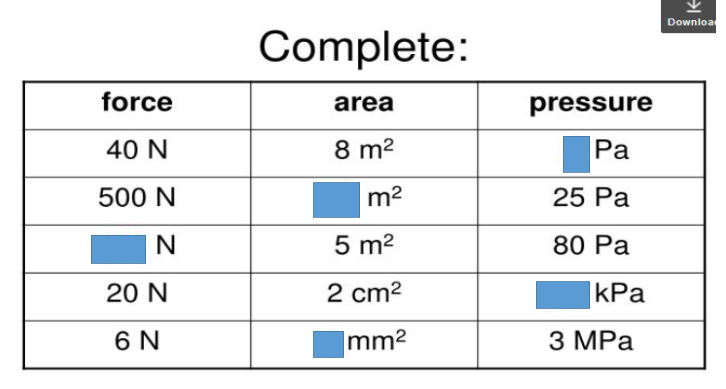
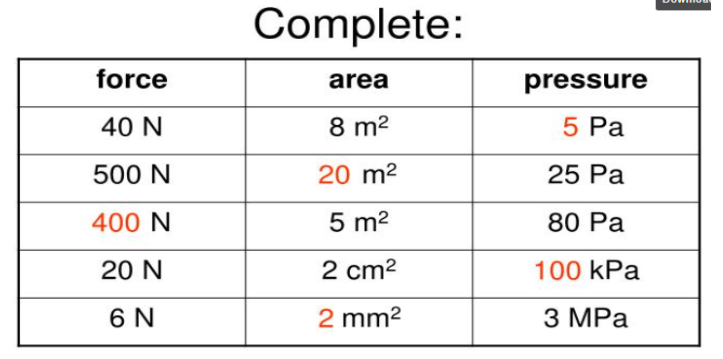
What are the units for pressure, force, and area?
Pressure = Pa (Pascal)
Force = N (Newtons)
Area = m² (square meter)
Force = N (Newtons)
Area = m² (square meter)
51
New cards
Write Pressure, Force, and Area in equation form:
Pressure = Force ÷ Area
Force = Pressure x Area
Area = Force ÷ Pressure
Force = Pressure x Area
Area = Force ÷ Pressure
52
New cards
Note:
1 Pascal is the same as 1 Newton per square meter.
53
New cards


54
New cards


55
New cards
56
New cards


57
New cards
If a material dissolves, it is ____.
Soluble
58
New cards
If a material doesn't dissolve, it is ____.
Insoluble
59
New cards
What is a solute?
The solid that dissolves.
60
New cards
What is a solvent?
The liquid that the solute dissolves in.
61
New cards
What is a solution?
The mixture of a solute and a solvent.
62
New cards
What is solubility in water?
- Water solubility is a measure of the amount of chemical
substance that can dissolve in water at a specific temperature.
- The unit of solubility is generally in mg/L (milligrams per liter) or ppm (parts per million).
substance that can dissolve in water at a specific temperature.
- The unit of solubility is generally in mg/L (milligrams per liter) or ppm (parts per million).
63
New cards
What are the different types of solutions?
- Saturated Solution:
~ Holds the maximum amount of solute.
- Unsaturated Solution:
~ Holds less than the maximum amount of solute.
- Supersaturated Solution:
~ Holds more than the maximum amount of solute.
~ Holds the maximum amount of solute.
- Unsaturated Solution:
~ Holds less than the maximum amount of solute.
- Supersaturated Solution:
~ Holds more than the maximum amount of solute.
64
New cards
What is solubility?
The amount of solute that dissolves in a solvent.
65
New cards
What are the factors affecting solubility?
- Temperature
~ As temperature increases, the solubility of solids in liquids increases.
~ As temperature increases, the solubility of gases in liquids decreases.
~ As temperature increases, the solubility of solids in liquids increases.
~ As temperature increases, the solubility of gases in liquids decreases.
66
New cards
What solubility does pressure affect?
- Pressure only affects the solubility of gases.
~ As air pressure increases, solubility of a gas increases.
~ As air pressure increases, solubility of a gas increases.
67
New cards
Solubility of a solute in a solvent purely depends on the ____ of both solute and solvent.
nature
68
New cards
What is the meaning of chromo and graphy?
Chromo - meaning colour
Graphy - meaning the representation of something on paper.
Graphy - meaning the representation of something on paper.
69
New cards
What is chromatography?
- Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyse, purify and/or quantify the mixture of components.
70
New cards
What is a chromatogram?
- The pattern left by the colours is called chromatogram.
- Each colour is made of different ink, meaning they will have their own chromatogram.
- Each colour is made of different ink, meaning they will have their own chromatogram.
71
New cards
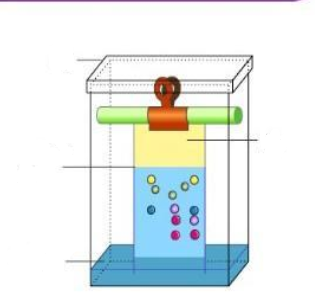
Label this diagram:
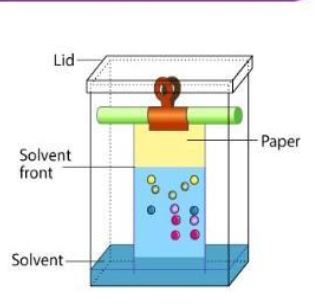
72
New cards
Light travels in _(a)_ lines.
Light travels much _(b)_ than sound.
We see things because they _(c)_ light into our eyes.
Shadows are formed when light is _(d)_ by an object.
Light travels much _(b)_ than sound.
We see things because they _(c)_ light into our eyes.
Shadows are formed when light is _(d)_ by an object.
(a) Straight
(b) Faster
(c) Reflect
(d) Blocked
(b) Faster
(c) Reflect
(d) Blocked
73
New cards
What is light reflection?