Sleep & Biological Rhythms
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
sleep is a…
behavior and change in consciousness
ultradian rhythms
patterns of biological variation occurring on cycles less than 24 hours
measuring sleep
electroencephalogram (EEG; neural)
electro-oculogram (EOG; eye movements)
electrocardiography (EKG, heart rate)
electromyogram (EMG; muscular)
EEG measuring
looks at changes in postsynaptic potentials
record many neurons all at once, reporting on the sum of their electrical activity
if cells are active, at about the same time, electrical messages are synchronized and appear as a large, clear wave in the data
amplitude: how many neurons doing this at same time
frequency: firing rate/sec
action potentials
voltage spikes beginning in axon hillock down the terminals
postsynaptic potentials
voltages in the postsynaptic membrane when NTs bind to receptors
the neurons are primarily pyramidal neurons (which are most abundant in the cortex)
adrenergic
dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine
associated w/ arousal and stress during wakefulness
many mood disorders are associated w/ disrupted REM sleep
adrenergic NTs are typically reduced during REM
some anxiety disorders assoc. w/ elevated levels during sleep
this might underly hyperarousal and axaggerated amygdala activity during wakefulness in ppl with anxiety disorders
decreased adrenergic NT levels
associated with decreased gamma EEG activity, which can be used as a proxy
sleep in the amygdala
decreased amygdala activity in response to emotional stimuli during wakefulness — probably due to stronger connections that form between the amygdala and ventral medial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC)
activity in vmPFC anticorrelated w/ activity in amygdala (vmPFC can tell amnygdala to calm down)
vmPFC supports inhibition of emotional, impulsive R’s
REM sleep depotentiates amygdala activity to previous emotional experiences
subjects completed two-day study protocol
day 1: view and rate (scale 1-5) the emotional intensity of each image (fMRI recorded)
12 hours of restfulness (sleep w/ EEG rec) or wakefulness
day 2: same viewing task (fMRI rec)
people able to sleep → tendency to lower valence ratings (ex. if rate as a 4 at beginning, more likely to rate as a 3 after sleeping)
people awake → not much change in valence ratings for emotional pics
ppl who slept showed decreased amygdala activity but increased vmPFC activity
ppl who slept who showed lowest gamma activity during REM also showed greatest reduction in amygdala activity
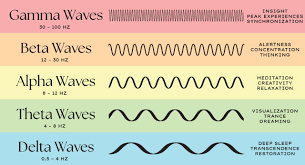
alpha waves
regular, medium-frequency waves
8-12 Hz
produced when person resting quietly and awake
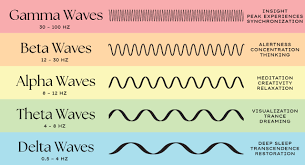
beta waves
irregular, mostly low-amplitude waves of 13-30 Hz
person awake and alert, attentive, or actively thinking
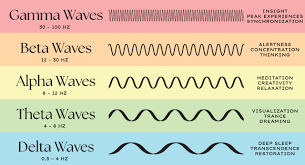
theta waves
stage 1 sleep
firing of neurons in neocortex becoming more synced
transition stage between sleep and wakefulness
3.5-7.5 Hz, early stages of slow-wave and REM sleep
sleep spindles
short bursts of waves 12-14 Hz that occur between 2-5 times a minute in stages 1-3 of sleep

K-complexes
sudden, sharp waveforms only found in stage 2 sleep
spontaneously occur at rate of about 1 per sec

slow-wave sleep
a non-REM stage of sleep characterized by delta waveform activity in an EEG record
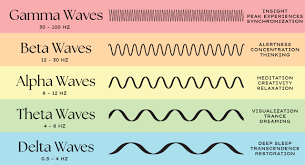
delta waves
less than 3.5 Hz
regular, synchronous electrical activity during deepest stages of slow-wave sleep