Ch. 16: Autonomic Nervous System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/74
Last updated 8:38 AM on 12/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
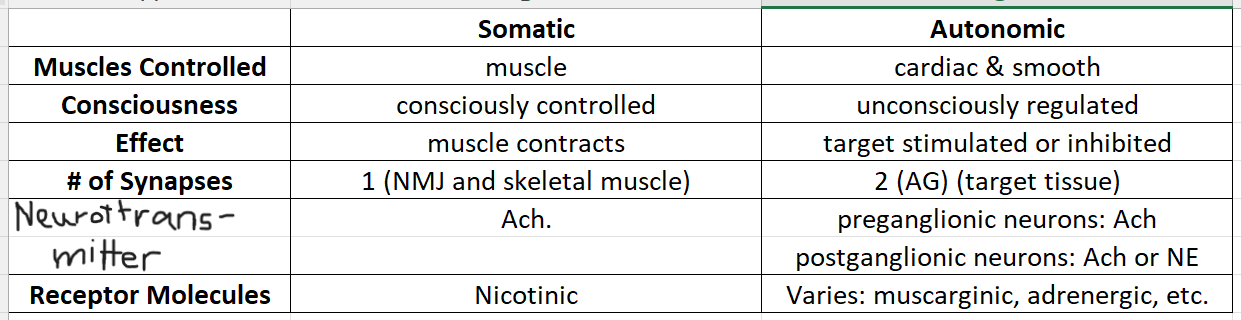
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System Image
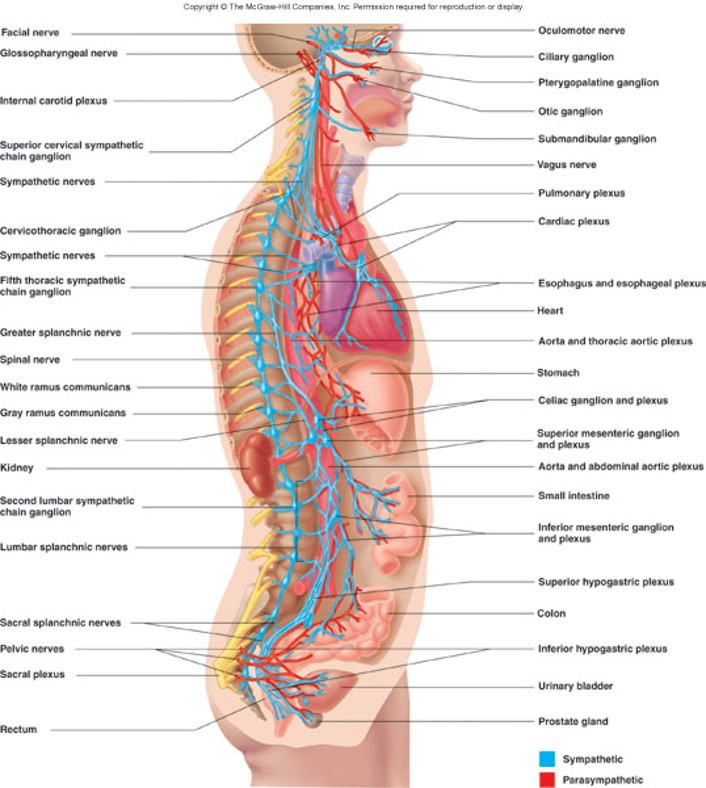
2
New cards
Peripheral nerves control
both motor and sensory neurons
3
New cards
2 types of motor neurons
somatic and autonomic
4
New cards
Somatic system controls what muscles vs. autonomic system controls what muscles?
Somatic: skeletal muscles
Autonomic: smooth and cardiac, glands
Autonomic: smooth and cardiac, glands
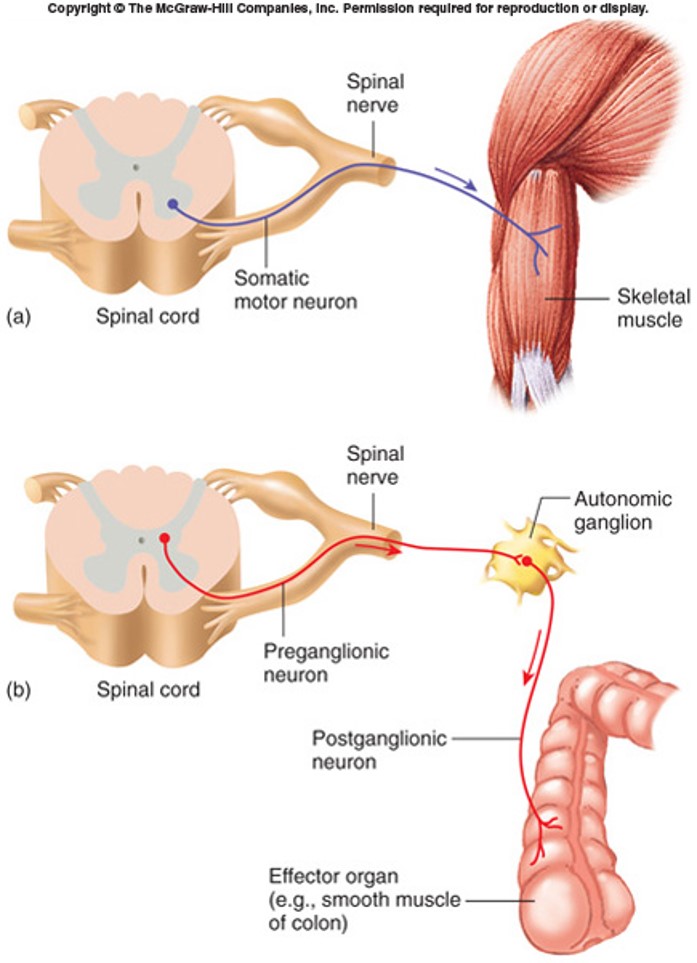
5
New cards
Sensory neurons are not divided into somatic and autonomic, but
there is still an overlap in function
6
New cards
Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems often supply the same organs, but
their function differs
7
New cards
Somatic vs. Autonomic NS
8
New cards
Table 16.1 - Comparison of the Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems
"stimulated and inhibited"
"postganglionic axons are unmyelinated"
"postganglionic axons are unmyelinated"
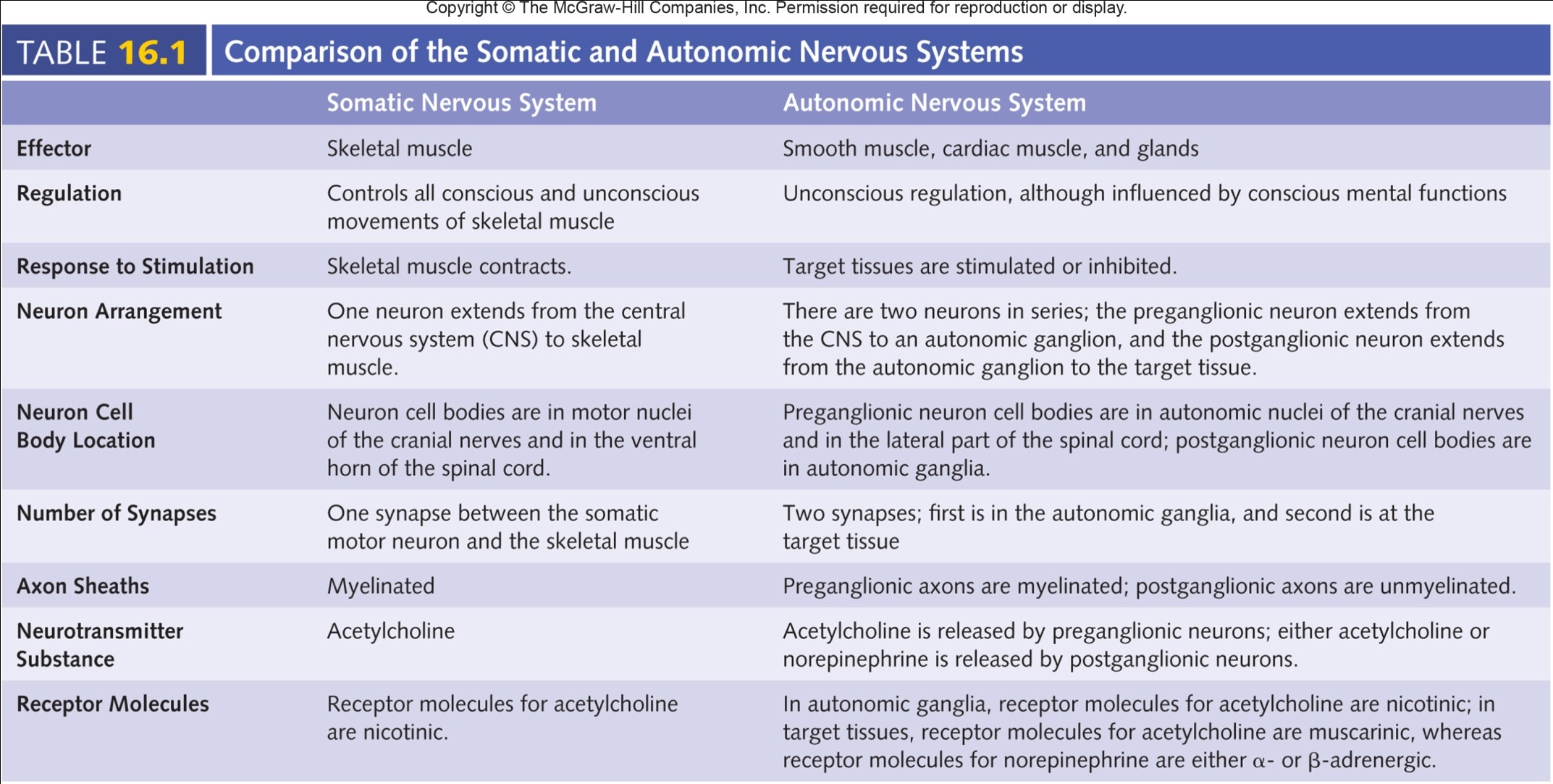
9
New cards
Which of the following is NOT an effector controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
A. cardiac muscle
B. skeletal muscle
C. glands
D. smooth muscle in blood vessels
A. cardiac muscle
B. skeletal muscle
C. glands
D. smooth muscle in blood vessels
B. skeletal muscle
10
New cards
3 divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
1. Sympathetic (thoracolumbar) - prepares body for physical activity
2. Parasympathetic (craniosacral) - (controls veg. functions like digestion, defecation, & urination)
3. Enteric (digestive system)
2. Parasympathetic (craniosacral) - (controls veg. functions like digestion, defecation, & urination)
3. Enteric (digestive system)
11
New cards
Sympathetic (Thoracolumbar) Division consists of
preganglionic cells bodies in the lateral horns of T1-L2
12
New cards
Preganglionic axons pass through ___ to ___
ventral roots to white rami
13
New cards
What does the white rami communicate with?
the retroperitoneal sympathetic chain ganglia
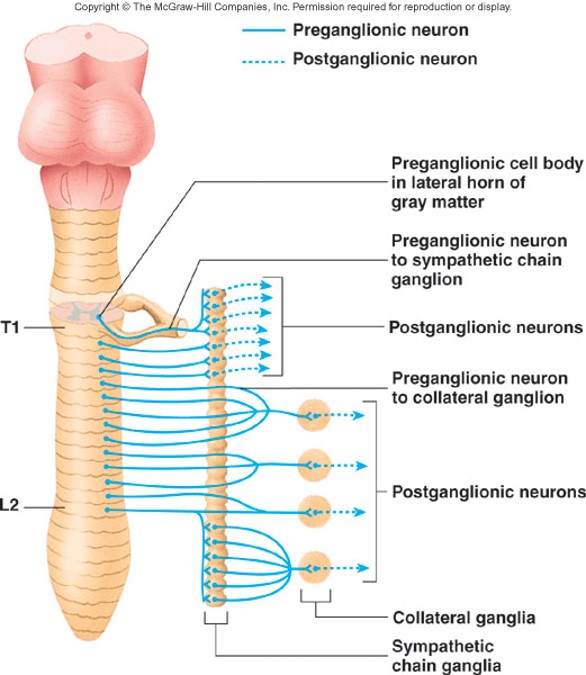
14
New cards
Sympathetic chain (or paravertebral) ganglia
15
New cards
How do the sympathetic nerves connect to:
- smooth muscle?
- cardiac muscle?
- gland tissue?
- smooth muscle?
- cardiac muscle?
- gland tissue?
16
New cards
4 routes of sympathetic axons as they exit the sympathetic chain ganglia
1. Spinal nerves
2. Sympathetic nerves
3. Splanchnic nerves
4. Innervation to the adrenal medulla
2. Sympathetic nerves
3. Splanchnic nerves
4. Innervation to the adrenal medulla
17
New cards
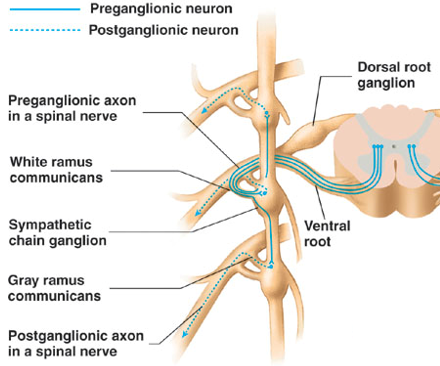
Spinal nerve route (Skn/Sk. M.)
Preganglionic axons synapse with postganglionic neurons within sympathetic chain.
These postganglionic neurons exit ganglia through the gray rami, which communicates and re-enters spinal nerves.
These postganglionic neurons exit ganglia through the gray rami, which communicates and re-enters spinal nerves.
18
New cards
Sympathetic nerve route (organs in thoracic cavity)
Preganglionic axons synapse with postganglionic neurons, which exit the ganglia through sympathetic nerves to the heart.
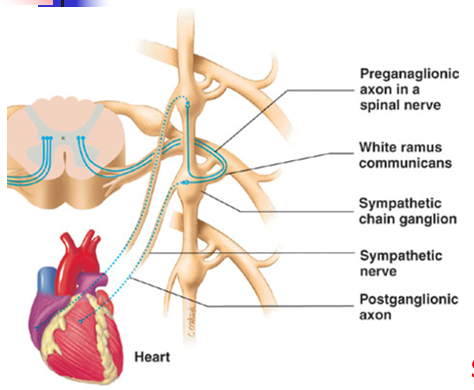
19
New cards
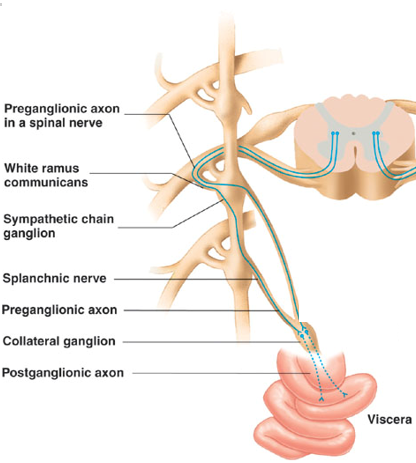
Splanchnic nerve route (effectors in abdominopelvic cavity)
Preganglionic axons pass through ganglia without synapsing and are carried out via splanchnic nerves.
Then they synapse with postganglionic neurons in collateral ganglia.
Postganglionic neurons then innervate organs.
Then they synapse with postganglionic neurons in collateral ganglia.
Postganglionic neurons then innervate organs.
20
New cards
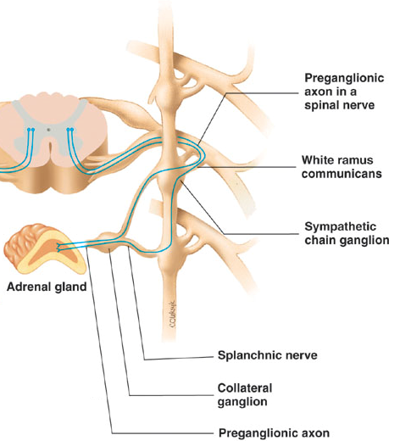
Innervation to adrenal medulla route
Preganglionic axons synapse with the cells of the adrenal medulla, which then releases Ep and NE (hormones that prepare for physical activity)
21
New cards
T or F: the adrenal medulla developed from the same cells as postganglionic ANS cells
true
22
New cards
Distribution of Sympathetic ANS Fibers (Sympathetic axons reach organs through: 3 things, and what they innervate)
1. Spinal nerves, head and neck nerve plexuses: sweat glands, smooth muscle of blood vessels to skeletal muscle and skin, & arrector pili
2. Thoracic nerve plexuses: cardiac and pulmonary systems
3. Abdominopelvic nerve plexuses: celiac organs (diaphragm, stomach, spleen, etc.), mesenteric organs, (colon, pancreas, small intestine), and other organs of the abdominopelvic cavity
2. Thoracic nerve plexuses: cardiac and pulmonary systems
3. Abdominopelvic nerve plexuses: celiac organs (diaphragm, stomach, spleen, etc.), mesenteric organs, (colon, pancreas, small intestine), and other organs of the abdominopelvic cavity
23
New cards
Sympathetic fibers leave the spinal cord in the
A. cranial and sacral regions.
B. lumbar and sacral regions.
C. cranial and thoracic regions.
D. thoracic and lumbar regions.
A. cranial and sacral regions.
B. lumbar and sacral regions.
C. cranial and thoracic regions.
D. thoracic and lumbar regions.
D. thoracic and lumbar regions.
24
New cards
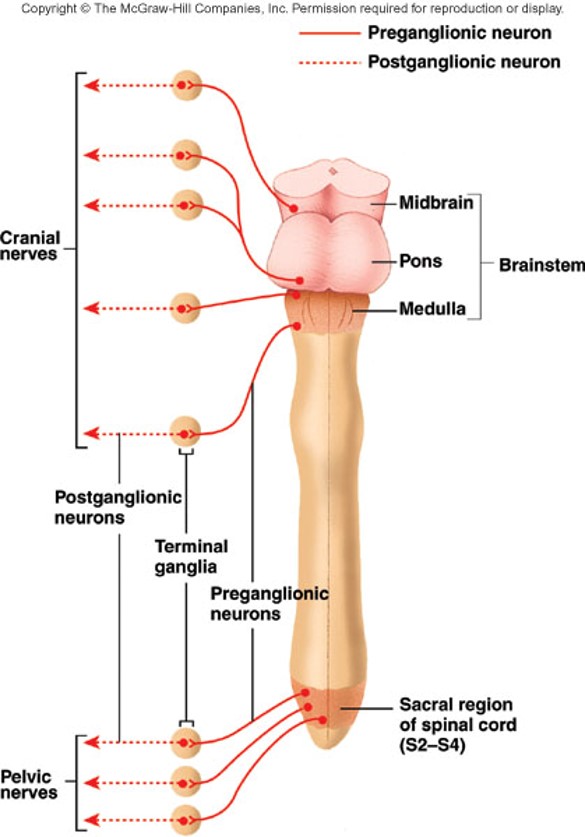
Parasympathetic (craniosacral) division
preganglionic cell body nuclei are in the brainstem or lateral gray matter in the spinal cord from S2-S4
25
New cards
In the parasympathetic division, preganglionic axons go through cranial nerves to _____.
terminal ganglia (through CN III, VII, IX and X).
26
New cards
In the parasympathetic division, preganglionic axons from sacral region go through ___ to ___.
pelvic splanchnic nerves to terminal ganglia
27
New cards
Why are terminal ganglia located near or on the effector organ in the parasympathetic division?
So the postganglionic axon has only a short distance to go to its effector
28
New cards
Distribution of Parasympathetic ANS Fibers (Parasympathetic axons reach organs through: 4 things and what they innervate)
1. Cranial nerves (oculomotor - III: ciliary ganglion->ciliary and iris muscles & facial - VII: pterygopalatine ganglion/submandibular ganglion->lacrimal and salivary glands) supplying the head and neck
2. Vagus nerve (X) & thoracic nerve plexus to heart & lungs
3. Abdominopelvic nerve plexuses & parts of vagus to stomach & other viscera
4. Pelvic splanchnic nerves and nerve plexuses to colon, urinary bladder, & reproductive organs.
2. Vagus nerve (X) & thoracic nerve plexus to heart & lungs
3. Abdominopelvic nerve plexuses & parts of vagus to stomach & other viscera
4. Pelvic splanchnic nerves and nerve plexuses to colon, urinary bladder, & reproductive organs.
29
New cards
The enteric nervous system consists of
nerve plexuses within wall of digestive tract
30
New cards
The enteric nervous system has contributions from 3 sources:
1. Sensory neurons (digestive tract -> CNS)
2. ANS motor neurons (CNS -> digestive tract)
3. Enteric neurons (confined within enteric plexuses)
2. ANS motor neurons (CNS -> digestive tract)
3. Enteric neurons (confined within enteric plexuses)
31
New cards
2 functions of the enteric NS (bc it can control the digestive tract independent of the CNS)
1. Stimulate/inhibit smooth muscle and gland secretions.
2. Detect changes in contents of the lumen (GI tract cavity for digestive food)
2. Detect changes in contents of the lumen (GI tract cavity for digestive food)
32
New cards
Arrange the following in correct sequence:
1) autonomic ganglia and ganglionic synapse
2) synapse with target tissues
3) preganglionic neuron
4) postganglionic neuron
A. 2, 3, 4, 1
B. 1, 3, 2, 4
C. 3, 1, 4, 2
D. 4, 1, 3, 2
1) autonomic ganglia and ganglionic synapse
2) synapse with target tissues
3) preganglionic neuron
4) postganglionic neuron
A. 2, 3, 4, 1
B. 1, 3, 2, 4
C. 3, 1, 4, 2
D. 4, 1, 3, 2
C. 3, 1, 4, 2
33
New cards
What are neurotransmitters produced by in the ANS?
its neurons (neurons of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems)
34
New cards
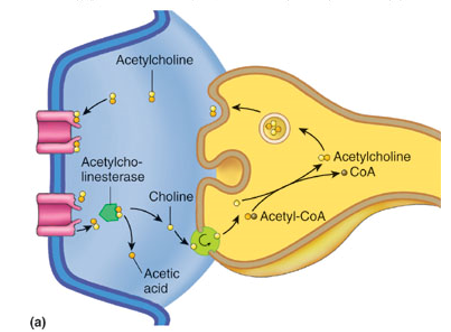
What type of neurons is acetylcholine released by?
cholinergic neurons
35
New cards
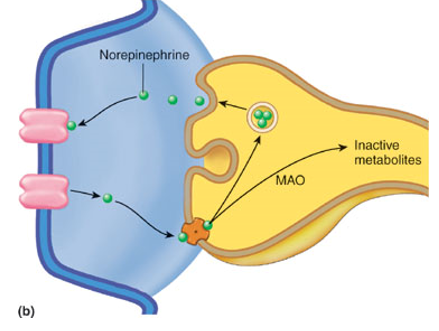
What type of neurons is norepinephrine released by?
adrenergic neurons
36
New cards
What two different forms of cholinergic receptors bind acetylcholine?
nicotinic and muscarinic
37
New cards
Where are nicotinic receptors located? (3 places)
1. in the membranes of all postganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia
2. in the membranes of skeletal muscle cells
3. on the cell bodies of autonomic postganglionic neurons in the autonomic ganglion
2. in the membranes of skeletal muscle cells
3. on the cell bodies of autonomic postganglionic neurons in the autonomic ganglion
38
New cards
What effect does the binding of ACh to a nicotinic receptor have?
an excitatory effect
39
New cards
Where are muscarinic receptors located? (2 places)
1. the membranes of effector cells that respond to ACh released from postganglionic neurons.
2. on the cells of all parasympathetic effectors & some Sympathetic effectors, such as sweat glands
2. on the cells of all parasympathetic effectors & some Sympathetic effectors, such as sweat glands
40
New cards
What effect does the binding of ACh to a muscarinic receptor have?
either excitatory or inhibitory
41
New cards
What do adrenergic receptors bind? (2 things)
norepinephrine and epinephrine
42
New cards
Where are adrenergic receptors located?
on most sympathetic effectors
43
New cards
What effect does the binding of NE to a adrenergic receptor have?
either excitatory or inhibitory effect (ex. Bl V.)
44
New cards
What 2 receptors are adrenergic receptors further subdivided into?
alpha and beta receptors
45
New cards
What neurotransmitter has a greater effect on alpha and beta receptors?
Epinephrine
46
New cards
Location of ANS Receptors image
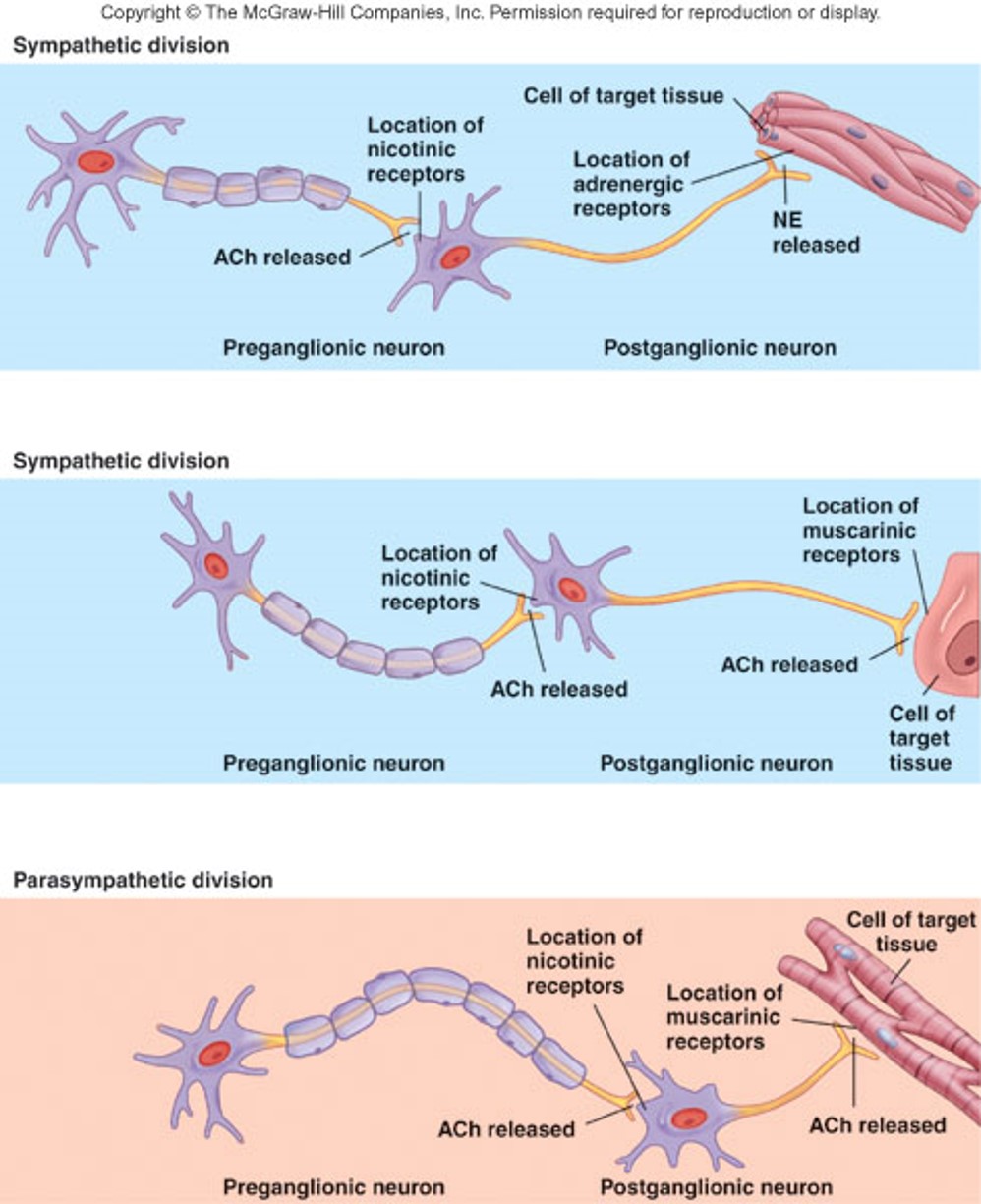
47
New cards
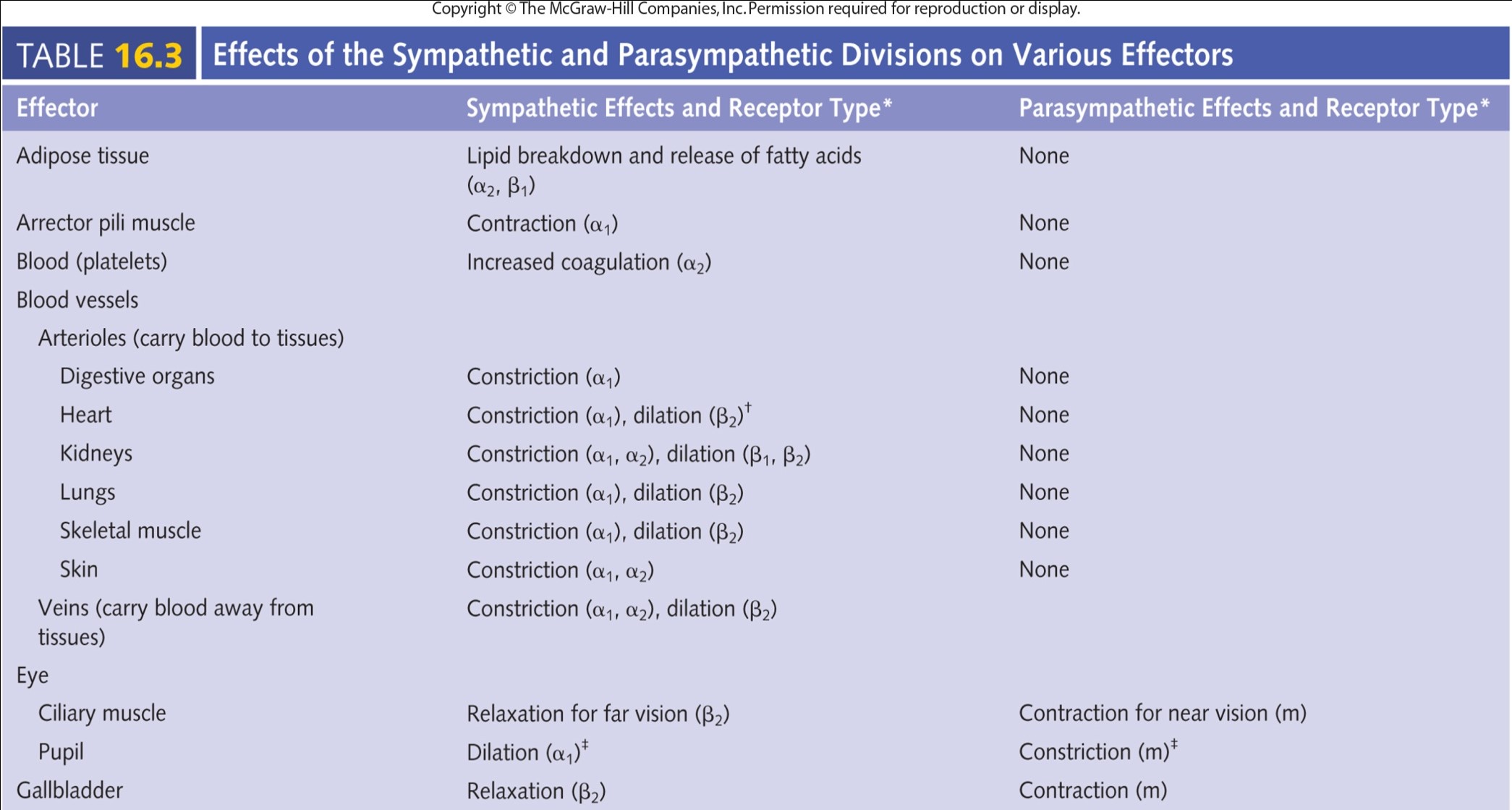
Table 16.3a - Effects of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions on Various Effectors
48
New cards
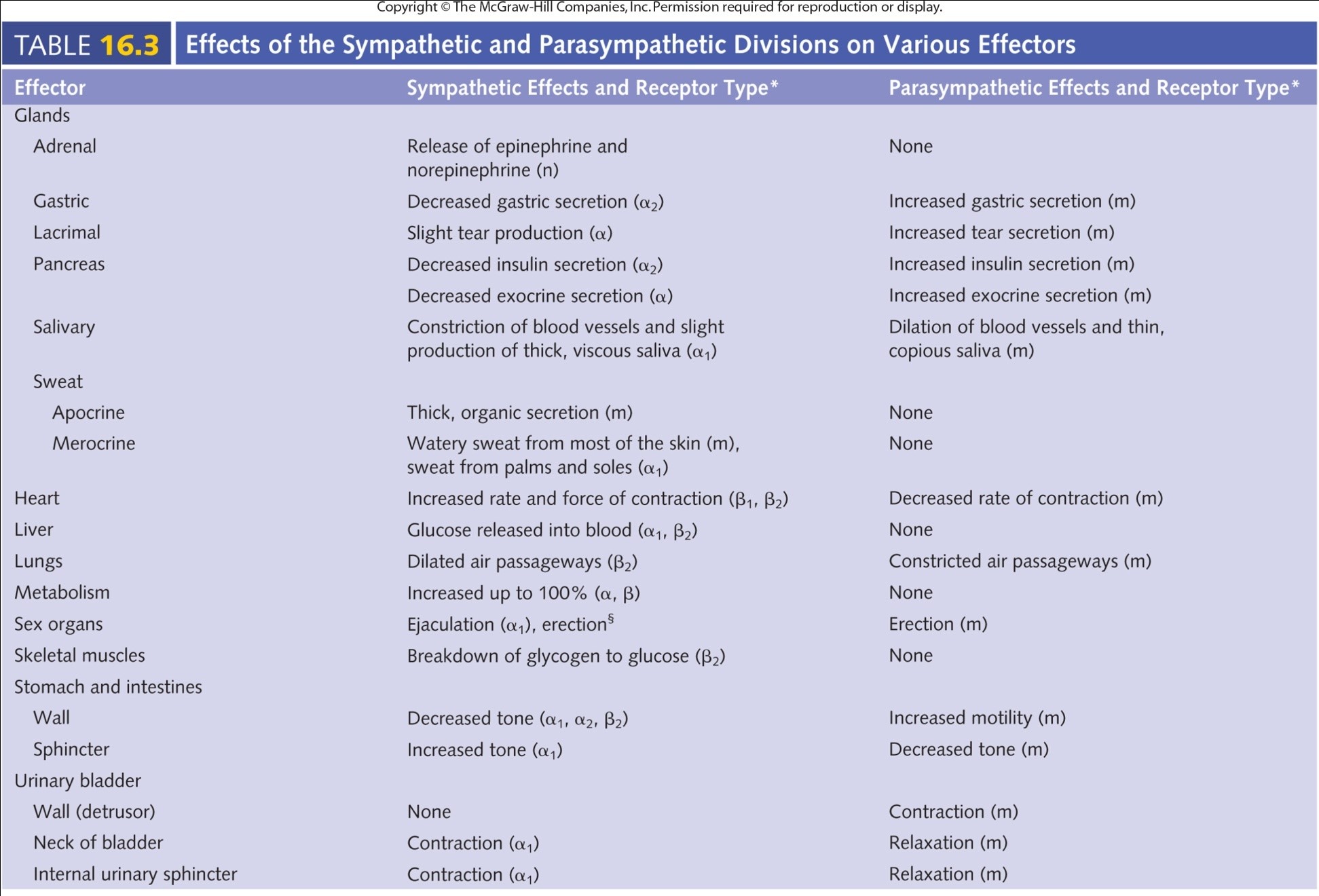
Table 16.3b - Effects of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions on Various Effectors
"thick organic secretion"
"watery sweat from most of the skin (m), sweat from palms and soles (a1)
"dilated air passageways (B2)"
"constricted air passageways"
"watery sweat from most of the skin (m), sweat from palms and soles (a1)
"dilated air passageways (B2)"
"constricted air passageways"
49
New cards
Which of the following is a sympathetic effect?
A. constriction of the pupils of the eye
B. decreased heart rate
C. dilation of the bronchioles in the lungs
D. increased gastric secretions
A. constriction of the pupils of the eye
B. decreased heart rate
C. dilation of the bronchioles in the lungs
D. increased gastric secretions
C. dilation of the bronchioles in the lungs
50
New cards
Adrenergic receptor stimulant and what it does
Albuterol dilates bronchioles in lungs
51
New cards
Adrenergic receptor blocking agents and what it does
Lopressor treats high blood pressure
52
New cards
Regulation of the ANS
autonomic reflexes control most of the activity of visceral organs, glands and blood vessels, but autonomic reflex activity is influenced by the hypothalamus and higher brain centers.
The hypothalamus has overall control of the ANS.
The hypothalamus has overall control of the ANS.
53
New cards
The results of adrenal medulla secretions (Ep and some NE) on target tissues (8 things)
1. Increased glucose release from liver into blood
2. Increased release of fatty acids from adipose tissue into the blood
3. Increased HR
4. Decreased blood flow through most internal organs
5. Increased blood flow to skeletal muscles and the heart
6. Increased BP
7. Decreased function of visceral organs
8. Increase MR of skeletal muscles
2. Increased release of fatty acids from adipose tissue into the blood
3. Increased HR
4. Decreased blood flow through most internal organs
5. Increased blood flow to skeletal muscles and the heart
6. Increased BP
7. Decreased function of visceral organs
8. Increase MR of skeletal muscles
54
New cards
2 autonomic reflexes and their effects
1. Parasympathetic reflex via vagus lowers heart rate
2. Sympathetic reflex via cardiac nerve (sympathetic nerve to heart) causes increased heart rate
2. Sympathetic reflex via cardiac nerve (sympathetic nerve to heart) causes increased heart rate
55
New cards
Parasympathetic reflex via vagus image
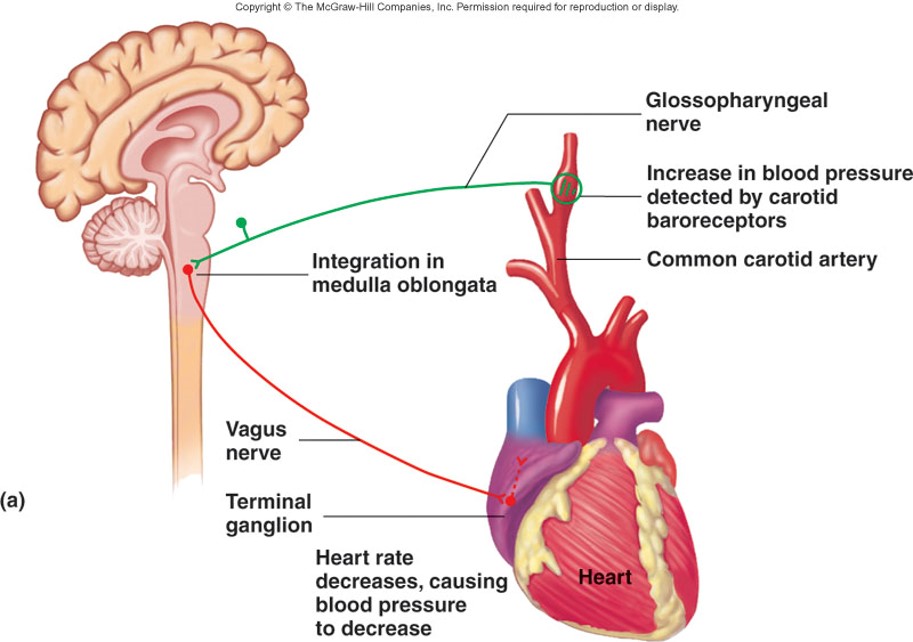
56
New cards
Sympathetic reflex via cardiac nerve image
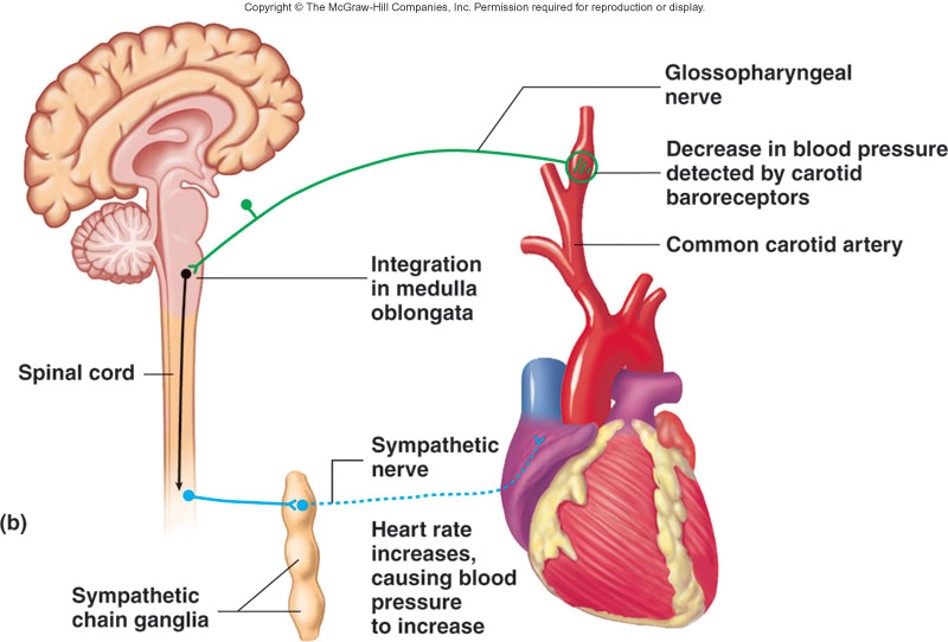
57
New cards
Enteric NS autonomic reflex
sensory neurons of the enteric plexuses supply CNS with information
58
New cards
Enteric NS local reflex
does not involve CNS, it produces an involuntary and unconscious response
59
New cards
Example of a local effect in the enteric NS
the stretch of the wall of the digestive tract is detected by sensory neurons (Ind. of CNS), which send APs that lead to contraction or relaxation of smooth muscle
60
New cards
What has overall control of Autonomic Nervous System?
A. pituitary gland.
B. cortex of the brain.
C. cranial and thoracic regions of spinal cords.
D. hypothalamus.
A. pituitary gland.
B. cortex of the brain.
C. cranial and thoracic regions of spinal cords.
D. hypothalamus.
D. hypothalamus.
61
New cards
Functional Generalizations of ANS
1. Dual innervation (ex: GI tract, heart, urinary bladder)
2. Opposite effects (ex: sympathetic -> physical activity, parasympathetic -> rest - SLUDD)
2. Opposite effects (ex: sympathetic -> physical activity, parasympathetic -> rest - SLUDD)
62
New cards
What is the exception to the sympathetic ANS regulating functions needed for physical activity?
BP: Blood vessel walls only have sympathetic stimulation - at rest, sympathetic is responsible for maintenance of BP
63
New cards
What does SLUDD stand for?
salivation
lacrimation
urination
digestion
defecation
lacrimation
urination
digestion
defecation
64
New cards
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic image
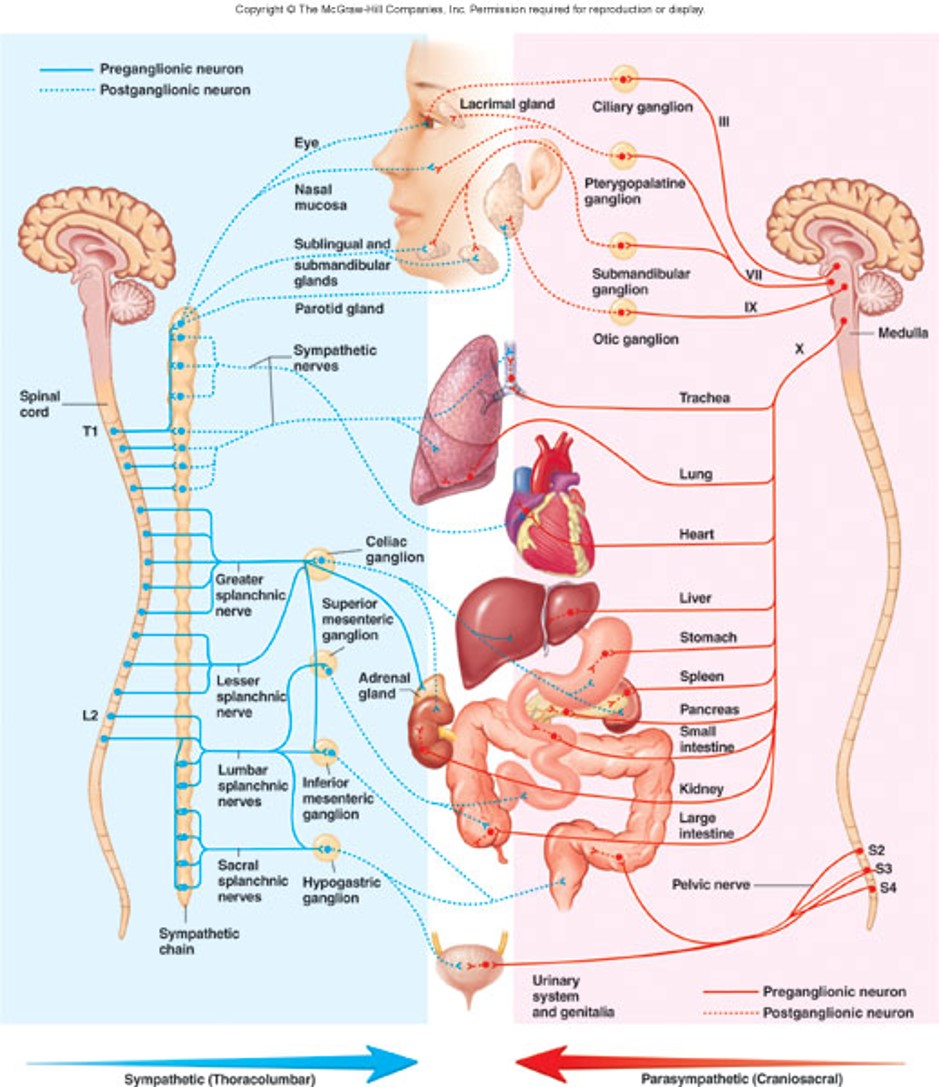
65
New cards
Responses to exercise (fight or flight) - 7 things
1. Increased heart rate and force of contraction
2. Blood vessel dilation in skeletal/cardiac muscles
3. Dilation of air passageways (bronchial tubes)
4. Energy sources availability increased (ex: glycogen -> glucose & the breakdown of triglycerides by fat cells to free fatty acids)
5. Muscles generate heat to increase body temperature
6. Sweat gland activity increases
7. Decrease in nonessential organ activities
2. Blood vessel dilation in skeletal/cardiac muscles
3. Dilation of air passageways (bronchial tubes)
4. Energy sources availability increased (ex: glycogen -> glucose & the breakdown of triglycerides by fat cells to free fatty acids)
5. Muscles generate heat to increase body temperature
6. Sweat gland activity increases
7. Decrease in nonessential organ activities
66
New cards
Reynaud's disease image
extremities turn white then blue
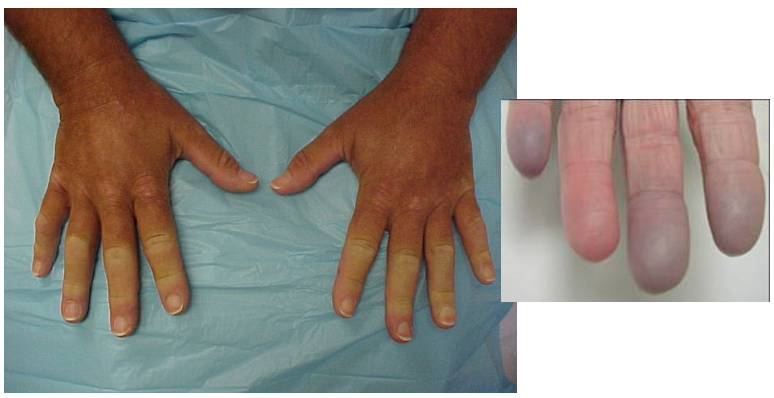
67
New cards
Acetylcholine is used as a neurotransmitter substance in this system.
A. somatic motor nervous system
B. autonomic nervous system
C. both somatic and autonomic nervous system
D. neither somatic nor autonomic nervous system
A. somatic motor nervous system
B. autonomic nervous system
C. both somatic and autonomic nervous system
D. neither somatic nor autonomic nervous system
C. both somatic and autonomic nervous system
68
New cards
Target tissues may be stimulated or inhibited.
A. somatic motor nervous system
B. autonomic nervous system
C. both somatic and autonomic nervous system
D. neither somatic nor autonomic nervous system
A. somatic motor nervous system
B. autonomic nervous system
C. both somatic and autonomic nervous system
D. neither somatic nor autonomic nervous system
B. autonomic nervous system
69
New cards
Increases activity of GI tract.
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
70
New cards
Can produce widespread sweating.
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
71
New cards
Release of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
72
New cards
Craniosacral division.
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
73
New cards
Vegetative functions.
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
A. Sympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
B. Parasympathetic
74
New cards
The vagus (X) nerve carries parasympathetic impulses to the
A. salivary glands.
B. lacrimal glands.
C. smooth muscle of the eyes.
D. thoracic and abdominal viscera.
A. salivary glands.
B. lacrimal glands.
C. smooth muscle of the eyes.
D. thoracic and abdominal viscera.
D. thoracic and abdominal viscera.
75
New cards
Short answer: It is final exam time. You need a B to keep your B+ in the class.
What physiologic changes, mediated by the autonomic nervous system, might you be exhibiting as you take the final exam?
What physiologic changes, mediated by the autonomic nervous system, might you be exhibiting as you take the final exam?
Increase in sympathetic activity resulting in increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, sweating, vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels causing the skin to be cold, increased metabolism, dilated bronchi, more glucose released into the blood, and a decrease in gastrointestinal activity.