Neuromuscular Junction
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is a neuromuscular junction?
A synapse between the membrane of the axon of a motor neurone and the sarcolemma of a muscle fibre
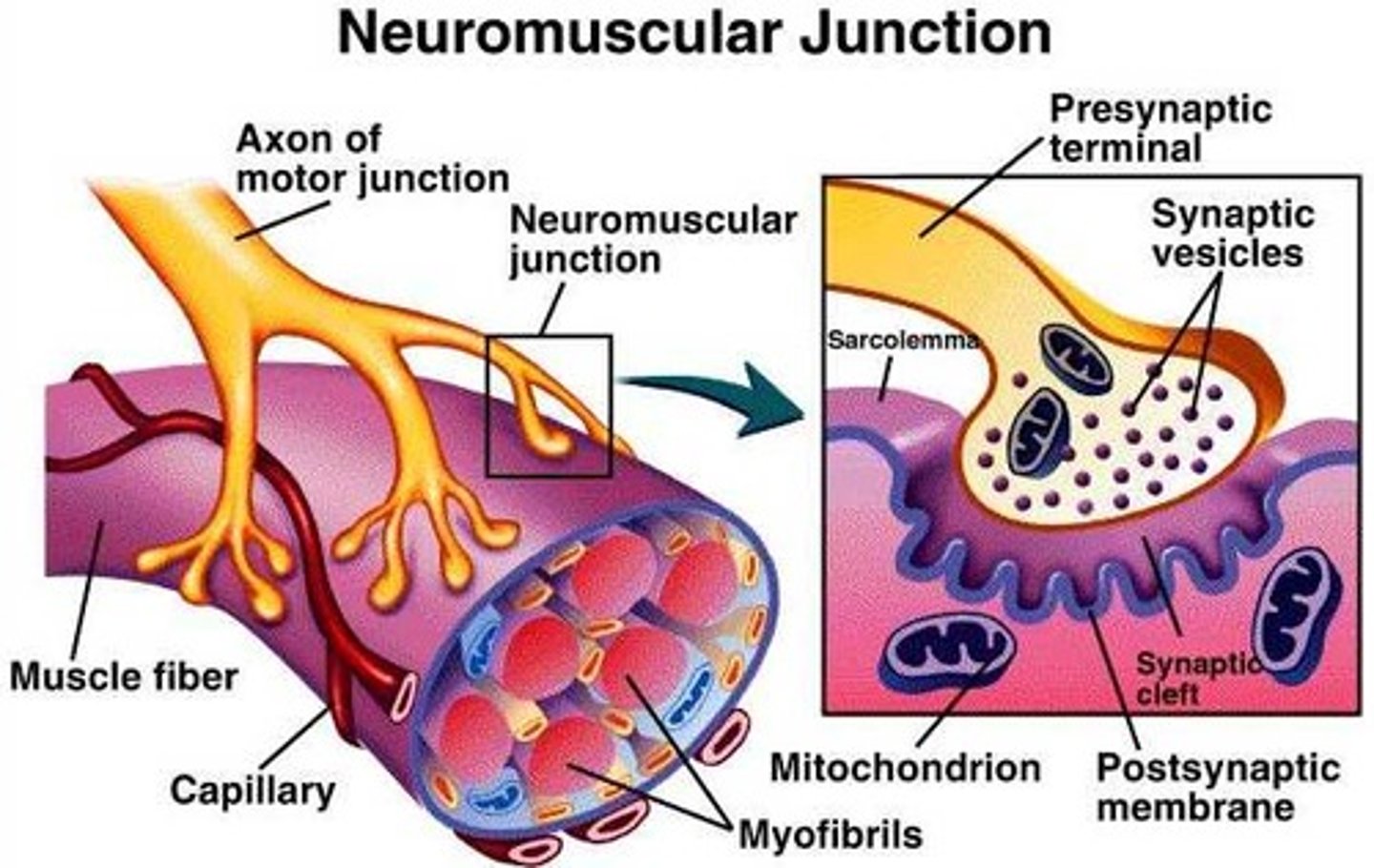
Motor end plate
The motor neurone axon divides into several branches so it can stimulate different muscle fibres
When is muscle contraction triggered?
When an action potential arrives at a neuromuscular junction
Why are there many neuromuscular junctions along the length of a muscle?
It ensures that all the muscle fibres contract simultaneously. If only one existed, then the muscle fibres would not contract together and the contraction would therefore not be as powerful.
What's a motor unit?
All the muscle fibres supplied by a single motor neurone are known as a motor unit.
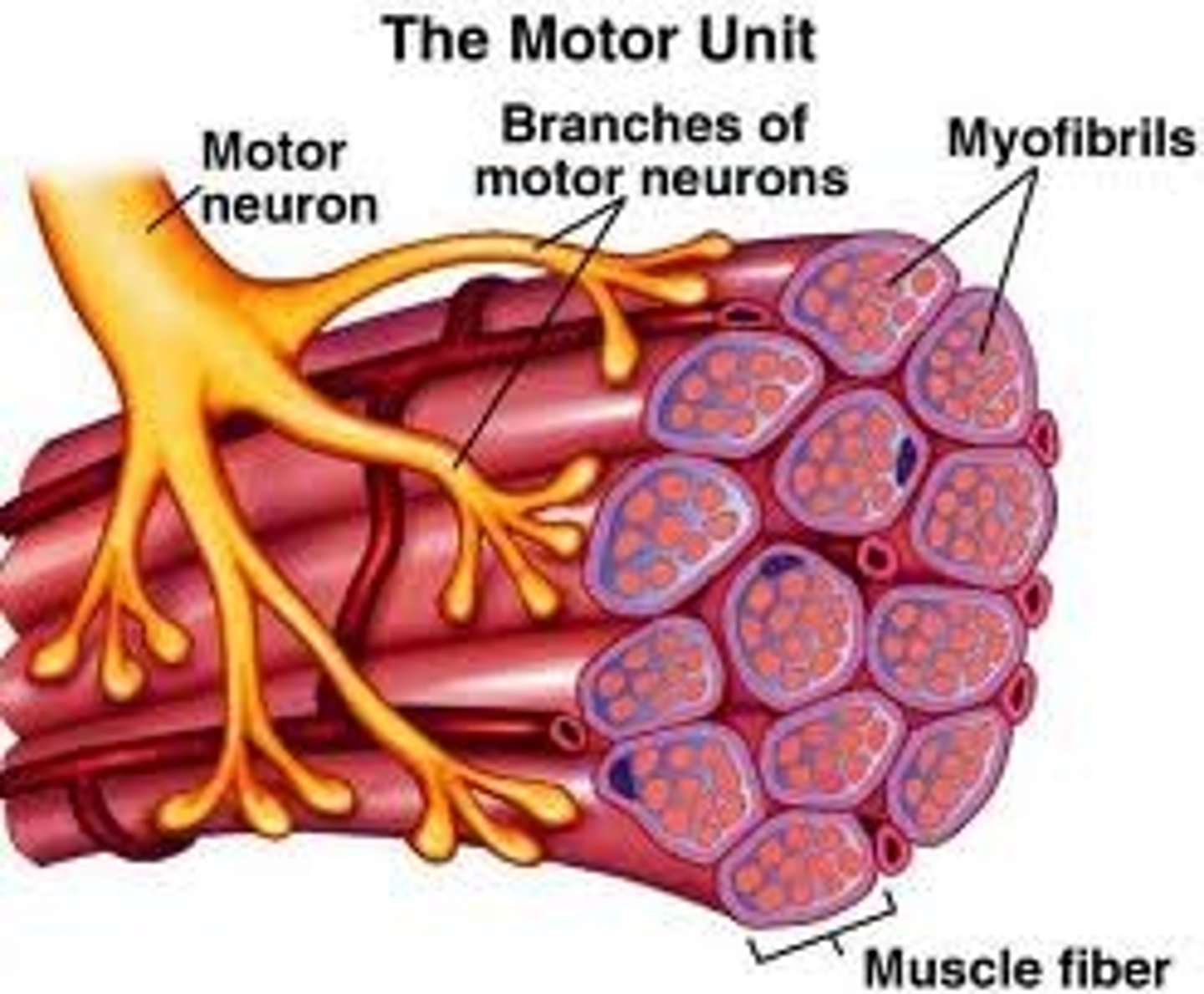
If a strong force is needed...
....a large number of motor units are stimulated
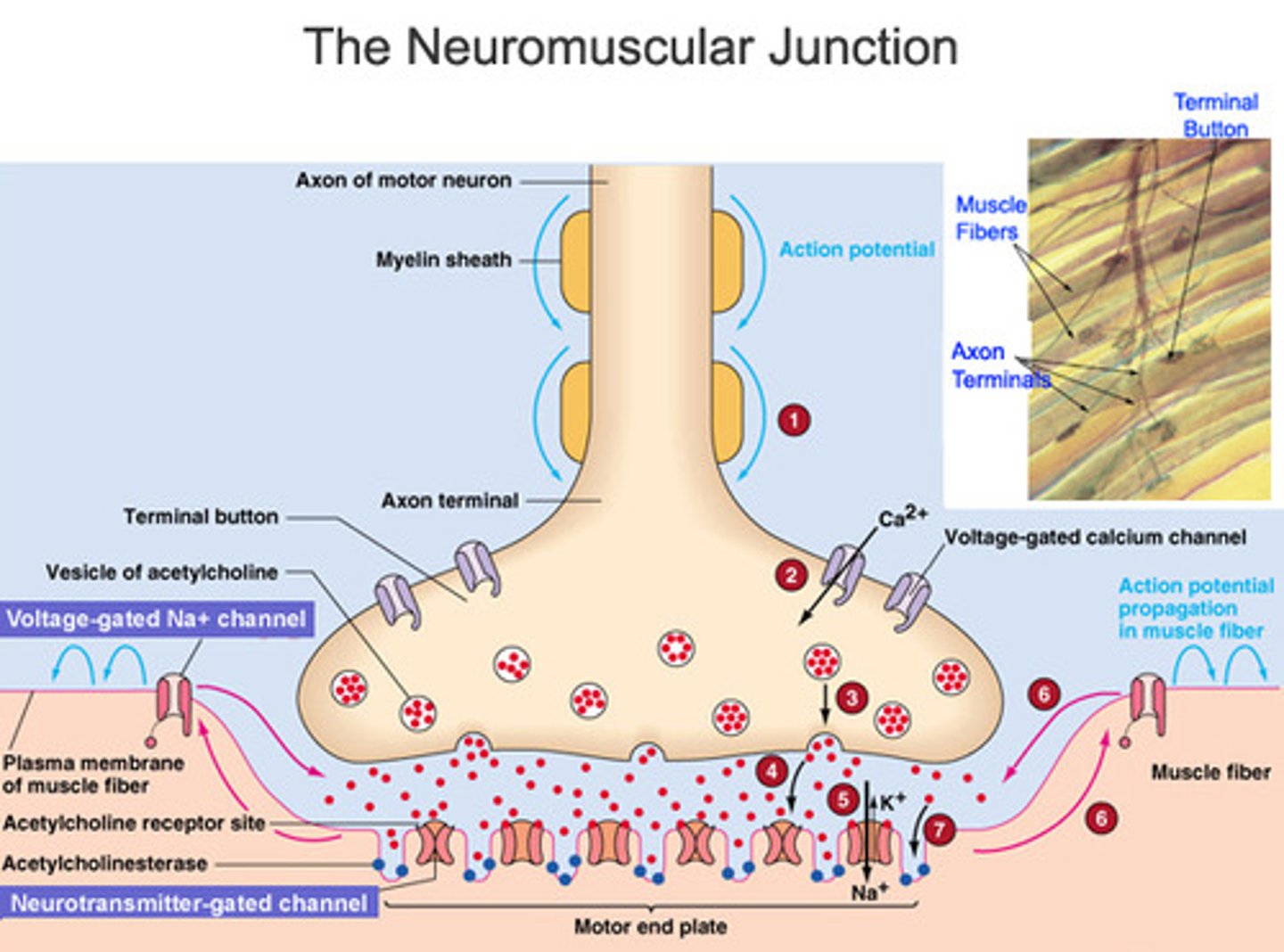
Neuromuscular Junction Action Potential Proccess:
An action potential reaches the neuromuscular junction, stimulating Ca2+ channels to open
Ca2+ diffuse from the synapse into the synaptic knob, where they cause synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane
Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis and diffuses across the synapse
It binds to the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane (sarcolemma), opening Na+ channels and resulting in depolarisation
Acetylcholine is then broken down by acetylcholinesterase, into choline and ethanoic acid.
This prevents the muscle being overstimulated.
Choline and ethanoic acid diffuse back into the neurone, where they are recombined into acetylcholine, using the energy from the mitochondria.
How does depolarisation travel into the muscle fibre?
Depolarisation spreads through the T-tubules.
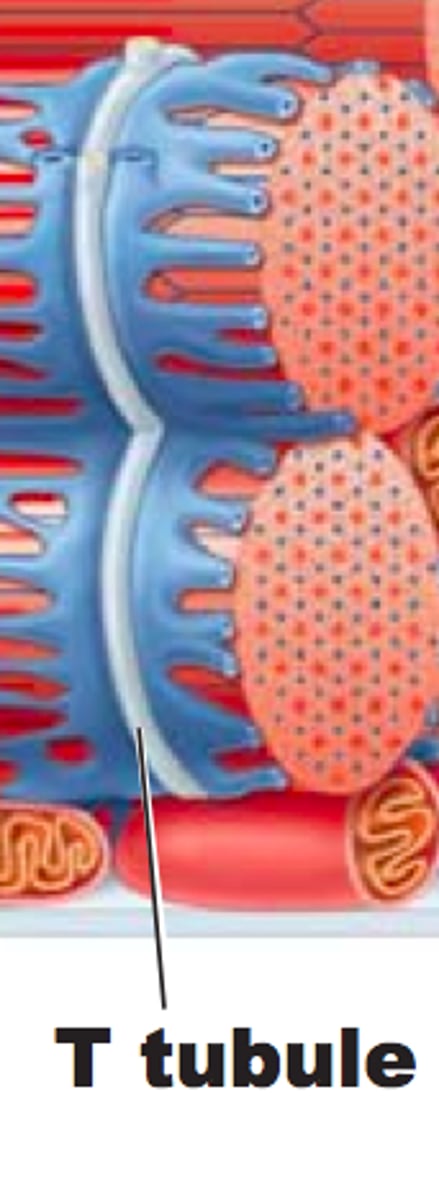
What is the relationship between T-tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
T-tubules are in contact with the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which contains Ca²⁺ ions.
What happens when the action potential reaches the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
The action potential stimulates Ca²⁺ channels to open, causing Ca²⁺ to diffuse into the sarcoplasm.
What do calcium ions do during muscle contraction?
Calcium ions bind to tropomyosin, causing it to change shape and move away from the actin-myosin binding sites, exposing them for myosin binding.
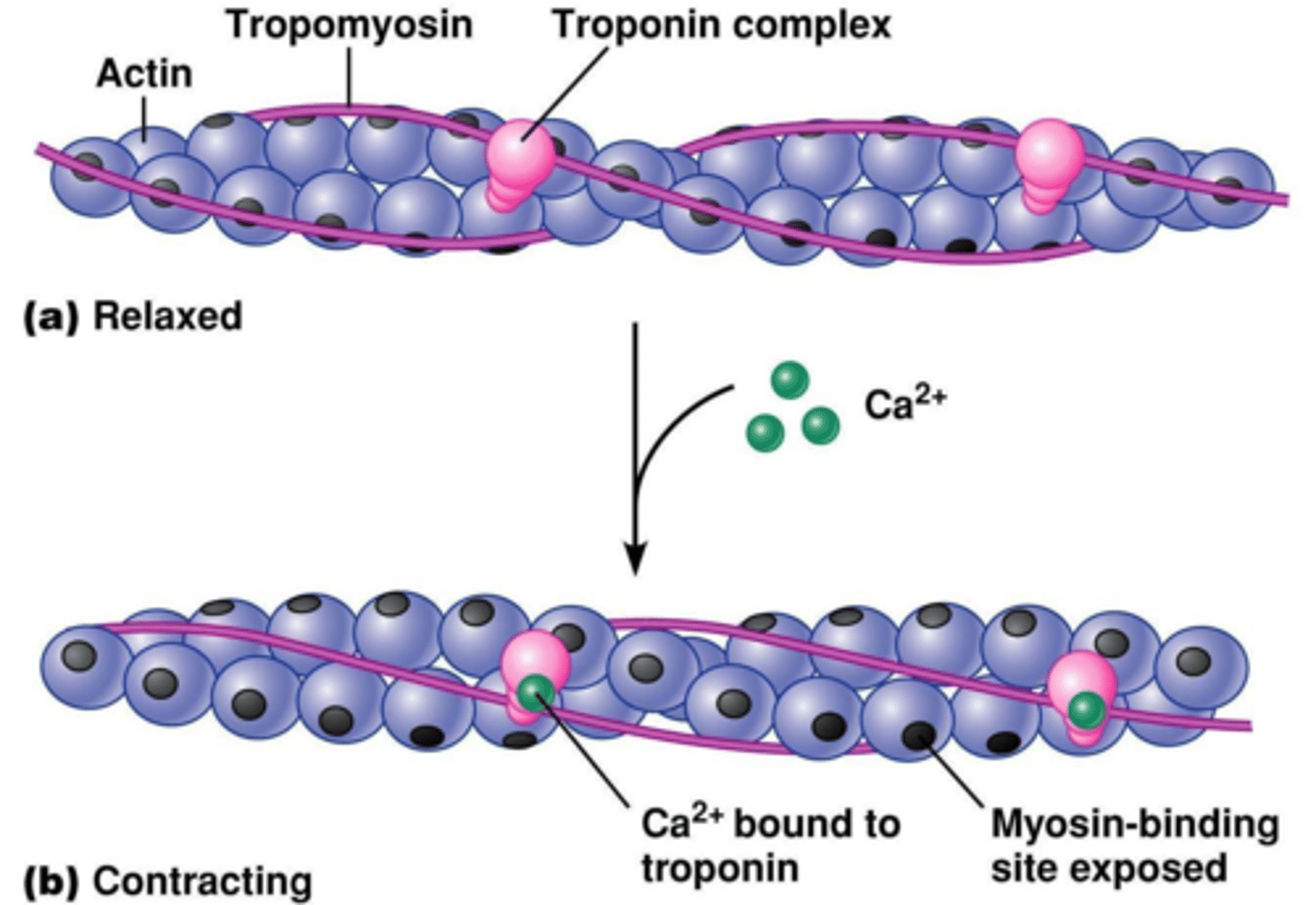
What happens when myosin binds to actin?
Myosin heads bind to the actin filament, forming cross-bridges, and then flex, pulling the actin filament along.
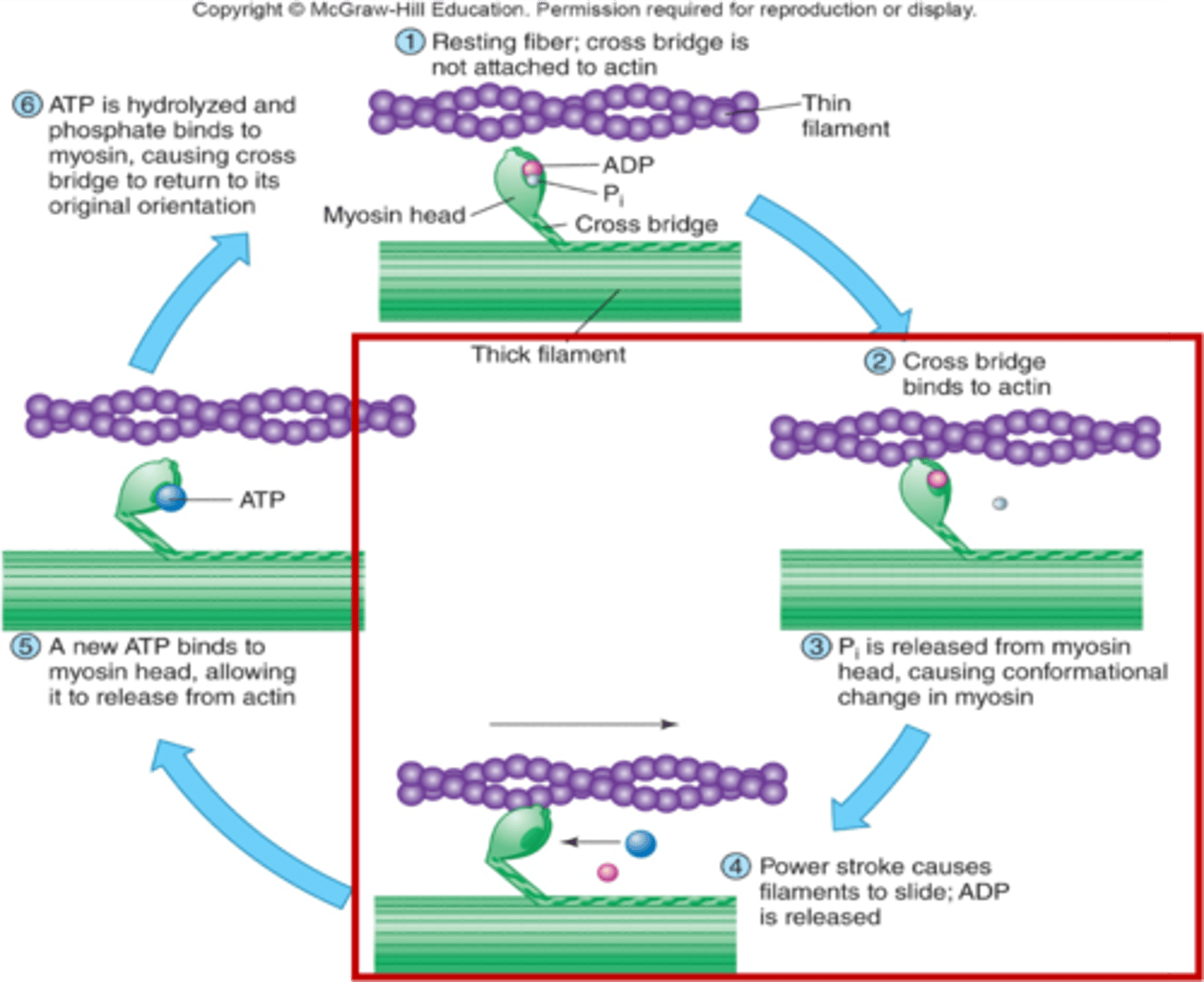
What happens after myosin heads flex?
ADP is released, and ATP binds to the myosin head, causing it to detach from the actin filament.
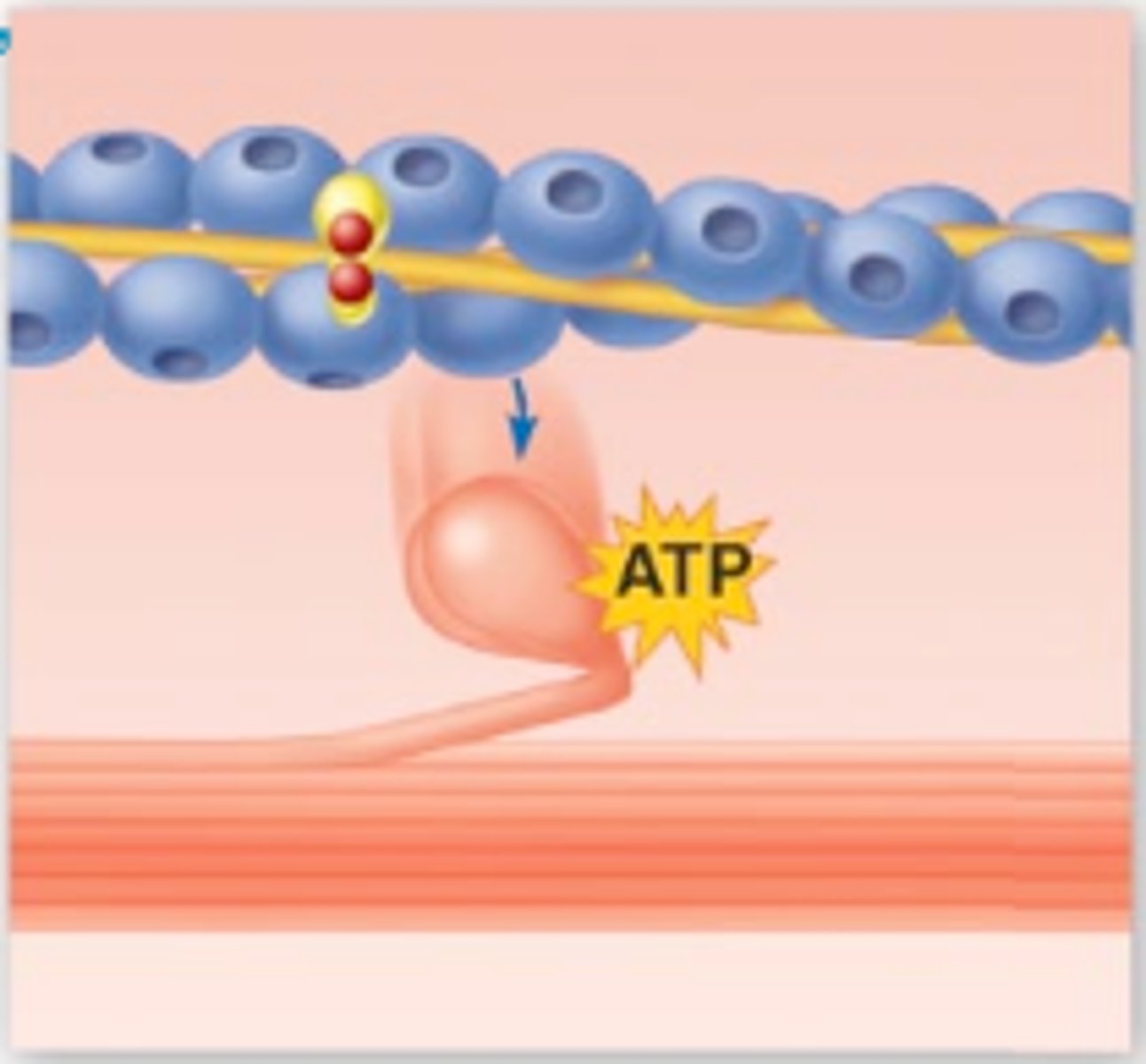
How does ATP impact the myosin head?
Calcium ions also activate the enzyme ATPase, which catalyses the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and Pi, releasing energy, allowing the myosin head to return to its original position.
What happens after the myosin head returns to its original position?
The myosin head attaches to a new actin-myosin binding site, and the cycle repeats.
What occurs during continued muscle stimulation?
The cycle of actin-myosin bridge formation and breaking continues, pulling the actin filament and shortening the sarcomere, causing muscle contraction.