ANS 1: ganglion
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sympathetic and parasympathetic, autonomic and somatic, receptors, NA synthesis, NA inhibition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are the 2 nervous systems
CNS: brain + spinal cord
PNS: Cranial nerves (12 pairs) + spinal nerves (31 pairs)
Draw an overview of the nervous system organisation
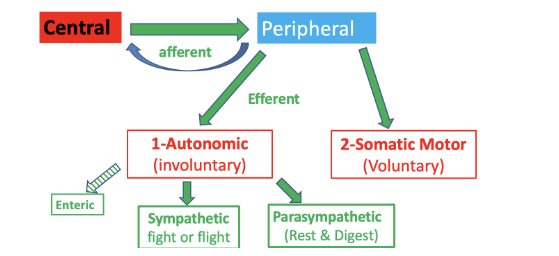
What is the function of the peripheral nervous system:
conveys signals between the CNS and the tissues
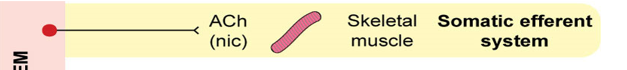
What neurotransmitter and receptor type are used in the somatic efferent system, and what is the target organ?
Acetylcholine (ACh) binds to nicotinic (nic) receptors on skeletal muscle.
What neurotransmitters and receptors are involved in the sympathetic response for blood vessels and other organs?
Acetylcholine (ACh) binds to nicotinic (nic) receptors at the ganglion, and norepinephrine (NA) is released at the target organs like blood vessels.
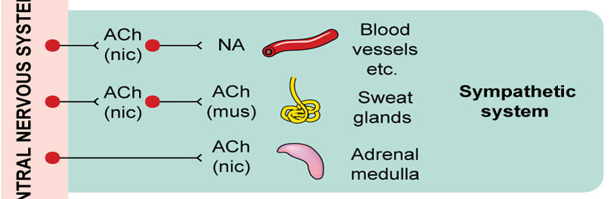
What neurotransmitters and receptors are involved in the sympathetic innervation of sweat glands?
Acetylcholine (ACh) binds to nicotinic (nic) receptors at the ganglion, and ACh binds to muscarinic (mus) receptors on the sweat glands.
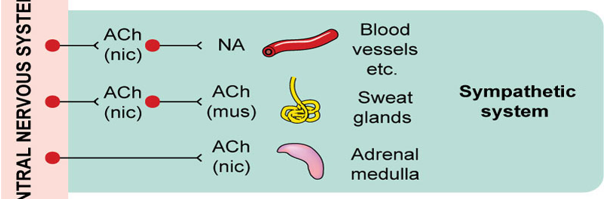
What neurotransmitter and receptor type are involved in the adrenal medulla's activation in the sympathetic system?
Acetylcholine (ACh) binds to nicotinic (nic) receptors on the adrenal medulla, which then releases epinephrine into the bloodstream.
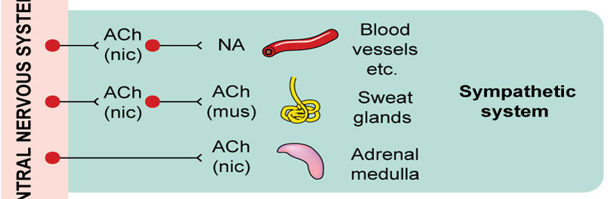
What neurotransmitters and receptors are involved in the parasympathetic system?
Acetylcholine (ACh) binds to nicotinic (nic) receptors at the ganglion, and ACh binds to muscarinic (mus) receptors on glands, smooth muscles, and the heart.

What is the autonomic nervous system
Automatic
subconscious control of organs and homeostasis
controls all outputs from CNS to the body except to skeletal muscle that is controlled by somatic efferent system
Give a brief overview of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
Consists of pre and post-ganglionic
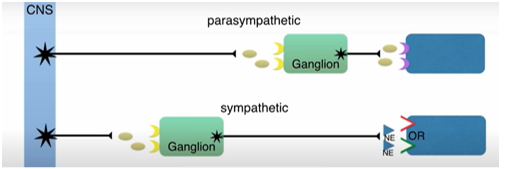
Describe Preganglionic Neuron
Cell body in CNS
Small diameter & myelinated
Synapses at autonomic ganglia
Releases ACh (acetylcholine)
ACh acts on nicotinic receptors on post synaptic neuron
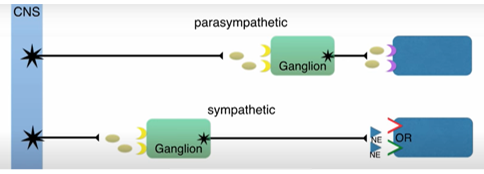
Describe Postganglionic Neuron
Cell body in autonomic ganglion
Small diameter & unmyelinated
Synapses close to target organ
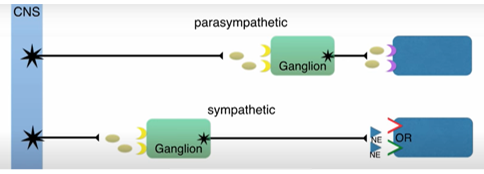
What is the exception with adrenal medulla
Adrenal medulla is the specialised ganglion and chromaffin cells are specialised post synaptic neuron
What is the autonomic ganglion, location, neurotransmitter, function
Location: between pre and post ganglionic neurons of ANS
Neurotransmitter: ACh
Function: Generates a fast Excitatory post synaptic potential via ganglionic nicotinic ACh receptors, conducts Na+ in and K+ out
Which organs are controlled by sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
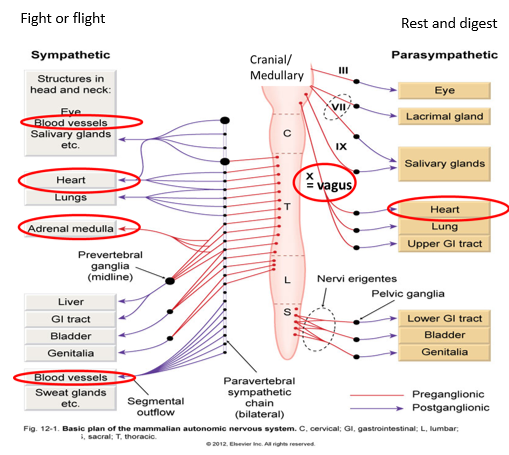
How does the ANS regulate the heart
controls heart rate
contracts + relaxes smooth muscle in blood vessels and organs
glandular secretion
metabolism
What happens when the ANS stimulates ganglionic nicotinic receptor
Activates sympathetic and parasympathetic post-synaptic nerve
Secretes adrenaline from adrenal medulla
Sympathetic responses dominate
tachycardia, increase in BP, increase in secretions
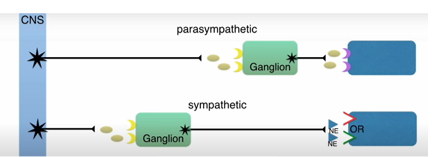
Name 2 ganglion blocking drugs, MOA and uses
Hexamethonium: binds to nic receptor, blocks ACh but doesn’t contract muscle, used to relax e.g. anti-hypertensives
Local anaesthetic: blocks pain receptors in SNS + given with adregenic receptors (regulate BP, HR) e.g. lidocaine
What are the key features of the sympathetic nervous system regarding transmitters at the target organ? e.g. what do post synaptic sympathetic fibres release, where is NA stored
Most postsynaptic sympathetic fibers release noradrenaline (NA). Cell bodies are located in sympathetic ganglia and send axons that end in varicosities, where noradrenaline is synthesized, stored, and released.
except sweat glands release ACh and Renal vessels release dopamine
What does the adrenal medulla release
It also releases adrenaline like a post synaptic nerve
Where does NA act and what is its effect
Receptors a1,a2,b1
effect: vasoconstriction, increased heart rate
How is Noradrenaline synthesised
L-tyrosine is the precursor
Converted by tyrosine hydroxylase into L-DOPA (rate-limiting step)
L-DOPA is decarboxylated by DOPA decarboxylase into dopamine
Dopamine is converted into noradrenaline by dopamine β-hydroxylase on the membrane of synaptic vesicles
In chromaffin cells, noradrenaline is converted to adrenaline by phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
How are neurotransmitters synthesised overall
Synthesis of enzymes in cell body
Slow axonal transport of enzymes
Synthesis and packaging of neurotransmitter at nerve terminal
Release and diffusion of neurotransmitter into synapse
Postganglionic fibers send axons to target organ
Enzymes for synthesis made in cell body, transported to the nerve terminus, where the transmitter is made at terminal varicosities
NA SYNTHESIS: How and what does Metirosine inhibit and what are the side effects
Metirosine inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase (1º enzyme) , inhibits NA
Useful for treating catecholamine (stress hormone) tumours
S/E: Headaches, heavy sweating, rapid HR, High BP
NA SYNTHESIS: How and what does Carbidopa
Inhibits DOPA decarboxylase (2º enzyme), prevents dopamine and NA
Used: Parkinson’s disease by blocking L-DOPA
Effects: reduces L-DOPA effects on periphery, reduces HR/BP
ADV: doesn’t cross BBB ↑Availability in CNS
How is noradrenaline release regulated (hint: Action potentials)
Ca2+ channels open due to depolarisation
Leads to vesicle exocytosis
NA released
activates presynaptic receptors that inhibit adenylyl cyclase
Prevents Ca2+ opening again, limits further release if NA
Termination of Noradrenergic Transmission - Uptake 1
Key Term: Neuronal Epinephrine Transporter (NET)
Location: Presynaptic nerve terminals
Function: Actively transports noradrenaline (NA) back into nerve varicosities
Recycling: Recycles ~70% of NA
Storage: NA taken up into vesicles by Vesicular Monoamine Transporter (VMAT)
Co-transmitter: ATP stored with NA, prevents leakage, co-released with NA
Termination of Noradrenergic Transmission - Uptake 2
Key Term: Extraneuronal Monoamine Transporter (EMT)
Location: Postsynaptic cell
Function: Actively transports catecholamines into the postsynaptic cell
Metabolism: Catecholamines metabolized by Catechol o-Methyl Transferase (COMT)
How else can NA transmission be terminated
Metabolism VIA:
Monoamine oxidase
Catechol-methyl transferase
How does methyldopa inhibit the release of NA
False precursor methyl NA
a2 agonist
inhibits DOPA decarboxylase
Effect: relaxes Blood vessels, treats HBP, preferred for pregnancy
How does Guanethidine inhibit the release of NA
Substrate for NET
Substrate for VMAT
Accumulates in vesicles
Stabilises vesicles
Displaces NA (slowly)
Free NA metabolised by MAO
High doses – destroys neuron
Overall effect: block of adrenergic neurons
Historically used as antihypertensive

How does reserpine inhibit the release of NA
-Inhibits VMAT
-Prevents transport of NA into vesicles
-NA metabolised by MAO
used as hypertensive
useful experimental tool
What are some unwanted effects of inhibiting NA synthesis/release
Hypotension
Bradycardia
Digestive disorders
Nasal congestion
Sexual dysfunction
Central effects common (i.e. not directly via autonomic system)
Sedation
Mood disturbances
Less with carbidopa - does not enter CNS
