Unit 4 Reproductive system
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the function of the reproductive system?
To produce, store, nourish, and transport gametes (sperm and eggs) and support the development of offspring in females.
What is meiosis? What are the steps?
A type of cell division that produces four genetically unique haploid cells from one diploid cell.
Steps:
Meiosis I (Reduction Division)::
Prophase I: Homologous chromosomes pair (tetrads), crossing over occurs
Metaphase I: Tetrads align at metaphase plate
Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate
Telophase I: Two haploid cells form (chromosomes still duplicated)
Meiosis II (Like Mitosis)::
Prophase II: Spindle forms in each haploid cell
Metaphase II: Chromosomes align at metaphase plate
Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate
Telophase II: Four unique haploid gametes result
Know these vocabulary terms: haploid, diploid, gametes, ovum, spermatozoa
Haploid (n): A cell with one set of chromosomes (23 in humans)
Diploid (2n): A cell with two sets of chromosomes (46 in humans)
Gametes: Reproductive cells (sperm and egg)
Ovum: Mature female gamete (egg)
Spermatozoa: Mature male gamete (sperm)
What is spermatogenesis? Where does it occur?
The production of sperm cells, occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
Know the difference between primary and secondary spermatocytes, and spermatids
Primary spermatocyte: Diploid, enters meiosis I
Secondary spermatocyte: Haploid, enters meiosis II
Spermatids: Result of meiosis II, immature sperm cells
What is oogenesis? Where does it occur?
The production of ova (eggs), occurs in the ovaries.
Describe the timing of the different steps of meiosis in the female.
Begins in fetal development → paused in prophase I
Resumes at puberty (monthly) → completes meiosis I just before ovulation
Meiosis II completed only if fertilization occurs
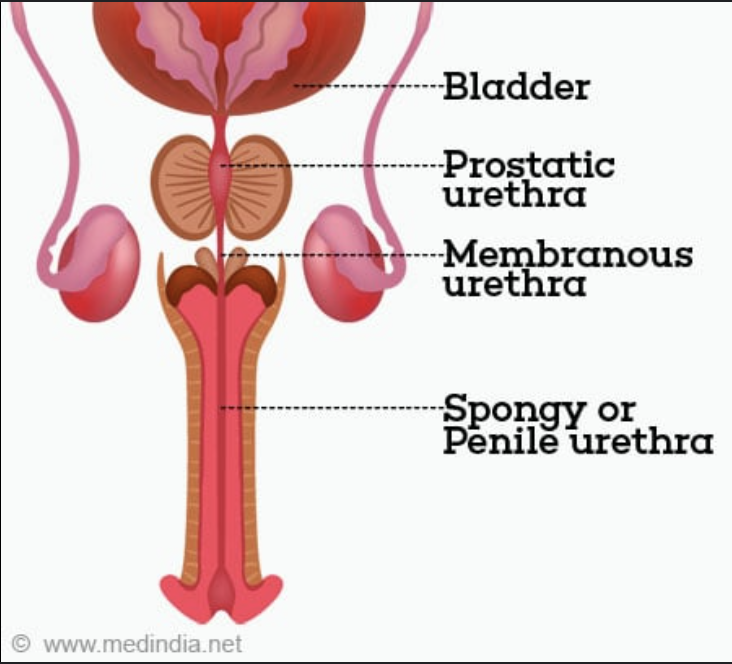
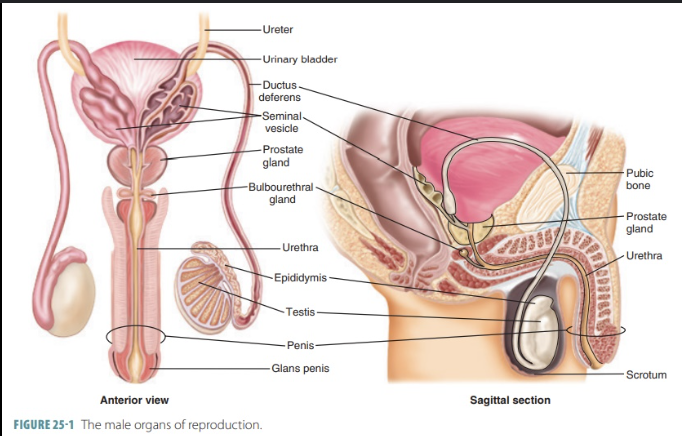
Male anatomy: Know these structures:
a. Testis
b. Epididymis (Head, body,
tail)
c. Scrotum
d. Ductus deferens
e. Prostatic urethra
f. Membranous urethra
g. Spongy urethra
h. Spermatic cord
i. Inguinal canal
j. Penis (Body, glans)
k. Cremaster muscle
l. Dartos muscle
(see gross anatomy flashcards for more photos)
a. Testis – sperm production
b. Epididymis – sperm maturation/storage (head, body, tail)
c. Scrotum – sac holding testes
d. Ductus deferens – transports sperm
e. Prostatic urethra – through prostate
f. Membranous urethra – shortest portion
g. Spongy urethra – in penis
h. Spermatic cord – contains vas deferens, vessels, nerves
i. Inguinal canal – passageway for spermatic cord
j. Penis (Body, Glans) – external organ for sperm delivery
k. Cremaster muscle – raises/lowers testes
l. Dartos muscle – wrinkles scrotal skin
What do the muscles of male anatomy do?
Cremaster muscle: Regulates testicular temperature by raising/lowering testes
Dartos muscle: Reduces surface area of scrotum to conserve heat
What is an inguinal hernia?
Occurs when intestines protrude through the inguinal canal
Know the pathway of the spermatozoa from the testes to exiting the body
Testes → Epididymis → Ductus deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Prostatic urethra → Membranous urethra → Spongy urethra → External urethral orifice
What are the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum?
Corpora cavernosa: Two dorsal erectile columns
Corpus spongiosum: Single ventral column, surrounds urethra and forms glans
What happens physiologically to cause erection?
Parasympathetic stimulation → nitric oxide release → vasodilation of erectile tissue → blood fills sinuses → erection
What is semen? Which glands contribute to its production? Which part of the nervous system controls this?
Mixture of sperm and glandular secretions
Contributing glands:
Seminal vesicles (fructose, prostaglandins)
Prostate gland (enzymes, PSA)
Bulbourethral glands (mucus)
Nervous control: Sympathetic division (ejaculation)
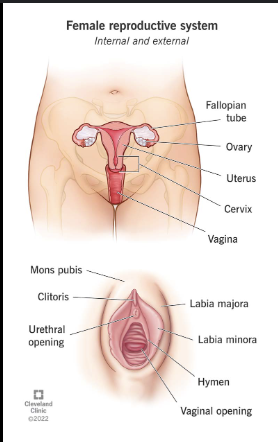
Female anatomy: Know these structures:
a. Ovary
b. Uterine tube (Fimbriae,
ampulla, isthmus)
c. Uterus (Fundus, body,
uterine cavity, isthmus,
internal and external os)
d. Cervix
e. Vagina
f. Clitoris
g. Labia majora
h. Labia minora
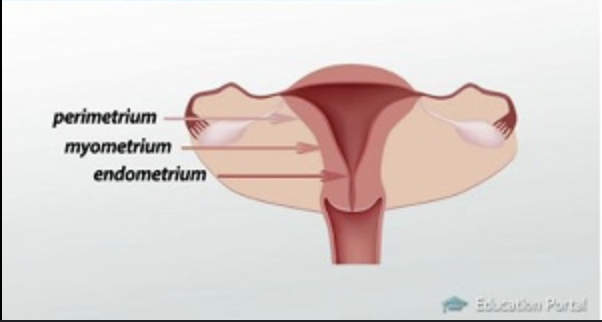
i. Perimetrium
j. Myometrium
k. Endometrium
l. Broad ligament of uterus
m. Round ligament of uterus
(see gross anatomy flashcards for more photos)
a. Ovary – produces ova and hormones
b. Uterine tube – transports egg
• Fimbriae: finger-like projections
• Ampulla: site of fertilization
• Isthmus: narrowest part
c. Uterus – supports embryo/fetus
• Fundus: upper dome
• Body: main portion
• Uterine cavity: central space
• Isthmus: between body and cervix
• Internal/external os: uterine openings
d. Cervix – connects uterus to vagina
e. Vagina – muscular canal to exterior
f. Clitoris – erectile tissue
g. Labia majora/minora – external folds
i. Perimetrium – outer serosa
j. Myometrium – muscular middle layer
k. Endometrium – inner lining (shed monthly)
l. Broad ligament – supports uterus
m. Round ligament – helps keep uterus in position
16. Ovulation structures::
a. Primary follicle – early egg + support cells
b. Secondary follicle – developing fluid-filled cavity
c. Tertiary follicle – mature Graafian follicle
d. Released secondary oocyte – ovulated egg
e. Corpus luteum – produces progesterone
f. Corpus albicans – scar tissue after luteum degenerates
Know these structures in ovulation:
a. Primary follicle
b. Secondary follicle
c. Tertiary follicle
d. Released secondary
oocyte
e. Corpus luteum
f. Corpus albicans
a. Primary follicle – early egg + support cells
b. Secondary follicle – developing fluid-filled cavity
c. Tertiary follicle – mature Graafian follicle
d. Released secondary oocyte – ovulated egg
e. Corpus luteum – produces progesterone
f. Corpus albicans – scar tissue after luteum degenerates
What happens to the endometrium during the ovarian cycle?
Proliferative phase: builds up (estrogen)
Secretory phase: thickens (progesterone)
Menstrual phase: sheds if no pregnancy
What kind of epithelium lines the vagina?
Stratified squamous epithelium
What causes female sexual arousal?
Parasympathetic nervous system increases blood flow to clitoris and vaginal secretions
What is fertilization? Where does it usually happen?
Fusion of sperm and egg, usually in the ampulla of uterine tube
How do the spermatozoa get to the site of fertilization?
Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Uterine tube (ampulla)
What are mammary glands? What do they do?
Modified sweat glands that produce milk after childbirth
Know these structures of the breast:
a. Lactiferous duct
b. Suspensory ligament
c. Areola
d. Nipple
a. Lactiferous duct – carries milk to nipple
b. Suspensory ligament – supports breast tissue
c. Areola – pigmented skin around nipple
d. Nipple – outlet for milk
Describe the basics of the endocrine function of the reproductive system
Testes: produce testosterone (spermatogenesis, male traits)
Ovaries: produce estrogen and progesterone (oogenesis, female traits, cycle regulation)
Hormonal control by hypothalamus (GnRH) → pituitary (FSH, LH)