PSYC 1F90 Textbook
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Self-determination theory
We are motivated by competence (desire to experience mastery over our environment), autonomy (desire to control our own lives), and relatedness (desire to be connected to other people).
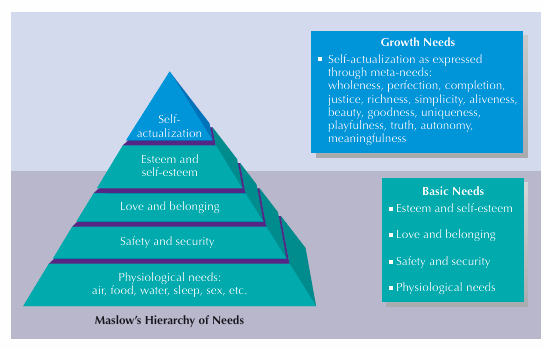
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Basic needs are more dominant, and are at the bottom of pyramid. Growth needs/self-actualization at the top. If basic needs are met, we move on to actualizing our potential.
Sex drive
Non-homeostatic. In men is related to the amount of androgen provided by the testes. In women is related to estrogen levels.
Circadian rhythm
24 hour biological clock that impacts body temperature, blood pressure, amino acid levels.
Pain
Occurs in distinct episodes (episodic) when bodily damage occurs
Extracellular thirst
Water is lost from the fluids surrounding cells
Intracellular thirst
Fluid is drawn out of cells due to an increased salt concentration
Hunger
Hypothalamus receives neural signals from the tongue and digestive system. The lateral hypothalamus acts as a feeding start button. Ventromedial hypothalamus acts as a stop button. Paraventricular nucleus keeps blood sugar levels steady by starting and stopping eating.
Long term weight control
Brain maintains a set point by keeping track of the amount of fat in fat cells. These cells release leptin which tells your brain that you are full.
Dieting (Fad Diets)
Slows metabolism, increases amount of calories conserved and stored as fat
Behavioural Diets
Changing exercise and eating habits rather than self starvation
Anorexia Nervosa
Fear of gaining weight, disturbance in body image, purging behaviour
Bulimia Nervosa
Binge eating, purging behaviour, excessive exercise, fasting
Experience (emotion)
We know how to label emotional feelings
Physiology (emotion)
Sympathetic branch activates body for emergency. Parasympathetic branch calms the body.
Expression (emotion)
Facial, touch, posture, voice. Can be regulated through situation selection, situation modification, redirecting attention, cognitive reappraisal (changing your interpretation), and response modulation (controlling outward signs of emotion)
Cognitions (emotion)
Appraisals (evaluating the personal meaning of a situation), and attributions (explanations about why things happen).
James-Lange Theory
We are first physiologically aroused and express our behaviour’s (smile), then the subjective experience follows (happy feeling)
Cannon-Bard Theory
Physiological arousal and emotional experience occur at the same time.
Schachter and Singer Two Factor Theory
First: emotions come when we experience general physiological arousal
Second: Use cognitive processes to label its cause
Basic Emotion Theories
An emotion is a brief state that arises after cognitive appraisals of an event, involves broadly distinct expressions, physiology, and behaviour.
Ekman’s BET
There are 6 emotions: surprise, happiness, sadness, anger, disgust, and fear. Emotions are unlearned, common across all cultures, and expressed in early childhood.
Alfred Adler
We are social creatures governed by urges, not biological instincts. We strive for superiority that stems from feelings of inferiority
Karen Horney
Failure to strike a balance between moving towards other, moving away from others, and moving against others.
Carl Jung
A persona or mask exists between the ego and the outside world, and this is what is presented to others.
Humanistic theory of learning
Human nature is inherently good, and we are not just a bundle of moldable responses.
Central and secondary traits
Central traits are the core traits that characterize individual personality (honest, cheerful, intelligent) and secondary traits are traits that are inconsistent or superficial (food preferences, political opinions)
Source Traits
Basic underlying traits of personality.
Big Five
Extroversion: How introverted or extroverted someone is
Agreeableness: How friendly, nurturant, and caring a person is as opposed to cold and self-centered
Conscientious: Self-disciplined, responsible
Neuroticism: Negative, upsetting emotions
Openness to experience: Creative and open to new ideas
HEXACO
Honesty/humility: Truthful, honest, sincere
Causes of Mental Illness
Factor: |
| Summary/Description of its Role in Psychopathology: |
Biological | Organic | Tumors or hormonal influences. |
| Environmental | Head injuries sustained during accidents, or exposure to toxic chemicals or drugs. Can cause intellectual disability, hallucinations, delusions, and loss of emotional control. |
| Genetic | For example, studies say that there are 128 gene variations associated with schizophrenia. Genes also play a role in neurodevelopmental (Down syndrome, due to nervous system damage) and neurocognitive disorders (Parkinson's disease, mental impairments in old age caused by deterioration of the brain). Alzheimer's disease causes victims to slowly lose the ability to work, cook, drive, read, write, or do arithmetic. Related to unusual webs and tangles in the brain that damage areas important for memory and learning. |
Psychosocial | Psychological | Stress, psychological trauma, learning disorders, and a lack of knowledge, control, or mastery. |
| Social | Poverty, stressful living conditions, homelessness, social disorganization, and overcrowding. |
Types of delusions
Type of Delusion: | Summary: |
Erotomanic | Erotic delusions that they are loved by another person, especially by someone famous or of higher status. |
Grandiose | Delusions that they have some great, unrecognized talent, knowledge, or insight. Might also believe that they have a special relationship with an important person or God, or that they are a famous person. |
Jealous | Having an all-consuming, but unfounded, belief that your spouse or lover is unfaithful. |
Persecutory* | Belief that you are being conspired against, cheated, spied on, followed, poisoned, maligned, or harassed. |
Somatic | Believe that their bodies are diseased or rotting, infested with insects or parasites, or that parts of their bodies are defective. |
Schizophrenia symptoms
Symptom: | Description: |
Disturbed thinking | Selective attention - it is hard to focus on one item of information at a time. Paranoid delusions of grandeur and persecution. |
Disturbed perception | Hallucinations such as hearing voices, insects crawling under their skin, taste poison in their food, smell gas that their 'enemies' are using to get them. Sensory changes such as numbness, extreme sensitivity to head, cold, pain or touch. They may think that someone is controlling their minds, which might cause violence. |
Disturbed emotions | Emotions might be inappropriate to the situation, or display no emotion at all. |
Disturbed behavior | Withdrawal from contact with others, apathy, loss of interest in external activities, a breakdown of personal habits, and an inability to deal with daily events. Catatonia - remaining mute while holding odd postures for hours or days. |
Schizophrenia causes
Cause: | Description of Risk Factors/Causes: |
Prenatal | Women exposed to the influenza virus or to rubella during the middle of pregnancy have children who are more likely to become schizophrenic. Malnutrition and complications at birth might also have this impact. |
Psychosocial | Exposed to psychological trauma such as sexual abuse, death, divorce, separation, or other stresses in childhood. |
Genetics | Can inherit the potential to develop schizophrenia, making them more vulnerable to the disorder. |
Brain Functioning | Brains of people with schizophrenia are shrunk, or atrophied, activity tend to be low in the frontal lobes, and tend to have enlarged ventricles. |
Depressive disorders
Type of Depressive Disorder: | Description/Summary: |
Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia) | Mildly depressed for at least 2 years. |
Major Depressive Disorder | Much deeper depression. Everything looks bleak and hopeless. Failure, worthlessness, and total despair. |
Seasonal Affect Disorder (Major Depressive Disorder with Seasonal Pattern) | Depression that occurs only during fall and winter, presumably related to decreased exposure to the sun. |
Bipolar disorders
Type of Bipolar Disorder: | Description/Summary: |
Cyclothymic Disorder | A long-lasting but relatively moderate alternation between depression and mania. |
Bipolar I Disorder | Experience both extreme mania and deep depression. |
Bipolar II Disorder | The person is mostly sad and guilt-ridden but has had one or more mildly manic episodes. |
Anxiety disorders
Type of Anxiety Disorder: |
| Description/Summary: |
Generalized Anxiety Disorder |
| Nearly constant exaggerated worries for at least six months. Typically complain of sweating, a racing heart, clammy hands, dizziness, upset stomach, rapid breathing, irritability, and poor concentration. |
Panic Disorder |
| Highly anxious and feel sudden, intense, unexpected panic. During panic attacks, victims experience chest pain, a racing heart, dizziness, choking, feelings of unreality, trembling, or fears of losing control. |
Phobias | Agoraphobia | Excessive, irrational fear of being in public places. Fear that something extremely threatening will happen in public. |
| Social Anxiety Disorder | People fear situations in which they can be scrutinized evaluated or humiliated by others. |
| Specific Phobia | Persons fear, anxiety, and avoidance are focused on specific objects, activites, or situations. |
Theoretical perspectives on anxiety disorders
Theoretical Perspective: | Description/Summary: |
Psychodynamic | Internal motives, conflicts, unconscious forces, and other dynamics of mental life. Disturbances like those we have described represent a raging conflict among subparts of the personality - the id, ego, and superego. |
Humanistic | Emphasize subjective experience, human problems, and personal potentials. Anxious individuals have built up unrealistic mental images of themselves. |
Behavioral | Emphasize overt, observable behaviour and effects of learning and conditioning. Behaviorists assume that the symptoms of anxiety disorders are learned, just as other behaviours are learned. |
Cognitive | Distorted thinking causes people to magnify ordinary threats and failures, leading to anxiety and distress. |
Anxiety related disorders
Type of Anxiety-Related Disorder: |
| Description/Summary: |
Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders |
| Extreme preoccupations with certain thoughts and compulsive performance of certain behaviours. People with OCD are preoccupied daily with distressing, repetitive thoughts and urgers to perform certain rituals. |
Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders |
| Behaviour patterns that are associated with high levels of fear or anxiety brought on by experiencing traumatic stress. An adjustment disorder occurs when ordinary stresses push people beyond their ability to cope with life. |
Dissociative Disorders |
| Experience a disintegration of consciousness, memory, or self-identity. Temporary amnesia, or multiple personalities. |
Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders | Somatic Symptom Disorder | Typically display some combination of the following: interpreting normal bodily sensations as proof that they have a terrible disease; expressing their anxieties through various bodily complaints; and experiencing disabling pain that has no identifiable physical basis. |
| Factitious Disorder | Can be either imposed on self if the person fakes his or her own medical problems, or imposed on another if person fakes the medical problems of someone in his or her care. |
| Conversion Disorder | Severe emotional conflicts are converted into symptoms that actually disturb physical functioning or closely resemble a physical disability. |
Aversion therapy
Treatment to reduce unwanted behaviour by pairing it with an unpleasant stimulus
Types of exposure therapy
Type of Exposure Therapy: | Summary/Description: |
Flooding | Repeatedly exposing people to the object or circumstances that concern them, either in real life or in their imagination. |
Systematic Desensitization | Much slower and guided reduction in fear that is attained by gradually approaching a feared stimulus while maintaining relaxation. |
Modeling | The problem is handled by having clients observe models, including the therapist, who are performing the feared behaviour. |
Humanistic therapies
Type of Humanistic Therapy: | Summary/Description: |
Client-Centered | Individual being treated talks without direction, judgement, or interpretation from the therapist. |
Existential | An insight therapy that focuses on the elemental problems of existence, such as death, meaning, choice, and responsibility, emphasizes making courageous life choices. |
Gestalt | An approach that focuses on immediate experience and awareness to help clients rebuild thinking, feeling, and acting into connected wholes; emphasizes the integration of fragmented experiences. |
Brain Stimulation Therapies
Therapy: | Summary/Description: |
ECT | Treatment for severe depression in which electrical current is applied to the brain, cause a seizure. |
DBS | Electrical stimulation of precisely targeted brain regions; a surgical procedure is necessary to implant electrodes in the brain that allow for the stimulation. |
TMS | A device that uses magnetic pulses to temporarily block activity in specific parts of the brain. |
Psychosurgery
Type of Surgery: | Summary/Description: |
Lobotomy | The frontal lobes are surgically disconnected from other brain areas, which was supposed to calm persons who didn’t respond to other types of treatment. Produced many negative side effects. |
Deep Lesioning | Small target areas are destroyed in the brain's interior. Cannot be reversed. |
Cognitive dissonance
There is a need for consistency in our thoughts, so we experience discomfort when our attitudes contradict one another
Situation: | Summary/Description: |
Being forced to choose between two opinions | When you choose to believe something, the other option becomes less appealing and you alter your opinions to make your choice better. |
Disconnect between the cognitive and behavioural aspects of attitudes | What we believe vs. what we do. (ex. We know that exercising is good for us, however many people still do not do it). |
Social influence, social facilitation, and social interference
Social influence is changes in behaviour caused by the actions of other people.
Social facilitation is the improvement of performance.
Social interference is the impairment of performance.
Mere presence
The tendency for people to change their behaviour because there are other people nearby
Social loafing
The tendency for people to exert less effort when they are in a group setting than they do when they are working individually
Self-assertion vs. aggression
Self-assertion involves standing up for your right to refuse, to request, and to right a wrong by speaking out on your own behalf. Aggression involves hurting another person or achieving one’s goals at the expense of another.
Types of love
Type of Love: | Summary/Description: |
Romantic | Based on intimacy and high levels of passion. |
Companionate | Intimacy and commitment. Common among couples who have been together a long time. |
Fatuous | Passion and commitment. |
Consummate | Intimacy, passion, and commitment. |
Adult attachment
Type of Adult Attachment: | Summary/Description: |
Secure | Caring, intimacy, supportiveness, and understanding. |
Avoidant | Fear of intimacy, tendency to resist commitment to others, skeptical about love, find it hard to trust and depend on others. |
Ambivalent | Mixed feelings about love and friendship. Regard themselves as misunderstood and unappreciated. Worry that their partners don’t really love them or might leave them. |
Prosocial behaviour
Any behaviour that has a positive impact on other people.
Motive: | Summary/Description: |
Evolutionary Forces | The chances of survival increased when individuals lived in groups. |
Self-Oriented | Celebrities donating to help their public image, for example. |
Other-Oriented | Wanting to improve the living conditions of immigrant families and having nothing to gain from it, for example. |
Organizational culture vs organizational citizenship
Organizational culture refers to the blend of customs, beliefs, values, attitudes, and rituals that give each organization its unique "flavor". Organizational citizenship is making positive contributions to the success of an organization in ways that go beyond one's job description.