325
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
1
New cards
igneous rocks
formed by cooling from a melt. crystal structure
2
New cards
sedimetary rocks
formed from erosion of existing rocks. weaker than igneous
3
New cards
metamorphic rocks
formed by application of intense heat and pressure. stronger than sedimentary
4
New cards
fine particles
5
New cards
coarse particles
>5mm
6
New cards
max agg size
the smallest SEIVE opening
7
New cards
Nominal agg size
smallest seive size that majority of sample passes through
8
New cards
__ is preferred for workability of conc
rounded agg
9
New cards
___ is preferred in mechanical properties of portland cement
angular
10
New cards
OD (oven dry)
all moisture is removed
11
New cards
AD (AIR DRY)
all moisture is removed from surface but not from pores
pores are partially full
pores are partially full
12
New cards
SSD (saturated surface dry)
all aggregate pores are full but surface is dry
13
New cards
wet or moist
agg pores are completely filled and there is a film of water on the surface of particles
14
New cards
surface/free water
moisture in excess in SSD state
15
New cards
specific gravity
ratio of agg mass to mass of an equal vol of water
16
New cards
what does strength and toughness depend on
bonding between the grains
porosity of particles
porosity of particles
17
New cards
what is freeze thaw
when water is in agg pores and freezes and expands
* will create fractures in agg
* causes popout in portland cement
* causes cracking in concrete
* will create fractures in agg
* causes popout in portland cement
* causes cracking in concrete
18
New cards
what is a deletrious substance
organic impurities that delay setting and reduce strength of portland cement
19
New cards
Alkali silica reaction
silica in aggregates react with alkali hydroxides in concrete
* causes excessive expansion in cement paste
* causes excessive expansion in cement paste
20
New cards
C3S properties
early strength gain
50-70% mass
50-70% mass
21
New cards
C2S
late strength gain
15-30% mass
15-30% mass
22
New cards
C3A
flash set
5-10% mass
generates heat in early hydration
5-10% mass
generates heat in early hydration
23
New cards
C4AF
flash set
give concrete its colour
1-10%
give concrete its colour
1-10%
24
New cards
flash set
rapid development of ridgitity with considerable heat evolution
25
New cards
false set
rapid development of ridgitiy without heat
26
New cards
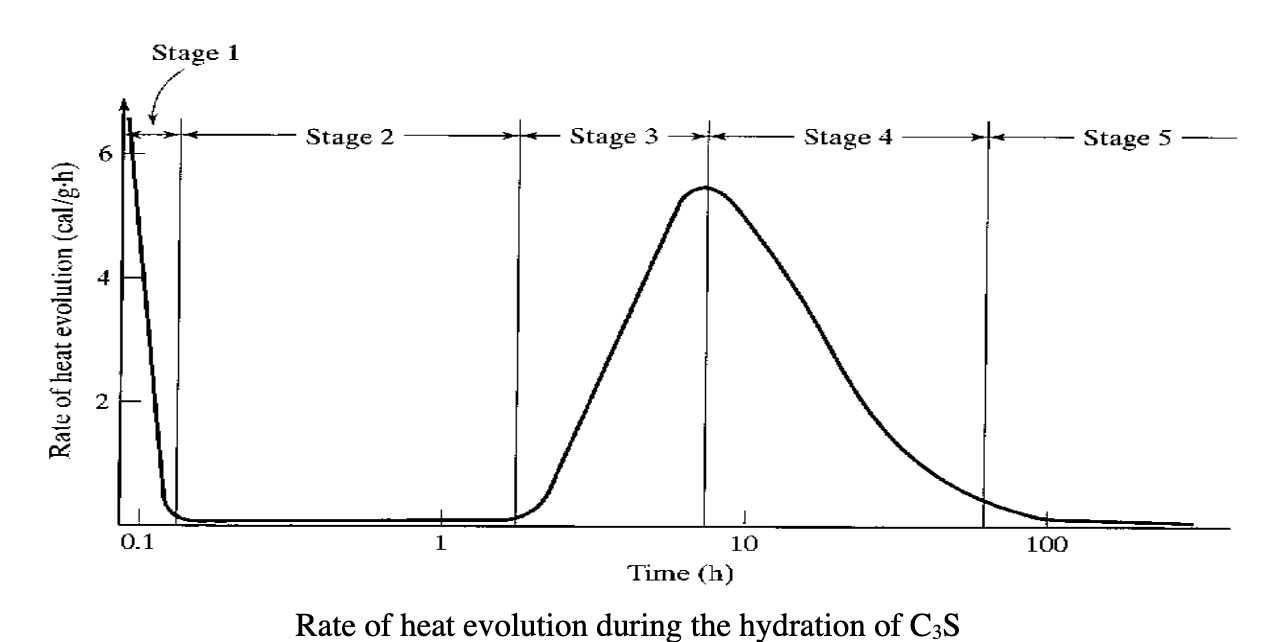
name all of the stages
stage 1: Rapid heat evolution
stage 2: period of realitive inactivity
stage 3:initial set (2-4 hrs)
stage 4: reaction slows down
stage 5: steady state (18-36 hrs)
stage 2: period of realitive inactivity
stage 3:initial set (2-4 hrs)
stage 4: reaction slows down
stage 5: steady state (18-36 hrs)
27
New cards
rate comp strength of c3s, c2s, c3a, c4af
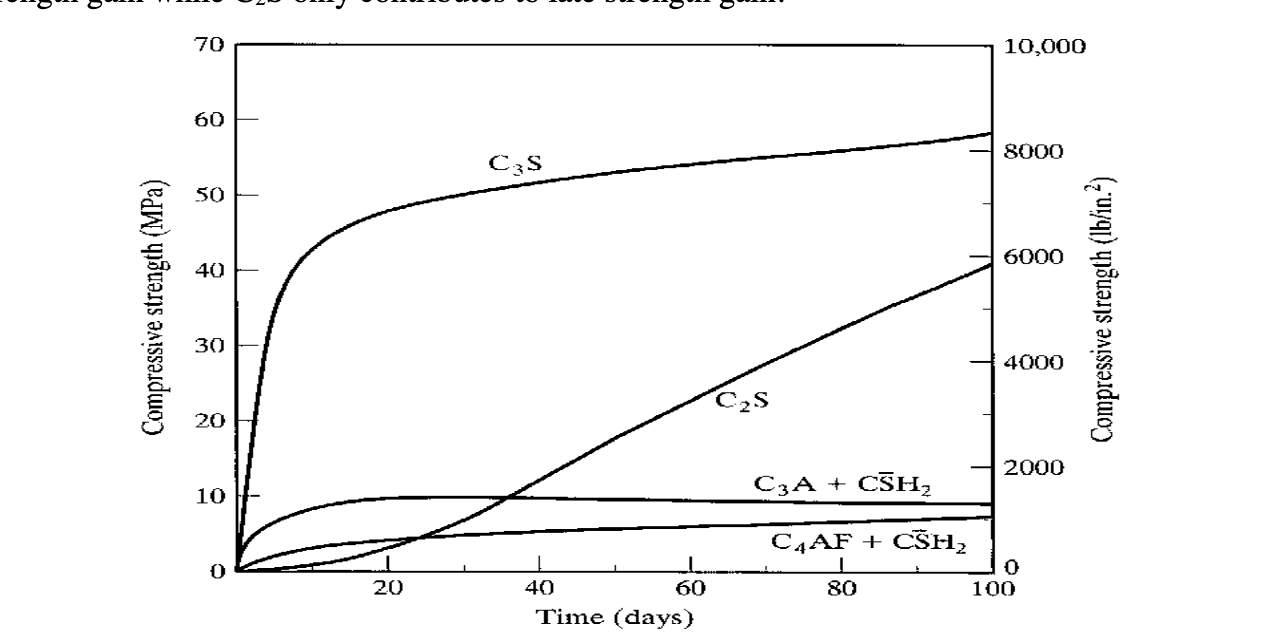
28
New cards
types of portland cement
GU
HE
MS
HS
MH
LH
HE
MS
HS
MH
LH
29
New cards
GU - general use
no specific requirements
30
New cards
HS - High early strength concrete
reduced c2s
increased c3s
used in cold weather
increased c3s
used in cold weather
31
New cards
MS - moderate sulphate resistence
reduced c3a (5-8%)
normal structures exposed to soil or ground water
low w/cm ratio
normal structures exposed to soil or ground water
low w/cm ratio
32
New cards
HS - High sulphate resistence
reduced c3a (
33
New cards
MH - moderate heat of hydration
reduced c3a (5-8%)
generates less heat than GU
hydrates slower than GU
for structures of considerable mass
good for warm weather
generates less heat than GU
hydrates slower than GU
for structures of considerable mass
good for warm weather
34
New cards
LH - low heat of hydration
reduced c3s
increased c2s
develops strength slower
for massive structures
increased c2s
develops strength slower
for massive structures
35
New cards
what is concrete composed of
coarse agg
cementing material
water
sand
admixtures
cementing material
water
sand
admixtures
36
New cards
conc advantages
* can be cast into any shape
* can use local materials (low cost)
* very durable
* fire resistant
* efficient to produce
* can use local materials (low cost)
* very durable
* fire resistant
* efficient to produce
37
New cards
limitations of conc
* brittle material
* low strength to weight ratio
* irriversible shrinkage
* low strength to weight ratio
* irriversible shrinkage
38
New cards
workabilitu factors
* concrete consistency
* water content
* aggregate size, texture, grading
* uniform distribution of agg
fresh con should be plastic and semi fluid
* water content
* aggregate size, texture, grading
* uniform distribution of agg
fresh con should be plastic and semi fluid
39
New cards
what is consolodation
vibrate fresh concrete to make sure there arent any bugholes
moves around particles to avoid friction and increase mobility
\
moves around particles to avoid friction and increase mobility
\
40
New cards
what is air entrained concrete
has small air bubbles to resist freeze thaw damage and improve workability and durability
\
\*lowers compressive strength
\
\*lowers compressive strength
41
New cards
stress strain graph of highstrngth concrete
has sharper peaks and sudden failiure characteristics
42
New cards
types of concrete voids in hardened concrete
* entrapped voids
* macro cracks
* entrained voids
* microcracks
* transition zone
* capillary voids
* macro cracks
* entrained voids
* microcracks
* transition zone
* capillary voids
43
New cards
entrapped voids
rock pockets
honeycomb
voids pf incomplete consolidation
honeycomb
voids pf incomplete consolidation
44
New cards
macro cracks
visible cracks
* structural
* thermal
* plastic damage
* drying shrinkage
severe effect on concrete durability
* structural
* thermal
* plastic damage
* drying shrinkage
severe effect on concrete durability
45
New cards
entrained voids
reduces strength significantly
intentional for freeze thaw
intentional for freeze thaw
46
New cards
micro cracks
naturally occur around aggregates from restraint shrinkage
as load increases, microcracks increase
influence durability and strength
as load increases, microcracks increase
influence durability and strength
47
New cards
transition zone
weak and porus around aggregates
influence durability and strength
influence durability and strength
48
New cards
capillary voids
residue from water filled spaces
significantly reduces strength
significantly reduces strength
49
New cards
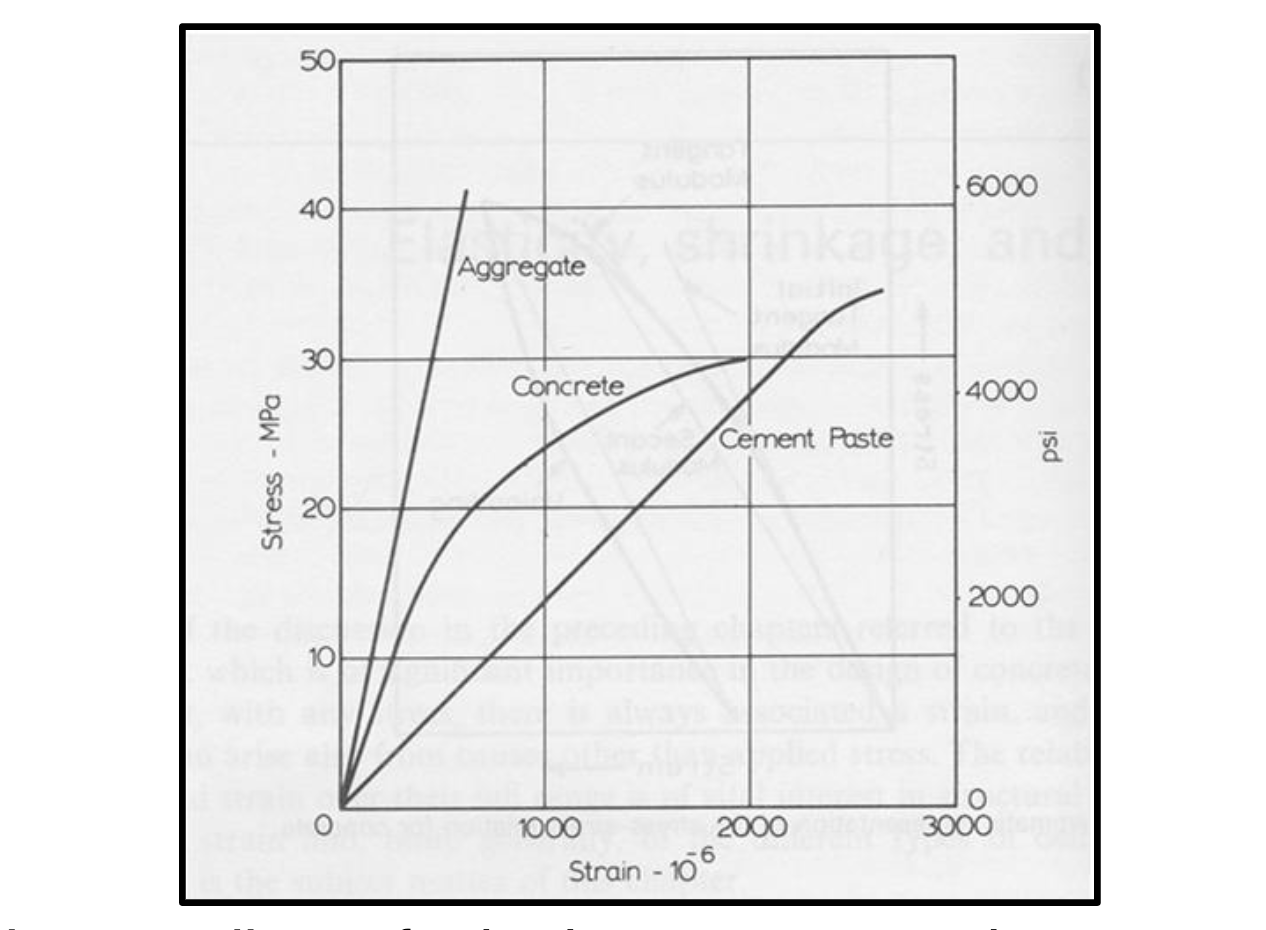
why is stress strain curve of concrete not linear
because it is a composite material of agg and cement paste
if cement paste and agg have similar strength and modulus of elasticity, the conc one will be more linear
if cement paste and agg have similar strength and modulus of elasticity, the conc one will be more linear
50
New cards
what is maturity index
strength of conc depends on time and temp
samples with same maturity index have equal strength
samples with same maturity index have equal strength
51
New cards
how to prevent bugholes in concrete
reduce amount of sand in mix
thoughroughy internally vibrate
thoughroughy internally vibrate
52
New cards
how to prevent consolodation
reduce amount of coarse particles
or
increase sand
insert at 600mm intervals and vibrate
or
increase sand
insert at 600mm intervals and vibrate
53
New cards
concrete curing methods to MAINTAIN mixing water
* ponding
* spraying
* wet coverings
* spraying
* wet coverings
54
New cards
concrete curing methods to PREVENT LOSS mixing water
* impervious paper
* plastic sheets
* membrane forming compounds
* plastic sheets
* membrane forming compounds
55
New cards
types of shrinkage
plastic shrinkage
drying shrinkage
drying shrinkage
56
New cards
what is plastic shrinkage
when conc looses moisture
may cause cracking
may cause cracking
57
New cards
drying shrinkage
when conc is not properly cured
development of cracks
development of cracks
58
New cards
how to prevent shrinkage
use proper curing
low water cement ratio
low cement content and high agg content
low water cement ratio
low cement content and high agg content
59
New cards
what is creep
gradual increase in strain over time
sustained load over a long period of time
affects stress reinforcement and increases deflection
sustained load over a long period of time
affects stress reinforcement and increases deflection
60
New cards
types of asphalt pavement
flexible
ridgid
ridgid
61
New cards
types of asphalt
asphalt cement
asphalt binder
asphalt cutback
asphalt binder
asphalt cutback
62
New cards
asphalt cement
excellent adhesion characteristics
blend of carbohydrates
semisolid material
blend of carbohydrates
semisolid material
63
New cards
asphalt emulsiion
produced by dispersing asphalt cement in water
60-70% A Cement
30-40% water
60-70% A Cement
30-40% water
64
New cards
asphalt cutback
produced by dissolving A cement in hydrocarbin solvent
65
New cards
asphalt binder acts as a newtonian fluid when…
Temp > Tg (140 C)
66
New cards
asphalt binder acts as a viscoelastic solid when…
Temp < Tg
67
New cards
asphalt binder acts as a very brittle matrial when…
very low temp
68
New cards
physical properties of asphalt
aging
viscosity
stiffness
tensile properties
viscosity
stiffness
tensile properties
69
New cards
aging of A cement
caused by going through a wide range of temps
asphalt becomes less ductile and hardens
volitization of hydrocarbons
oxidization
asphalt becomes less ductile and hardens
volitization of hydrocarbons
oxidization
70
New cards
viscocity of asphalt cement
if temp goes up, viscosity goes down
low viscosity = rutting and bleeding
high viscoisty = thermal cracking
low viscosity = rutting and bleeding
high viscoisty = thermal cracking
71
New cards
stiffness of asphalt
low temp and short duration = elastic behavior
high temp long duration = depends on viscosity
high temp long duration = depends on viscosity
72
New cards
draw out asphaplt denisty distribution
73
New cards
VTM
voids in total mix
total vol of small pockets of air btwn COATED agg particles
total vol of small pockets of air btwn COATED agg particles
74
New cards
VMA
voinds in mineral agg
voids between agg particles
voids between agg particles
75
New cards
VFA
voids filled with asphalt
portion of voids in agg that is filled with binder
portion of voids in agg that is filled with binder
76
New cards
advantages of wood
aesthetic
adequate strength:weight
cost effective
renewable resource
minimum pollution
adequate strength:weight
cost effective
renewable resource
minimum pollution
77
New cards
disadvantages of wood
fire
bacteria
insects
imperfections
bacteria
insects
imperfections
78
New cards
endogenous trees
intertwined growth
strong and lightweight
not used for eng projects
strong and lightweight
not used for eng projects
79
New cards
exogenous
outward growth
conncentric rings
eng applications
conncentric rings
eng applications
80
New cards
what are the orthogonal directions of wood
draw them
draw them
longitudinal
radial
tangential
radial
tangential
81
New cards
what is fibre saturation point
point at which cell walls are compleetly saturated but the cavities are empty
\
no free water
only bound water
\
when MC 25-30%
\
no free water
only bound water
\
when MC 25-30%
82
New cards
compressive strength paralell to wood grain
good
wood cells act as tiny colums
wood cells act as tiny colums
83
New cards
compressive strength perpendicular to wood grain
increases with deformation
\
max comp @ decrese thickness by 1/3
\
max comp @ decrese thickness by 1/3
84
New cards
tensile strength parallell to wood grain
strong
85
New cards
felxural strength of wood
very strong in bending
failiure in compression side
failiure in compression side
86
New cards
types of wood defects
knots
checks
shakes
wanes
warp
checks
shakes
wanes
warp
87
New cards
what are the most important design parameters
strength and ductility
88
New cards
when we increase carbon content in steel, what happens
strength increase
hardness increase
ductility decrease
toughness decrease
hardness increase
ductility decrease
toughness decrease
89
New cards
what is ductility
ability of a member to undergo large deformations without fracture
90
New cards
advantages of steel
linear service bahavior
high strength
high E
high ductility
simialr tension and comp behavior
high strength
high E
high ductility
simialr tension and comp behavior
91
New cards
disadvantages of steel
buckling
continous maintences
fireproofing cost
\
continous maintences
fireproofing cost
\
92
New cards
steel production - blast furnace
reduces ore to iron
93
New cards
steel production - oxygen furnace
removes excess carbon
94
New cards
what is allyoing
adding carbon into structure of iron atoms
95
New cards
what is work/strain hardening - cold rolling
passing metal through roller
increases yeild and tensile strength
compresses structure
increases yeild and tensile strength
compresses structure
96
New cards
what is work/strain hardening - strain aging
loaded sample to strain hardening range and leave at room temp
97
New cards
what is heat treatment of steel
reheating and cooling metal to reorganize microstructure
98
New cards
cooling metal slowly does..
more ductile metal
ferrite and pearlite at equilibrium arrangement
ferrite and pearlite at equilibrium arrangement
99
New cards
cooling metal fast does..
more britttle and harder
forms marntensite
forms marntensite
100
New cards
advantages of FRP
duracble
will not corrode'
low thermal conductivty
versatile
will not corrode'
low thermal conductivty
versatile