Building Utilities Finals
1/229
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MODULE 4-7: Electronics, HVAC Systems and Equipment, HVAC Plan Reading and Symbols + MODULE 8: Vertical Transportation System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
Perimeter protection
first level of protection for any security system
doors and windows
CCTV system
alarm contacts
Tyoes of Perimeter Protection
Plunger Type
Magnetic Types
Fiber Optic Type
Electric Type
Watchman’s Tour Equipment
Interior protection
provides backup to perimeter protection
Types of Interior Protection
Infrared Motion Detectors
Glass Break Detectors
Floor Mat Detectors
Merchandise Anti-Theft
Electronic Access Control System
used by large companies
used to control employee entrance by identifying an authorized individual
improves employee productivity by preventing unrestricted traffic
tracks and recalls employee movement
Types of Electronic Access Control System
Electronic cardkey
Keypass
Face/Photo Identification
Biometric Identification
CCTV acronym meaning
closed-circuit television
CCTV (Closed-circuit television)
referred to as video surveillance or security TV
a system of video feeds that are transmitted within a closed system from various security cameras
Components of a CCTV
Surveillance cameras
Monitor
Digital Video Recorder (DVR)
Telecommunication
the transmission, emission, or reception of signs, signals writing, images, sounds, or information of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic systems.
uses electricity, light (visible and infrared), or radio waves
how do telecommunication systems function?
when a transmitter converts sound waves or data into signals, which travels along wires or through the air before reaching their destination.
when the receiver intercepts the signals, they are converted back into useful data or sound waves that become distinguishable by the human ear and recognized by the brain.
Transceiver
a device that functions as a transmitter and receiver
Types of transmission formats
Analog transmission
Digital transmission
Analog Transmission
the conversion of sound or data into electrical impulses
Digital Transmission
the transmission of a signal that varies in voltage to represent one of two separate states (e.g. on and off or 0 and 1)
Telecommunication network
a collection of communication equipment and devices that are interconnected so they can communicate in order to share data, hardware, and software or perform an electronic function.
Nodes
a series of connecting points in a network
Common Types of Telecommunication Topologies
Bus Topology
Star Topology
Ring Topology
Tree Topology
Bus Topology
connects each node (workstation) to a single cable trunk.
All signals are broadcasted to all workstations; each computer checks the address matches; and the computer processes the
signal.
If the address does not match, the computer takes no
action and the signal travels down the bus to the next compute.
Star Topology
All nodes in a star typology are connected to a central unit called hub.
Home runs are cables that extend from the hub to the terminal without splicing or other connections.
Hub
central unit in a star topology where all nodes are connected
Homeruns
cables that extend from the hub to the terminal wihtout splicing or other conenctions in a star topology
Ring Topology
connects workstation equipment and devices in a point-to-point serial manner in an unbroken circular configuration
Tree Topology
compirses groups of nodes, usually a star topology, with each hub of a star topology branching out from a main hub
Types of Spatial Networks
Personal Area Network (PAN)
Local Area Network (LAN)
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Wide area Network (WAN) / Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN)
Personal Area Network
a network that enables communication between a computer and
devices near a person.
can be wired, such as USB or wireless, such as Bluetooth.
Local Area Network
used in buildings to connect computers and hardware such as printers located relatively close together and sharing resources, equipment, and files.
Types of LANs include Ethernet, ARCnet, and Token Ring, each
having their own method of transmitting data.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
a network that has coverage larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN
Wide area Network (WAN)
a computer network in which the computers connected may be far apart, generally having a radius of half a mile or more
Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN)
through wireless communication that can span across a country or across different countries
Types of Transmission Media
Open wires
Multi-pair cables
Transmission cables
T1 Cable
Optical Fibers
Single Mode Fibers
Multimode Fibers
Open wires
bare copper onductors attached to glass insulators on crossarms of utility poles
PROS: excellent voice transmission, carries signals farther and with less interference or distortion
CONS: wires had to be kept a foot apart so that they wouldn’t clash together in the wind
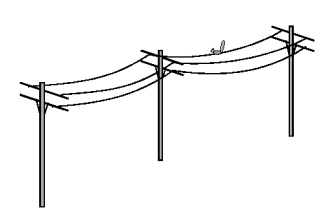
Multi-pair cables
squeezed more wires into a smaller space via insulation (without shorting out against one another)

Main cables are made with up to —— pairs of conductors (——- separate wires)
4 200 pairs of conductors
8 400 separate wires
Types of Transmission Cables
Twisted Pair Cable (TP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Screen Shielded Twisted Pair (SSTP) / Screen Foiled Twisted Pair (SSFP)
Coaxial Cable (COAX)
Thin Coaxial Cable (Thinnet)
Thick Coaxial Cable (Thicknet)
Twin Axial Cable (Twinax)
Triax Cable
Twisted Pair Cable (TP)
consists of pairs of copper wires that are twisted to certain specifications
each pair is twisted with a specified number of twists per inch

Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
consists of multiple pairs of twisted insulated copper conductors bound in a single sheath
unshielded from electromagnetic waves (sensitive to electrical interference)
used for basic voice, fax or data

AWG 22
used for telephone and UTP wire
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
has an outer covering or shield that is added to the ordinary twisted pair that functions as a ground
suitable where electrical interference occurs
the extra shielding makes the cable bulky

Screen Shielded Twisted Pair (SSTP) / Screen Foiled Twisted Pair (SSFP)
eliminates crosstalk (ideal networking cable)
the twisting of the pairs and number of turns per unit length increases RF shielding and protects from crosstalk

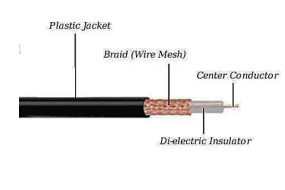
Coaxial Cable (COAX)
have 2 conductors: an inner solid wire surrounded by an outer braided metal sheath
conductors both run concentrically along the same axis (thus the name: coaxial)

Thin Coaxial Cable (Thinnet)
8 mm in diameter and is very flexible
looks like a regular TV cable
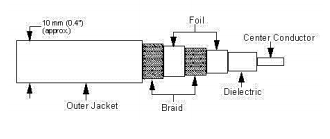
Thick Coaxial Cable (Thicknet)
has an extra protective plastic cover that helps keep moisture away from the center conductor
good for running longer lenghts in linear network
does not bend easily and is difficult to install
Twin Axial Cable (Twinax)
2 center conductors at the center surrounded by an insulating paper
usually braid, foil, or both
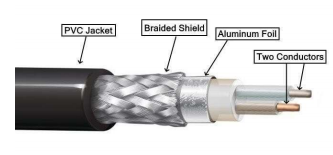
Triax cable
type of coax cable with an additional outer copper braid
insulated from signal carrying conductors
has a core and 2 concentric conductive shields
T1 cable
powerful phone and internet line
acts as a tube to funnel information at a fast rate
24 channels
always an active line between two places

Optical Fibers
log thin strand of very pure silicon glass or plastic (about the diameter of human hair)
typically consists of 2 strands: sending and receiving

Types of optical fiber connectors
Straight tip (ST) - common
Subscriber connector (SC) - common
Local connector (LC)
Ferrule connector (FC
Straight tip (ST) - optical fiber connector
common

Subscriber connector (SC) - optical fiber connector
common

Local connector (LC) - optical fiber connector

Ferrule Connector (FC) - optical fiber connector

Single mode fibers
used to transmit one signal per fiber
used in telephone and cable TV
Multimode fibers
used to transmit many signals per fiber
used in computer networks, LANs
Wireless Transmission
term used to describe telecommunications in which electromagnetic waves, instead of wires, carry the signal
microwave, geosynchrono satellite, low-earth orbit satellite, cellular, personal communication service (PCS)
Types of Wireless Network
Peer-to-Peer
Access Point / Base Station
WLAN (Wi-fi)
Fixed Wireless Internet
Peer-to-Peer (wireless network)
P2P
consists of computers equipped with a wireless networking interface card
e.g. printers
Access Point / Base Station (wireless network)
has a computer or receiver that serves as the point at which the network is accessed
WLAN (Wi-fi)
provide internet access using wireless network devices
Fixed wireless internet
uses RF or IR to provide WAN or MAW services
Internet
global system of interconnected computer networks
uses Transmission Control Protocol or Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Types of Internet service
Dial-up
DSL
Cable
Satellite
Fixed wireless internet
Fiber internet
Internet Hardware
Modem
Router
Wi-Fi Booster / Repeater / Extender
Modem
primary piece of internet hardware setup
type of internet access determines the type of modem
Router
hardware device that allows connection of several computers and other devices to a single internet connection (home network)
with the use of ethernet cables
many modems alr include a built-in router
Wi-Fi booster / repeater / extender
used to extend the coverage area of a Wi-Fi network
receives existing Wi-Fi signal, amplifies it, and then transmits the boosted signal
Telephone
device that converts sound and electrical waves into audible relays and is used of communication
two parts: microphone and speaker
Types of Telephone Service Systems
Plain Old Telephone Services (POTS)
Multi Line Phone System (For business)
Key System Unit Phone System
Private Branch Exchange / Private Automatic Branch Exchange
Intercom System
IP Telephony (IPT) / Voice Over IP (VoIP) or Internet Telephony
Plain Old Telephone Services (POTS)
analog telephone service
Multi Line Phone System
improve office communications and productivity
Key System Unit Phone System
has the capacity for multiple lines and multiple telephones
Private Branch Exchange / Private Automatic Branch Exchange
PBX
connects the telephones within a company to one another
also connects them to the public switched telephone network (PSTN)
Intercom System
one or more master stations (administrative) and several remote stations (staff)
IP Telephony / Voice Over IP (VoIP) / Internet Telephony
deals with the digital side of telecommunication through internet protocol (Voice over IP)
Heating, Ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system
mechanical system designed to satisfy the environmental conditions within an air-conditioned space in or for a building
Fundamentals / Modes of Heat Transfer
Conduction
Convection (natural, forced)
Radiation (ultraviolet, visible light, infrared)
Conduction
movement of heat through a substance or between two substances in contact with each other
most efficient mode of heat transfer
Convection
heat transfer by the motion of a heated or cooled mass
transfer of heat between a surface and a moving fluid (gas or liquid)
Natural Convection
free convection
when the warm fluid rises and the cold fluid falls due to buoyancy
Forced Convection
tends to cool the object much faster by means of mechanical intervention
more efficient
Radiation heat transfer
involves movement of energy by electromatic waves
does not require a molecular medium for a transfer to occur
Ultraviolet radiation (UV)
short-wavelength radiative energy
not visible to the human eye
rays that product sunburn and degrades plastics
Visible Light radiation
middle wavelengths
human eye can perceive this
Infrared radiation
long wavelengths of thermal radiation
Transmission Heat Loss
heat passing through materials in a building envelope or through an assembly of materials
Transmission Heat Loss terms
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductance
Thermal resistance
Total thermal resistance
Thermal conductivity
describes a homogeneous (solid concrete) material’s ability to transfer heat
expressed in Btu
is inversely proportional to the insulting value of that material
Thermal conductance
a heterogeneous or composite material’s ability to transfer heat
expressed in BTu/hr
Thermal Resistance (R)
measure of the ability of a material to resist heat transfer
Total Thermal Resistance (Rt)
insulating ability of a construction assembly of materials
Rt = R1 + R2 + R3 and so on
Overall Coefficient of Heat Transmission (U)
ability of a construction assembly to transfer heat
from exterior
Exposed Radiator (equipment symbols)

Recessed radiator (equipment symbols)

Flush enclosed radiator (equipment symbols)

Projecting enclosed radiator (equipment symbols)

Unit Heater propeller plan (equipment symbols)
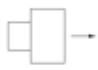
Unit Heater centrifugal plan
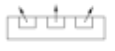
Unit Ventilator plan

Steam
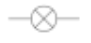
Duplex Strainer