Chapter 5 - Homeostasis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
homeostasis
maintainence of a relatively constant internal environment
maintain optimum condition for cellular function
positive feedback
response amplifies stimulus(change in internal environment)
NOT homeostasis
EG: childbirth - as head of fetus push against cervix, brain stimulate pituitary gland to secrete oxytocin, oxytocin stimulate increase uterine contractions and push fetus towards cervix
negative feedback
response by effectors initiated in opposing direction of stimulus to conteract change
HOMEOSTASIS
EG: core body temp
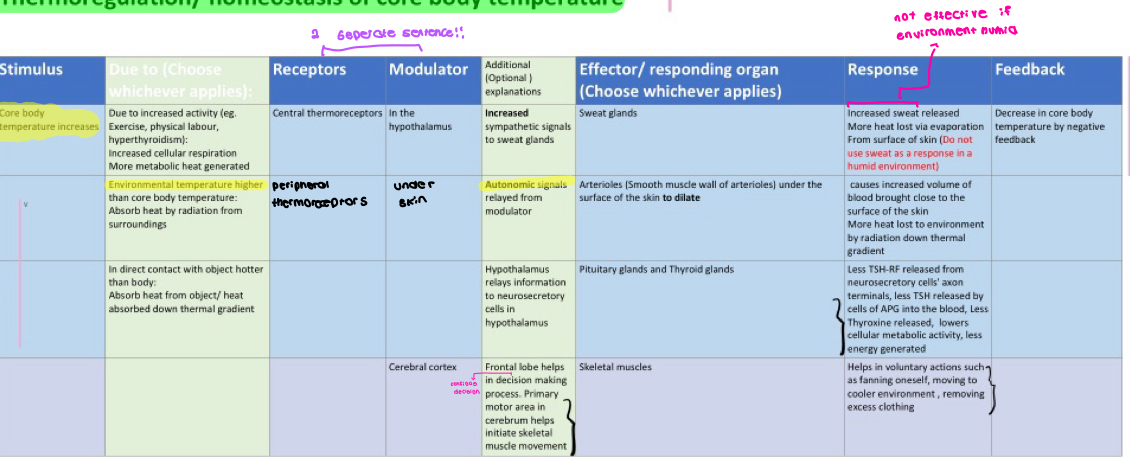
thermoregulation - core body temp HIGH
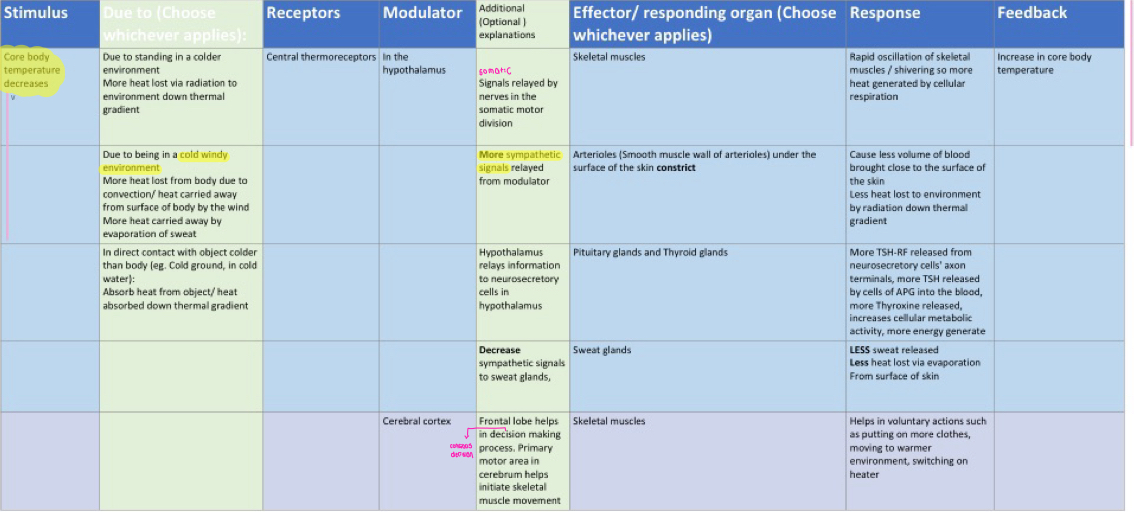
thermoregulation - core body temp LOW
heat gain/loss by
excretion
metabolism
conduction
convection
evaporation
thermal radiation
excretion
warm urine and faeces
warm air exhaled
metabolism
cellular respiration produce heat and energy
conduction
heat transferred between objects in direct contact with each other
thermal radiation
emission of heat into space around a warm object
OR gain heat by radiation
convection
moving air/water transfer heat
heat move down thermal gradient
heated air/water constantly move away from body
evaporation
evaporation of water from body surface COOL body
peripheral thermoreceptors
in skin
provide info about external environment
central thermoreceptors
in hypothalamus and internal organs
provide info about core body temp
modulator
control centre responsible for processing info from receptor and sending signals to effector
hyperthErmia
temp and humidity high
body temp rise, above set point
hypOthermia
person core body temp fall below 33 celc
metabolic rate so low that heat production unable to replace heat loss
heat exhaustion
extreme sweating and vasodilation
loss of water, reduced blood pressure
blood glucose levels ABOVE set point
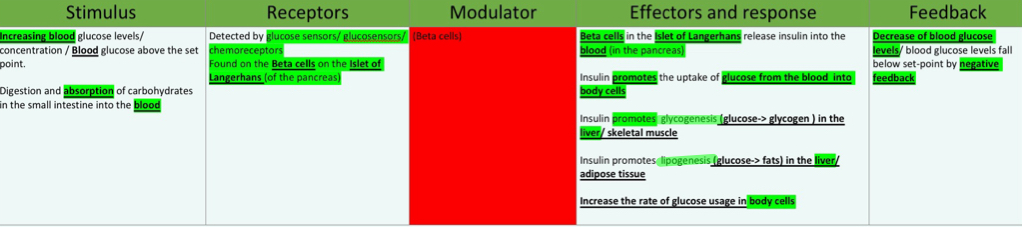
blood glucose levels BELOW set point
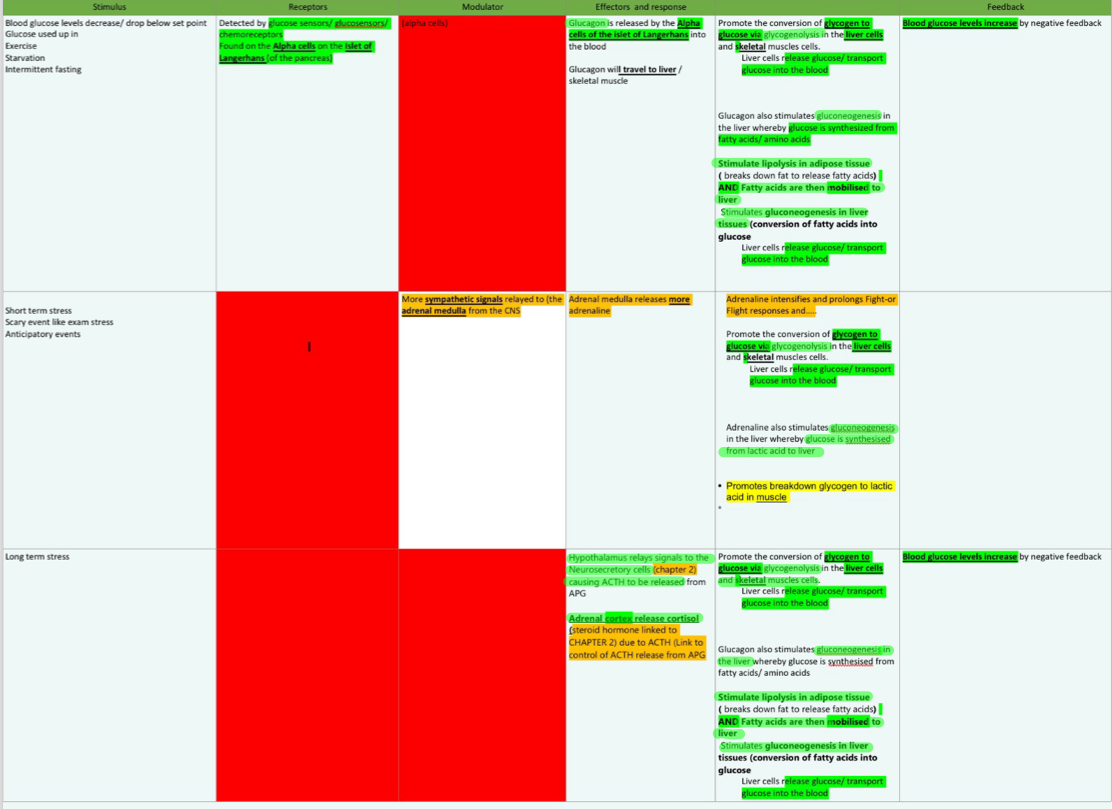
adrenal cortex
secretes cortisol
stimulate glycogenolysis(glycogen to glucose)
stimulate protein breakdown, gluconeogenesis(amino acids to glucose)
adrenal medulla
secrete adrenaline and noradrenaline
stimulate glycogenolysis(glycogen to glucose)
nephron system
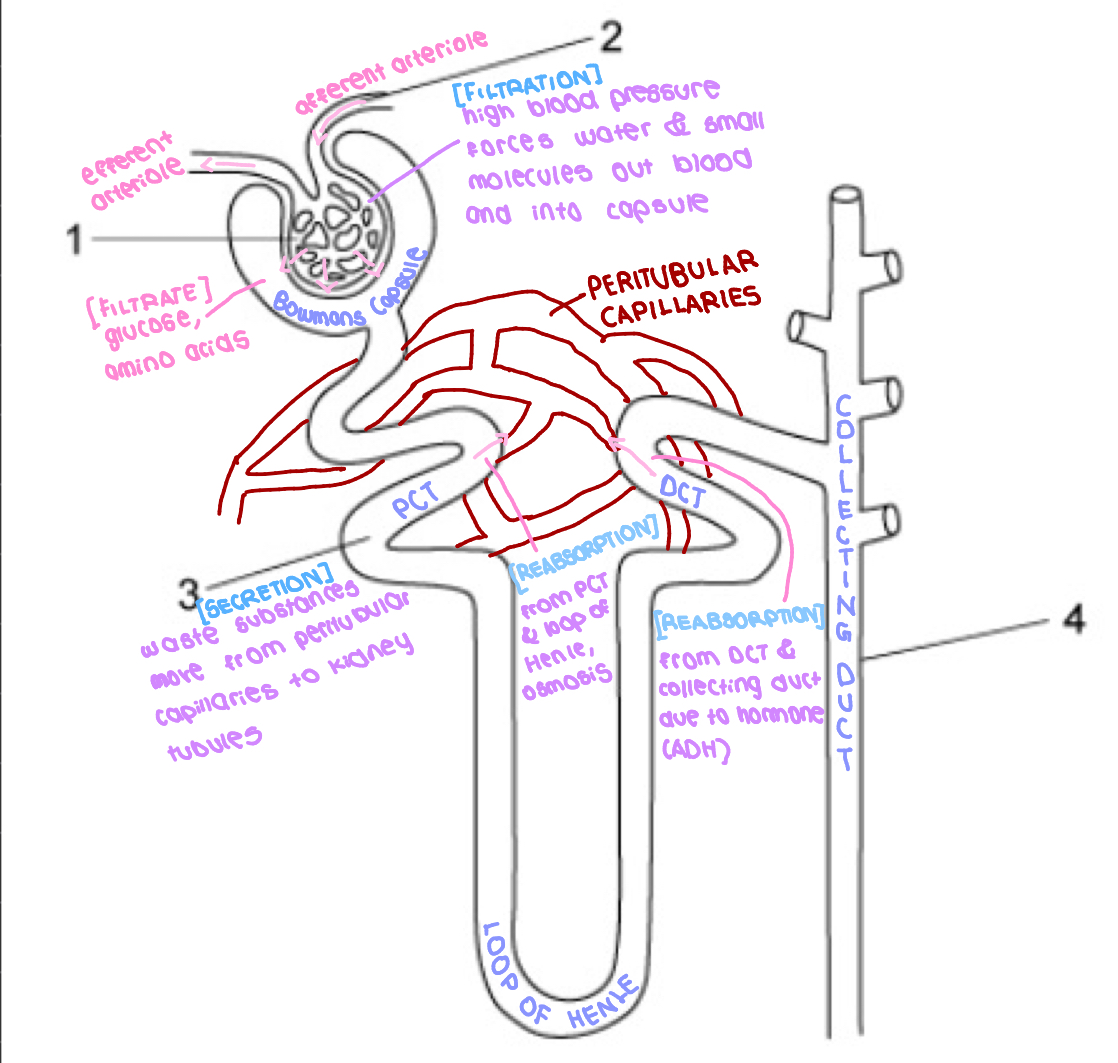
process of ultrafiltration/formation of filtrate
afferent arteriole has larger diameter than efferent arteriole
hydrostatic pressure high in glomerulus
pushes plasma through filtration barriers
form filtrate in capsular space
reabsorption of water in PCT
glucose and ions axtively transported back into plasma from tubule to peritubular capillaries
filtrate has HIGH water potential
plasma have LOW water potential
water diffuse down water potential gradient via osmosis
water diffuse back into PCT
blood osmotic pressure HIGH(solute conc in blood high)
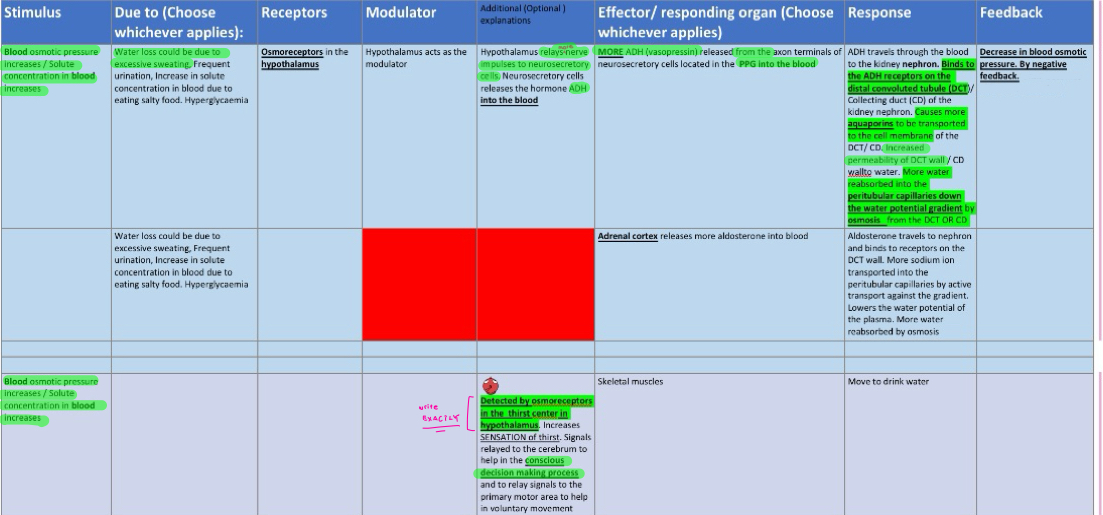
blood osmotic pressure HIGH(aldosterone ver)

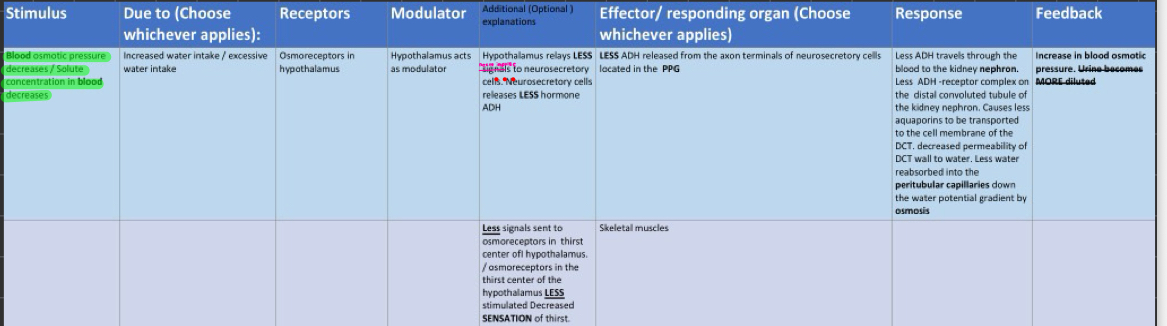
blood osmotic pressure LOW(solute conc in blood low)
blood carbon dioxide conc HIGH
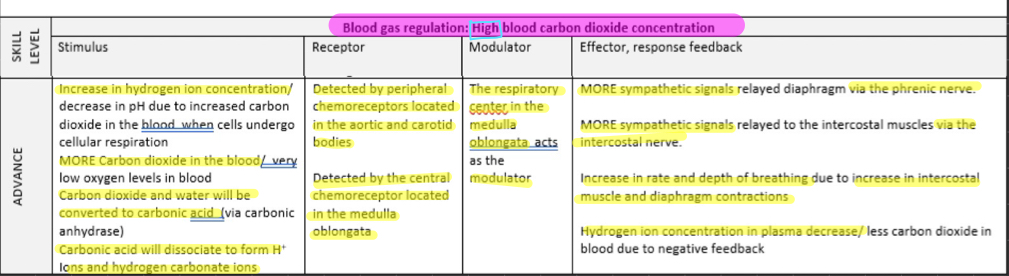
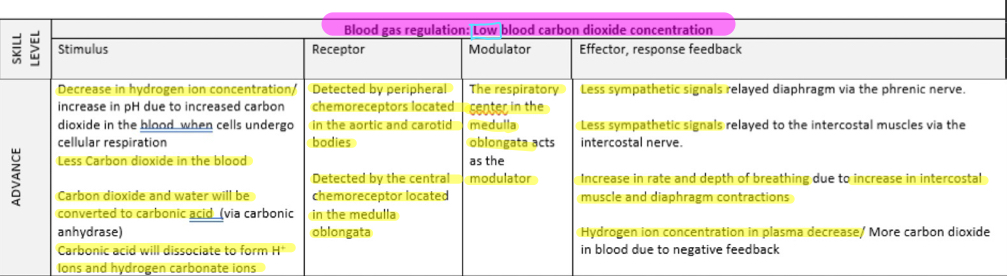
blood carbon dioxide conc LOW