Lecture 11 - Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Meiosis
Only occurs in sexually reproducing eukaryotic organisms. Occurs in the GONADS. Produces four cells called gametes, each with a single chromosome
Gonads
Ovaries and Testes
Haploid
Only contains a single chromosome set (if parent had 46, haploid would only have 23) Originate from a diploid parent cell. Ex: reproductive cells = gametes (sperm and egg cells)
Diploid
Contains 2 complete “sets” of chromosomes. Parent cell.
Heredity or inheritance
The transmission of traits to the next generation
Genetic Variation
Offspring differ from what their parents or siblings resemble.
Genes
ARE SEGMENTS OF DNA that hold instructions for building specific proteins that in turn govern the traits and characteristics, and behaviors that emerge in organisms as they develop. Cells convert this info into synthesis of proteins.
Genome
the sum total of all the genes of a given species.
Most genes program cells to synthesize specific enzymes and other proteins that result in the production of an organism’s inherited traits.
It is the number, type, timing, and interaction of these proteins that give an organism its physical traits & biochemical characteristics.
Gene locus
the specific location of a gene — each chromosome has hundreds or thousands of genes along the length of chromosome, each gene located at specific spots
Asexual reproduction
Produces a clone of the parent cell - mutations may occur that result in any genetic variation.
Single-celled eukaryotes can reproduce asexually by mitotic cell division.
Sexual Reproduction
when two parents produce offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents.
Karyotype
Image of all chromosomes arranged in pairs produces a ____ display.
Have the same gene loci, length, centromere, position, and staining pattern
Homologous chromosomes (two chromosomes in a pair) have the same,,,,
Homologous
Carries identical genes, control the same inherited traits. However, they may have different versions of the gene called alleles.
Alleles
different version of the same gene. gene locus remains the same between homologous chromosomes, but have different types of that gene.
Sex chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes are called ______. Make up one chromosome pair. they are not homologous but are paired together.
Autosomes
Not the sex chromosomes, but the other 22 pairs of chromosomes are called…
We inherit one chromosome of each homologous pair from each parent. The 46 chromosomes in each somatic cell are two sets of 23 (maternal set and paternal)
Inheritance of chromosomes…
Diploid
Any cell with two full sets of chromosomes (2n)
Sperm cells contain 22 autosomes and an X or Y chromosome, Ovum has 22 autosomes and an X chromosome.
Sperm and Ova sets of chromosomes
Meiosis I
separates homologous chromosomes… A Reductional division that halves the number of chromosome sets from two to one.
Meiosis II
Separates sister chromatids - equational division (2 haploid cells divide to yield 4 haploid cells)
Synapsis - during prophase I… homologs pair up and form synaptonemal complex, holding them together in synapsis
Crossing over - sister chromatid cohesion along the arms resulting in formation of chiasma indicating the location of crossing over
Unique events occuring during Meiosis I Prophase (do not happen in mitosis)
Chiasma
The x-shape indicating the location of crossing over
Homologs on the metaphase plate - unlike mitosis pairs of homologs rather than individual chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate
Unique events occuring during Meiosis I, metaphase
Separation of homologs - duplicated chromosomes of each homologous pair separate and move towards opposite poles, while sister chromatids of each duplicated chromosome remain attached
Unique to Meiosis I during Anaphase I
Life Cycle
The generation to generation sequences of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
____ starts at the conception of the organism and continues until the organism produces its own offspring.
Both haploid and diploid cells can undergo mitosis, but only diploid can undergo meiosis.
Haploid vs diploid replication
Gametes do not divide but fuse (fertilize) to form a diploid zygote that divides during mitosis to produce a multicellular diploid organism
First type of life cycle in which gametes are the only haploid cell
Alternation of Generations - plants and some algae
Type of Life cycle where it includes 2 multicellular stages… sporophyte generation produces gametophyte as its offspring and the gametophyte generation produces the next sporophyte generation
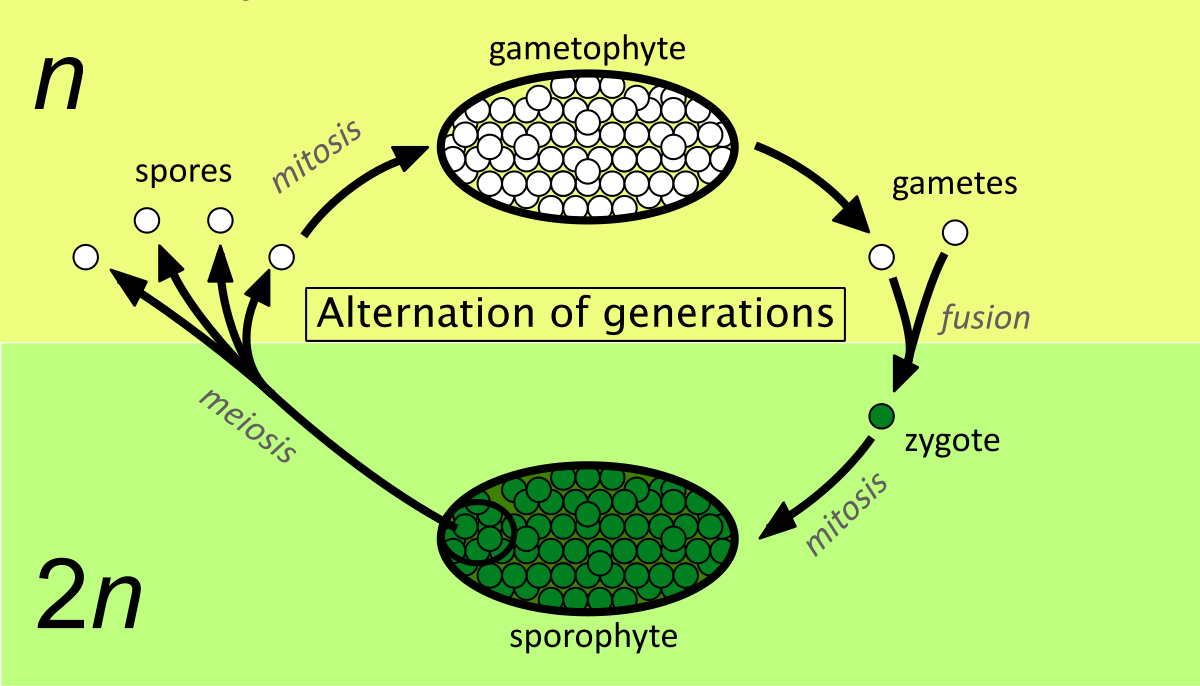
Sporophyte — meiosis in sporophytes produces haploid spores
Multicellular diploid stage found in plants
Unlike a gamete, haploid spore do not fuse together, they replicate through mitosis to form a multicellular haploid gametophyte stage.
Haploid spore
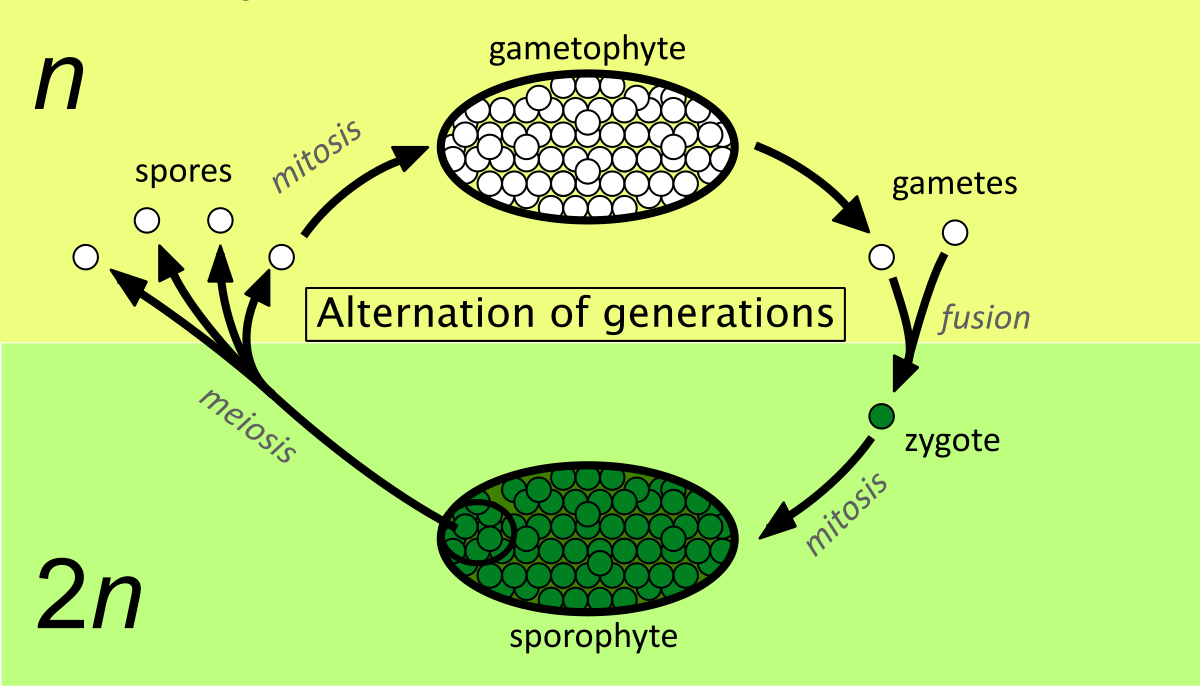
Gametophyte
Multicellular haploid found in plants
Gametes fuse to form a zygote (only diploid phase), haploid adult produces gametes by mitosis
Life cycle of most fungi and some protists
Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
This adds to the genetic variability due to the random orientation of homologous pairs of chromosomes at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
-fifty fifty chance that a particular daughter cell from meiosis I will get the maternal chromosome or the paternal.
Each homologous pair separate independently of each other, not related.
Number of combinations possible when chromosomes separate independently of each other = 2n
Recombinant Chromosomes
Crossing over results in ____. which combine genes inherited from each parent. During crossing over each gene is alined with its corresponding gene found on the other homolog
Random Fertilization (adds to genetic variation)
Any sperm can fuse with any egg… crossing over adds even more variation to this.
Mutations are the original source of different alleles, which are then mixed and matched during meiosis (increasing allele combinations and in so doing, genetic variation).
New and different combinations of alleles may work better than previous ones.
Charles Darwin recognized the importance of genetic variation in evolution.