Concept 9.1: Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
1/19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
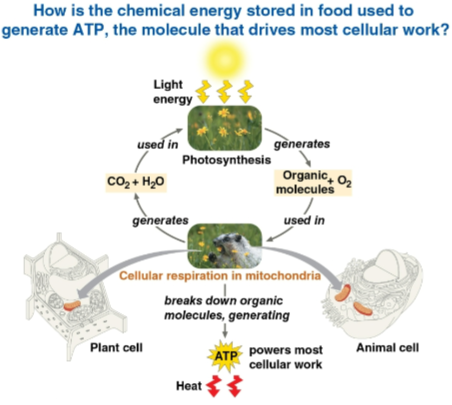
Cellular respiration
The process by which plant and animal cells break down organic molecules within mitochondria
Uses O2 and organic molecules to make ATP with waste CO2 and H2O
Includes aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Photosynthesis
The use of light, CO2, and H2O to make organic molecules and O2
Catabolic pathways
Chains of exergonic reactions that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules using electron transfers from food molecules
Only linked to work by ATP as they do not power work
Fermentation
A partial degradation of sugars that occurs without oxygen; is a type of anaerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration
Process that utilizes oxygen and organic molecules to yield ATP
Represented by the equation: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Energy takes the form of ATP and heat
Electron transfer
The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions to release stored energy in organic molecules for ATP synthesis
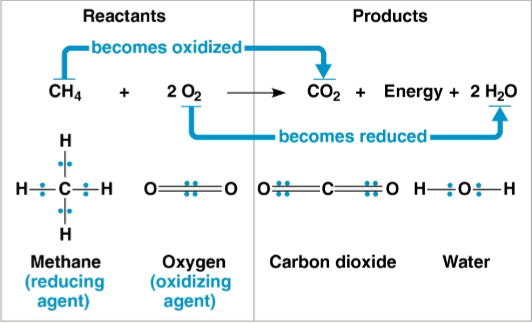
Redox reactions (reduction-oxidation reactions)
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants
Some electrons are shared via covalent bonds in these
Oxygen atoms attract electrons and do not share them equally; this still constitutes one of these
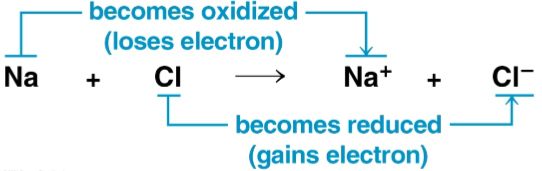
Oxidation
The loss of electrons from a substance in a redox reaction
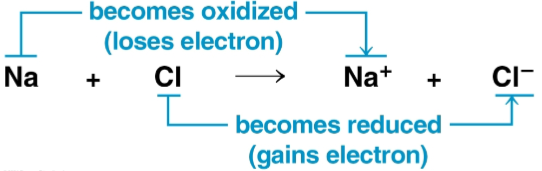
Reduction
The addition of electrons to a substance in a redox reaction
Refers to the positive charge
Reducing agent
The electron donor in a redox reaction
Reduces the electron acceptor
Seen with food molecules in cellular respiration due to their high abundance of hydrogen
Oxidizing agent
The electron acceptor in a redox reaction
Oxidizes the electron donor
Seen with oxygen during cellular respiration
Electronegativity
The attraction of electrons toward an atom; higher levels of this attract more electrons
Electrons lose potential energy when shifting to atoms with higher levels of this, releasing kinetic energy for ATP synthesis
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
A coenzyme that functions as an electron carrier and oxidizing agent during cellular respiration
NADH
The reduced form of NAD+, representing stored energy tapped to synthesize ATP
Passes electrons to the electron transport chain through a series of redox reactions, releasing a small amount of energy
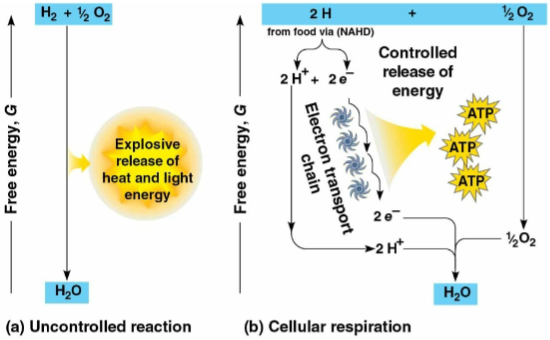
Electron transport chain
A series of molecules built into the inner membrane of the mitochondria to break the fall of electrons to oxygen in several energy-releasing steps
Oxygen
The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain that captures electrons and hydrogen nuclei to form H2O
Yields energy through the attraction of electrons in redox reactions
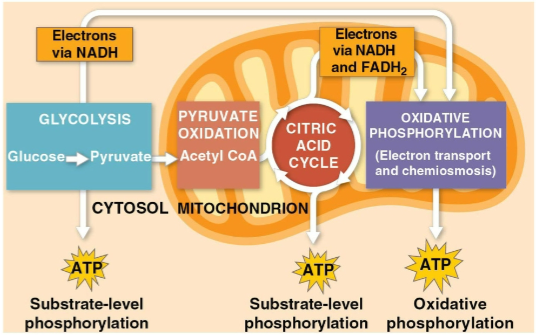
Glycolysis
The first step of cellular respiration, breaking down one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
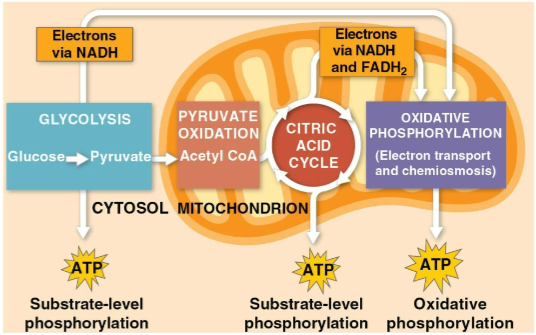
Citric acid cycle
The second step of cellular respiration with pyruvate oxidation, completing the breakdown of glucose to CO2
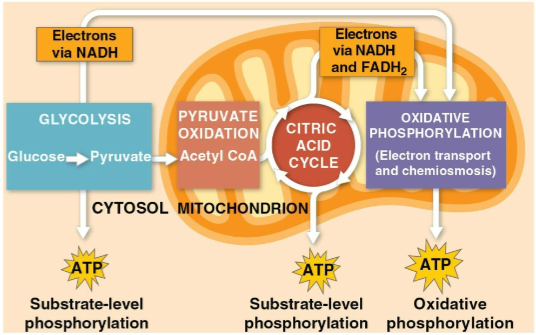
Oxidative phosphorylation
The closing of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain to facilitate synthesis of 90% of the cell’s ATP
Powered by redox reactions
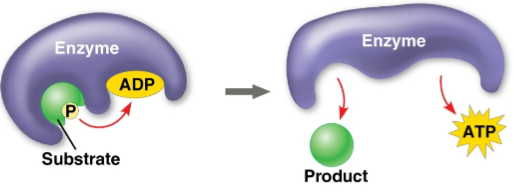
Substrate-level phosphorylation
The formation of some ATP in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle after an enzyme transfers a phosphate group directly from a substrate to ADP